Lighting and Sound Final
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Ellipsoidal Reflector Spotlight
What does ERS stand for?
Iris, Film Effects, Glass Gobos, etc
What are some examples of things we would put in the accessory slot of an ERS?
Swap the Barrel
How do you change the beam width of an ERS?
Use the focus knob (forward = wider, backwards = smaller)
How do you change the beam width of a Fresnel?
Swap the lamp for one with a different lens
How do you change the beam width on a PAR 64
Very Narrow Spot Clear Glass
What type of lens is this?

Narrow Spot Strippled Glass
What type of lens is this?

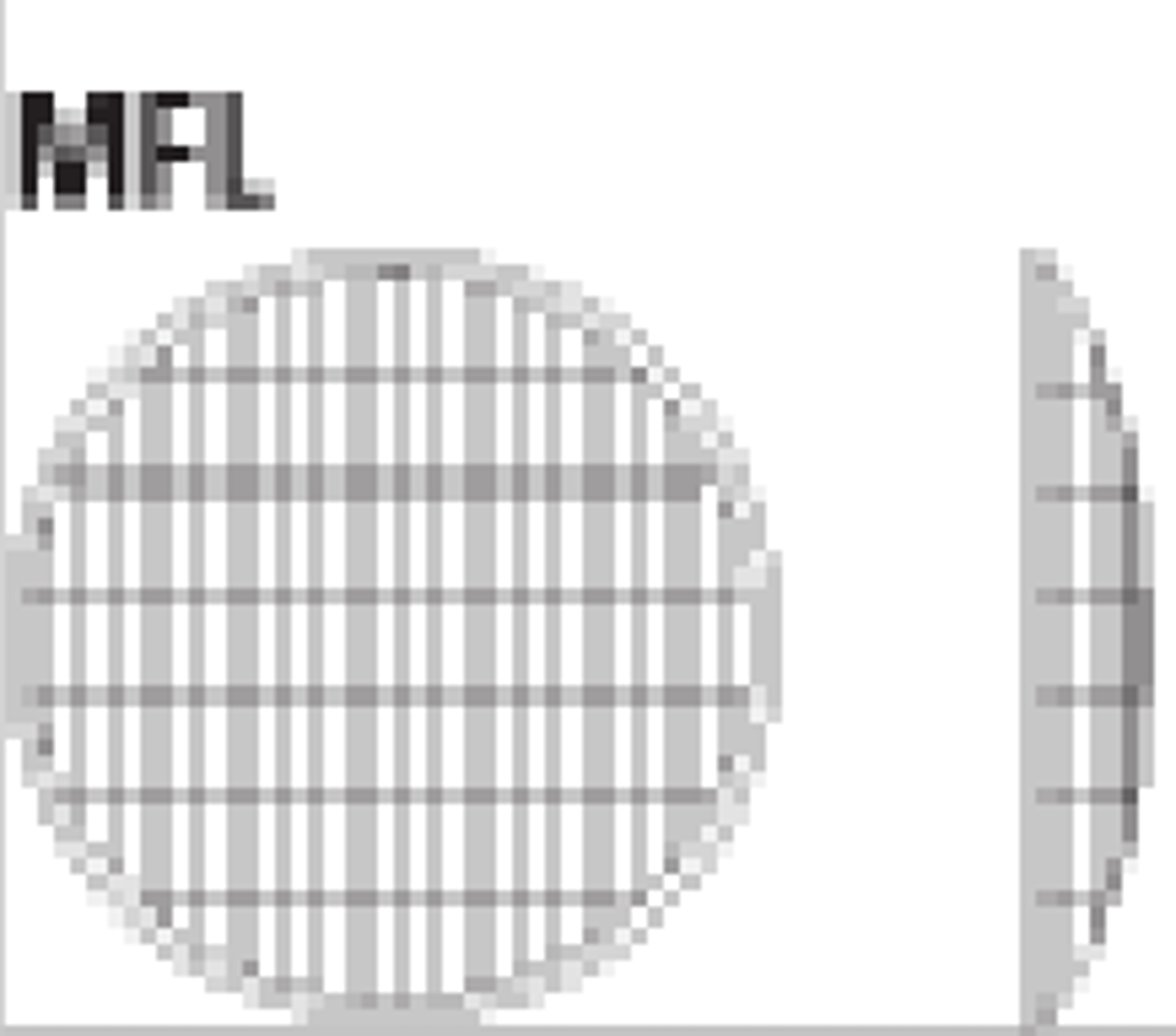
Medium Flood Fewer Facets
What type of lens is this?
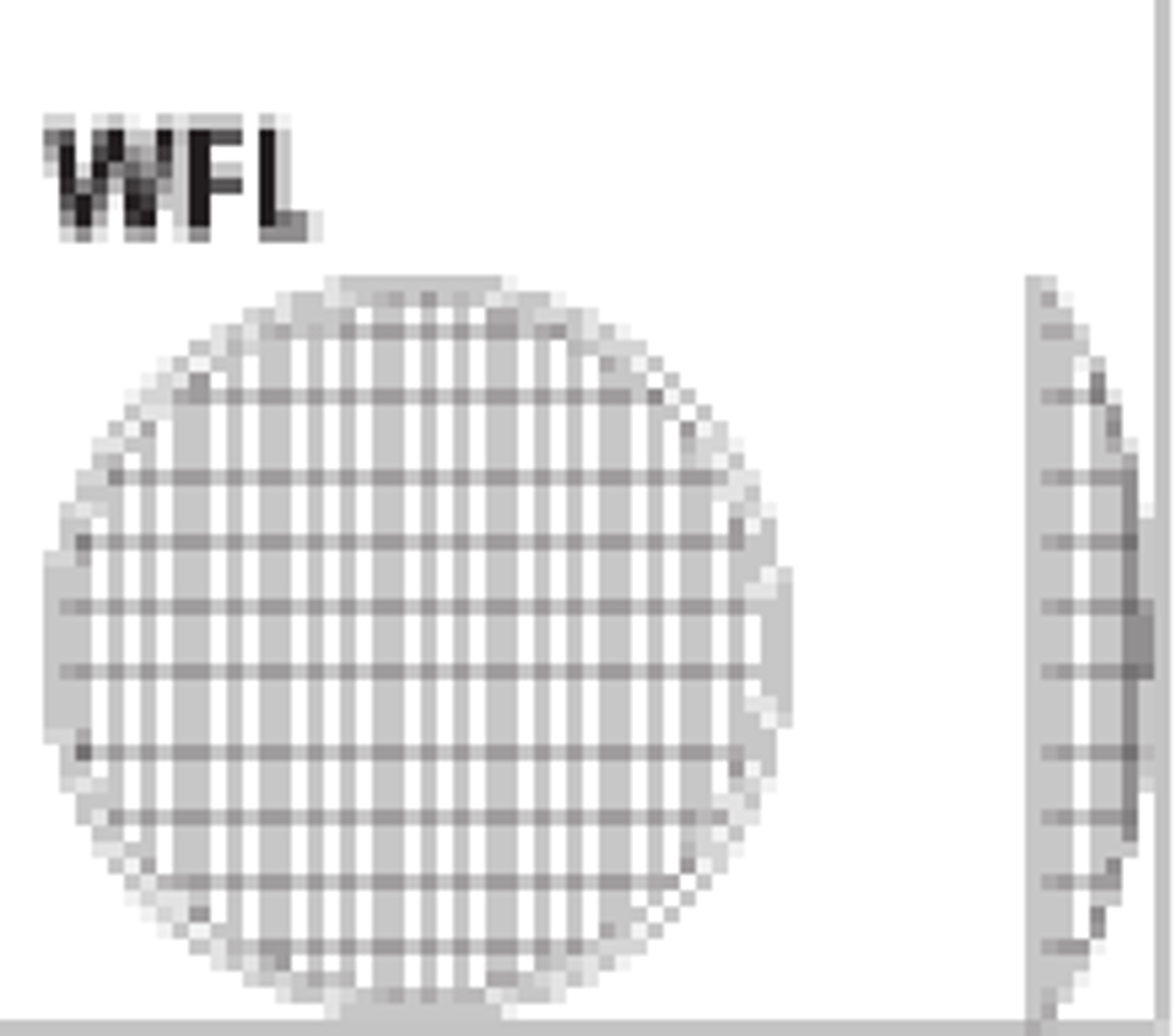
Wide Flood Many Facets
What type of lens is this?
Adjustable barrel changing the beam edge to hard or soft focus, rotation knob that rotates the barrel and shutters, interchangeable barrels to change beam width, four shutters for shaping and narrowing, slot for metal gobos, further slot for additional accessories.
Name some of the UNIQUE characteristics of an ERS.
AC - Alternating Current
DC - Direct Current
What are the two basic kinds of electricity?
Alternating Current
With this current, the movement of the electric charge periodically changes direction.
Alternating Current
This type of power is usually used in things plugged into the wall.
Direct Current
With this current, the electric charge moves constantly in one direction.
Direct Current
This type of power is usually used in batteries.
Volts
Electromotive force or "pressure".
Amps
The amount of electron flow or the "current".
Watts
The amount of useable power.
Volts
Watts / Amps = ?
Amps
Watts / Volts = ?
Watts
Volts x Amps = ?
Hard Patch
Physically connecting the circuit to the dimmer - like on the spaghetti board.
Soft Patch
On the light board connecting the dimmer to the channel.
Powercon
What cord sends power to intelligent lighting fixtures?
DMX
What cable sends data to intelligent fixtures.
The Address
What do we tell intelligent fixtures to listen to?
Purpose
What tells us what area the light is pointing to on the light plot?
Helps us know what colors are pointing where and how we can use them together.
What is the point of an effects plot?
Groups List and Effects Plot
What pieces of paperwork can be useful to a lighting deisgner, specifically during cueing and tech?
512 Channels
How many channels are in one DMX universe?
1 through 512
What universes do we usually use for our regular dimmers?
513 through 1025
What universes do we usually use for our intelligent fixtures?
2
How many DMX channels do hazers need?
8
How many DMX channels do paint cans need?
18
How many DMX channels do studio spots need?
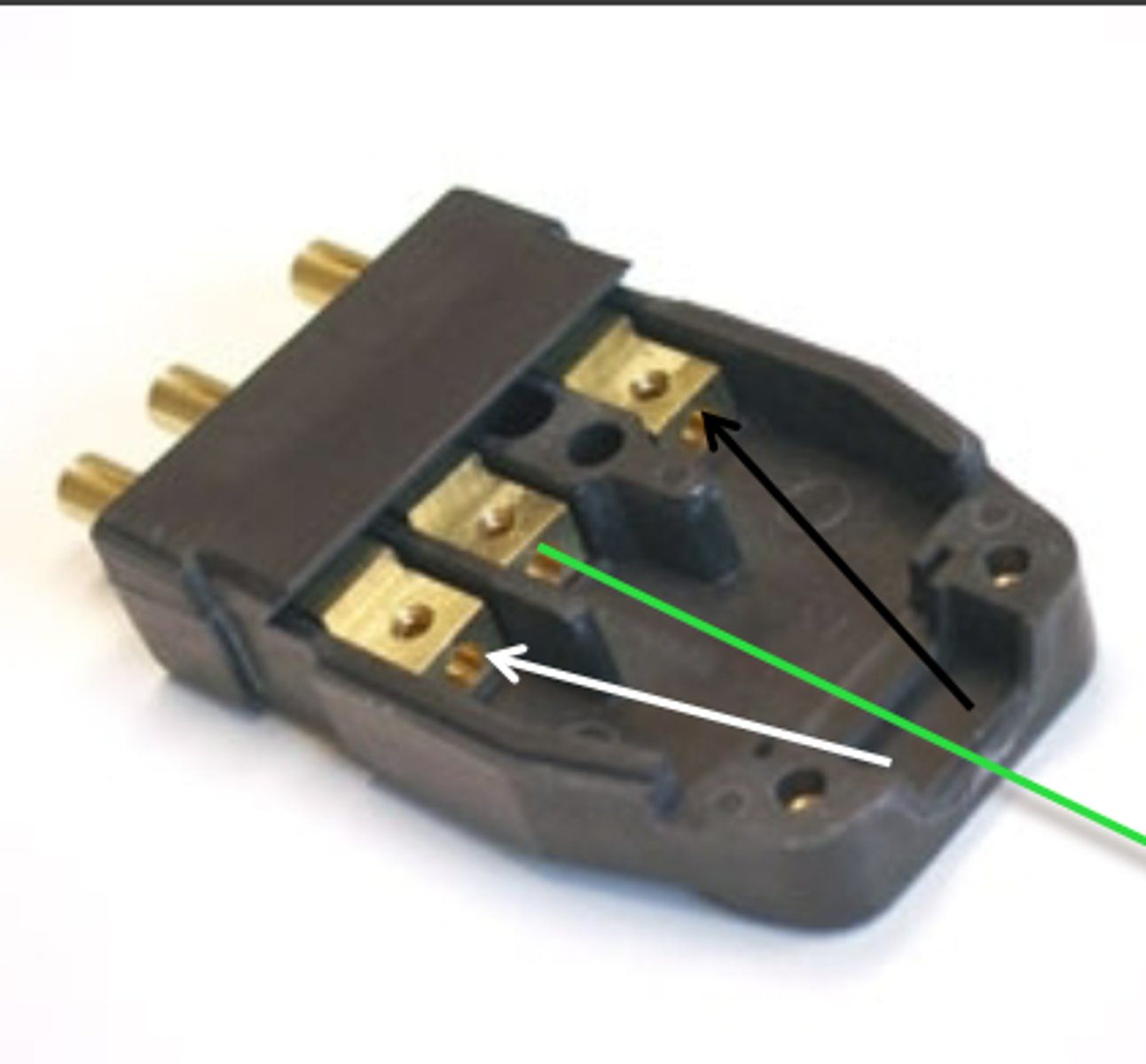
This is the "hot" wire, it carries the power.
What is the black wire called and what does it do?
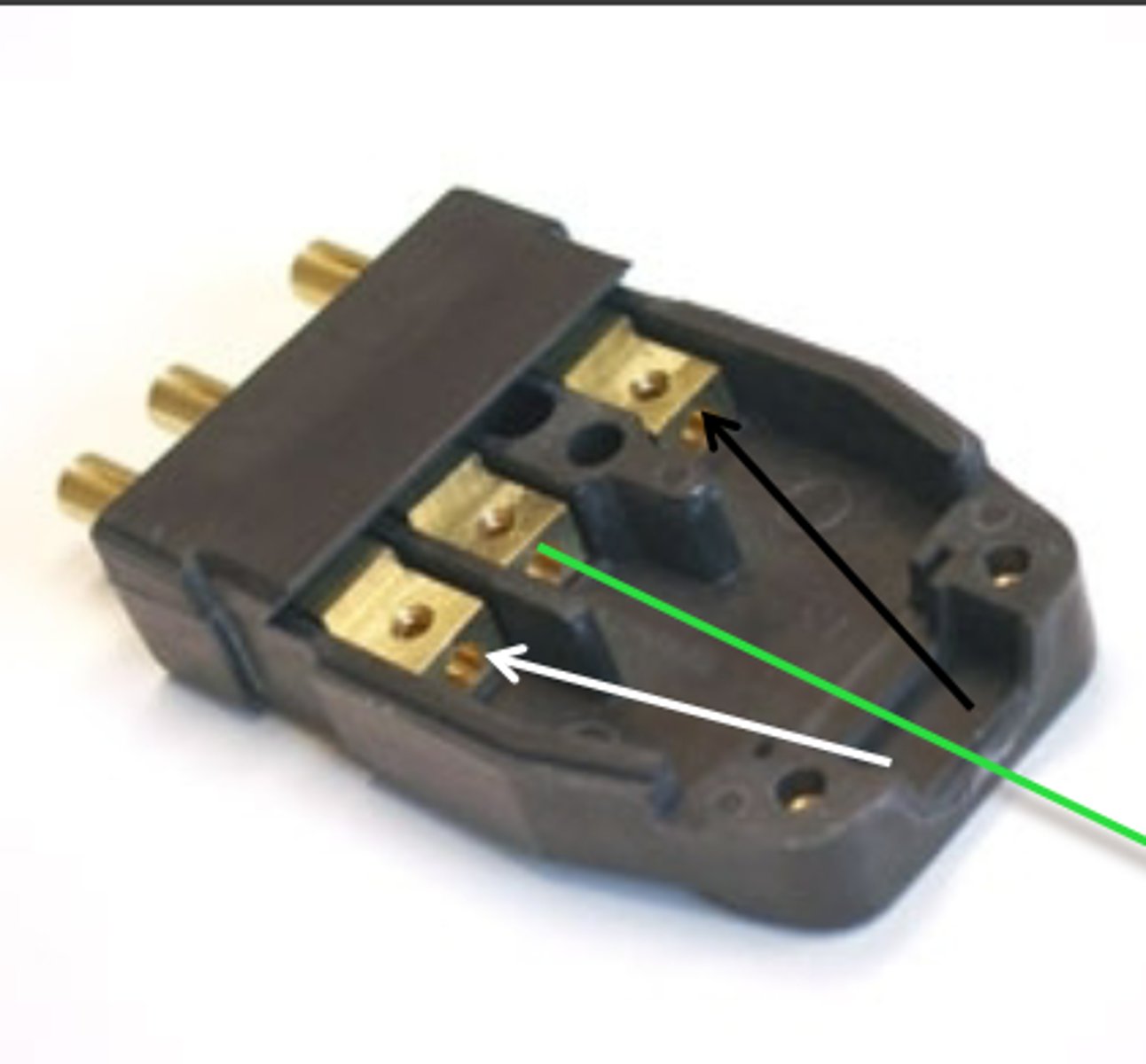
This is the "ground" wire, it keeps the circuits safe and makes sure we don't die.
What is the green wire called and what does it do?
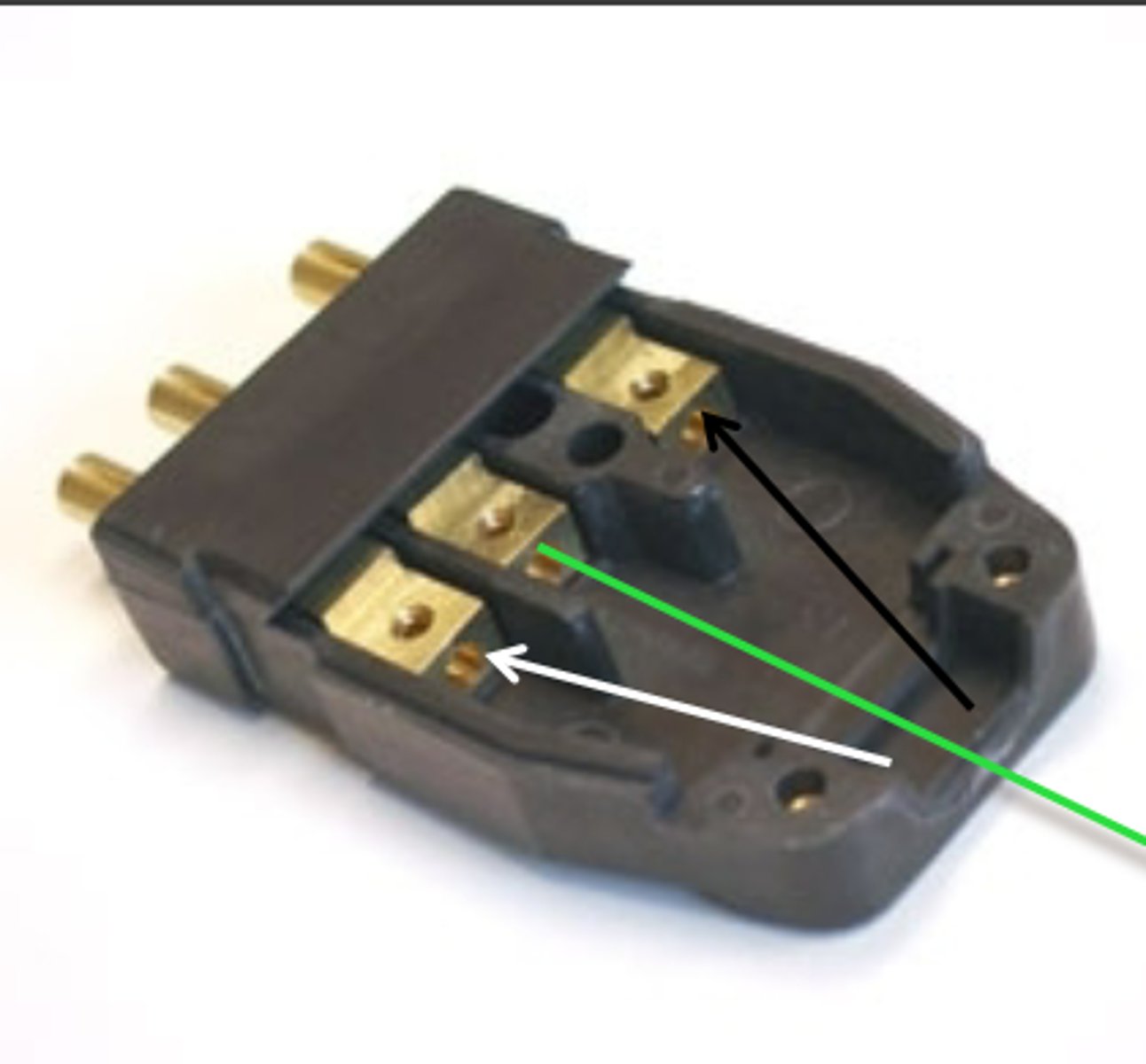
To make the connection to the circuit first.
Why is the ground wire longer than the others?
This is the "neutral" wire.
What is the white wire called?
Red, blue, and green.
What are the tree primary colors of light?
Magenta
What do red and blue light mix to make?
Cyan
What do blue and green light mix to make?
Yellow
What do green and red light mix to make?
Additive Color Mixing
What is it called when we are adding colors to make a new light color?
Subtractive Color Mixing
What is it called when we are taking away colors to make a new light color?
Complimentary Tints
What do we call primary and secondary light colors that "complement" eachother.
Magenta
What is the complimentary tint for green?
Cyan
What is the complimentary tint for Red?
Yellow
What is the complimentary tint for Blue?
Color Temperature
A measurement in degrees kelvin that indivates the hue of a specific type of light source.
The cooler the light looks
The higher the color temperature...
The warmer the light looks
The lower the color temperature...
Stanley Mccandless
Who is credited for creating face light?
Distribution, intensity, movement, and color.
What are the qualities of stage light.
Visibility, selective focus, modeling, and mood.
What are the functions of stage light?
Direction
What is the primary element used in modeling?
1/4" Tip Ring Sleeve - can send balanced mono or unbalanced stereo signal
What does 1/4" TRS stand for and what can it do?
1/4" Tip Sleeve - only carries unbalanced mono signal.
What does 1/4" TS stand for and what can it do?
Connects microhpnes to a console, and sometimes connects consoles to speakres.
What is an XLR cable used for?
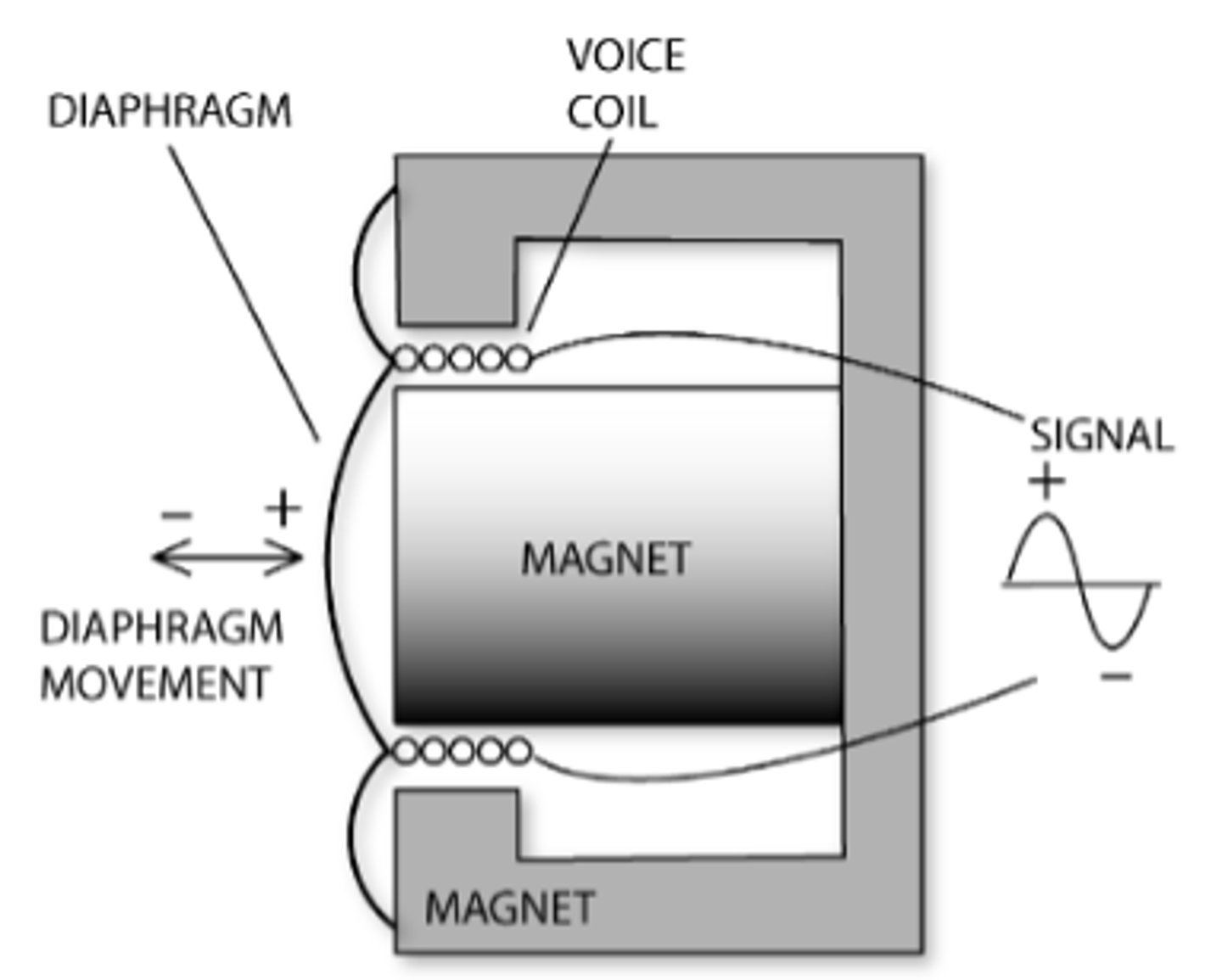
Dynamic
What type of microphone is this?
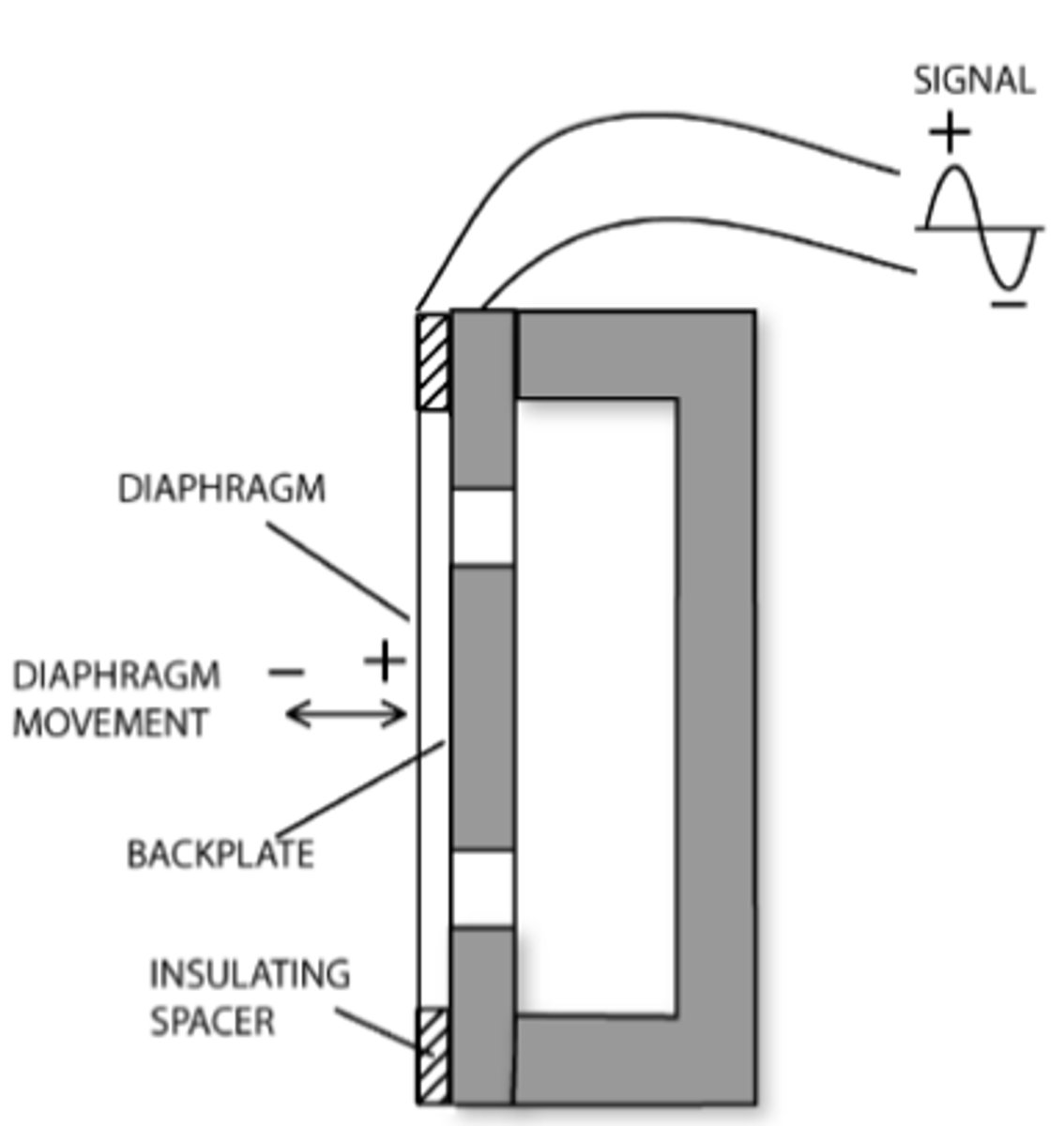
Condensor
What type of microphone is this?
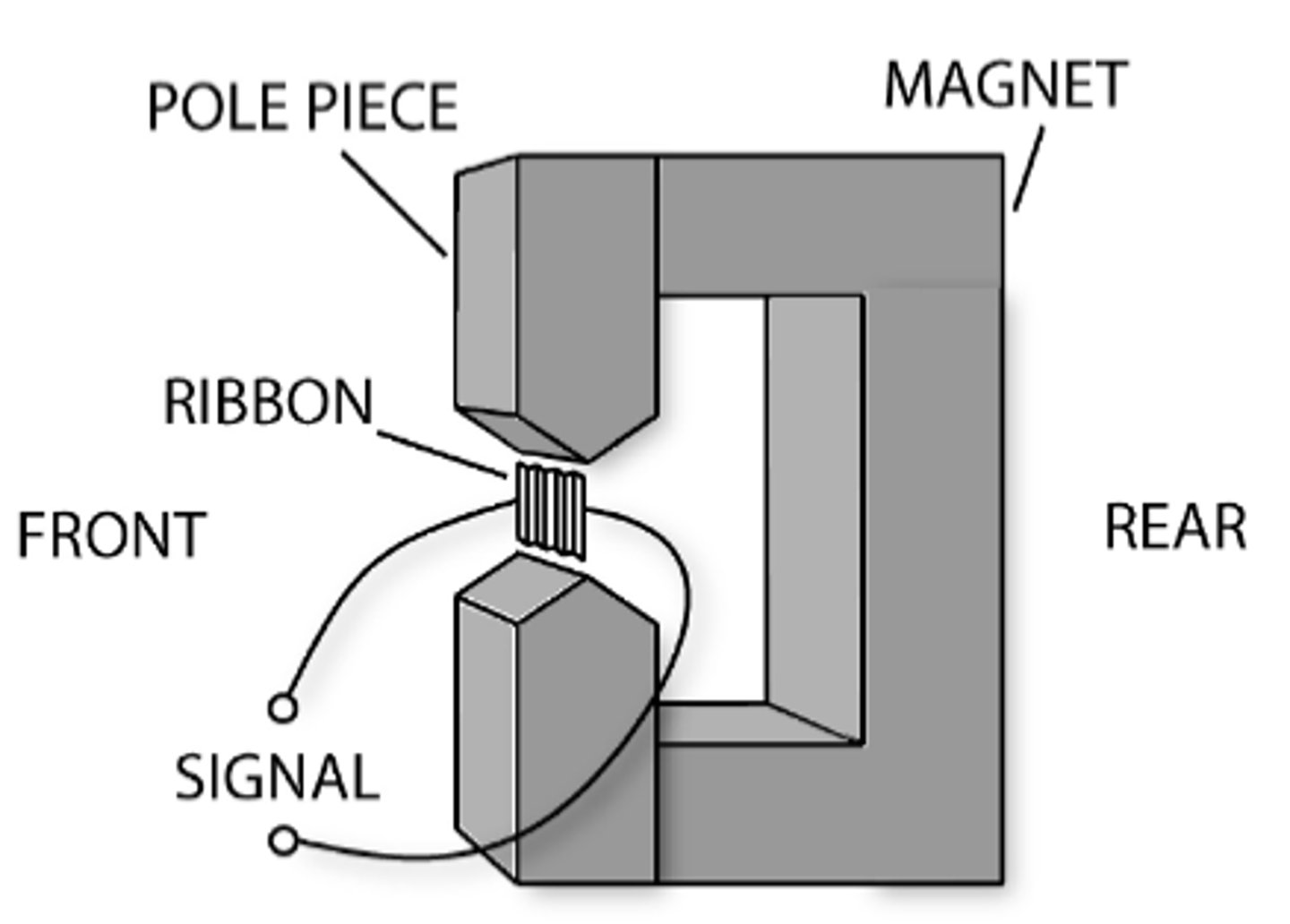
Ribbon
What type of microphone is this?
Condensor
What type of microphone needs phantom power?
48v
What else can you call phantom power?
Condesor
What type of microhpne can be miniaturized?
Face Mics
What are condensor mics most commonly used for?
Allows or restricts the amplitude.
What does the gain knob do?
Turn up or down different frequencies
What does the EQ do?
Source, pre amp, signal processor, amplifier, speaker.
What are the 5 parts of signal flow IN ORDER?
Audio Cue
What QLab cue allows you to play sound cues with control over levels, timing, directionality, and effects?
Fade Cue
What QLab cue allows you to make changes over time?
Group Cue
What QLab cue allows you to put cues into a "folder" for organization?