Bio Chem Metabolism
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
metabolism
heterotrophs
organic sources
autotrophs
makes glucose on its own, inroganic sources
anaerobe
aerobe
What is the end product of heterotrophic carbon metabolism, and returned to the atmosphere for reuse by photoautotrophs?
Advantage of protein-centric maps?
Catabolism
involves the oxidative degradation of complex nutrient molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins) obtained either from the environment or from cellular reserves.
Anabolism
synthetic process in which the varied and complex biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, and lipids) are assembled from simpler precursors
Catabolic reactions are usually ___, and often the chemical energy released is
captured in the form of ATP
exergonic
Amphibolic
alcoholic dehydrogenase
oxidative phosphorylation
phosphoric anhydride
TCA Cycle components
What does malate do in forward TCA? Backwards TCA?
glycosidic linkage
amylopectin
amylose
alpha amylase
glucogen
endoglycosidase
glucanotransferase
beta amylase
exoglycosidae
branched starch
unbranched starch
oligosaccharide
maltotriose
alpha 1→6 glycosidase
limit dextrin
glycogen superstructure
Glucose 6 phosphate
phoshpglucomutase
UDp glucose
glycogen synthease
UDP glucose pyrophosphorylase
Glucose 1 phosphate
glycogen phophorylase
glycogenesis
gl
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis sources, carbohyrdare or nott?
glycogenesis
why is there an energetic advantae to the cell in glycogen phosphorolysis
Pi
inorganic phosphate
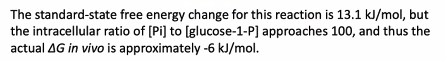
because the over abundance of g____, the body wants to make more ____
How is glucose synthesized?
glucose + Glucokinase = glucose 6 phosphate,
glucose 6 phophate + phosphoglucomutase = glucose 1 phopshate,
glucose 1 phosphate + UDP glucose pyrophosphorylate - Uracil diphosphate glucose
glycogenin
nucleus of glycogen
glycogenin gets glucose from udp glucose, syntase makes the striaght chains on it, then the other thing does something
alpha phoshprus of UTP relevency
tyrosine-OH relevancy
oxonium ion intermediate
amylo (1,4 → 1,6) transglycosylase
easier to make a sphere with branching or striaght?
branching
seven residue terminal segment to C(6)-OH group
alosteric regulation
insulin in glycogen synthase regulation
glucagon epinephrine
glucagon epinephrine
what cells cant break down fats for energy and why
red blood cells have no mitochondria
What enzyme drives the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex