B3.2 Transport
1/199
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
Where is there a large density of capillaries?
at an exchange of materials
What are the three adaptations in capillaries?
Large SA, thin walls with pores, and fenestrations
What is the narrowest blood vessel?
Capillaries
What is the diameter of the capillaries?
10 μm
How do blood molecules aline through capillaries?
in a single file
What does multiple capillaries branching form?
Capillary networks
What do capillary walls consist of?
Endothelium cells
Name two properties of endothelium cells in capillaries
thin and permeable
What is the endothelium cells in capillaries coated in which provides support?
extracellular fibrous proteins
What is the role of the basement membrane in the capillaries?
Filters what enters and exits the capillary
What does the basement membrane of a capillary let through?
small and medium sized molecules
What doesn’t a basement membrane allow into the capillary?
macromolecules (proteins)
What causes fluid to leak out of capillaries?
High blood pressure
What does the fluid in capillaries contains?
oxygen, glucose, and substances in blood plasma
What does the fluid which leaks out of capillaries not contain?
plamsa proteins
What causes the fluid whoch leaked out of capillaries to re-enter the capillaries?
Low blood pressure
What are fenestrations?
Large pores
What do fenestrations allow in capillaries?
the production of large volumes of tissue fluid
What exchanges do fenestrations speed up?
Between blood cells and tissue cells
What is the blood pressure in arteries?
High
What is the blood pressure in veins?
Low
Which direction do arteries carry blood?
away from the heart
Which direction do veins carry blood?
towards the heart
What is the relative thickness of arteries?
Thick
What is the relative thickness of veins?
Thin
What is the relative size of lumen in arteries?
Narrow
What is the relative size of lumen in veins?
Wide
What is the inner-surface of arteries like?
corrugated
What is the inner-surface like in veins?
Smooth
Are fibres visible in arteries or veins?
Arteries
What are collagen fibres?
Tough rope-like proteins
Name a property of collagen fibres
High tensile strength
What is the function of collagen in arteries?
To stop arteries bursting
What is the name for the heart chambers contract?
systole
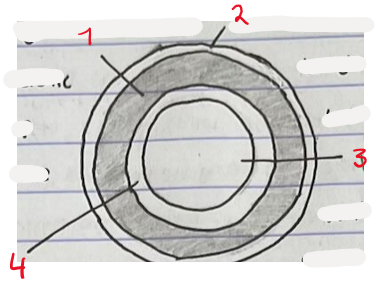
Label this diagram of an artery
Turnica Media
Turnica Externa
Luman
Tunica Intima
Describe the tunica media in arteries
Thick layer containing smooth muscle and elastic
What is the role of the tunica media in arteries?
help pump blood by transmitting the pusle
Describe the turnica externa in arteries
Outer coat of connective tissues with tough collagen fibres
What is the role of the turnica externa in arteries?
To prevent swelling/bursting during high blood pressure
Describe the tunica intima in arteries
Smooth endothelium lining
What is the role of the tunica intima in arteries?
Reduce resistance to flow
Describe the lumen in arteries
Narrow space through which blood flows
What is the role of the lumen in arteries?
help maintain high blood pressure and velocity
What is the name for when heart chambers don’t pump?
Diastole
What is the name of given when arteries narrow?
Vasocontriction
What is the name of given when arteries widen?
Vasodilation
What are the names given to branches of arteries?
arterioles
What is in high density in arterioles?
muscle fibres
What is the use of muscle fibres in arterioles?
flow rate can be adjusted
What are the two arteries where the pulse can be felt?
Radial and coratid artery
What is used to digitally measure pulse?
A pulse oximeter
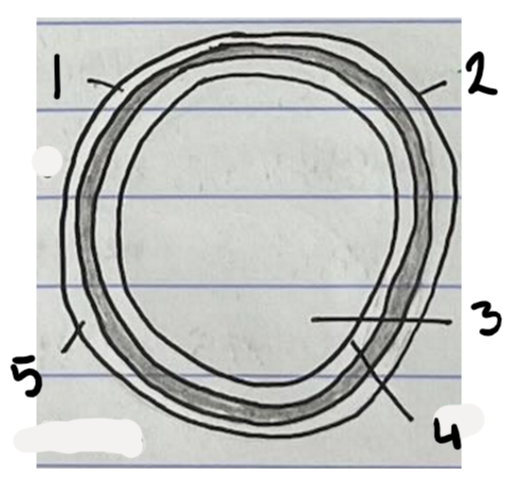
Label the diagram of a vein
Tunica Externa
Tunica Media
Lumen
Tunica Intima
Thin Wall
What is the role of the tunica externa in veins?
to prevent leaks
Is there a presence of elastics or collagen fibres in veins? Why?
No as the blood is at low pressure
What is the main feature veins have which arteries do not?
Valves
What is the role of valves in veins?
Prevent backflow
What aids the flow of blood in veins?
skeletal muscles adjacent to veins
How does a skeletal muscle aid the flow in veins?
It widens to apply pressure to the vein
Where does the left ventricle pump blood into?
The aorta
Where does the aorta not go?
The lungs
What is the name of the first 3 branches of the aorta?
The coronary arteries
What is the role of the coronary arteries?
To provide blood to the heart walls
What causes the build up of plaque?
deposition of lipids
What is the effect of plaque deposition in arteries?
tehy narrow restricting blood flow
What are the three consequences of a build up of plaque in the coronary arteries?
Occlusions, angina, and coronary heart disease
What is epidemiology?
The research into the natrue and spread of diseases
What are the 8 causes of CHD? (HINT: Hoof disc)
Hypertension
old age
obesity
Family history of CHD
diabetes
inactive lifestyle
smoking
cholestrol (high)
What does correlation NOT equal?
Causation
Where is water in plants transported to and from?
Roots to leaves
What transports water in flowering plants?
Xylem
In the xylem, what s water transported as a part of?
Xylem sap
Where does water evaporate from in a plant?
Walls of spongy mesophyll
Where does water diffuse out of in plants?
Stomata
What is the name of the process by which water is lost by a plant through diffusion out of the leaf?
Transpiration
Where is water drawn from to replace the water lost from evaporation in leaves?
Pores between cellulose molecules
What is the process by which water sticks to cellulose molecules?
Adhesion
What is the process by which water molecules stick to themselves?
Cohesion
Water moving from cellulose into the leaf is a form of what kind of transport?
Capillary action
When water is drawn out of the xylem into the leaf, what is generated in the xylem?
Tension (pulling forces)
Pulling forces in xylem vessels which descend the column of water generate what?
A transpiration pull
What energy drives the transpiration pull?
Heat energy from tanspiration
What is broken down during the development of xylem vessels?
End walls
Why are end walls broken down during the development of xylem vessels?
To allow a continuous column of water
What substance is used to thicken xylem walls?
The polymer lignin
What is the role of lignin in the xylem vessels?
Prevents collapsing due to low pressure
What allows water to enter and exit xylem vessels?
Gaps in the thickening
What is formed in young plants to allow water passage in the xylem?
rings or helixes
As a plant rows, what do the rings or heliwes in xylem vessels develop into?
Pits
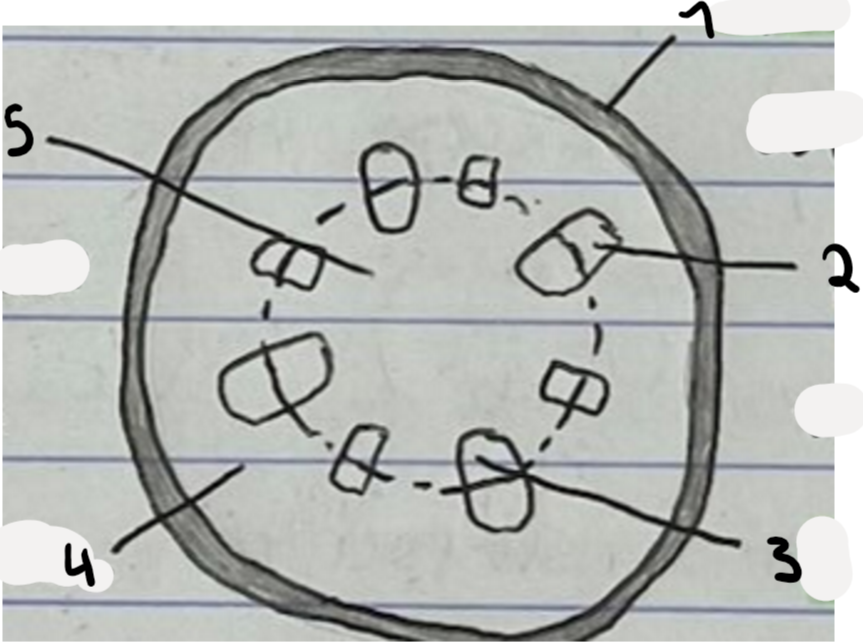
Label this diagram
Epidermis
phloem
xylem
cortex
pith
Describe an epidermis in a plant
single layer of cells with waxy cuticle
What is the role of an epidermis?
Reduce water loss
describe a phloem
small thin-walled cells
What is the role of the phloem?
to transport sugars and other foods
describe a xylem in a stem
wide tubular structure with thick walls and round in cross sections
What is the role of xylem in the stem?
transport water and mineral ions
Describe the cortex in the stem
medium-seized thin walled cells
What is the role of the cortex in the stem?
strengthen the stem with turgid
Describe a pith in a stem?
large thin-walled cells
What is the role of pith in stems?
Fill the center of the stem
What is the role of epidermis in root cells?
Absorb water and mineral ions from the soil