A level Chemistry - Mr Crawford
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Which substances are soluble and insoluble?
all nitrates are soluble
all chlorides are soluble except lead + silver
all sulphates are soluble except lead, calcium + barium
all carbonates are insoluble except ammonium, potassium + sodium
all hydroxides are insoluble except ammonium, potassium, sodium, lithium + calcium
What are the mole equations?
moles = mass/ Mr
moles = concentration x volume
moles = no of particles / Avogadro’s constant
volume = mol x 22.4 (at room temp)
What is Avogadros constant?
6.02 × 1023 atoms per mole
1 mol of any substance contains an Avogadro number of particles and 1 mol of any gas occupies the same volume at the same pressure and temperature
How to calculate percentage yield?
actual mass / theoretical mass x 100
What is a limiting reagent and a reagent in excess?
reagent in excess - there will be some left over at the end of the reaction, as more moles of it were added than were needed to react
limiting reagent - one which will run out, meaning the reaction stops, as all moles have been used up and converted to product
How to work out limiting reagent and reagent in excess?
find number of moles of each provided and check mole ratio
What is atom economy?
The atom economy of a reaction is a measure of the amount of starting materials that end up as useful products. Important for sustainable development and for economic reasons to use reactions with high atom economy.
Mr of chosen products / total Mr
What does Avogadros law state?
equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure, contain the same number of molecules
one mol of gas = vol of 24dm³
What equation can we use to calculate molar mass of liquids and gases NOT at room temp?
pV=nRT
p = pressure in Pa
V = volume in m³
n = number of mols
R = gas constant (8.31)
T = temp in K
How to convert between Kelvin and Celsius?
C + 273 = K
How to calculate percentage uncertainty?
% uncertainty = precision / reading x 100
if a piece of equipment is used multiple times (eg burette for initial and final readings), you have to multiply by the number of times used
How can you decrease percentage uncertainty?
increase precision of measuring equipment
increase value of readings taken (eg use larger volume or mass)
What is absolute uncertainty and why does it exist?
listed on front of pieces of equipment
if the value is read off the nearest line, the actual value may be slightly above or below, but since the scale is not finer you cannot be more accurate
RP1 - Finding the Molar Volume of a Gas
RP2 - Preparation of a Standard Solution and Titration
Back titrations
What is displayed formula?
shows all the atoms and all the bonds
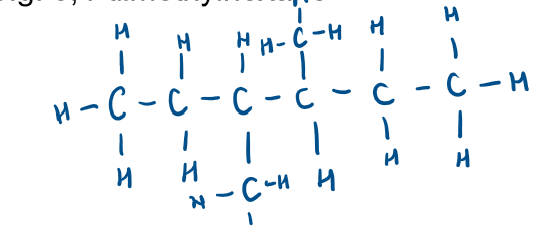
What is structural formula?
shows relative positions of atoms in the molecule, side chains written in brackets
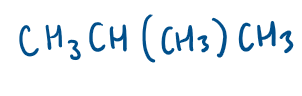
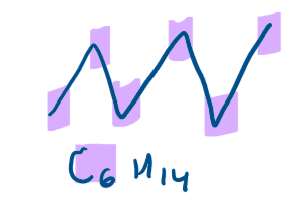
What is skeletal formula?
carbon skeleton shown by zigzag
Stages to name an organic compound?
name the longest unbranched carbon chain
name the substituent groups
give positions (number) of substituent groups counted from end which will give lowest number
name substituents in alphabetical order
What is an isomer?
molecules with the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms within the molecule
What is structural isomerism?
same molecular formula but atoms are arranged in a completely different order
three types:
chain isomerism - possibility of branching in carbon chains
position isomerism - basic carbon skeleton remains unchanged but important groups are moved around the skeleton
functional group isomerism - isomers contain different functional groups (belong to different homologous series)
What is stereo isomerism?
same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement
two types:
geometric isomerism - atoms are joined together in the same way but some atoms are pointing in different directions, occurs when there are different groups attached to a double bond as a double bond cannot rotate so the groups cannot change order
optical isomerism -
What are the two types of geometric isomerism?
E-Z isomerism - E isomer has functional groups on opposite sides, Z isomer has functional groups on same side of double bond
Cis and Trans isomerism - cis isomer has functional groups on same sides, trans isomer has functional groups on different sides.
Cis and Trans can only be used when there are hydrogen atoms to compare the other 2 groups to, otherwise E-Z is used
Priority rules for E-Z isomerism?
atom immediately attached with the larger relative atomic mass gives that group higher priority
if two first atoms are identical the group with the largest overall relative atomic mass has higher priority
priority groups determine whether its E or Z
Alkanes definition and general formula?
saturated hydrocarbons
CnH2n+2
What happens to properties of alkanes and alkenes as chain length changes?
as chain length increases:
boiling point increases
volatility decreases
viscosity increases
flammability decreases
What happens to boiling point as length of alkanes increase and why?
melting and boiling points increase as chain length increases
number of electrons increases
strength of london forces increases
more energy is required to separate the molecules
How are boiling points of branched isomers different from straight chain ones?
boiling point decreases as molecules get more branched
they have less points of contact and lower surface area so the London forces cant act as strongly
Fractional distillation of crude oil stages?
crude oil heated till boiling then passed into a fractionating column
column is hotter at bottom than at top
vapour rises up column till it condenses then is tapped off
smaller alkanes have weaker London forces and low boiling points so condense near top of column
What order do alkanes distil out of the fractionating column?
from top down:
refinery gases, gasoline, naptha, kerosene, diesel, fuel oil, bitumen
What is an addition reaction?
reactants combine to form a single product
What is a substitution reaction?
one functional group is replaced by a different functional group
What is oxidation?
a species loses at least one electron, and gains oxygen
What is reduction?
a species gains at least one electron, and loses oxygen
What is a polymerisation reaction?
when monomers join together to form a polymer
What is heterolytic fission?
Breaking a covalent bond within a molecule to form ions
One atom receives the electron pair and becomes an anion, the other becomes a cation
e.g. Br-Br → Br+ + Br−
What is homolytic fission?
Breaking a covalent bond within a molecule to form radicals
Each atom receives one electron from the bonding pair and both atoms become radicals
e.g. Br-Br → Br⋅ + Br⋅
What is a free radical?
a species with an unpaired electron
shown by dot
What is chlorination of alkanes and what are the stages?
alkanes react with chlorine in the presence of UV light to produce halogenoalkanes
3 stages: initiation, propagation, termination
What happens in the initiation stage of chlorination of alkanes?
energy of UV light causes Cl-Cl bond to break homolytically
produces 2 chlorine radicals
Cl — Cl → 2Cl •
What happens in the propagation stage of chlorination of alkanes?
propagation is a radical reacting to produce another radical
chlorine radical removes a hydrogen atom from methane
produces a hydrogen chloride molecule and a methyl radical
Cl • + CH4 → HCl + CH3 •
then methyl radical removes a chlorine atom from a chlorine molecule
CH3 • + Cl2 → CH3Cl + Cl •
and so on
What happens in the termination stage of chlorination of alkanes?
termination is two radicals reacting to form a molecule (no radical produced)
CH3 • + CH3 • → CH3CH3
CH3 • + Cl • → CH3Cl
Cl • + Cl • → Cl2
Complete combustion of alkanes?
alkane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
contributes to global warming
Incomplete combustion of alkanes?
alkane + oxygen → carbon monoxide + water
2CH4 + 3O2 → 2CO + 4H2O
carbon monoxide is a toxic, colourless, odourless gas which replaces oxygen in the blood causing you to suffocate
nitrous oxide, sulphur dioxide and carbon particulates produced as byproducts
What is reforming of alkanes?
the process by which straight chain alkanes can be converted to branched chain or cyclical alkanes
Why is reforming alkanes necessary?
branched chain alkanes are preferable to straight chain alkanes as fuel straight chain alkanes have a tendency to auto ignite causing knocking in the engine
branched chain alkanes undergo combustion more efficiently than straight chain alkanes
Formation of pollutants during combustion?
nitrous oxides and sulphur dioxide formed through combustion can react with water in clouds to form acid rain (nitric and sulfuric acid)
catalytic converters in cars can be used to convert harmful products into more stable ones using a rhodium catalyst
Biofuels and production?
biofuels such as ethanol release fewer harmful products when burned
biofuels are sustainable (not finite) and carbon neutral
ethanol is produced by fermentation - enzymes break down starch into sugars which can be fermented, produced in batches so slow process, low percentage yield
What is cracking and why is it necessary?
longer, less useful carbon chains are broken down to form smaller, more useful molecules
carbon-carbon bonds are broken
always produces an alkane and at least one alkene
Thermal vs catalytic cracking?
thermal- more common, high temperatures around 1200K and pressures around 7000kPa
catalytic - produces aromatic compounds with carbon rings, lower temperatures around 720K, zeolite catalyst used
Alkenes definition and general formula?
unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon-carbon double bond
CnH2n
Why are alkenes reactive?
C=C double bond is an area of high electron density making it easy to attract electrophiles
doble bond made up of a sigma and pi bond overlapping
2 tests for alkenes?
bromine water used to identify the double bond
colour change from orange-brown to colourless
reaction with acidified potassium manganate (VII)
colour change from purple to colourless
What is a hydrogenation reaction?
when alkenes undergo electrophilic addition to produce alkanes
the C=C bond opens up and forms single bonds to each of the hydrogen atoms, requires a nickel catalyst
Example of a hydrogenation reaction?
propene + hydrogen → propane
CH2CHCH3 + H2 → CH3CH2CH3
used in the manufacture of margarine from unsaturated vegetable oils
What are alcohols?
organic compounds with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group
diols - alcohols with 2 hydroxyl functional groups
How are alcohols formed?
alkenes undergo addition reactions with steam to form alcohols
requires an acid catalyst e.g. phosphoric acid
What happens when an alkene is oxidised?
diol formed
double bond is oxidised by [O] and H2O from KMnO4 oxidising agent and H+ catalyst such as sulphuric acid
manganate ions must be cold, dilute and acidified
![<p>diol formed<br>double bond is oxidised by [O] and H2O from KMnO4 oxidising agent and H+ catalyst such as sulphuric acid<br>manganate ions must be cold, dilute and acidified</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a201d92f-9bbb-49ae-8694-86a4d408c1f0.png)
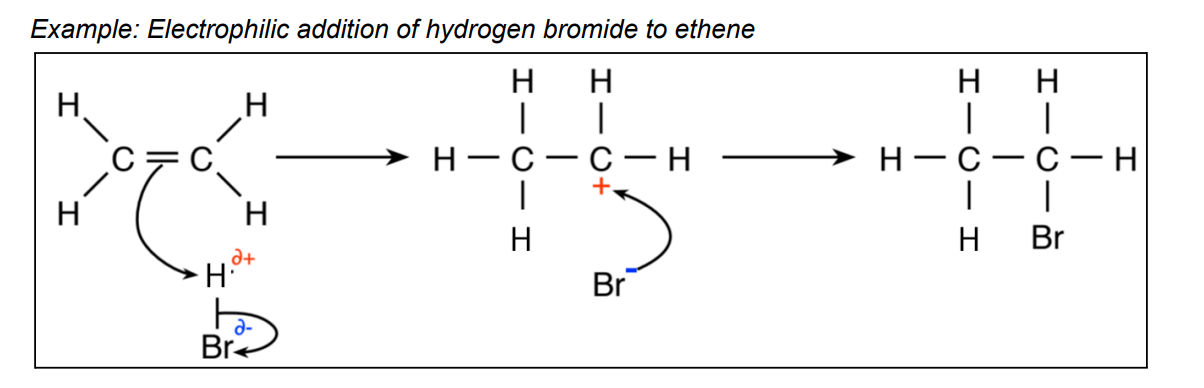
What is an electrophile?
electron deficient/electron acceptor species
attracted to areas of high electron density
What is a carbocation?
carbon atom with only three bonds
positively charged
have varying stability - the more stable it is the more likely it is to form, meaning major and minor products can be identified
What is electrophilic addition?
reaction mechanism that shows how electrophiles attack the double bond in alkenes
when double bond is broken a carbocation forms
What are the different mechanisms to form halogenoalkanes?
alkene + halogen → dihalogenoalkane
alkene + hydrogen halide → halogenoalkane
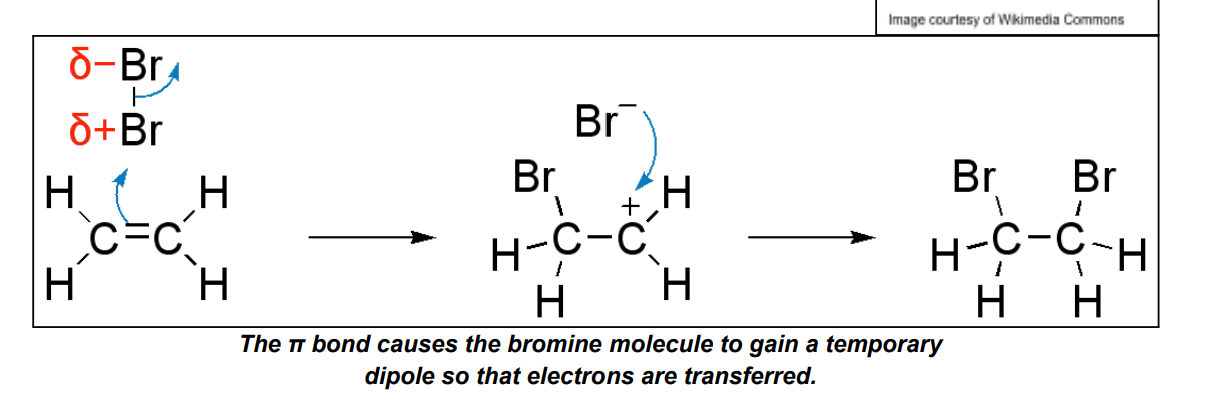
Why would major/minor products exist and how to identify them?
when an alkene is asymmetrical more than one product can be formed because the H atom can be added to either carbon
the carbocation with the most alkyl groups is more stable and therefore the major product as alkyl groups are electron donating
(groups are counted around the C+)
What is Markovnikov’s rule?
helps to identify the major product
that which has gets
carbon with the most H atoms attached gets the new H, leaving the other carbon to be attacked by the remaining atom
What are polymers and monomers?
polymer - long chain molecules made from joining many monomers
monomer - small unsaturated hydrocarbons
What is addition polymerisation?
process of adding monomers to the end of a growing chain by reacting C=C bonds to make a polymer
What is a repeat unit?
a structure that occurs in a polymer many times
represented using square brackets, extended bonds and n
has no double bond
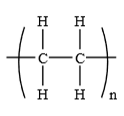
What are the problems with polymers?
they are not biodegradable
takes lots of energy and resources to extract and crack alkenes from crude oil and then convert alkenes into polymers
What are the uses of polymers?
unreactive hydrocarbons with strong non-polar covalent bonds
shopping bags and other everyday plastic objects
How can we dispose of polymers?
landfill sites: bad
recycling: reduce use of finite resources, very time consuming
feedstock for cracking: waste polymers broken down and products used as raw materials in production of new polymers or organic chemicals.
incineration to produce energy: releases CO2 so contributes to global warming
How can we produce polymers more sustainably?
scientists are currently working on developing biodegradable and compostable (eg plant starch bin liners) polymers
we can also reduce our use of polymers and reduce the energy use in making of them
improve atom economy and amount of chemicals used in production
What is a halogenoalkane?
compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been replaced by halogen atoms
What is the bonding like in halogenoalkanes?
contain polar bonds as halogens are more electronegative than carbon
therefore has London and permanent dipole - permanent dipole forces
What is a primary, secondary and tertiary molecule?
determined by the number of carbon atoms directly attached to the carbon atom that is attached to the halogen atom
1 carbon atom - primary
2 carbon atoms - secondary
3 carbon atoms - tertiary
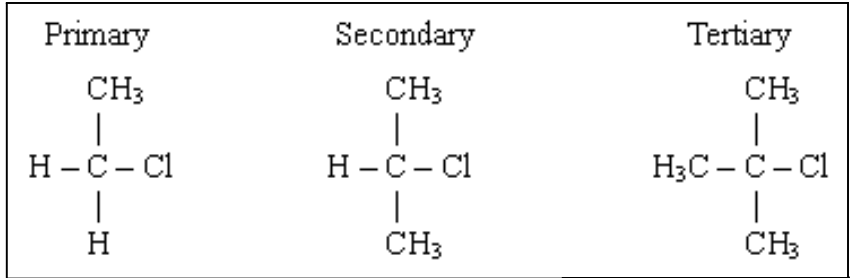
How does reactivity vary in the halogenoalkanes?
the rate of reaction increases for halogenoalkanes as you move down the group
the greater the Mr of the halogen in the polar bond the lower the bond enthalpy, and the higher the rate of reaction
How does boiling point vary in the halogenoalkanes?
electronegativity of the halogens decreases down the group therefore the bonds get stronger so the boiling point increases
How can halogenoalkanes react to produce alcohols?
react with aqueous alkali