Substance Abuse and Harm
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is substance use?
Ingestion of a substance.
What is substance abuse?
Harmful or hazardous use of substances, inc. alcohol and illegal drugs.
What is dependence on drugs?
Implying pharmacological effects and neuroadaptation.
What is substance use disorder (SUD)?
New category in DSM-5 to take into account dependence and hazardous use.
What is an addiction?
Understanding of the phenomenon that includes psychosocial factors.
What are the 2 types of substance? Give examples.
Legal: alcohol, tobacco, prescribed medication.
Illegal: heroine, cocaine, methamphetamine, MDMA, LSD, ketamine, cannabis, synthetic/novel substances.
How can legal status of substances change?
Regularly change depending on reports of harm, media coverage of an issue (high profile deaths) or political agenda.
What is the legal status of drugs in the UK? (4)
You can get a fine or prison sentence if you:
1. take drugs
2. carry drugs
3. make drugs
4. sell, deal or share drugs.
Penalties depend on type of drug/substance, its amount and whether you're involved in supplying.
What is the pattern of alcohol use in the UK (2018)?
- Professionals and managers (high-earners) more likely to drink alcohol in their last week.
- Highest alcohol consumers were 45-64.
What is the pattern of substance abuse in the UK (2018)?
- Cannabis wa smost used drug.
- 33% of drug-related hospital admissions were aged 25-34.
How is a substance problem diagnosed?
With the DSM-5, which established 9 types of substance-related disorders.

How is the alcohol use and disorder (AUD) criteria graded?
Mild: 2-3 symptoms
Moderate: 4-5 symptoms
Severe: 6+ symptoms.

What are the current 2016 guidelines on drinking alcohol in the UK?
No more than 14 units a week, with at least 2-3 alcohol free days per week. Spread drinking evenly over 3 or more days. These are gender-neutral guidelines.
How do you calculate alcohol units?
Alcohol by volume (% of pure alcohol on bottle) x ml/1000.
What are key communication skill techniques when speaking to patients about alcohol and substance use?
- Same person-centred approach.
- Avoid terms like 'drug abuser', 'addict' and 'junkie' and say 'person who has problems with alcohol'.
What are the risk factors for alcohol use disorders?
1. Genetic
2. Psychological
3. Environmental
Are AUDs inherited? (2015)
- WHO reports genes can influence alcohol metabolism.
- Mistreatment of children to AUDs can lead to problematic alcohol use in later life.
How is trauma and PTSD linked with AUDs? (2010)
- 70% of adolescents getting treatment for substance abuse had a trauma history.
- Physical abuse correlates with substance abuse.
- Sexual abuse correlates with cannabis and cocaine use (esp. in women).
- Emotional abuse correlates with cocaine use.
How is schizophrenia linked with AUDs? (2018)
- Schizophrenia can be a vulnerability factor for AUD.
- Characteristics of people with comorbidity are male, depression, low educational attainment, family history of SUDs and previous violent offenses.
How are depressive disorders and AUDs linked? (2018)
- People with depressive disorders have a 2-3 fold risk of AUDs.
- Long-term drinking can increase depression, or depression can trigger AUDs; direction is unclear.
How is age linked to AUDs?
Younger people are more at risk - due to adolescence and risk-taking. But there are different risk factors for older people.
How is gender linked to AUDs?
- Males linked w/ heavy alcohol consumption.
- Barriers for women to get treatment due to stigma of 'women don't get SUDs'.
- Professionals are reluctant to ask women about alcohol, and media can add to bias.
How is socioeconomic status linked to AUDs?
There is a contradiction in literature.
- Poorer communities abstain from alcohol whilst the wealthy drink more.
- But manual workers are more vulnerable to severe alcohol-related outcomes due to inability to avoid the aversive consequences and less access to healthcare and support.
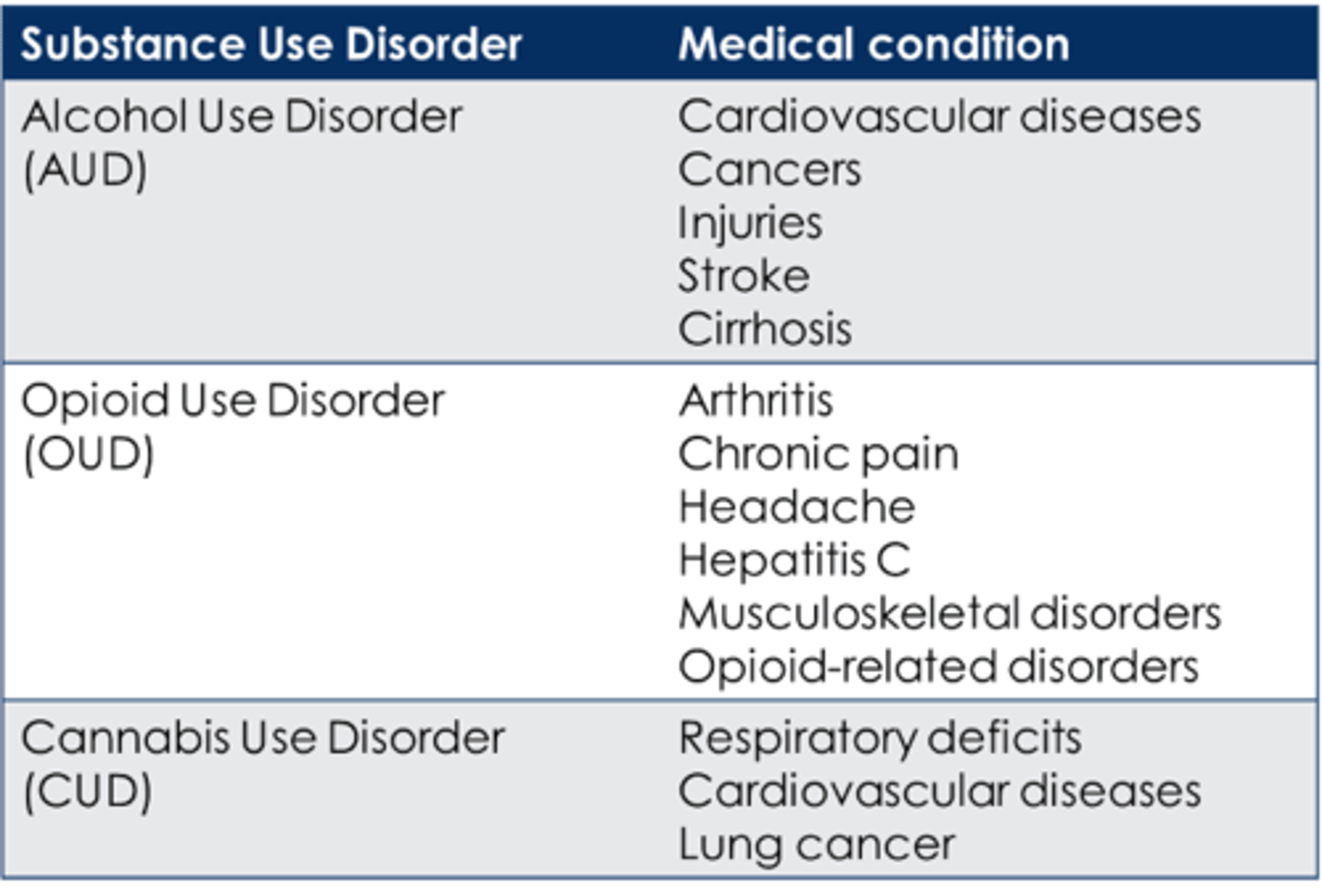
What are the medical conditions associated with SUDs?
AUDs - CV diseases, cancers, injuries, stroke, cirrhosis.
OUDs (opiod) - arthritis, chronic pain, headache, hep. C.
CUD (cannabis) - respiratory deficits, CV diseases, lung cancer.
What is the link between alcohol and liver disease? (2010)
- Low/moderate alcohol levels not associated with marked risk of cirrhosis.
- Risk increases iwth heavier drinking.
- For pts. with cirrhosis, risk of mortality is high even at moderate levels.
What are the main drug harms in the UK?
Alcohol is the most harmful drug, with cocaine, amphetamines and heroine next. Harm can be psychological and to others, not just physical.