ex 3 blood glucose level
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Blood glucose or blood sugar monitoring
the primary tool utilized to check diabetes control and to find out if the blood glucose levels are within the target range
good blood glucose control
Maintaining __ is the best defense to reduce the chances of developing complication from diabetes
Self blood glucose monitoring
allows checking of blood glucose levels as often as needed or as recommended by the physician
American Diabetes Association (ADA)
has an online tool known as Diabetes 24/7, or a printable blood glucose level log
Diabetes 24/7
a personal health record that allows management of diabetes and share valuable health information with others on the patient's healthcare team
a blood glucose meter or glucometer, lancet device with lancet, and blood glucose test strips
To check the blood glucose levels, it is required to have:
mg/dL or mmol/L unit
The test strip is inserted in the glucometer, which reads the strip and displays a number, either in __ or __
side of the fingertip
Take note that if the finger is used when collecting blood sample, prick the __ to avoid having sore spots on the frequently used part of the finger
before breakfast (fasting)
before bedtime
before lunch-dinner
before rigorous esercise
two hours after a meal
when feeling unwell
when to check for blood glucose
four
For people with type 1 diabetes, it is recommended to check __ times a day
-
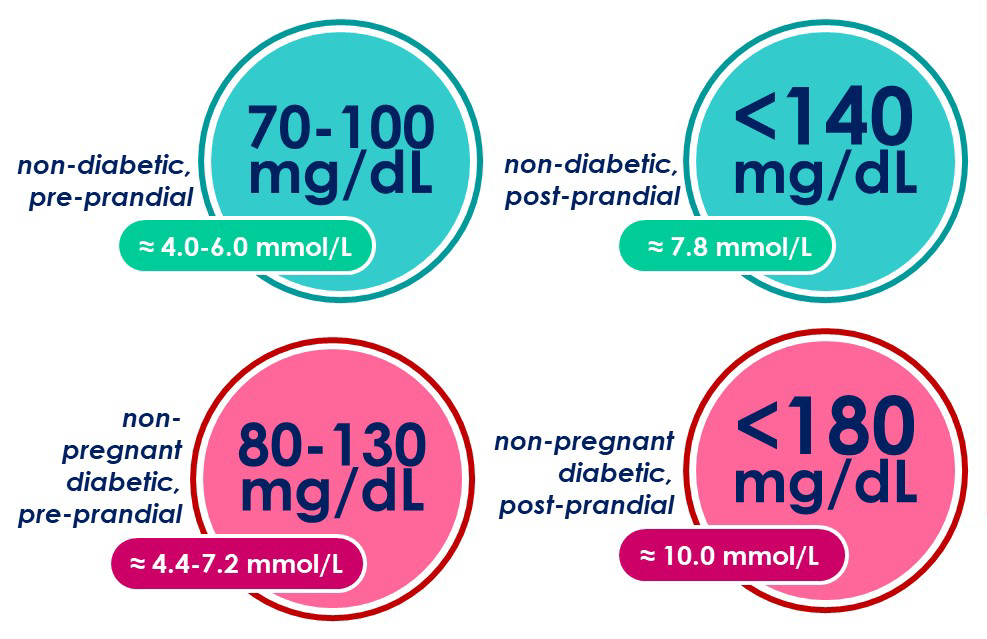
target rangs of blood glucose levels
Diabetes mellitus
is a serious, chronic metablic disease characterized by an increase in blood sugar levels associated with long term damage and failure of organ functions, especially the eyes, the kidneys, the nerves, the heart and blood vessels.
hormones
The body always maintain a balance in the blood glucose levels through feedback mechanisms using __
glucagon
When the blood glucose level drops, the body will act to bring the level back to normal through the secretion of the hormone __ by the pancreas
glucagon
will induce the adipose tissue to breakdown down fat and will trigger the liver to breakdown glycogen to glucose
insulin
if the blood glucose level increases, the hormone__ will work to bring it back to normal level.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
This is also known as insulin-dependent or juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
This diabetes type is thought to be caused by an auto-immune reaction where the body attack its own pancreas with antibodies.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
this diabetes is believed to be caused by genetic predisposition
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
This is also known as non insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes mellitus
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
This type is thought to be caused by insulin resistance usually on liver and muscle cells, or ineffective use of insulin by the body
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
is largely the result of excess body weight and physical inactivity which increases risk of heart disease and stroke
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
This diabetes triggered by pregnancy; pregnancy to some degree, leads to insulin resistance
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
This is commonly diagnosed in middle or late pregnancy period
Pre-diabetes
is a term used to described higher than normal blood glucose level but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes
polyuria
polyphagia
polydipsia
three P’s
polyuria
polyphagia
polydipsia
Individual patients may develop certain or combinations of varied symptoms of diabetes. Three of the most common symptoms include:
polyuria
frequent urination
polydipsia
frequent thirstiness
polyphagia
frequent feeling of being hungry
blood sample
Diabetes can only be diagnosed through different tests that requires __
A1C (Glycated hemoglobin)
This measures the average blood glucose for the past 2-3 months. This test does not require any fasting. An A1C below 5.7% is normal, between 5.7 to 6.4% indicates pre-diabetes, and 6.5% higher indicates diabetes.
FBS (Fasting blood glucose)
This measures the blood glucose level after fasting for at least 8 hours before the test. This is usually done in the morning, after a regular night sleep and before the breakfast. An FBS below 100 mg/dL is normal, between 100 to 125 mg/dL indicates pre-diabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
OGTT (Oral glucose tolerance test)
This is a 2-hour test that checks the blood glucose levels before and 2 hours after drinking a special sweet drink. The test requires fasting for 8 hours before determining the FBS, then the blood glucose level is measured again after 2 hours after drinking a liquid with glucose. At 2 hours, the blood glucose level lower than 140 mg/dL is normal, between 140 to 199 mg/dL indicates pre-diabetes, and 200 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
Random blood glucose test
This measure the blood sugar levels at the time the patient is testing. This test can be performed at any time and fasting is not required. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
7% or more
Losing just 5 to 10% of body weight can lower blood sugar levels, although a sustained weight loss of __ of the initial weight is ideal.
-
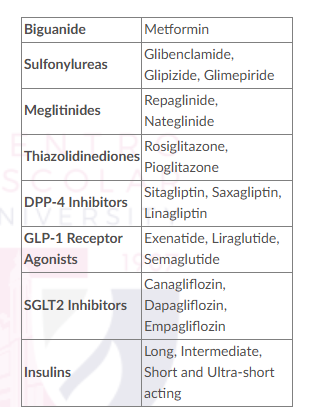
Metformin
Biguanide
Glibenclamide, Glipizide, Glimepiride
Sulfonylureas
Repaglinide, Nateglinide
Meglitinides
Rosiglitazone, Pioglitazone
Thiazolidinediones
Sitagliptin, Saxagliptin, Linagliptin
DPP-4 Inhibitors
Exenatide, Liraglutide, Semaglutide
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Canagliflozin, Dapagliflozin, Empagliflozin
SGLT2 Inhibitors
Long, Intermediate, Short and Ultra-short acting
Insulins