Mechatronics Devices 4: Temperature Sensors
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Name two types of temperature sensors and list the main types of electrical temperature sensors.
Electrical: Thermocouples, Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), Thermistors, Infrared Sensors, Semiconductors. Non-electrical: Thermometer.
What is the Seebeck effect?
The Seebeck effect is a phenomenon in which a temperature difference between two dissimilar electrical conductors or semiconductors produces a voltage difference between the two substances.
What is a thermocouple and why must it use two dissimilar metals?
A thermocouple is made of two dissimilar conductors that form a junction. It works by generating a temperature-dependent voltage via the thermoelectric effect. Using dissimilar metals allows for a measurable voltage difference due to the Seebeck effect.
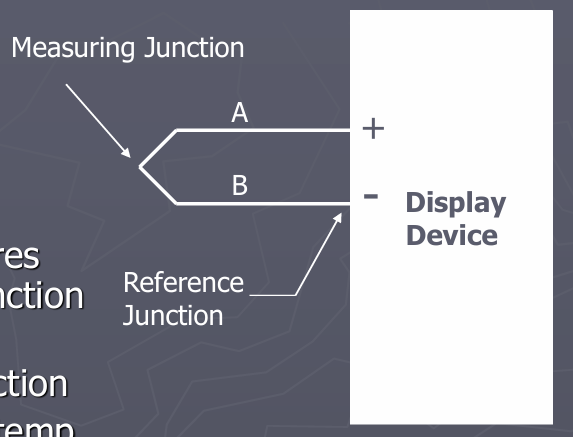
What is the typical temperature range for thermocouples?
Thermocouples can measure temperatures from sub-zero up to 4000°F (2000°C).
What is the function of the reference (cold) junction in a thermocouple?
The reference (cold) junction provides a known temperature point, usually set to 0°C, to allow accurate measurement of the temperature difference.
Give an example of two thermocouple types and their temperature ranges.
Type B: 870-1700°C; Type E: 0-900°C.
What is a key factor in selecting a thermocouple type?
Thermocouples are selected based on the required temperature range and sensitivity for the application.
List three industrial applications of thermocouples.
Plastic injection molding, food processing equipment, and heat treating.
State two advantages and two disadvantages of thermocouples.
Advantages: Simple, rugged, high temperature operation.
Disadvantages: Least stable/repeatable, low sensitivity to small temperature changes.
What is an RTD and what material is it commonly made from?
An RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) is a sensor that measures temperature by correlating resistance with temperature, commonly made from platinum.
Describe the construction of an RTD element.
An RTD element consists of fine coiled wire wrapped around a ceramic or glass core, often placed inside a sheathed probe for protection.
What is the relationship between resistance and temperature in an RTD?
The resistance of an RTD increases nearly linearly with temperature over a wide range.
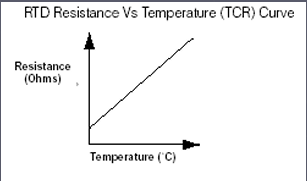
List two applications of RTDs.
Air conditioning/refrigeration servicing and medical research.
Why are RTDs rarely used above 660°C?
It is difficult to maintain the purity of platinum at high temperatures, affecting accuracy.
What is a thermistor and what is it made of?
A thermistor is a semiconductor temperature sensor made of a mixture of metal oxides pressed into a bead, wafer, or other shape.
Name two applications of thermistors.
Medical equipment and engine coolant temperature measurement in transportation.
Compare RTDs and thermistors in terms of sensitivity, response time, and state two pros and cons of RTDs.
RTDs are less sensitive and slower than thermistors, but offer better stability and a wider temperature range.
Advantages: Most stable, most accurate.
Disadvantages: High cost, slowest response time.
What is the difference between NTC and PTC thermistors?
NTC thermistors decrease in resistance as temperature increases (used for sensing), while PTC thermistors increase in resistance as temperature increases (used for current control).
What are the main advantages and disadvantages of thermistors compared to RTDs?
Thermistors have higher sensitivity to small temperature changes, but have a limited temperature range and are fragile.
List several applications of semiconductor temperature sensors in both industrial and domestic settings.
Applications include Hard Disk Drives, Personal Computers, Electronic Test Equipment, Office Equipment, and Domestic Appliances.
How are semiconductor temperature sensors used in process control?
They monitor and regulate temperature in various industrial processes.
What are the main advantages of thermocouples, RTDs, and thermistors?
Thermocouples: simple, rugged, low cost, and high temperature capable.
RTDs: most stable, accurate, and repeatable.
Thermistors: highly sensitive to small temperature changes and become more stable with use.
What is the Hall effect?
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (Hall voltage) across a conductor, transverse to an electric current and a perpendicular magnetic field.
What is a Hall effect sensor used for?
Hall effect sensors are used for proximity switching, positioning, speed detection, and current sensing.
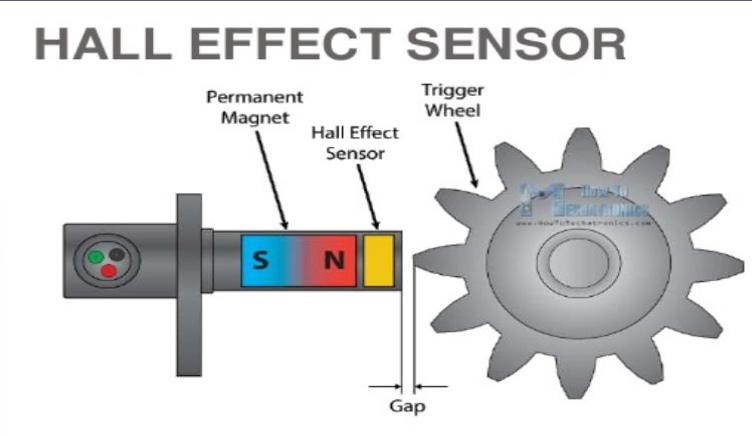
Describe the working principle of a Hall effect sensor.
A Hall effect sensor consists of a thin piece of semiconductor material. When placed in a magnetic field, the magnetic flux exerts a force on charge carriers, creating a potential difference (Hall voltage) across the material.
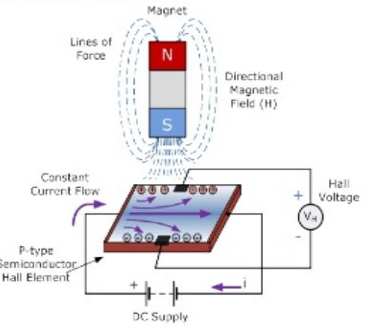
What is required for a Hall effect sensor to generate a voltage output?
The magnetic flux lines must be perpendicular (90°) to the current flow and of the correct polarity, usually a south pole.
What information can the Hall effect provide?
The Hall effect provides information about the type of magnetic pole and the magnitude of the magnetic field.
List two disadvantages of thermocouples compared to other sensors.
Least stable/repeatable and lowest accuracy.
List two disadvantages of RTDs compared to other sensors.
High cost and slowest response time.
List two disadvantages of thermistors compared to other sensors.
Limited temperature range and lack of standards for replacement.