International Finance - Foreign exchange risk and currency derivatives
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is a call option
is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset (like a stock, bond, or commodity) at a predetermined price (the strike price) by a specific date (the expiration date).
The call will be exercised as soon as ST ≥ Strike
what is a put option
is a derivative contract that grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset (like a stock) at a specified price (the strike price) by a certain date (the expiration date).
The put will be exercised as soon as ST ≤ Strike
what is the strike price
the exchange rate at which the foreign currency can be purchased (call) or sold (put)
what is the premium
the cost, price, or value of the option itself
what is the underlying
actual spot exchange rate in the market
what is the specificity of an American option
gives the buyer the right to exercise the option at any time between the date of writing and the expiration or maturity date.
what is the specificity of an European option
option can be exercised only on its expiration date, not before.
what does it mean at-the-money (ATM).
An option whose exercise price is the same as the spot price of the underlying currency
what does it mean in-the-money (ITM).
An option that would be profitable, excluding the cost of the premium, if exercised immediately
what does it mean out-of-the money (OTM).
An option that would not be profitable, excluding the cost of the premium, if exercised immediately
hedging : If you receive foreign currency
hedge for the risk of an appreciation (depreciation) of the domestic (foreign) currency
hedging : If you pay foreign currency
hedge for the risk of a depreciation (appreciation) of the domestic (foreign) currency
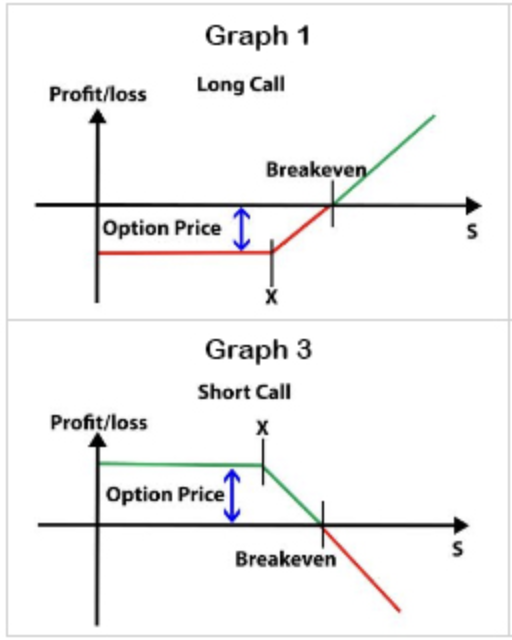
long / short call graphs
long / short put graphs
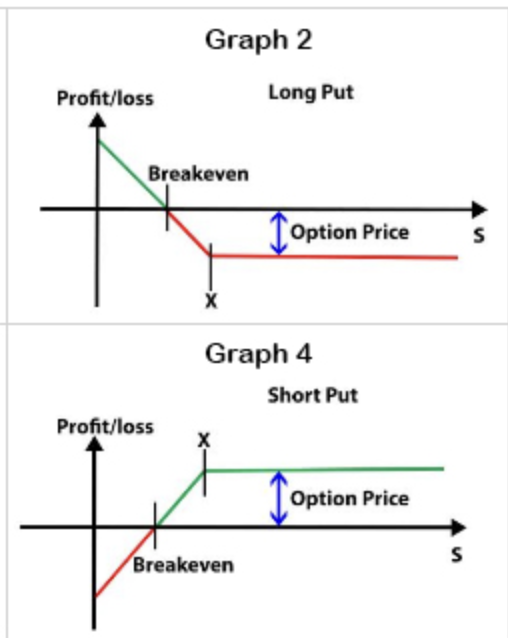
If future forex rate > K
the holder will not exercise the put, so you will have to buy in spot market and that is more expensive, although you still get the revenue from selling the put option
If future forex rate < K
the holder will exercise the put and you will be forced to buy at K. As long as the strike price is not too high relative to the spot rate, your revenue from selling the option should cover the additional cost
Increasing the exercise price of a call option →
Reduces the probability that the option will be exercised so it decreases the option’s value
Increasing the exercise price of a put option →
Increases the probability that the option will be exercised so it increases the option’s value
what are currency swap
is an agreement between two parties to exchange the cash flows of two long-term obligations denominated in different currencies.
change the currency denomination of debt, by exchanging streams of interest payments in different currencies for an agreed period of time.
what are interest rate swaps
allows a company to change the nature of its debts from a fixed interest rate to a floating interest rate.