1 . CELL PHYSIOLOGY. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF THE CELL. PROPERTIES OF THE CELL MEMBRANE; CELL JUNCTIONS.INTERCELLULAR SIGNALLING. TRANSPORT THROUGH THE CELL MEMBRANE
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
sections
define cell
structure and function of cell
function of organelles
properties of cell membrane
cell junctions
intercellular signalling
transport mechanism of transport through cell
define cell
a cell is the simplest structural functional unit
structure and function of cell
has nucleus, plasma membrane, cytoplasm (composed of five substances: water, ions, proteins, lipids and carbohydrates)
cell contains genetic code
cell arises from division (mitosis and meiosis - growth and reproduction)
cells acquire and utilize energy - ATP
chemical reactions, catabolism, anabolism and metabolism
mechanical activities, hormone responses
regulate activities: DNA synthesis
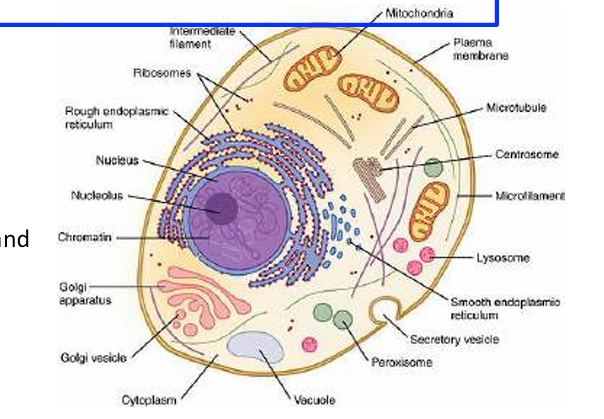
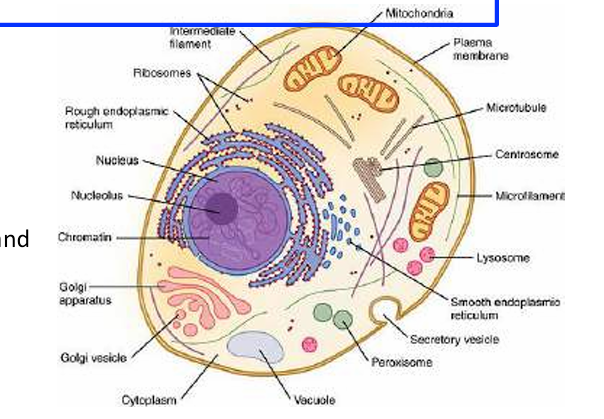
function of organelles
Nucleus - contains chromosomes, used for protein synthesis, contain DNA, makes ribosomes
Ribosomes - site of protein synthesis, DNA as loop
RER - transport protein, fold and process protein that were made at ribosome
SER - synthesis of lipids and steroids
Mitochondria - site of later stages of aerobic respiration, ATP production
Centrioles - hollow cylinders involved in spindle formation and cellular transport
Lysosomes - digestive enzymes, destroy cellular waste
Vesicle - fluid-filled sac, transport substances in and out of cell via cell membrane and between organelles, endocytosis (entering) exocytosis (exiting)
Peroxisomes - contains oxidases with catalase it can detoxify substances, oxidative organelles
properties of cell membrane
Cell membrane = outer layer
Primary functions:
encloses (protects)
fluid mosaic model components - has lipid membrane so lipophilic so impermeable, has channels
polar - can induce electric potential difference permeable to diff ions, diffusion potential that develops depends on concentration inside and outside of membrane
channels that are open in membrane
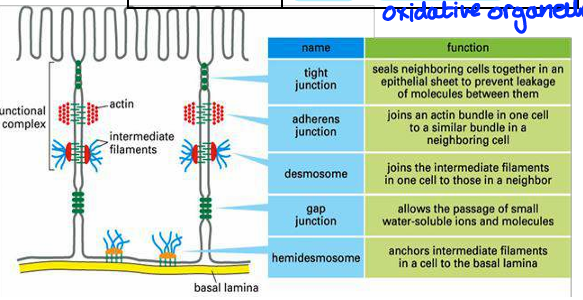
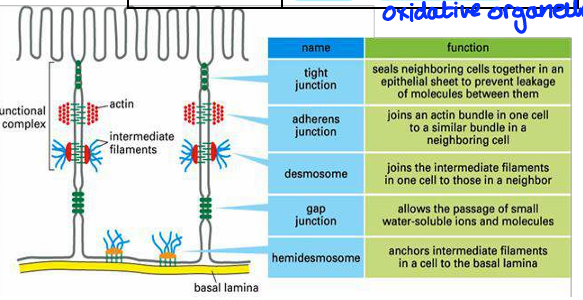
cell junctions
structural multiprotein complexes
provide contact between neighbouring cells or between cell and extracellular matrix
Function:
tight junction - prevent passage of molecules and ions through space between cells
Material must enter by diffusion or active transport
block movement of integral membrane proteins
adhere junction - joins actin filaments of cells together. Cadherins and catenin used for adhesion
Desmosomes - hold two cells tightly together, found in epithelia
Gap junction - intercellular channels allow passage between cells of ions and small molecules
intercellular signalling
coordinates cell actions
Synaptic way - neuronal signals are transmitted electrically along nerve cell axon
Paracrine way - signal released by cells into extracellular fluid and act locally
Endocrine way - hormones produced in endocrine glands are secreted into bloodstream and distributed widely throughout the body
Contact- dependent - cell surface bound signal molecule binds to a receptor protein on an adjacent cell
transport mechanism of transport through cell
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion:
Active transport: Depends on Permeability Passive transport of molecules
Diffusion: eg pulmonary capillaries.
Osmosis: isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic
Filtration: in the capillaries, adapted - thin diffusion easily takes place through them, pressure dependent. Large molecules filtered ou