Cell Cycle & Karyotype: Mitosis, Meiosis, and Chromosomal Abnormalities
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the four major events during cell division?
1. Cell division signals 2. DNA replication 3. DNA segregation 4. Cytokinesis
How do prokaryotes divide?
Prokaryotes divide by binary fission.
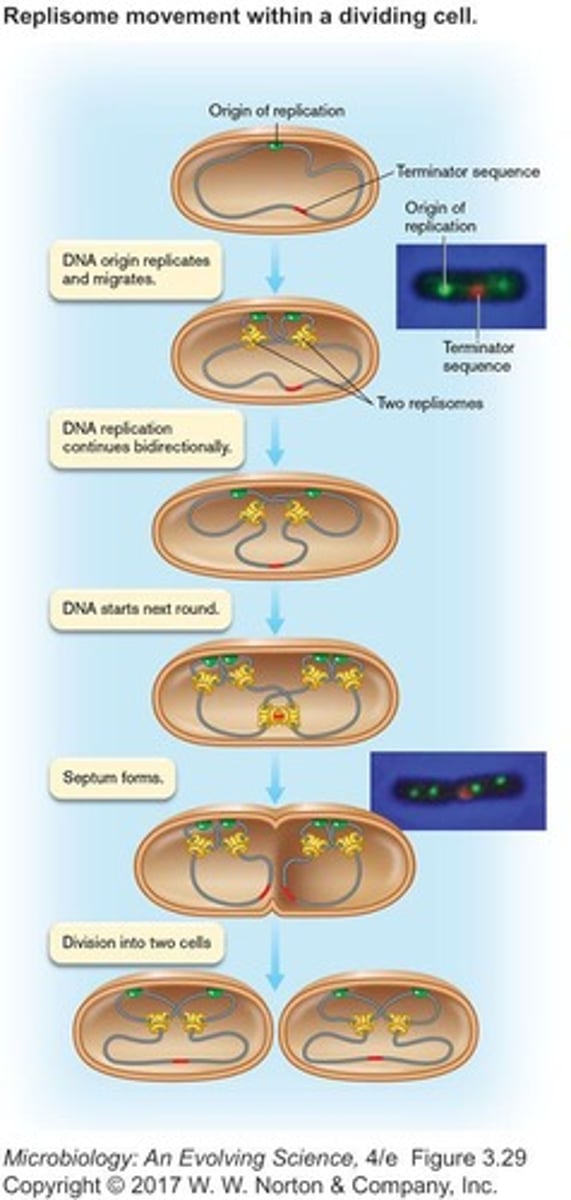
What is the significance of Ori and Ter sequences on bacterial chromosomes?
Ori is the origin of replication where DNA replication starts, and Ter is the termination sequence where replication ends.
What does it mean that DNA is replicated bidirectionally?
Replication starts at Ori and moves in both directions until it reaches Ter.
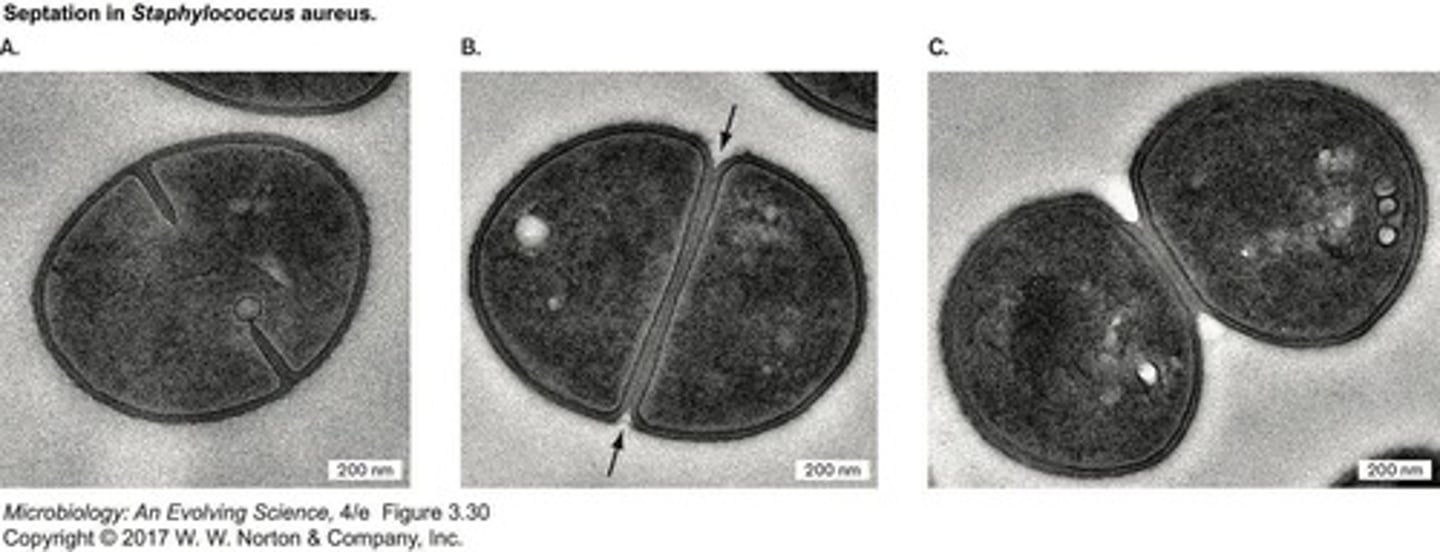
What is cytokinesis in prokaryotes?
Cytokinesis begins after chromosome replication, with the FtsZ protein forming a Z-ring to facilitate cell division.
What are the four phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase.
What occurs during the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
Cell growth, production of organelles, and regular functioning with unreplicated chromosomes.
What happens during the S phase of the cell cycle?
DNA replication occurs, resulting in chromosomes appearing as 'X' shapes with two sister chromatids.
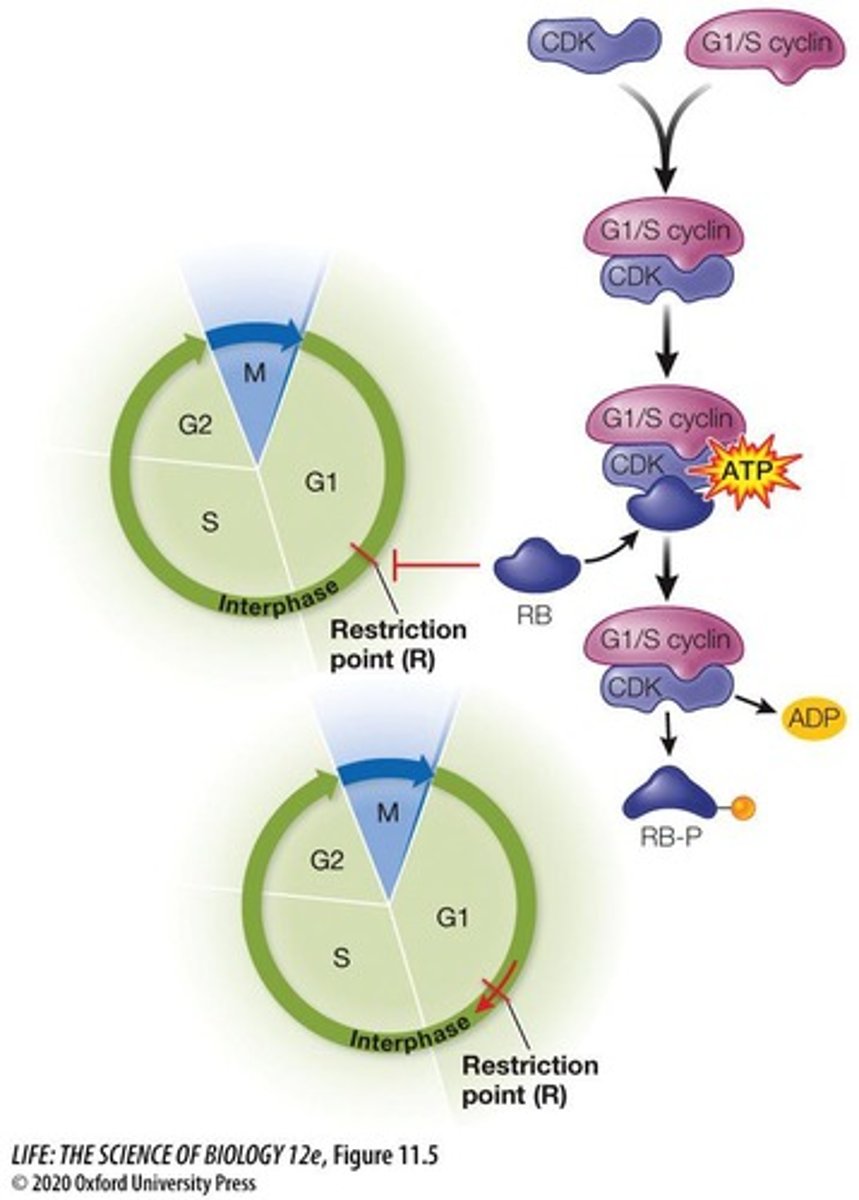
What is the role of cyclins and CDKs in cell cycle regulation?
Cyclins activate CDKs, which are always present, to regulate progression through the cell cycle.
How is the M-phase promoting factor (MPF) activated?
MPF is activated when cyclin binds to CDK, leading to phosphorylation and activation of M-phase effector proteins.
What is the restriction point in the cell cycle?
The restriction point is the transition from G1 to S phase, regulated by cyclin-CDK complexes.
What are tumor suppressors?
Tumor suppressors are regulatory proteins that halt the cell cycle or initiate apoptosis.
Describe the p21-p53-RB signaling pathway.
DNA damage activates p53, which induces p21, inhibiting cyclin-CDK activity and causing cell cycle arrest.
What are growth factors and give examples?
Growth factors stimulate cell division; examples include Platelet-derived growth factor and Erythropoietin.
What is a human karyotype?
A human karyotype consists of 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and 2 sex chromosomes.
Define ploidy.
Ploidy indicates the number of chromosomal sets in a cell; for humans, it is diploid (2n=46).
What type of chromosomal aberration is Klinefelter syndrome?
Klinefelter syndrome is characterized by an XXY chromosomal pattern.
What is Trisomy 21?
Trisomy 21 is a chromosomal aberration that leads to Down's syndrome.
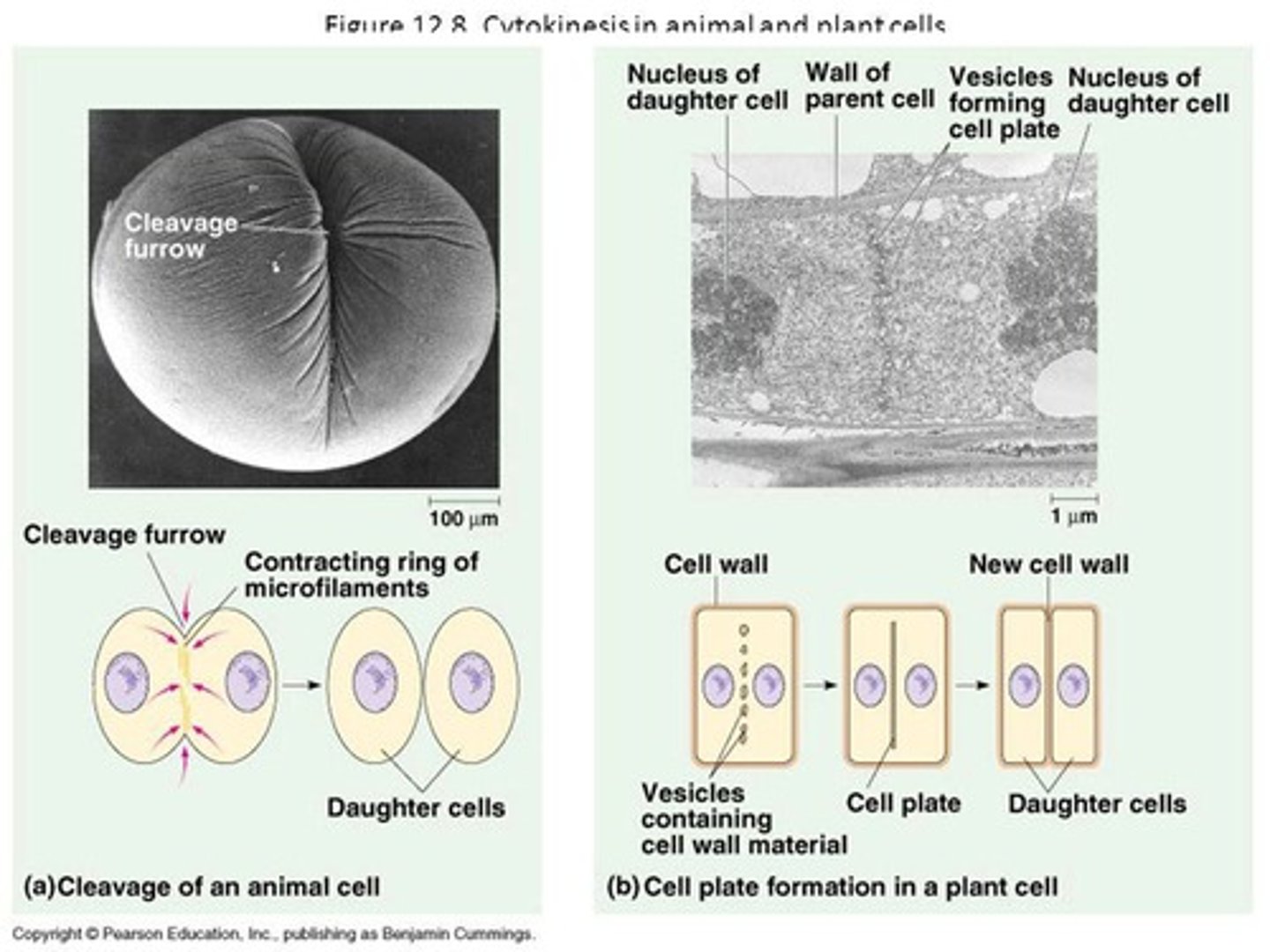
What is the difference between cytokinesis in animals and plants?
Cytokinesis in animals involves furrowing, while in plants, a cell plate forms to separate the daughter cells.
What is the duration of the G1 phase in rapidly dividing cells?
In rapidly dividing cells, the G1 phase lasts about 11 hours.
What is the role of FtsZ protein in prokaryotic cell division?
FtsZ protein assembles into a Z-ring to facilitate the pinching of the cell membrane during cytokinesis.
What is the significance of the four cell-cycle checkpoints?
They ensure proper progression through the cell cycle by checking for DNA damage, replication completeness, and other factors.