Nuclear Chemistry Terms
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Half-Life
Time required for half of a radioactive sample to decay.
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
Radioactivity
Spontaneous emission of particles or energy from an unstable nucleus.
Neutrons
Neutral particles in the nucleus, important for stability.
Transmutation
Process of one element changing into another.
Iodine-131; Carbon-14; Cobalt-60
Examples of radioisotopes used in medicine and dating.
Nuclear Reactions
Reactions that involve changes in an atom’s nucleus.
Nucleus
Dense center of an atom containing protons and neutrons.
Radioisotope
A radioactive form of an element.
Mass Number
Sums of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Radiation
Energy or particles emitted during radioactive decay.
Fission
Splitting of a large nucleus into smaller ones (used in nuclear power)
Fusion
Combining small nuclei to form a larger one (powers the sun)
Proton
Positively charged particles in the nucleus
Stable
A nucleus that does not undergo radioactive decay easily
Chemical reactions vs. Nuclear reactions
Chemical changes involve electrons; nuclear changes involve the nucleus
Band of stability
Region of the graph where stable nuclei exist
Transuranium elements
Elements with atomic numbers greater than 92
Particle accelerators
Devices used to produce high-speed particles
Chain Reaction
A self- sustaining fission reaction
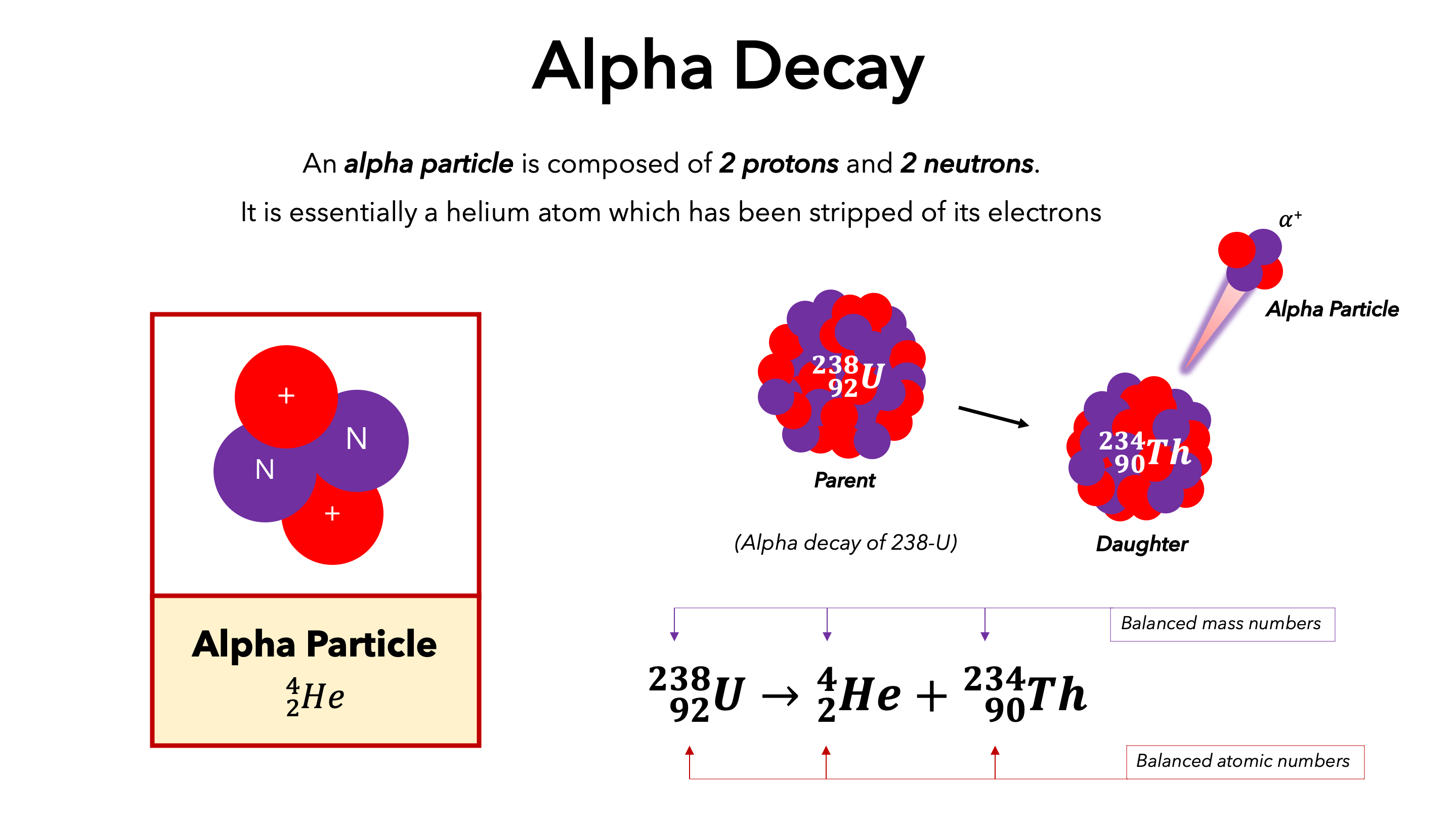
Alpha (α)
symbol: α or 4/2 He
Charge: +2
Mass: Heavy
Penetration: Low (stopped by paper)
Effect: Mass # decrease by 4, atomic number decrease by 2
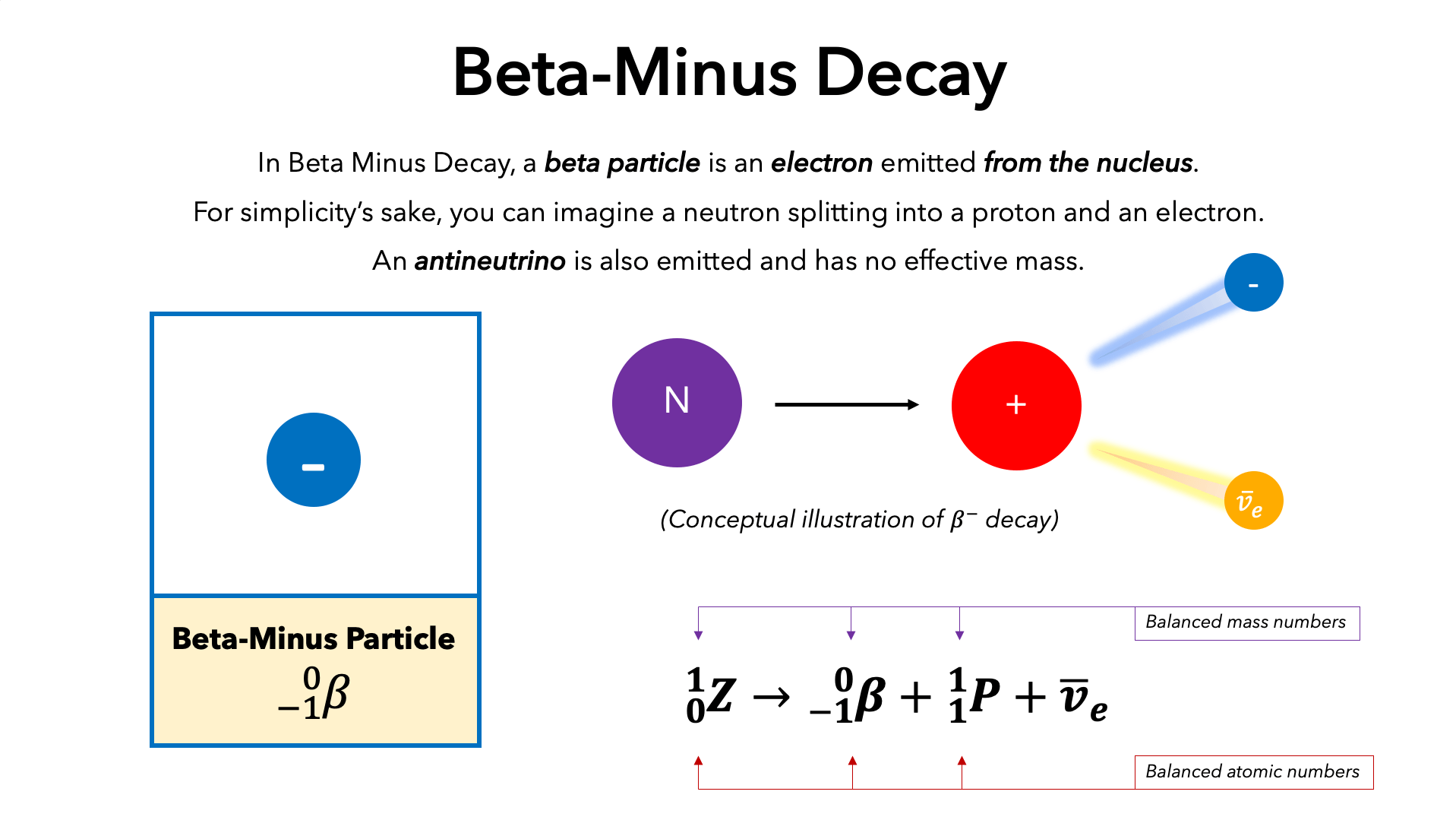
Beta (β)
Symbol: β
Charge: -1
Mass: very small
Penetration: Moderate (stopped by foil)
Effect: Neutron converts into a proton/ increases atomic number by one
Gamma (γ)
Symbol: γ/gamma
Charge: 0
Mass: 0
Penetration: Very high (needs lead to stop)
Often emitted with alpha or beta particles
Penetrating power of radiation in order of strength
Gamma
Beta
Alpha
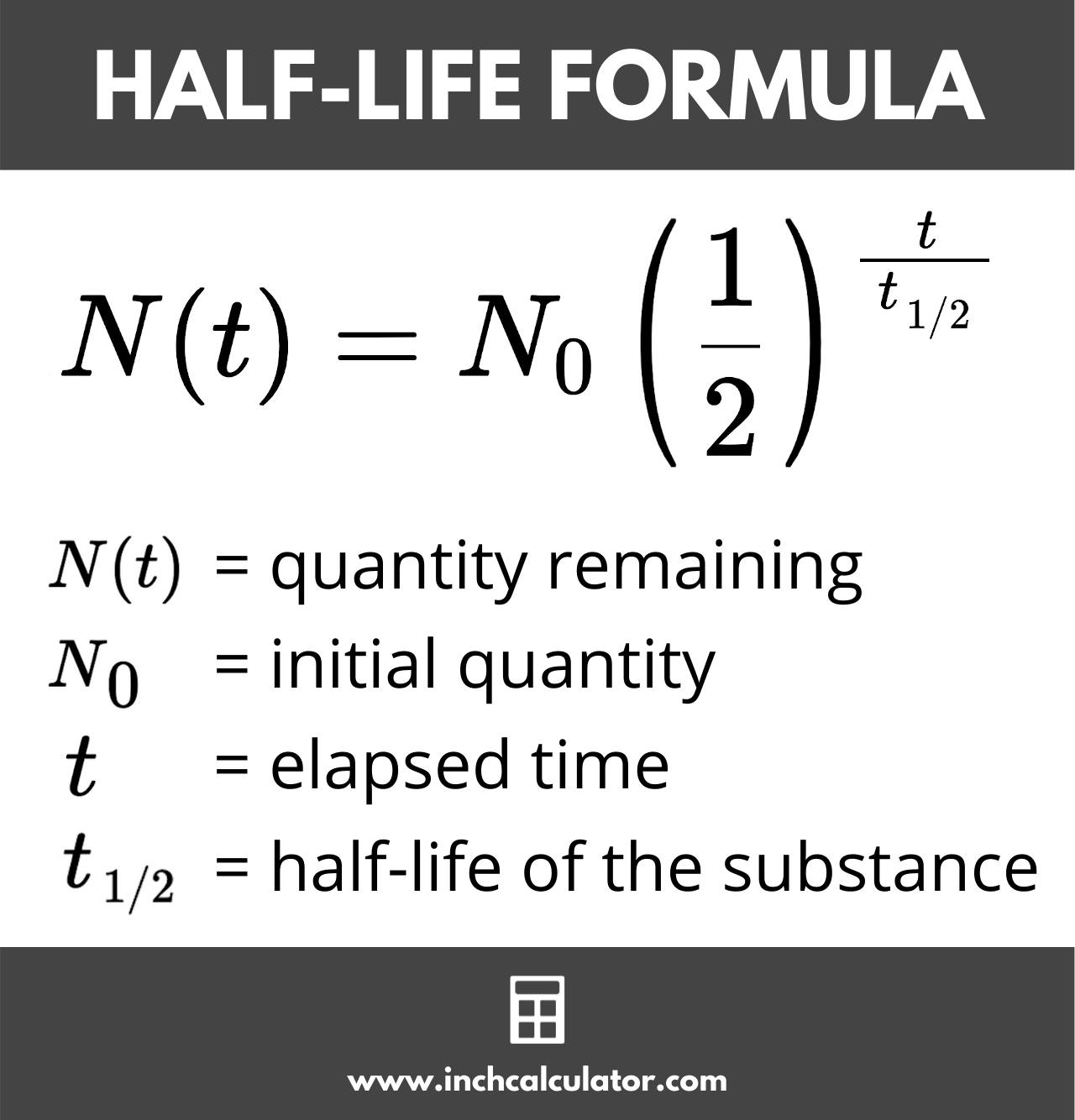
Half life
After on half life, 50% remains
use exponential decay to solve for remaining amounts
Stability of Uranium
some isotopes are unstable and undergo radioactive decay
Reverse Half-life
if 25% remains→ 2 half ives
Total time= 2× 12.3; Total time= 24.6 years