3- metal ceramic restorations
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What does a metal ceramic restoration consist of?
ceramic veneer mechanically and chemically bonded to metal substructure by firing
Why do we use metal ceramic prosthesis?(4)
Superior fit of a casting and aesthetic
Doesn’t discolour
Longevity
Combining brittle and elastic material achieves good physical properties
Porcelains resist…
Compressive loading but tend to succumb to tensile stress
To avoid fracture, veneer shouldn’t be over 2mm thic
More abrasive to opposing teeth
When should you prepare the framework design that lies underneath porcelain and what does proper evaluation allow for?
During treatment planning, evaluate during tooth prep and waxing stages- this allows for:
even thickness of porcelain
good connector design
optimal occlusal contacts
What are the 6 mechanical properties of major clinical relevance for dental-ceramic restorations?
Elastic modulus
Yield strength
Hardness
Creep or distortion at elevated temperatures
Thermal expansion/contraction
Density
What are the mechanical properties of minor clinical relevance for dental-ceramic restorations?
Ultimate tensile stress
Ductility
Toughness
Percentage of elongation
What are the percentages of noble elements in the 3 available alloy systems?
High noble- 60%- 40% of which is gold- not recommended for FDP
Noble- 25%, palladium based
Predominantly base metal- less than 25%, commonly use nickel-chromium, if allergic cobalt-chromium, high elastic modulus than noble
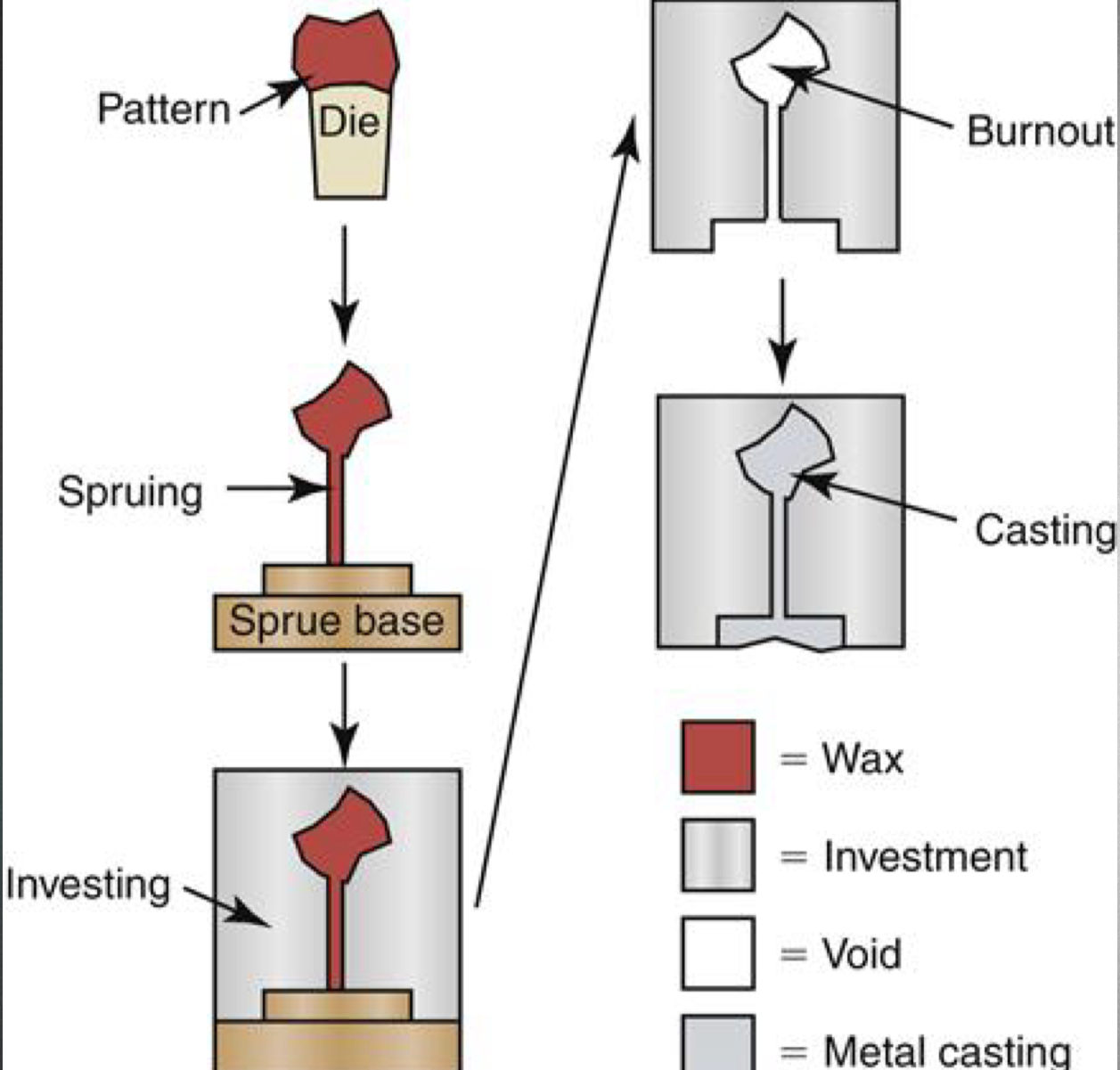
How to prepare metal?
Create a model with separator, shape the metal structure with wax
Spruce technique with investment removal
Complete the casting process, where wax replica is converted into a metal alloy

Sprue
channel in a refractory investment mold through which molten metal flows
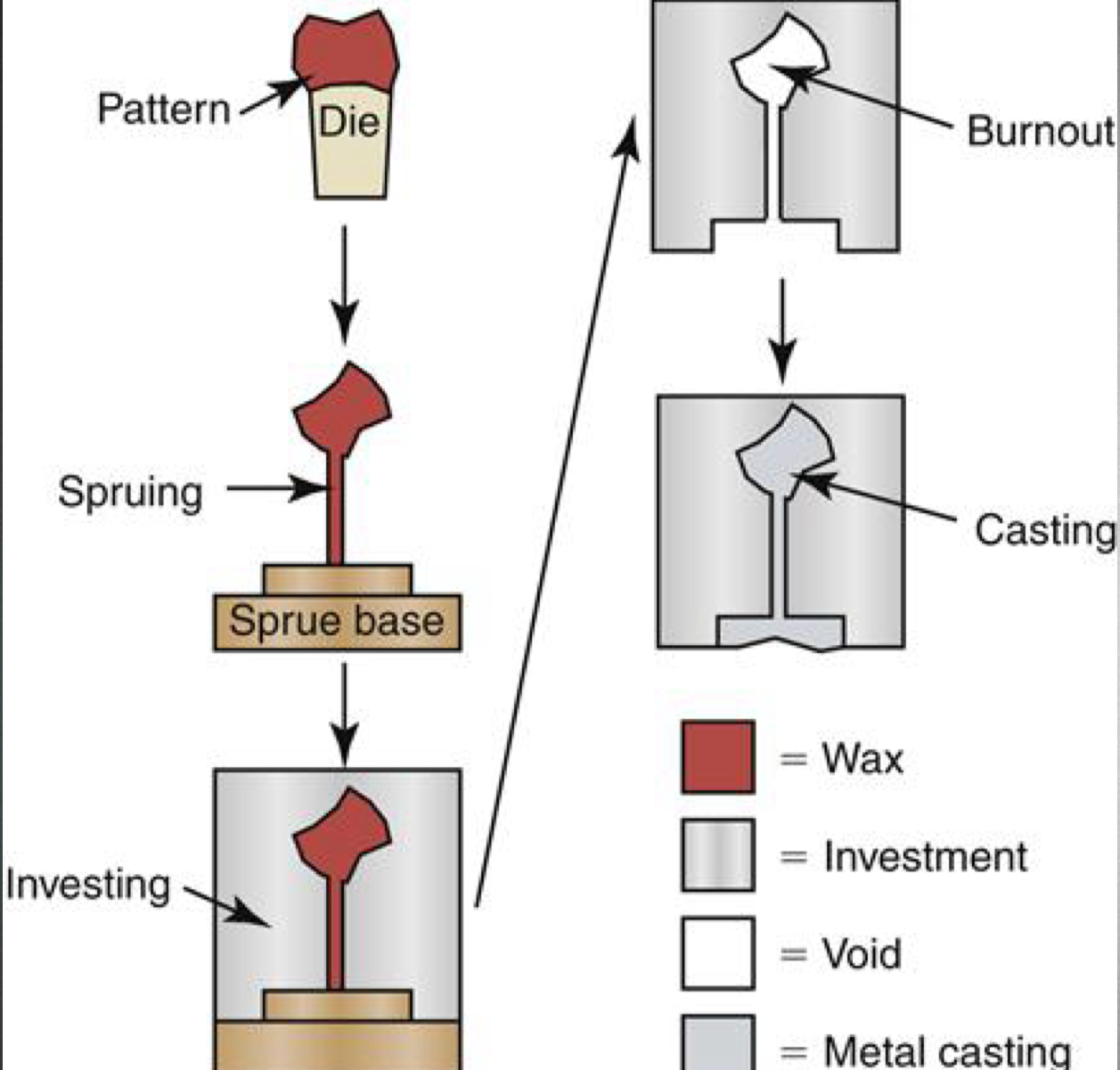
what is investment?
Refractory material that becomes the mold
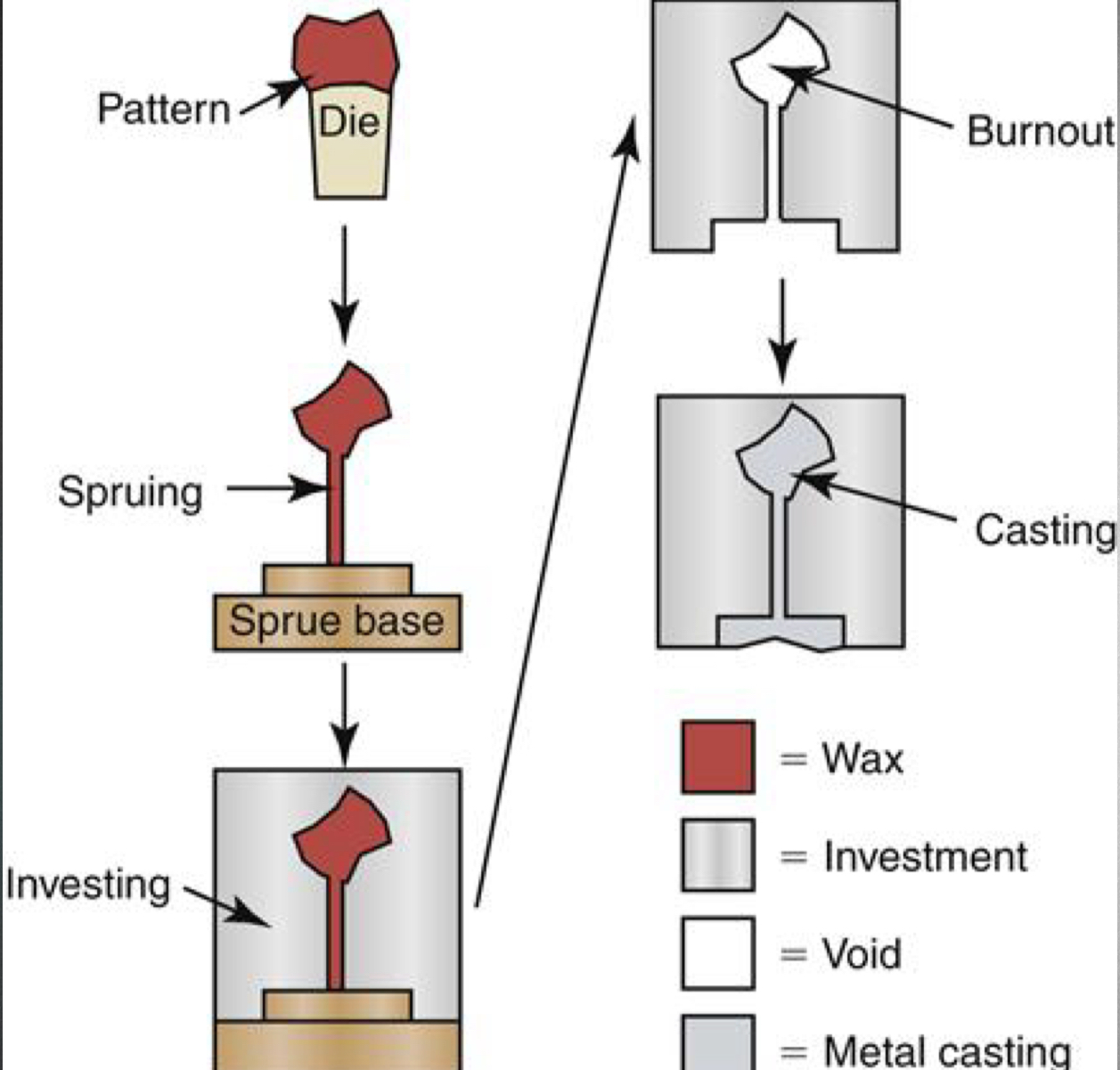
What is burnout?
Heating an invested mold to eliminate wax pattern
How is the oxide layer formed on the surface of metal during casting removed?
Partially remove with either acid or airborne particle abrasion- gives satin finish
How do you clean the prepared framework?
Either with cleaning solution in ultrasonic for 5 mins or steam cleaning then rinse with alcohol or distilled water
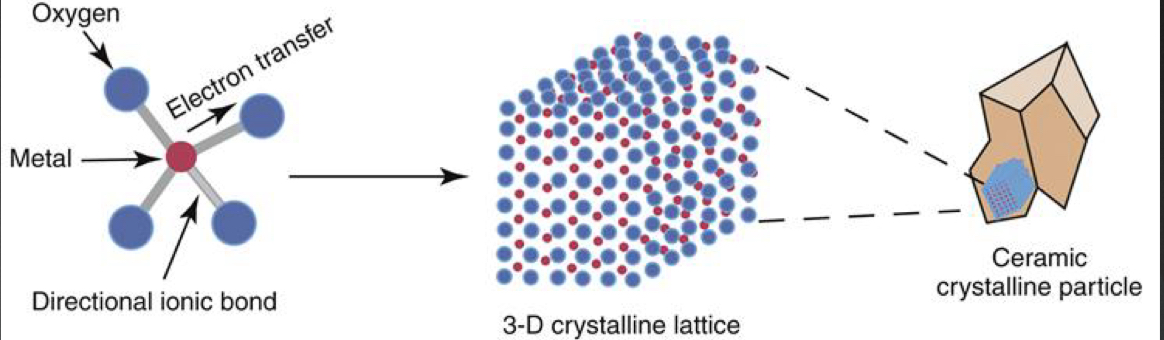
Why are ceramic materials distinct from alloys or polymers, its structure?
Ceramics contain strong directional ionic bonds between metal and oxygen- provide strength, intolerant to distortion- makes brittle
Metal and oxygen form 3D crystalline lattice
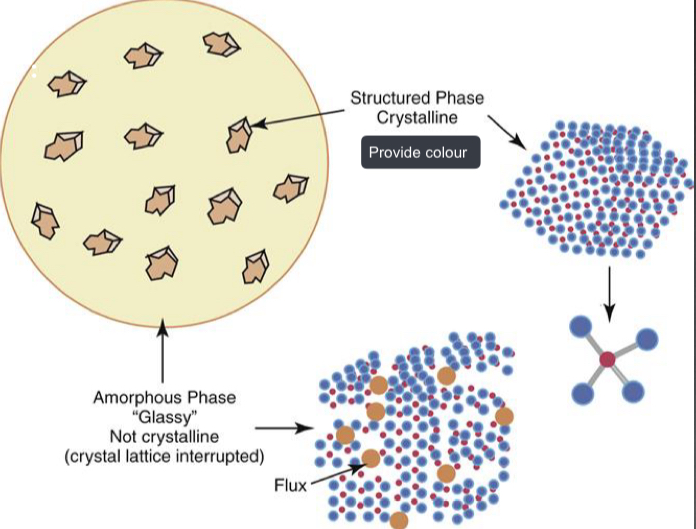
What areas do all ceramics contain?
Amorphous phase- metal ions disrupt metal oxygen crystal arrays, tend to be transparent
Crystal areas- opaque
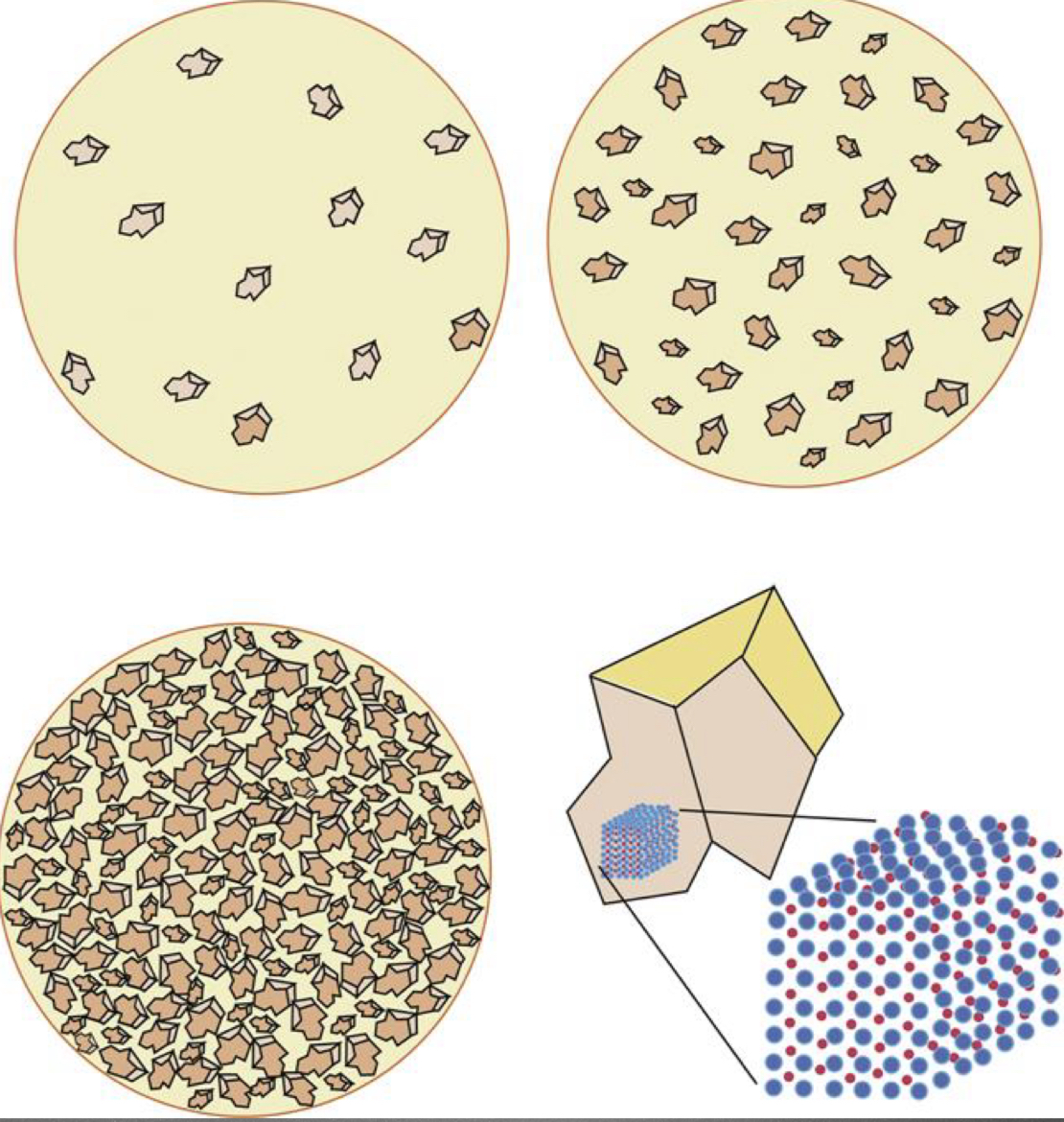
Porcelain is a type of ceramic that results when…
Feldspar
Silica
Alumina
Are fired together with fluxes like sodium or potassium carbonate
During firing large amorphous ceramic areas are formed
What are the 4 catergories of dental ceramics?
Feldespathic or glassy- Mostly amorphous glass with islands of crystalline phase-leucite
Crystalline dominated- mostly crystalline, many type of crystals,less transparent, stronger, opaque
Glass dominated
Crystalline- no glassy phase, strongest
How to combine ceramics with metal?
High, medium and low fusing
Metal ceramic veneer restorations fired in a range of 950-1020 degrees Celsius
How is porcelain manufactured?
Heat at high temp to form glassy mass
Quench in water to cool rapidly- mass fractures into small fragments- frit- repeat until desired particle size achieved
Wetting process- is powder and water/water based glycerin liquid

What are the 3 types of porcelain blends?
Opaque
Body
Incisal
What are the steps to make the metal look like a natural tooth?
Opaque masks colour of alloy, responsible for metal ceramic bond- done through porcelain wetting process
Why is it important that opaque porcelain must wet the surface easily?(3)
For proper mechanical bind and chemical interaction at interface
Primary source of colour of resto
Opaque thickness shouldn’t be over 0.1mm- will be overcontoured

What is the purpose of body porcelain?
Fired into opaque layer
Provides translucency, contains metallic oxides that help shade matching

What is the purpose of incisal porcelain?
Usually translucent
Colour of resto more influenced by body and opaque porcelain
5 Indications for metal ceramics?
Need complete coverage- aesthetic
Retainer for FDP
Long span FDP
Rest for removable prosthesis
Extensive tooth destruction/endo teeth
3 Contraindications of metal ceramic crowns
Active caries, untreated periodontal disease
Young patients with large pulp chambers
L/B walls intact
4 Advantages of metal ceramics?
Natural appearance
Retentive- all axial walls included in prep
Can correct axial form
Easy to prep
5 Disadvantages of metal ceramics?
Need significant tooth reduction to gain space
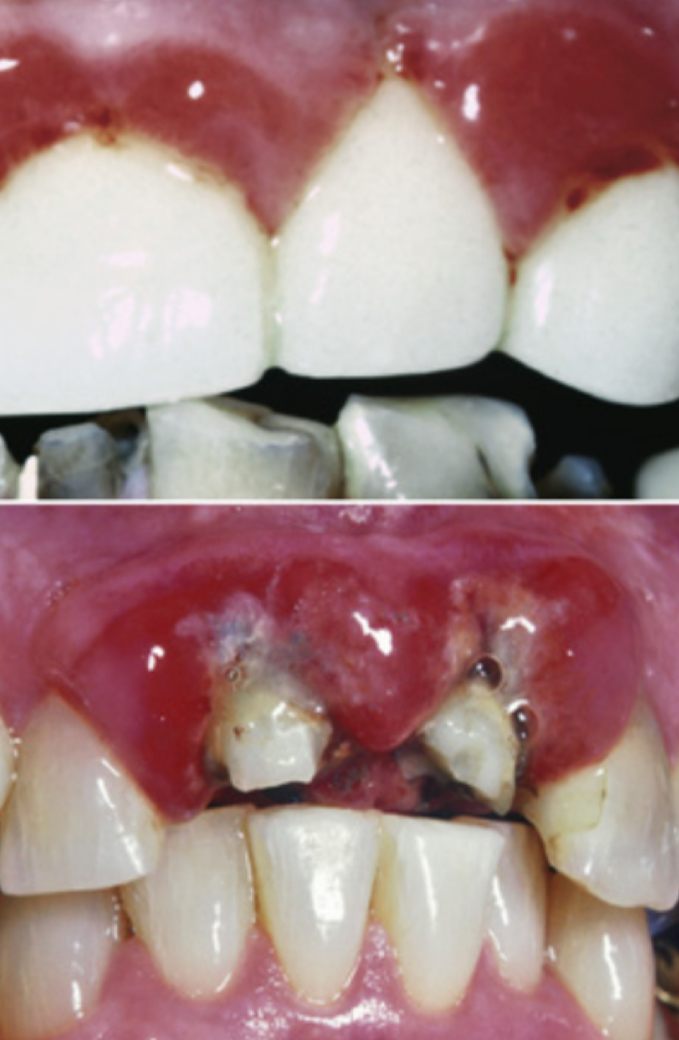
If facial margin on anterior resto is placed subgingivally- increase risk of periodontal disease
Inferior aesthetics- hard shade match
Brittle fracture
Expensive
Preparation steps for metal ceramic crowns in anterior teeth?look at ppt
Place 3 grooves in the cervical 1/3 and incisal 2/3
Place incisal depth grooves
Incisal edge reduction- 2mm
Facial reduction in two planes, break proximal contact
Proximal reduction- 0.5mm lingual chamfer line
Finish