MICROPARA 1ST LE (MISS BUSLON AND ALINSUG’S FLASHIES)
1/677
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
678 Terms
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
First described bacteria in 1677 with the use of a simple microscope utilizing crude lenses since first person to see live bacteria and protozoa
Fungi
Protozoa
Spermatozoa
What were the 3 major forms of bacteria discovered by Anton Van Leeuwenhoek?
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
Considered the Father of Microbiology, Bacteriology, Protozoology
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
Not a trained scientist, at various times a fabric merchant, surveyor, minor city official. As a hobby, ground tiny glass lenses, thus creating single lens microscopes.
Robert Hooke
Developed the compound microscope in 1678 and confirmed Leeuwenhoek’s discoveries

Compound microscope; 1678
What did Robert Hooke develop and when?
Robert Hooke
English scientist who 1st used the term cells in 1665 and describe the small chambers within the cork that he observed under a microscope of his own design
Robert Hooke
He isolated a mold of the surface of the leather and looked under the microscope of his own design (blue mold)
Spontaneous Generation Theory (Abiogenesis)
Evolutionary theory stating life arose from decomposing, nonliving material
Stanley Miller
Who is credited for the Spontaneous Generation Theory (Abiogenesis)?
Francesco Redi
The Spontaneous Generation Theory (Abiogenesis) was refuted by who by demonstrating the appearance of maggots in decomposing meat depended on the deposition of eggs by flies?
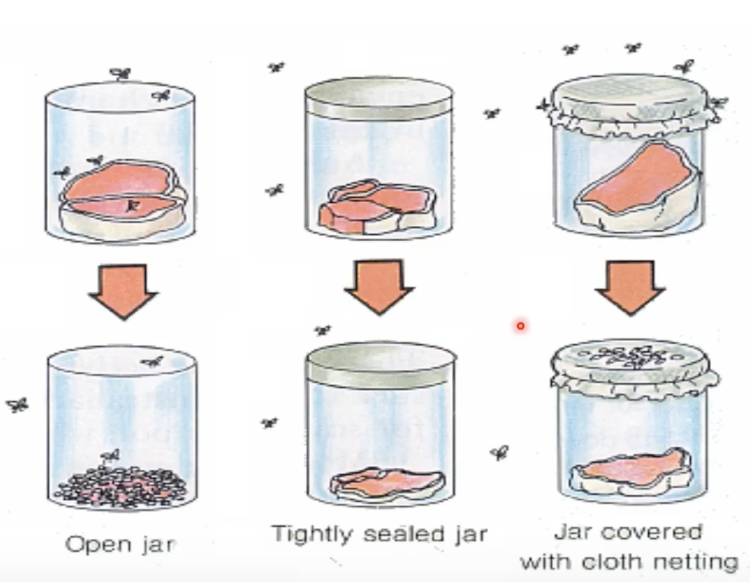
17th Century
When did Francesco Redi refute the Abiogenesis theory?
Pasteur and Tyndall
Who finally disproved the theory of Abiogenesis and proved that life must arise from preexisting life?
Rudolf Virchow
Who first proposed Theory of Biogenesis in 1858?
Rudolf Virchow
German physician and 19th century’s foremost leaders in medicine and pathology
Theory of Biogenesis
Theory that states living things can only arise from preexisting living things
Louis Pasteur
French chemist and microbiologist who was one of the most important founders of medical biology
Louis Pasteur
Able to filter microorganisms from the air and concluded this was the source of contamination
Louis Pasteur
One of the first people to successfully prove biogenesis theory
Louis Pasteur
Demonstrated the fermentation of fruits and grains by certain groups of microorganisms called “ferments”
Louis Pasteur
Developed the chicken cholera (by chance), anthrax and rabies vaccines.
Live Attenuated Vaccine
What type of vaccine is called a weakened form of a pathogen (like a virus or bacteria) to stimulate the immune system without causing the full-blown disease?
An example of this is the chicken cholera vaccine developed by Louis Pasteur.
Rabies
What was Pasteur’s first human vaccine?
John Tyndall
Proved that dust carried germs
John Tyndall
Irish physicist and avid promoter of science in Victorian era
Tyndallization
Bacteria could be killed by successive heating
Method which involves steaming liquids and food products at 100°C on several successive occasions or heating them in three to four occasions with a temperature of 100°C to 120°C and with an interval of 24 hours between occasions
Used for sterilizing medicinal preparations, processing of food products in special units equipped with thermoregulators
Roger Bacon
English philosopher, educational reformer who postulated during 13th century that diseases were caused by invisible living creatures called germs.
Louis Pasteur
Who developed the Germ Theory of Disease, even if he was not the first to propose the theory?
Germ Theory of Disease
What theory did the following experiment support?
Pasteur used a drop of blood from a sheep dying of anthrax
Then he grew this in a sterile culture and repeated the process 100 times, representing a huge dilution of the original culture
The final culture produced anthrax.
This proves that anthrax bacillus caused the disease
Germ Theory of Disease
Theory that states each specific infectious disease is caused by a specific microorganism
Joseph Lister
British surgeon and scientist who spearheaded medical use of antiseptic medicine and introduced aseptic surgery by demonstrating the value of spraying OR with aqueous phenol
Joseph Lister
Developed the first pure culture technique using liquid medium which was the key to the identification of bacteria
Robert Koch
German physicist and one of the founders of the bacteriology
Robert Koch
Perfected the techniques of the identification of microorganisms that are in use today like solid media (a particular germ can cause a particular disease)
Robert Koch
Established the etiologic role of bacteria for anthrax in 1876 by conducting the following:
Using a microscope, examined blood of cows that died of anthrax, and observed a rod-shaped material and suspected that this was the causative agent of the cows who died because of anthrax
He then infected the mice with the blood from anthrax-stricken cows,
The mice also developed the disease
tubercule bacilli
In 1882, Robert Koch discovered the ___ ___ and formulated criteria that provided proof that a specific bacterium caused a disease (TB)
Robert Koch
Who is called the father of Pathogenic Microbiology?
Koch’s Postulates
Forms the basis of pathogenic microbiology and the causality of all infectious diseases are based on these
The causative agent must be present in every case of the disease and must not be present in healthy animals
The pathogens must be isolated from the diseased animal host and must be grown in pure culture
The same disease must be produced when microbes from the pure culture are inoculated into healthy susceptible animals
The same pathogen must be recovered once again from this artificially infected animal host, and it must be able to grow again in pure culture
Robert Koch’s 4 criteria to determine that a certain germ causes a particular disease
(1) every (2) healthy
(One of Koch’s Postulates)
Causative agent must be present in (1) ___ case of the disease and must not be present in (2) ___ animals
(1) isolated (2) pure culture
(One of Koch’s Postulates)
The pathogens must be (1) ____ from the diseased animal host and must be grown in (2) ___ ___
(1) produced (2) inoculated (3) healthy susceptible
(One of Koch’s Postulates)
The same disease must be (1) ___ when microbes from the pure culture are (2) ___ into (3) ___ ___ animals
(1) recovered (2) grow
(One of Koch’s Postulates)
The same pathogen must be (1) ___ once again from this artificially infected animal host and must be able to (2) ___ again in pure culture
Viruses
Leprosy bacilli
Rickettsia
Chlamydia
What are exceptions to Koch’s postulation?
Viruses, Rickettsia & Chlamydia
Exceptions to Koch’s Postulates that are called obligate cellular pathogens/parasites that can survive and multiply only in the living host and cannot be grown in artificial medium
Leprosy Bacilli
Exceptions to Koch’s Postulates that are inoculated in food paths of mice and also need a host.
Microbiology
Branch of biology that deals with the study of microorganisms
Bacteriology
Virology
Mycology
Parasitology
Immunology
Branches of microbiology
Bacteriology
Study of bacteria (bacterium)
Bacteria
Minute, unicellular organisms that have all the necessary protoplasmic equipment for growth and self-multiplication at the expense of available foodstuffs
Widely distributed
Normal Flora
Microorganisms that live on another living organism without causing a disease;
However sometimes, they are opportunistic and adapt by undergoing mutation as they adjust to the environment, which becomes a pathogen
Pathogen
Bacteria/viruses/microorganisms that cause a disease
Virology
Study of viruses
Obligate Intracellular Parasites
Viruses are these, which are parasites that can reproduce only within a living cell (may survive for a short while outside cell, nonliving outside cells)
DNA or RNA, but NOT both
Viruses can either have _________
Capsid (protein shell)
floating shell of the virus
Protects nucleic acid from digestion by enzymes.
Contains special sites on surface allowing viruses to attach to host cell.
Provides proteins enabling viruses to penetrate the host’s cell membrane and eject infectious nucleic acid into the cell cytoplasm
3 Functions of the Capsid of a Virus
Bacteriophage
Virus may become this which is a virus that parasitizes a bacterium by infecting it and reproducing inside it.
Naked virus
Identify the type of virus shown.
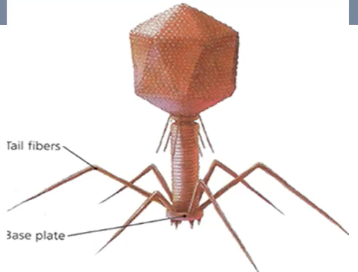
Virus with capsid inside
Identify the type of virus shown.
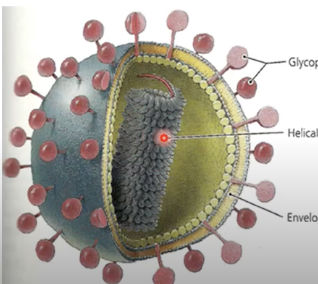
Mycology
Study of fungi
Yeast (Monomorphic)
Yeast & mold/filamentous (dimorphic)
Fungi can either exist as either…
Monomorphic
Fungi that exists as yeast
Dimorphic
Fungi that exists as yeast and mold
Mold
What type of fungi is shown?
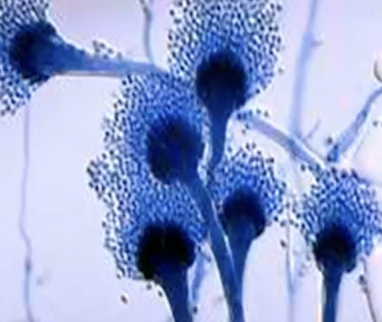
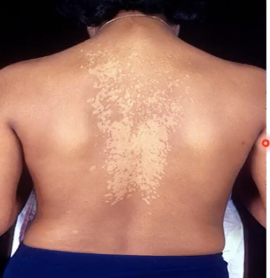
Malassezia furfur
What species of a fungus is naturally found on the skin surfaces of humans but may overgrows and interferes with the normal pigmentation of the skin which results to small discolored patches?
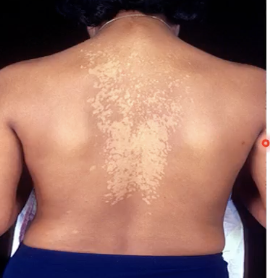
Tinea versicolor
Discolored patches on the skin caused by Malassezia furfur
Parasitology
Study of parasites
Flagellates
Amoebae
Sporozoans
Nematodes
Trematodes
Cestodes
Types of Parasites
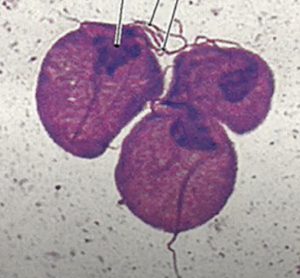
Trichomonas vaginalis
Identify the parasite (specifically a flagellate) shown in the picture, which is causative agent of the STD trichomoniasis.
Amoeba
Identify the parasite.
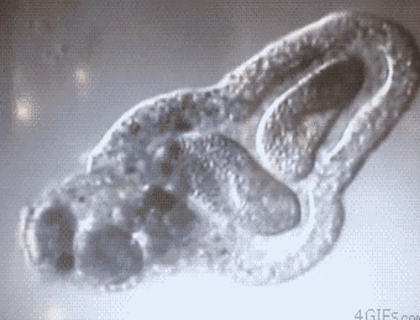
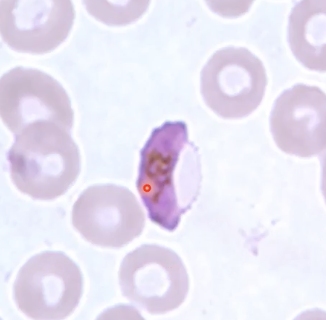
Plasmodium
Identify the parasite.
Flagellates
(parasitology)
Cells/organisms with one or more whiplike appendages (flagella)
Amoebae
(parasitology)
Single-cell eukaryotic organism with no definite shape and move by means of pseudopodia
Nematodes
(parasitology)
Round worms
Trematodes
(parasitology)
Flat worms
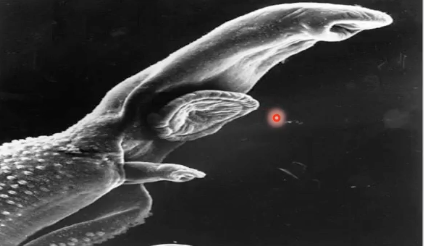
Cestodes
(parasitology)
Tape worms
Has hooks that allow it to attach to the host
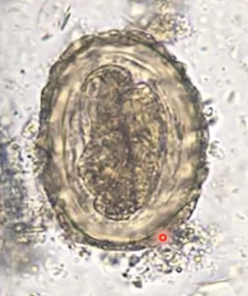
Ascaris Egg
Identify the type of parasite.
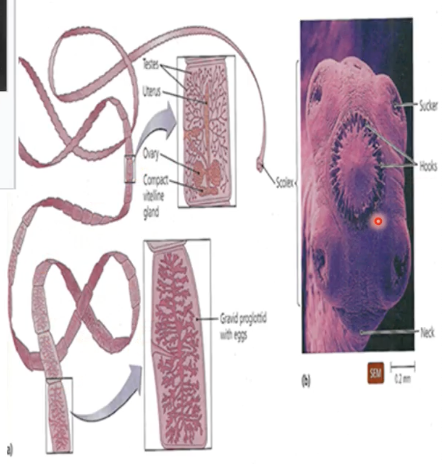
Schistosomes
(parasitology)
“Loving” flatworms
Gonochoristic = have distinct sexes (male or female)
Male surrounds female and encloses with gynecoforic canal and brings female along with him
Male feeds on host’s blood and passes to the female, as well as chemicals which help females develop
Sometimes “divorce” when female jump to another male
Elephantiasis
(parasitology)
caused by parasitic roundworms: wuchereria bancrofti and brugia malayi
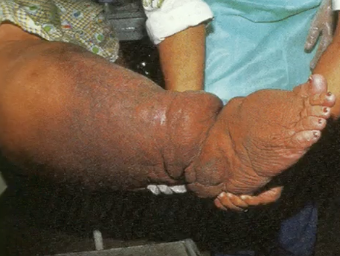
Wuchereria bancrofti and brugia malayi
(parasitology)
parasitic roundworms that cause Elephantiasis
Immunology
Study of the immune system
Cells, molecules and mechanisms, immunity
Phagocytosis
First line of defense in immune system
Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes
2 classification of organisms based on type of cell organization and function
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Taxonomists have placed all microorganisms into 3 domains which are:
Prokaryotes
Unicellular organisms that lack a membrane bound nucleus, a mitochondria and other membrane bound organelles
Distinctive structural feature is not what they have but what they lack
Lack membrane surrounding their DNA and nucleus, rather have a nucleoid
What do prokaryotes lack based on light microscopy (LM)?
Nucleoid
In prokaryotes, where the single chromosomal circular double-stranded DNA molecule is located
Lack the membrane-bound organelles
What do prokaryotes lack based on electron microscopy (EM)?
Bacteria
Archaea
2 domains included in prokaryotes
Archaea (Archaeobacteria)
Domain of bacteria that appears more closely to eukaryotic cells, found in microorganisms that grow in extreme environmental conditions.
Nucleotide sequence of their ribosomal RNA
Type of lipids in cytoplasmic membranes
Chemistry of cell walls
What do Bacteria and Archaea differ in?
Peptidoglycan
What does the archaea cell wall lack which is a major reason why they are placed in a separated domain from bacteria?
Gram (+) Archaea
Archaea that have thick walls and stain purple
Gram (-) Archaea
Archaea that have layer of protein covering cell wall and stain pink
Eukaryotes
Organisms whose cells have a membrane surrounding their DNA forming a nucleus.
Have internal membrane-bound compartments (organelles)
Cells of algae, protozoa, fungi, animals and plants are eukaryotic
Larger in size and more complex than prokaryotes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
(Eukaryote Organelle)
Process and transport proteins
Golgi Body
(Eukaryote Organelle)
Modification of substances and transport throughout the cell, including internal delivery of molecules, and exocytosis or secretion of other molecules
Mitochondria
(Eukaryote Organelle)
Generate energy (ATP)
Lysosomes
(Eukaryote Organelle)
Provide an environment for controlled enzymatic degradation of intracellular substances