health geog // history, what is health
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
In 400 BC, Hippocrates writes ________, which proposes theories about how ______ shapes health. Considered to be the _____ of health geography
On Airs, Waters, and Places, place, roots
what theory dominated pre-19th century thinking about how disease is caused…when was this theory abandoned?
miasma theory, which posited that disease was caused by a poisonous vapor or mist filled with particles from decomposed matter (miasmata) and was identifiable by foul smell. theory abandoned in mid 1800s in favor of the germ theory
Germ theory
first major paradigm shift in health history, posited that microbes caused disease. pioneers included Louis Pasteur (fermentation guy), Robert Koch (identified bacteria that caused a few diseases) and John Snow
John Snow + London cholera outbreak
“father of modern epidemiology,” suspected that the cholera outbreak in London in 1854 was due to contaminated water. he mapped pump locations in London and compared this with clusters of mortality to prove this theory
20th century challenges with disease
development of widely available antibiotics and insecticides after WWII…less focus on infectious diseases as there is a rise in complex chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes…complex etiologies need new theories because germ theory no longer fits
Medical geography emerges in the ______ with the help of the “father of epidemiology” in the United States ______
1950s, Jacques May. He wondered why patients in Vietnam responded differently to disease/treatment then European patients and produced the first maps of global disease distributions in the “Atlas of Diseases”
In the 1970s-80s there are two main schools of health geography: ______ and _______
disease ecology and health services
disease ecology
looks at the production of disease as being a combo of pathogens, host, and environment
health services
used to be no planning of where to put health services so in the 70s-80s they were like oh shit we should probably plan a little
in the ______, medical geography transitions into _______
1990s, health geography
3 broad themes of modern health geography
social theory, social determinants, and systems landscapes
what should i take away from health histoy?
health geography has ancient roots linked to place and has evolved through time as causes of disease changed (from primarily infectious to complex). today, health geography focuses on how place and space shapes health
define health geography
Subdiscipline of human geography, which deals with the interaction between people and the environment. Conceptualizes the role of place, location and geography in health, well-being and disease…BUT it’s difficult to define because of political, cultural, and personal factors
disease
a condition that disrupts normal bodily function or structure, often characterized by specific symptoms or signs
illness
subjective experience of feeling unwell or unhealthy
impairment
restricted general physical or mental function that do not necessarily limit daily activities
disability
a physical, mental, or sensory impairment that significantly limits one or more major life activities
WHO defines health…
A state of complete physical, mental and social well‐being and not merely
the absence of disease or infirmity
why is it so hard to define health
it’s an abstract concept, the absence of health is much easier to define and measure, it can be both personal and political, and it costs money to have
health as a social construct
Barbara Ellen Smith’s Black Lung: The Social Production of Disease (1977) — be able to summarize/explain
what is a MODEL OF HEALTH
concenptual framework to understand health. they include biomedical, disease ecology, behavioral, biopsychosocial, and socio-ecological
biomedical model of health
health is the presence or absence of biological/physiological factors and processes
biomedical model approaches
evidence based approaches, scientific methods, diagnostic testing
biomedical model criticisms
Under-appreciation of psychological, social, environmental
influences
disease ecology model of health
health is a state influenced by interaction between humans and their environments (habitats)
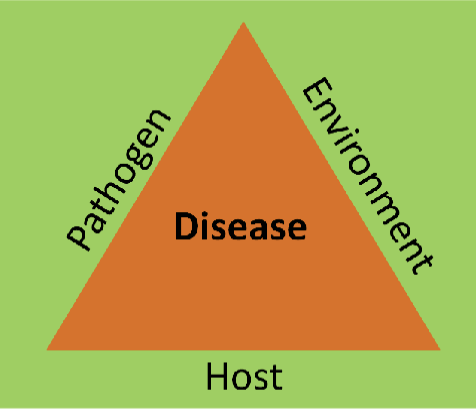
disease ecology model approach
systems thinking, ecological relationships, environmental dynamics, evolutionary processes
disease ecology model criticisms
no guidance on relative importance or casual mechanisms
behavioral model of health
health his the result of individual lifestyle choices and behaviors
behavioral model approaches
achieve positive changes via changing beliefs and attitudes and changing behaviors
behavioral model criticsms
over-reliance on individual choices and rational decision making
biopsychosocial model of health
health is a culmination of biological, psychological, social, and cultural interactions
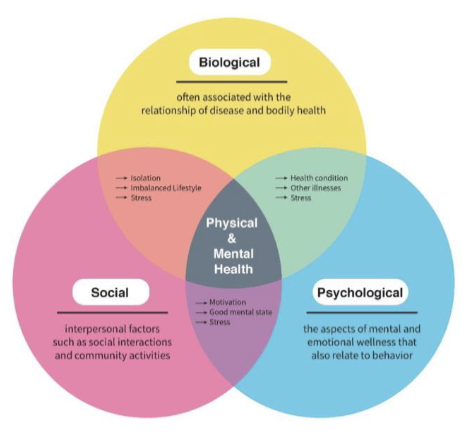
biopsychosocial model approaches
holistic understanding of human experience in a clinical encounter
biopsychosocial model criticisms
incomplete explanation of how factors interact and it’s expensive (bc doctor has to spend more time with patient, get more info)
socio-ecological model of health
health is the product of multiple levels that interact to produce behaviors and health…individual to interpersonal to organizational to community to public policy
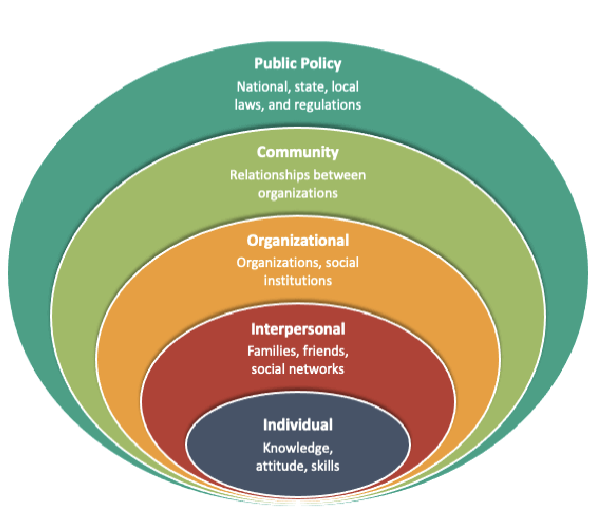
socio-ecological model approach
informs opportunities for broader interventions
socio-ecological model criticisms
limited guidance on interaction across levels and prioritization
interdisciplinary paradigms of health
public health, health promotion, population health
public health
focuses on protecting and improving health through organized efforts and policies. linked to epidemiology. includes things like surveillance, sanitation, immunization, and health systems.
epidemiology
science that provides the evidence base to inform public
health practice
health promotion
focuses on enabling people/groups to increase their control and improve their own health and wellbeing. views health as a resource.
Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion 1986
landmark international agreement that defined health promotion
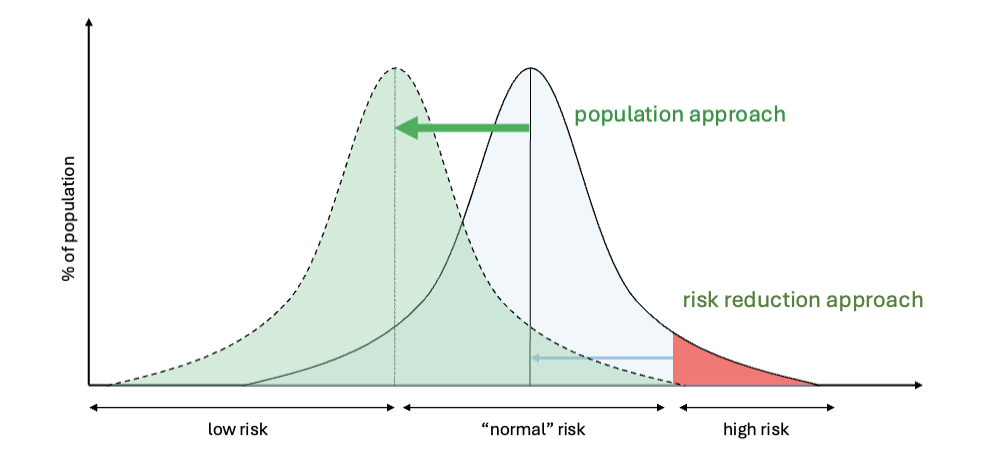
population health
focuses on upstream factors that influence the health of entire populations. looks at population-wide strategies as opposed to targeting high risk people and tries to address root causes as opposed to treating disease