Trauma, Pediatrics, Geriatrics, Additional
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What is the minimum amount of views that must be obtained in trauma?
two
What is apposition?
alignment/disalignment describing the relationship of the long axis of fracture fragments
What does anatomic apposition look like?
end to end contact
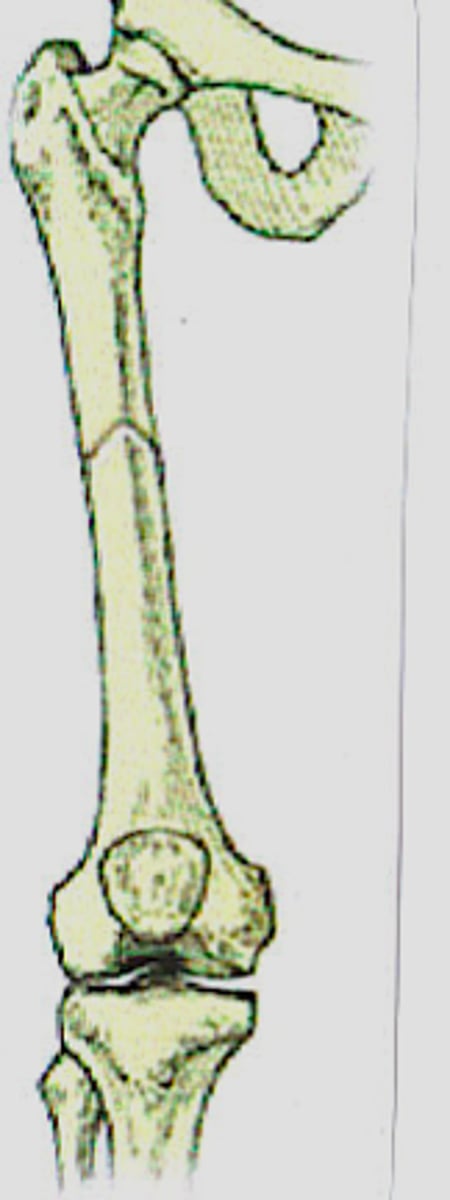
What does lack of apposition (distraction) look like?
ends pulled apart & not making contact
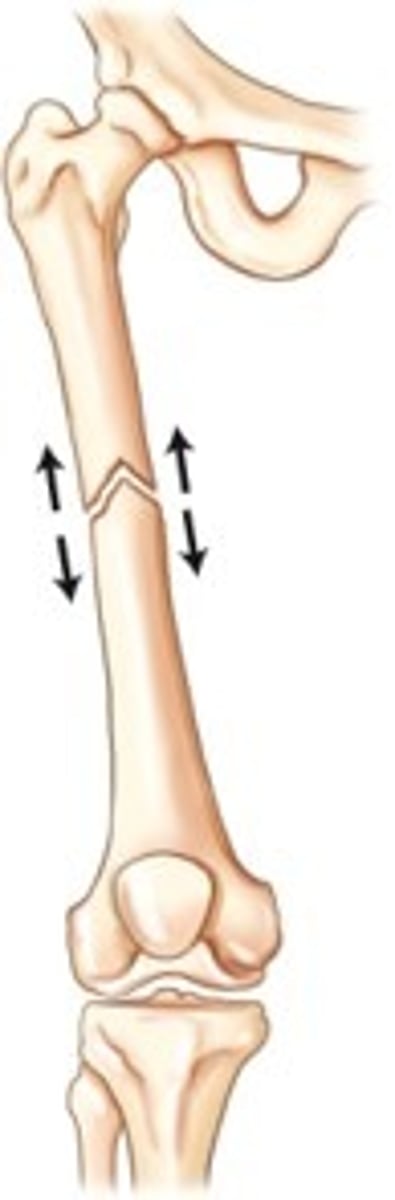
What does bayonet apposition look like?
ends overlap w/ shafts making contact (not ends)
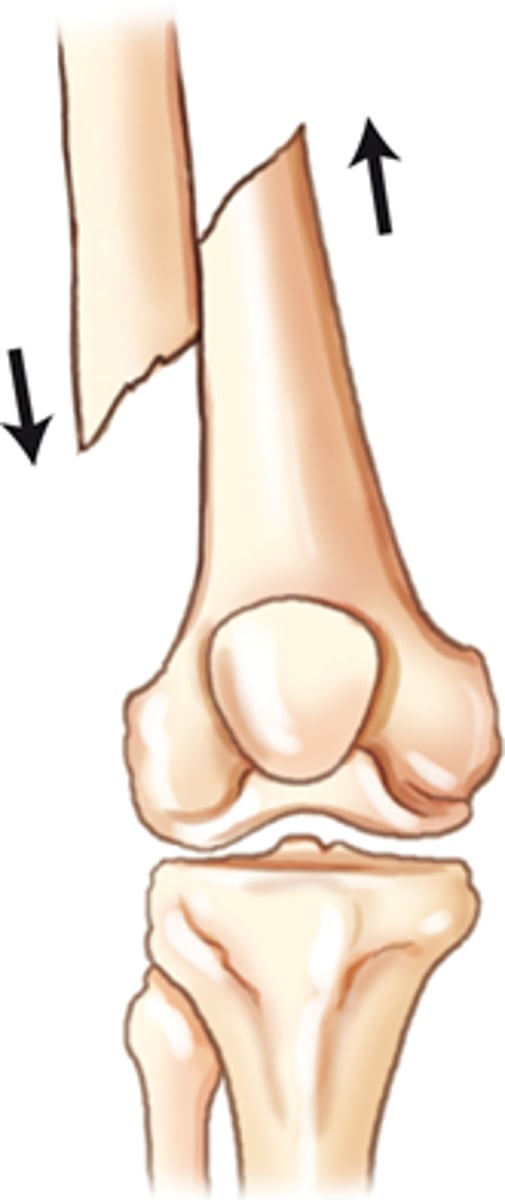
Angulation refers to the loss of _________
alignment
What does the term apex describe?
direction or angle of the apex of the fraction, medially/laterally
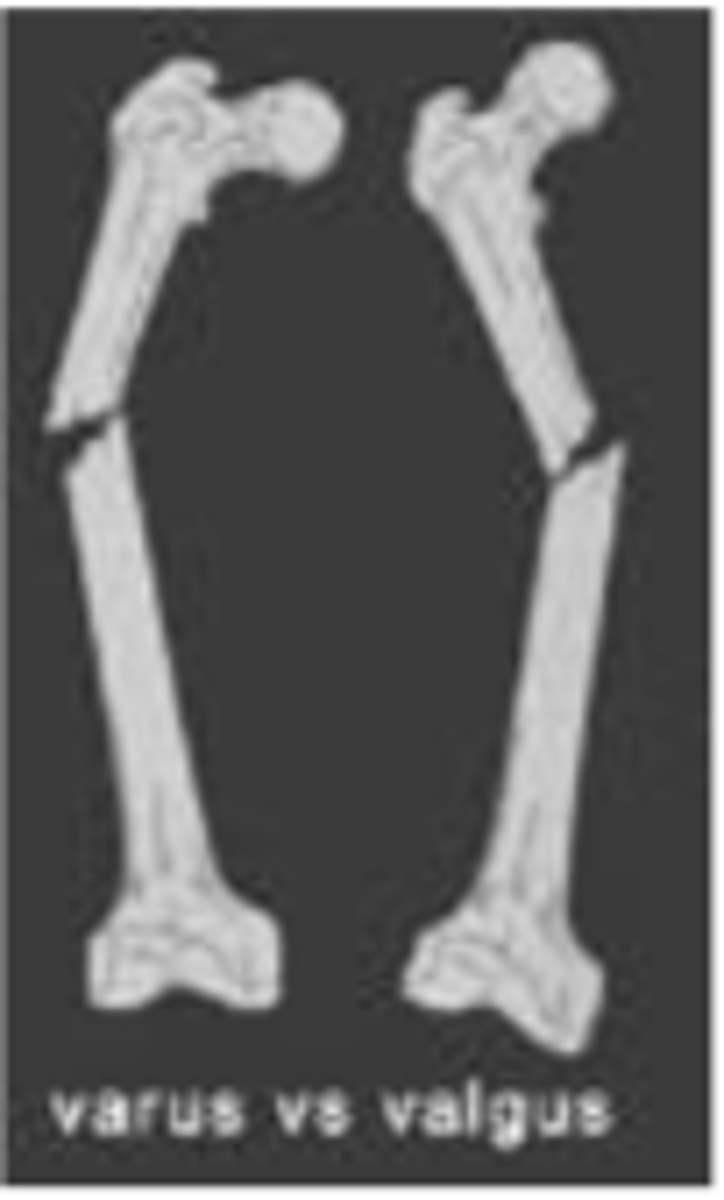
What does a varus deformity look like?
distal part of distal fragments angled TOWARD midline w/ apex angled AWAY from midline
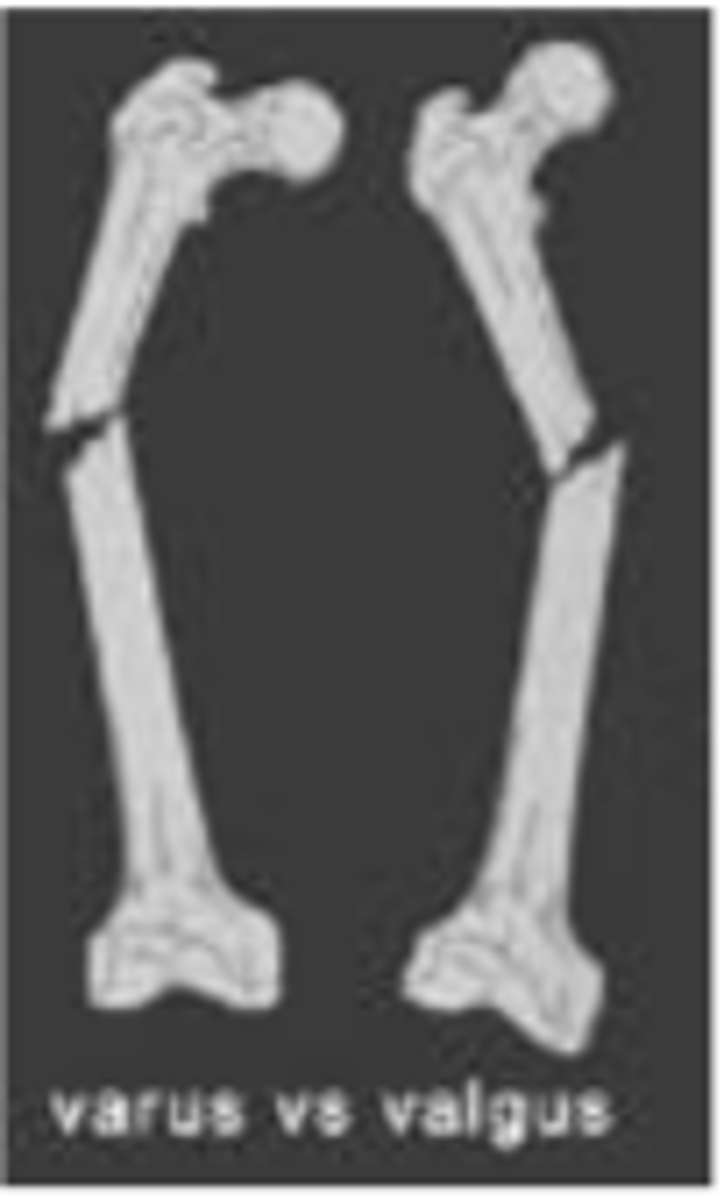
What does valgus deformity look like?
distal part of distal fragments angled AWAY from midline w/ apex angled TOWARD midline
Where do the most common dislocations occur?
shoulder, fingers/thumb, patella & hip
What is subluxation?
partial dislocation
What is a sprain?
forced wrenching/twisting of a joint resulting in a rupture or tearing of supporting ligaments w/o dislocation
What is a fracture?
break in bone
What is a contusion?
bruise type of injury w/ possible avulsion fx
What is a simple (closed) fx?
bone doesn't break skin
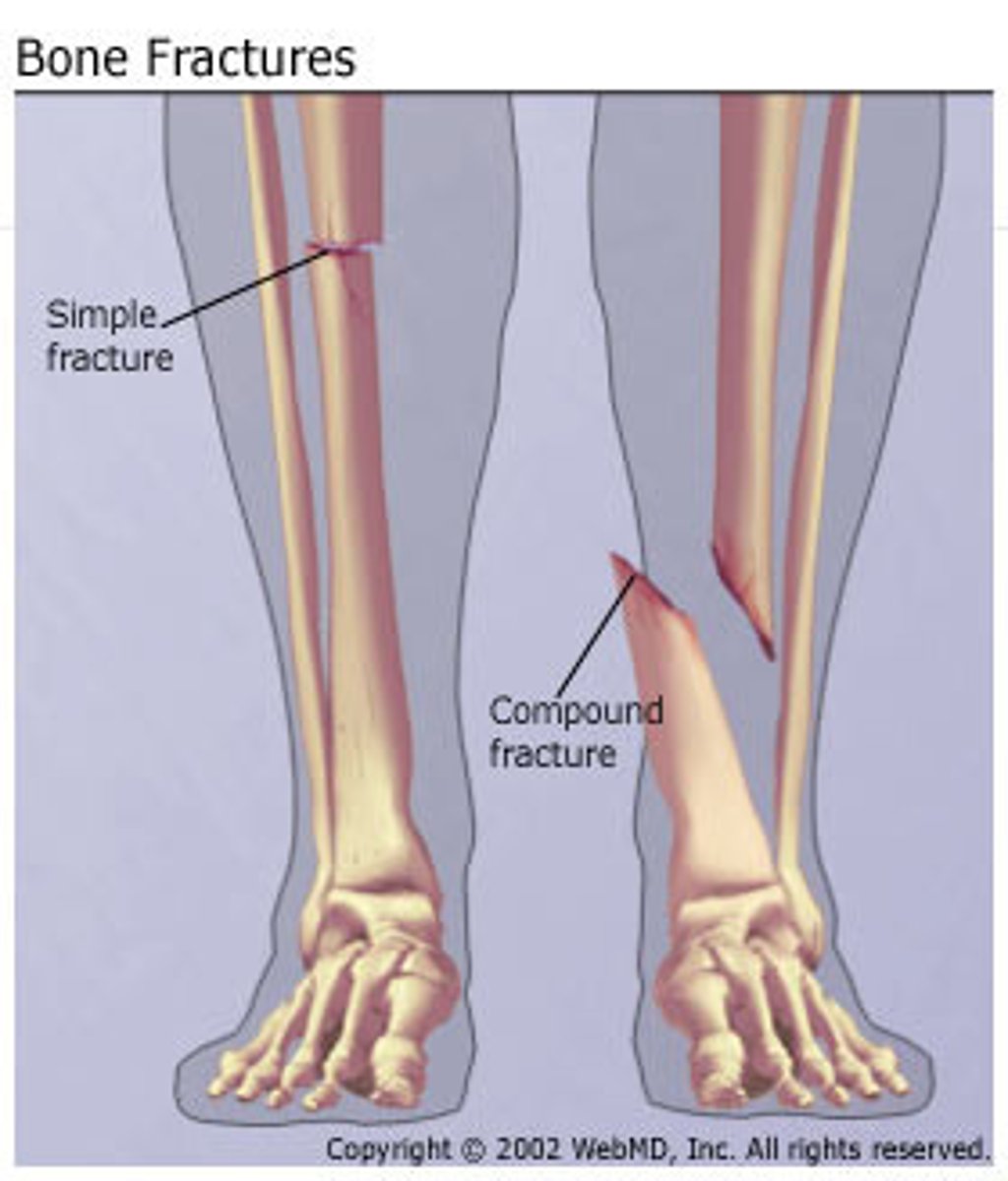
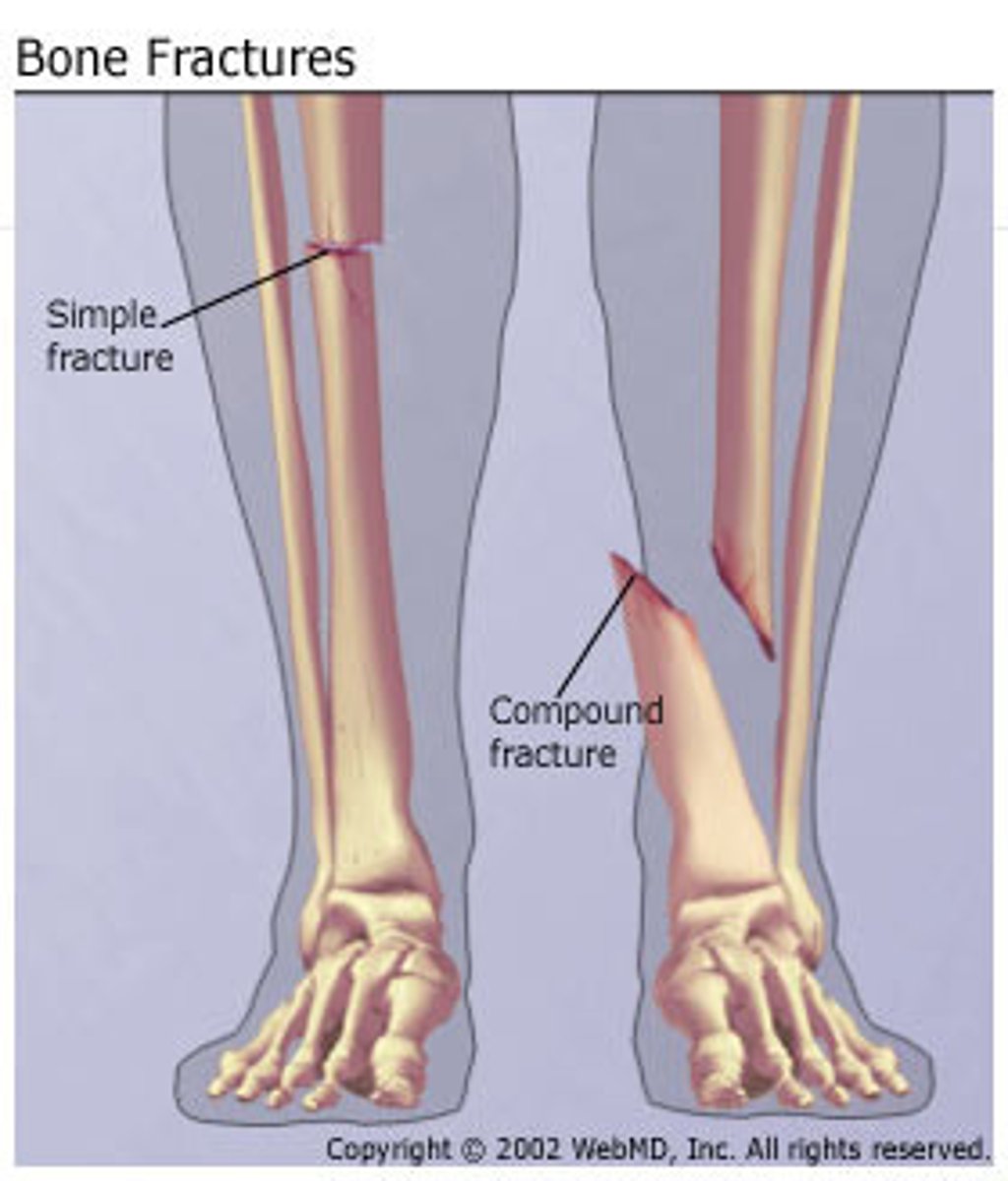
What is a compound (open) fx?
bone protrudes through skin
What is an incomplete fx?
fx doesn't transverse through the entire bone
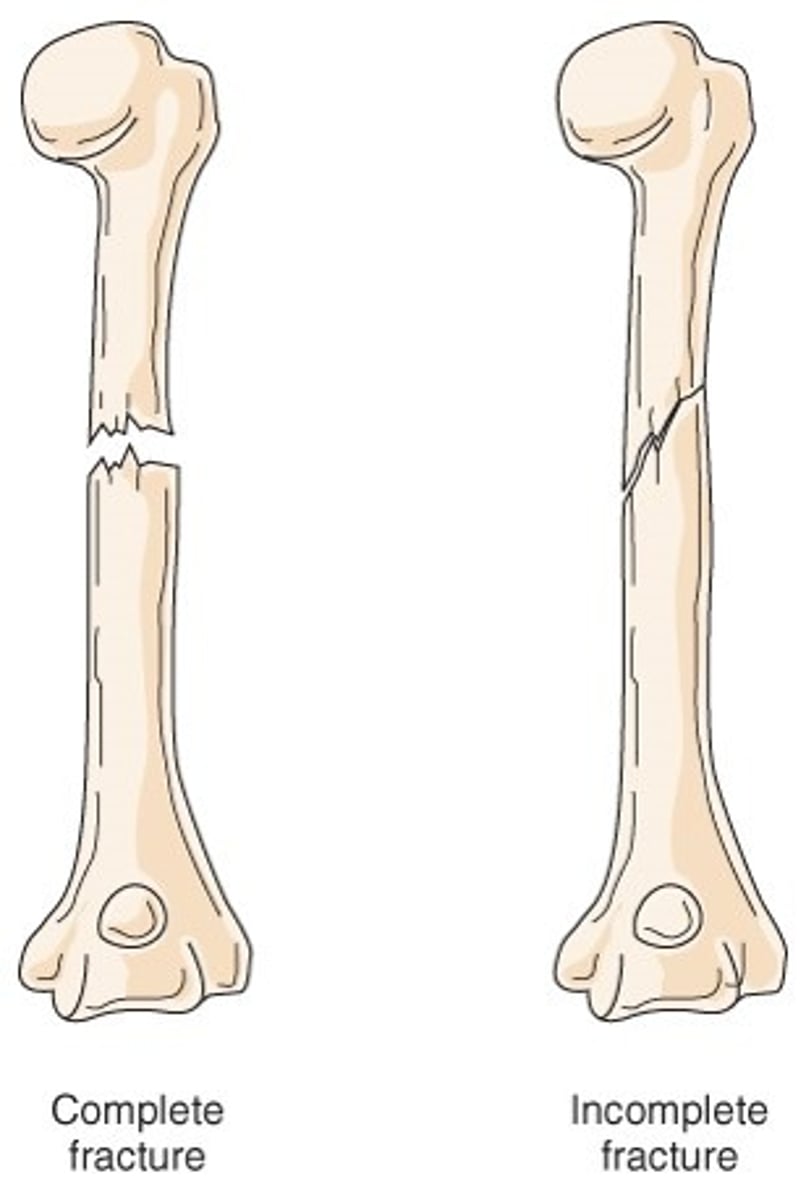
What are the two types of incomplete fx?
1. torus
2. greenstick
True/False: incomplete fractures typically happen in children
true
What is a complete fx?
break is complete (broken into 2 pieces & includes cross section of bone)
What are the three types of complete fx?
1. transverse
2. oblique
3. spiral
What is a comminuted fx?
bone is crushed/splintered at site of impact
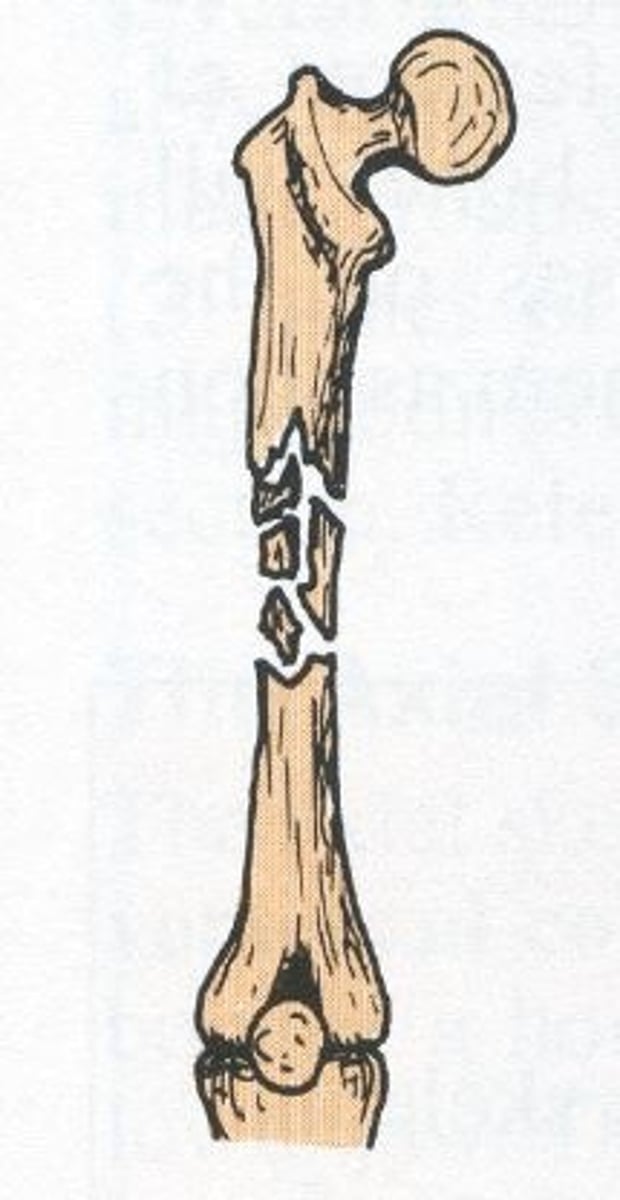
What are the three types of comminuted fx?
1. segmental
2. butterfly
3. splintered
What is an impacted fx?
one fragment driven into another
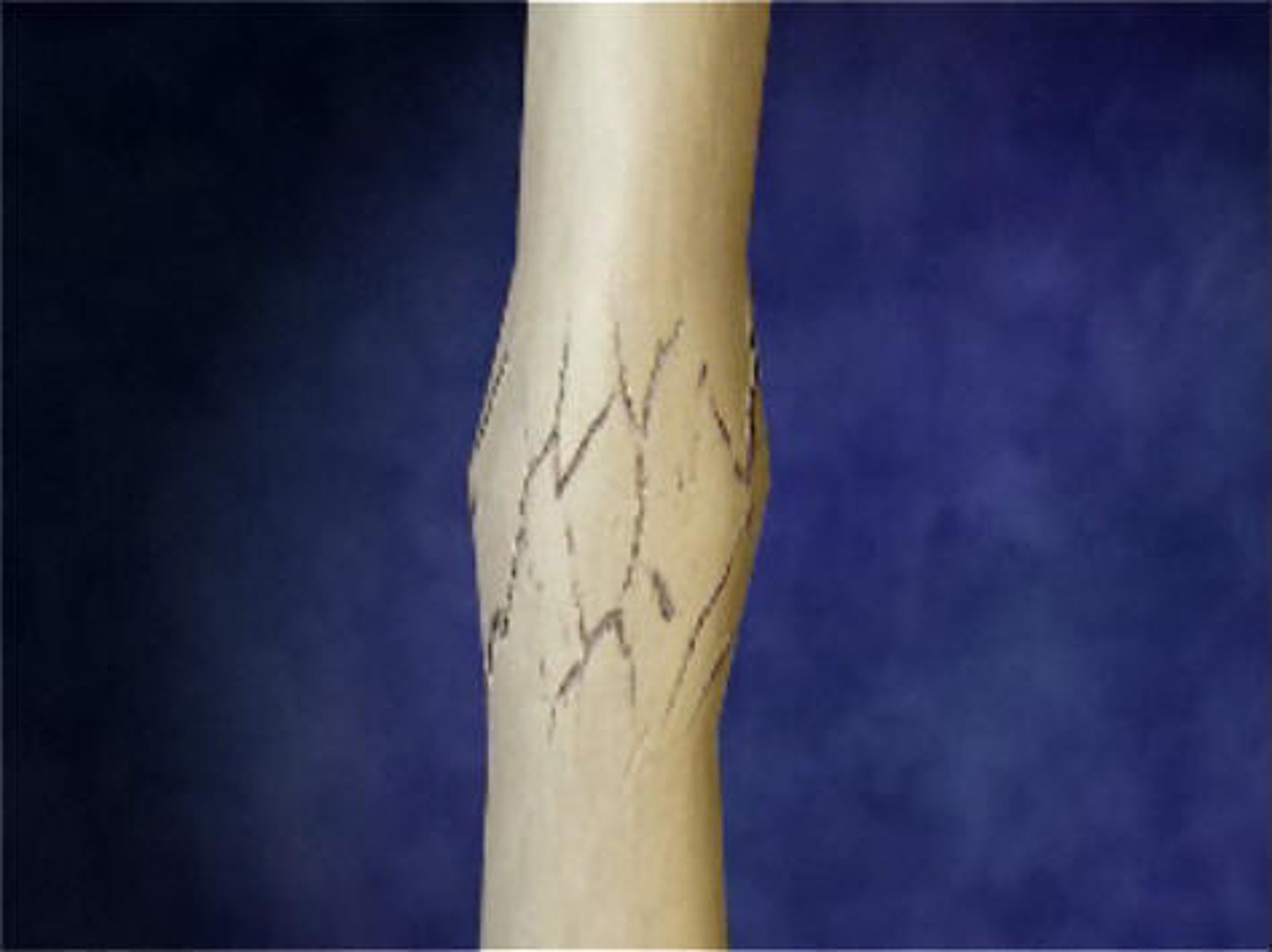
What is an avulsion fx?
fragment of bone is pulled away by the attached ligament/tendon
What is a blowout/tripod fx?
result of a direct blow to the orbit and/or maxilla/zygoma
What is a chip fx?
involves an isolated bone fragment
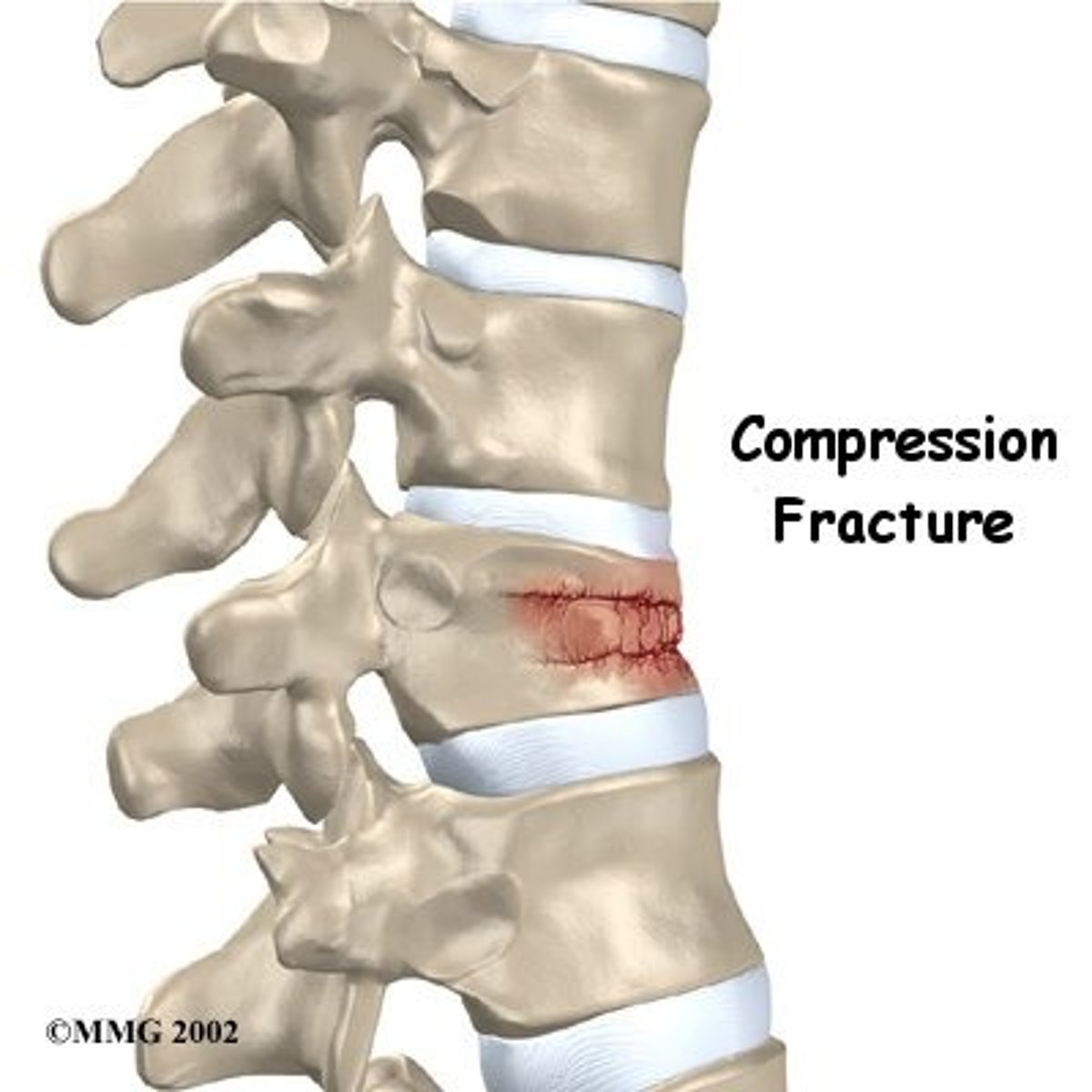
What is a compression fx?
vertebral fx in which the body collapses or is compressed
What is a depressed (ping-pong) fx?
fx of the skull, a fragment is depressed
What is an epiphyseal fx?
fx through epiphyseal plate (salter-harris 1-5 classifications)
What is a pathological fx?
fx due to disease in bone
What is a stress fx?
results from repeated stress on the bone
True/False: stress fxs are nontraumatic in origin
true
What is a stellate fx?
fx lines radiate from a central point w/ a starlike appearance
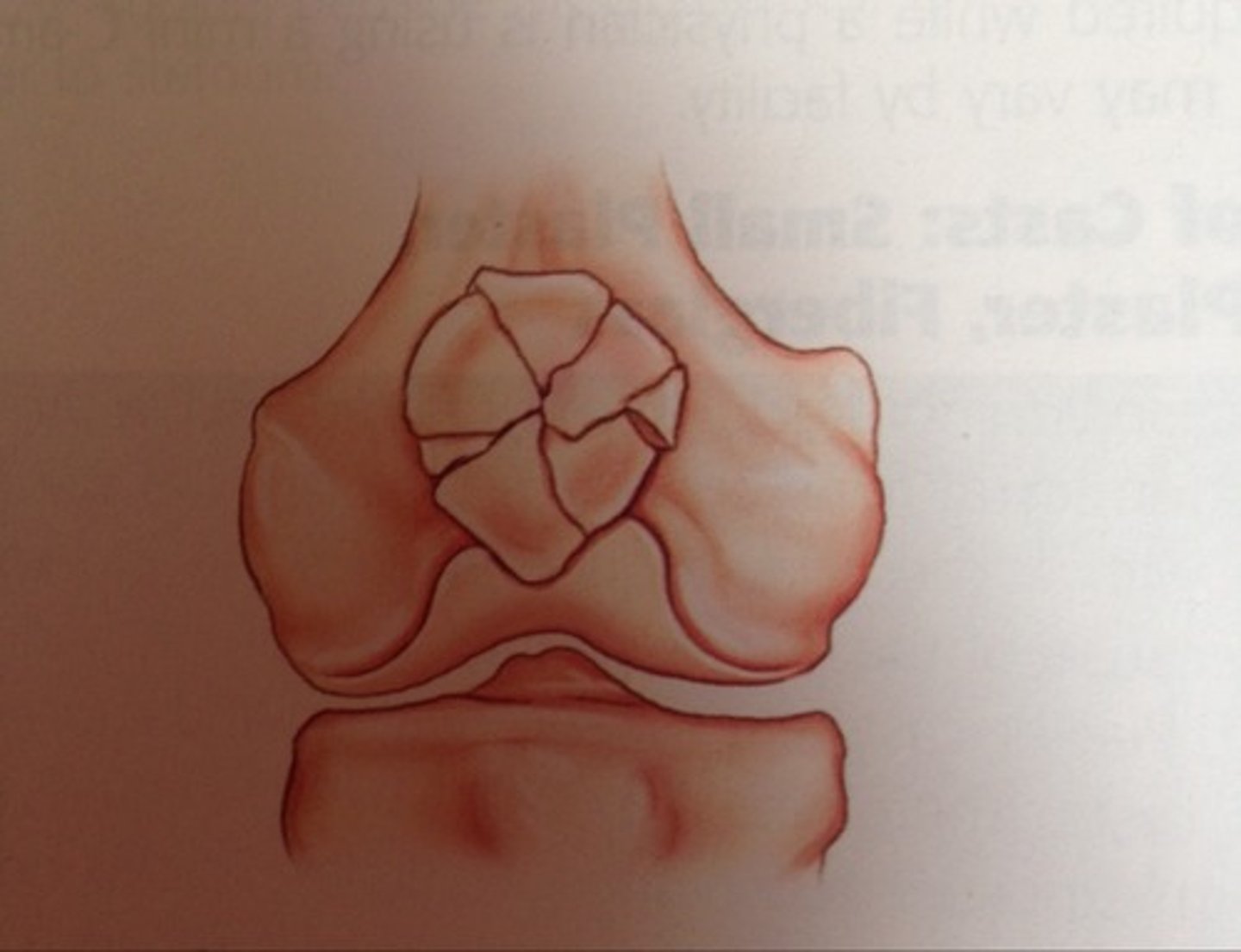
What is a trimalleolar fx?
fx of ankle involving both malleoli & posterior tib of distal tibia
What is a tuft fx?
comminuted fx of distal phalanx (usually crush injury)
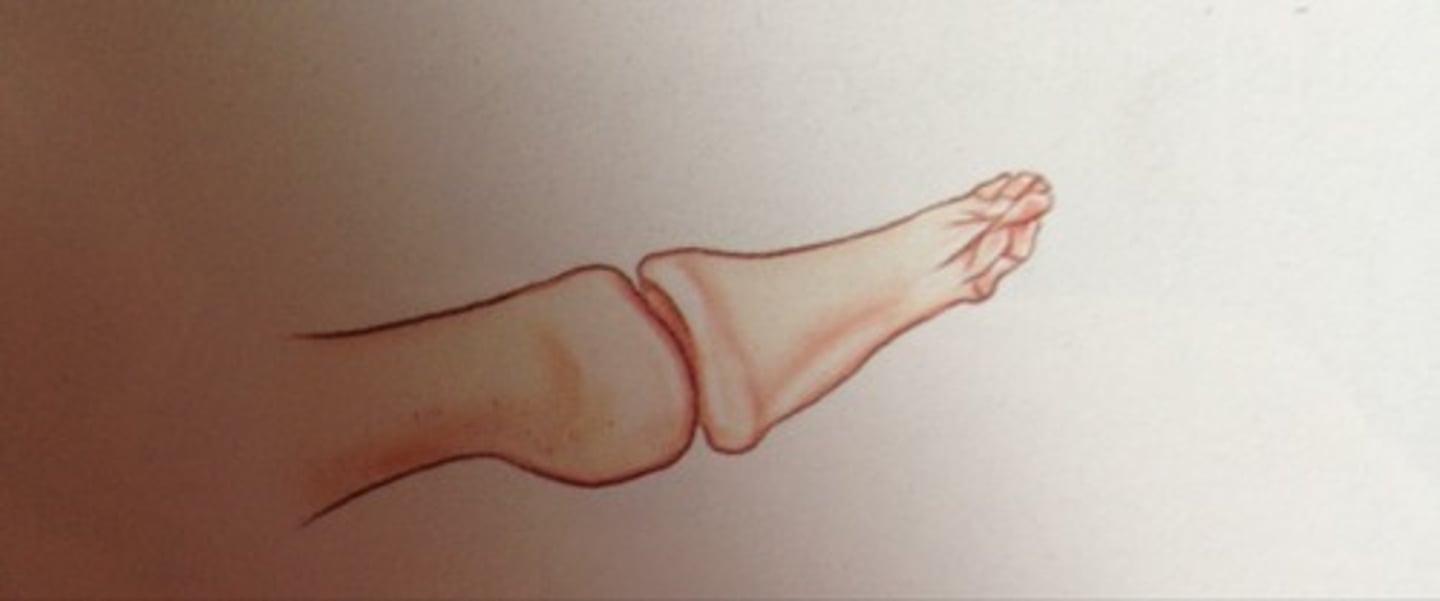
A colles fx has _________ displacement
posterior
A smiths (reverse colles) fx has ________ displacement
anterior
True/False: you should have good communication w/ your PT and/or coworkers in trauma
true
How should you hold a part with a fx if you have to move it?
hold above & below fx site to stabilize
What four rules can help prevent grid cutoff?
1. center along central axis of grid
2. angle along direction of lead strips
3. grid focal range
4. ensure tube side faces tube
What are four causes of grid cutoff?
1. off center
2. off level
3. off focus
4. upside down
What is the common portable focal range for grids?
6:1
8:1
What are the three types of mobile units?
1. battery driven, batter operated
2. standard power source, non-motor driven
3. c-arm fluoro
- honorable mention: o-arm
What should you NOT put the c-arm in "tube on top" position?
increases scatter & exposure to head/neck
decreases image resolution
Which side of the c-arm monitor is active and which is the hold?
left = active
right = hold
What are the three ways the c-arm can be draped or made sterile?
1. draping entire unit
2. draping the PT
3. shower curtain
Of the cardinal rules, which is the most effective at reducing exposure?
distance
A 30 degree c-arm tilt increases exposure to the face/neck by a factor of ____
4
If the PT has a small-medium plaster cast, how much should you increase kVp?
5-7
If the PT has a large plaster cast, how much should you increase kVp?
8-10
If the PT has a fiberglass cast, how much should you increase kVp?
3-4
Who does the surgical team consist of?
surgeon, anesthesiologist, surgical assistant, certified surgical technologist, circulator, scrub
Define asepsis:
absence of infectious organisms
True/False: when using the c-arm you should make sure everyone is the room is wearing an apron before exposing
true
What is a closed reduction procedure?
- nonsurgical procedure where fracture fragments are realigned by manipulation
- immobilized by cast or split
What is an open reduction procedure?
fracture site is exposed & screws, plates, rods are inserted to maintain alignment of bony fragments
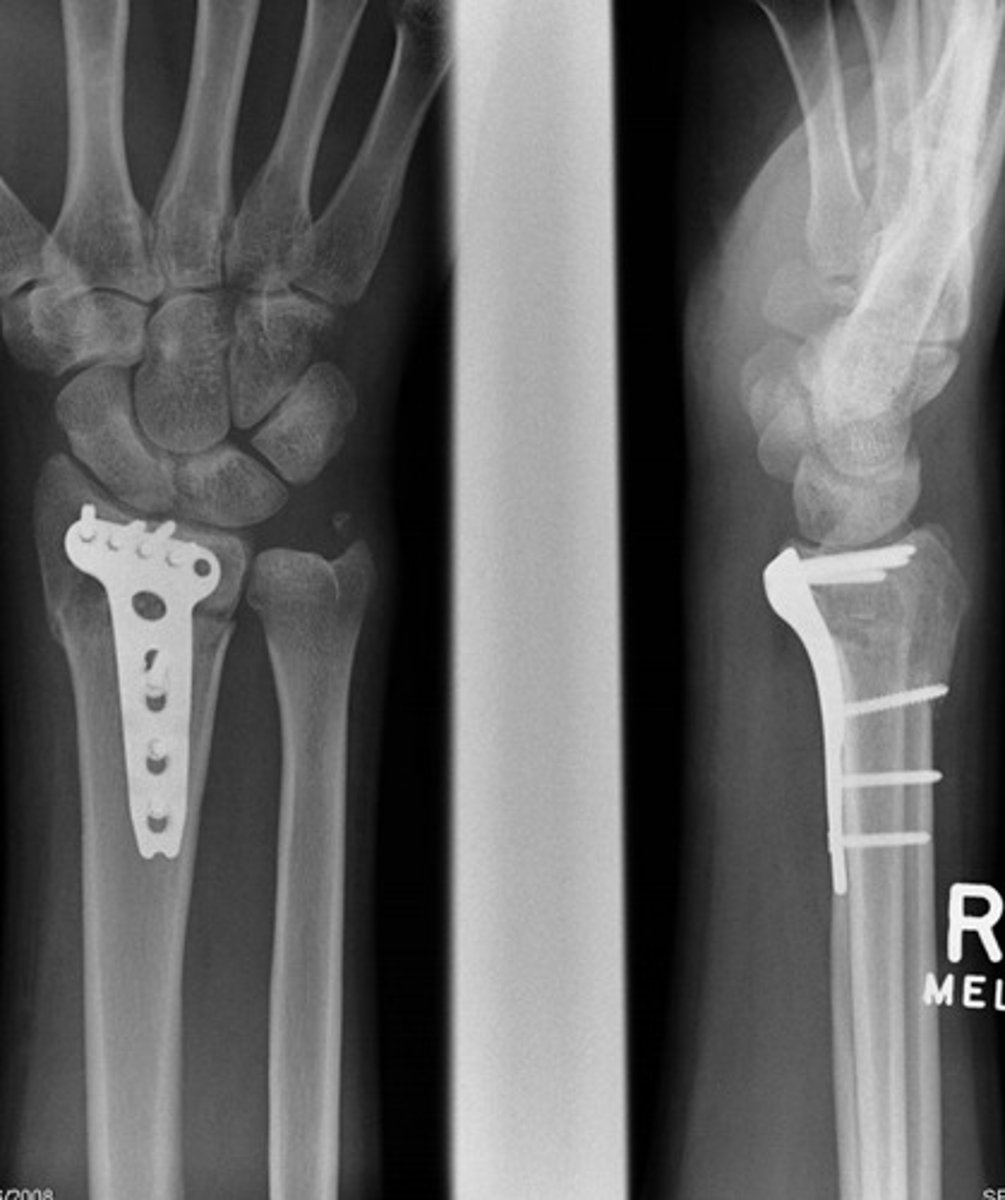
What is an internal fixation procedure?
during open reduction compression plates, screws, pins, intramedullary rods, nails, wires are applied to realign fracture
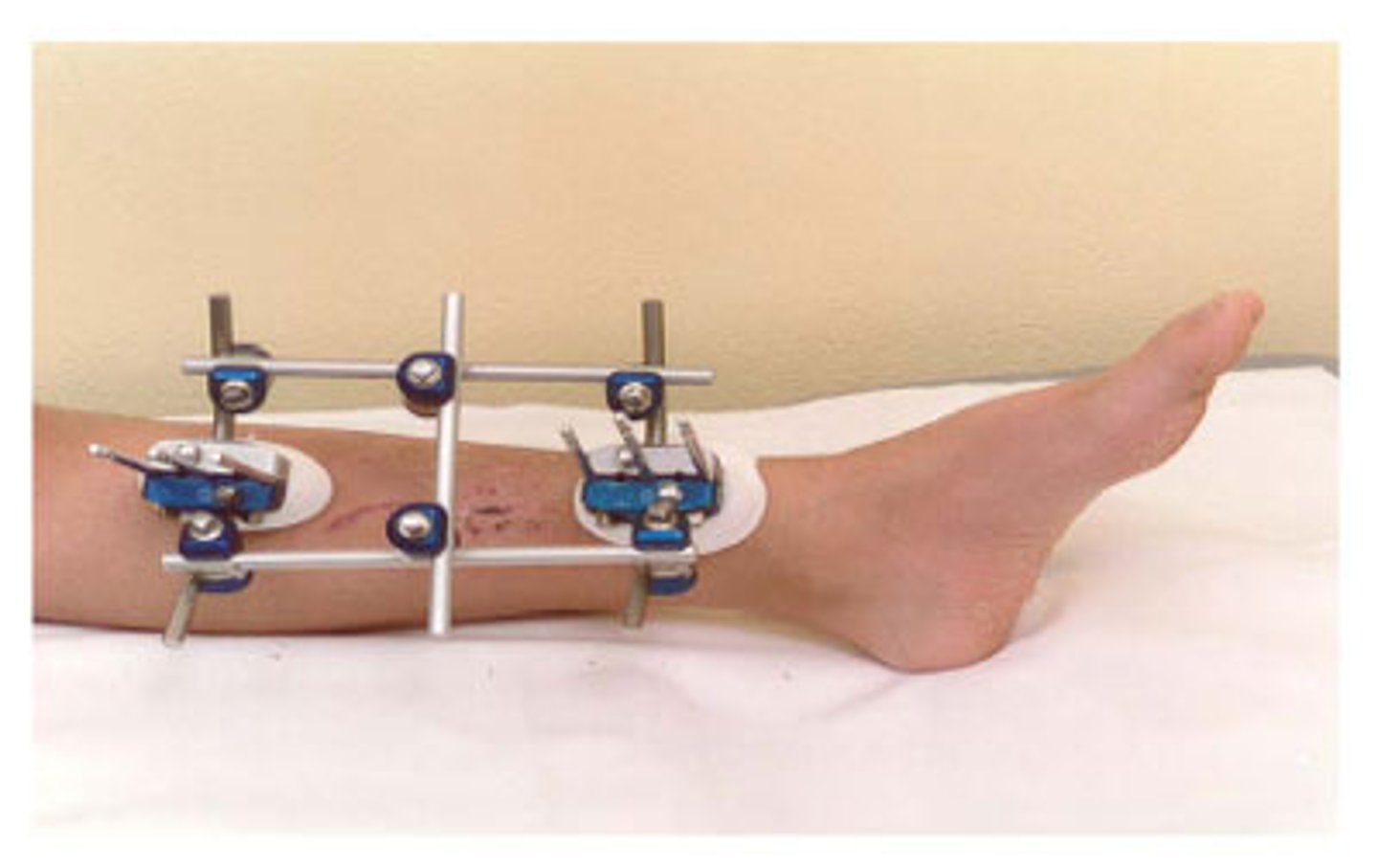
What is an external fixation procedure?
use of external fracture-stabilizing device permits bone healing
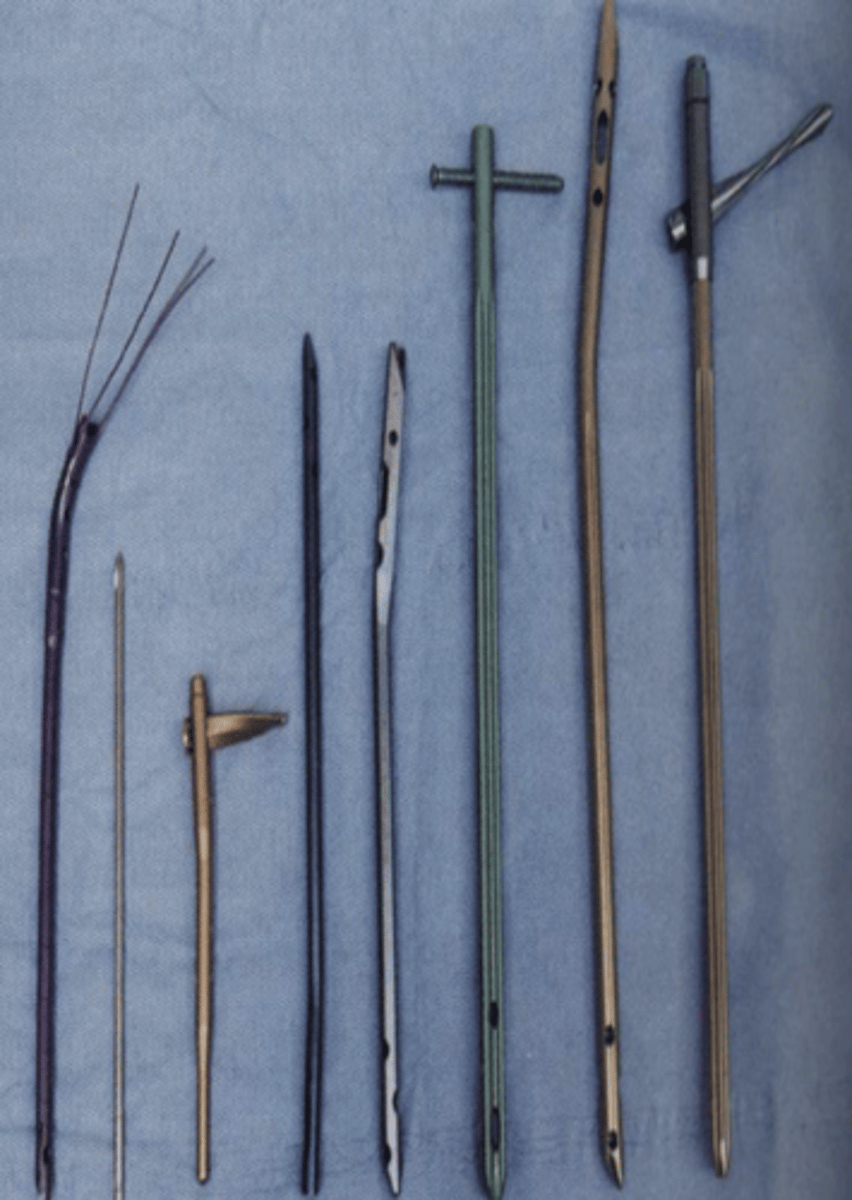
What is an intramedullary fixation procedure?
intramedullary rods/nails are inserted w/in shaft of long bones to stabilize fractures
By what age can most children be talked through a diagnostic study without aid from a parent or immobilization?
2-3
What are the three possible roles that a parent might play in pediatrics?
1. parent is in room as observer/comforter
2. parent assists in immobilization
3. parent is asked to wait in waiting room
What term for child abuse is used today?
nonaccidental trauma
What are the five types of abuse?
1. medical neglect
2. physical
3. sexual
4. psychological
5. other (nutritional, etc)
True/False: you should always use short exposure times in pediatrics for an optimal image
true
What are the two main types of immobilization?
1. tan-em board
2. pigg-o-stat
What is the primary center of bone formation called?
diaphysis
Where does bone growth occur?
metaphysis
What is the secondary center of bone formation called?
epiphysis
What is the space between the diaphysis and epiphysis called?
epiphyseal plate
What type of shield should the gonads of children always be shielded with?
contact type (unless exam doesn't allow it)
True/False: it is very important to remove any clothing, bandages, or diapers from the child before taking images
true
What is the greatest danger to premature infants?
hypothermia
How many ribs should be visible on a pediatric chest x-ray?
9
How many ounces of barium is given to ages newborn to 1 year?
2-4 oz
How many ounces of barium is given to ages 1 to 3 years?
4-6 oz
How many ounces of barium is given to ages 3 to 10 years?
6-12 oz
How many ounces of barium is given to ages over 10 years?
12-16 oz
When giving contrast for IVUs, how much is used for pediatrics?
one cc per pound
Why are bone age studies done?
determines skeletal maturation in children
What is arthrography?
contrast media study of SYNOVIAL joints & related soft tissue structures
What are the two most common arthrography procedures done?
shoulders, knees
What are the indications for arthrography?
tears in joint/menisci, degeneration of menisci, ligament injury
What are the contraindications for arthrography?
if PT is allergic to iodine based contrast
What is hysterosalpingography?
radiographic demonstration of female reproductive tract w/ contrast medium
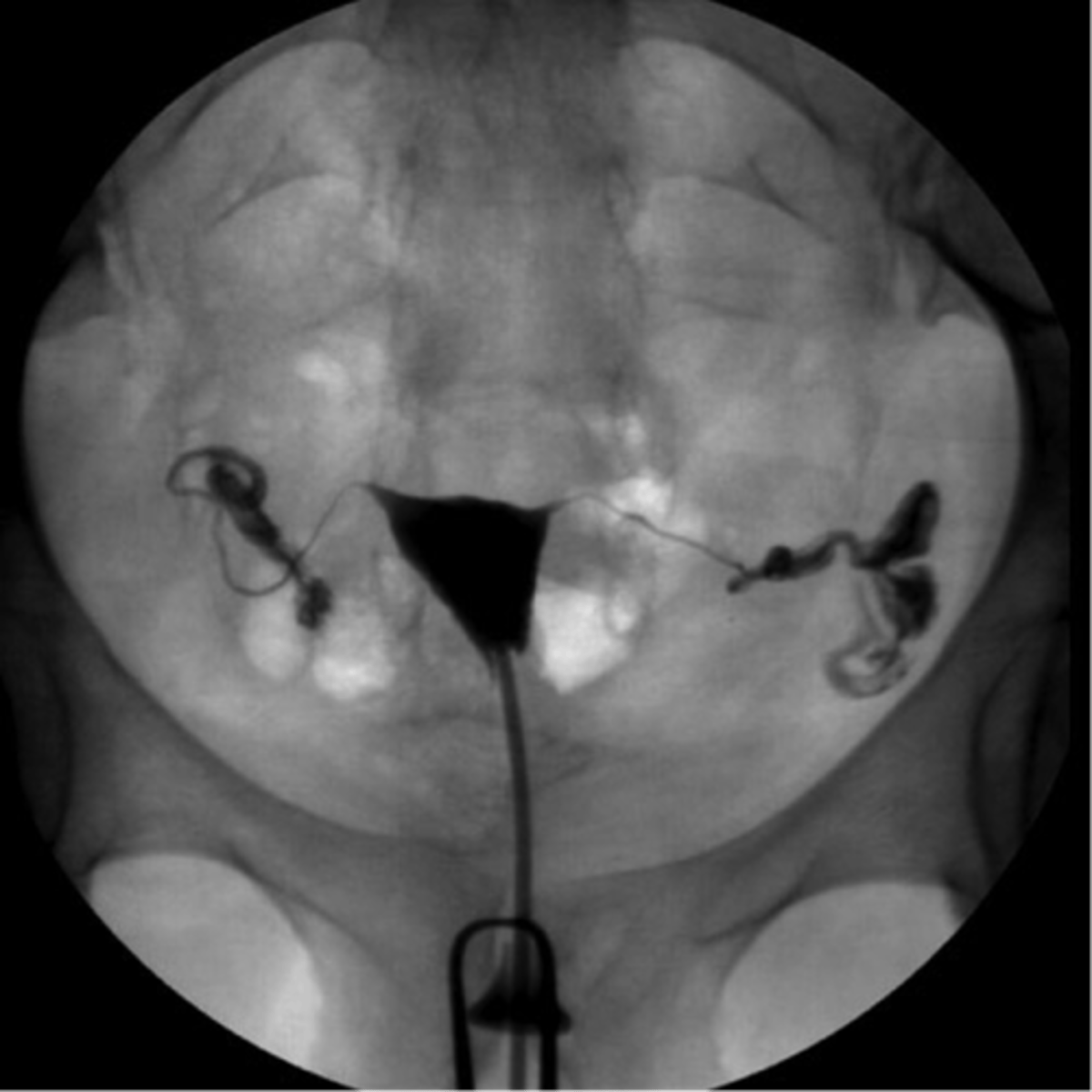
What is the primary indication for hysterosalpingography?
infertility
What are the contraindications for hysterosalpingography?
pregnancy, acute pelvic inflammatory disease, active uterine bleeding
How many ccs of contrast is injected for hysterosalpingography?
10 ccs of positive contrast
What are the four subdivisions of the uterus?
1. fundus
2. corpus (body)
3. isthmus
4. cervix (neck)
What is a myelogram?
radiographic study of spinal cord & its nerve root branches w/ contrast medium
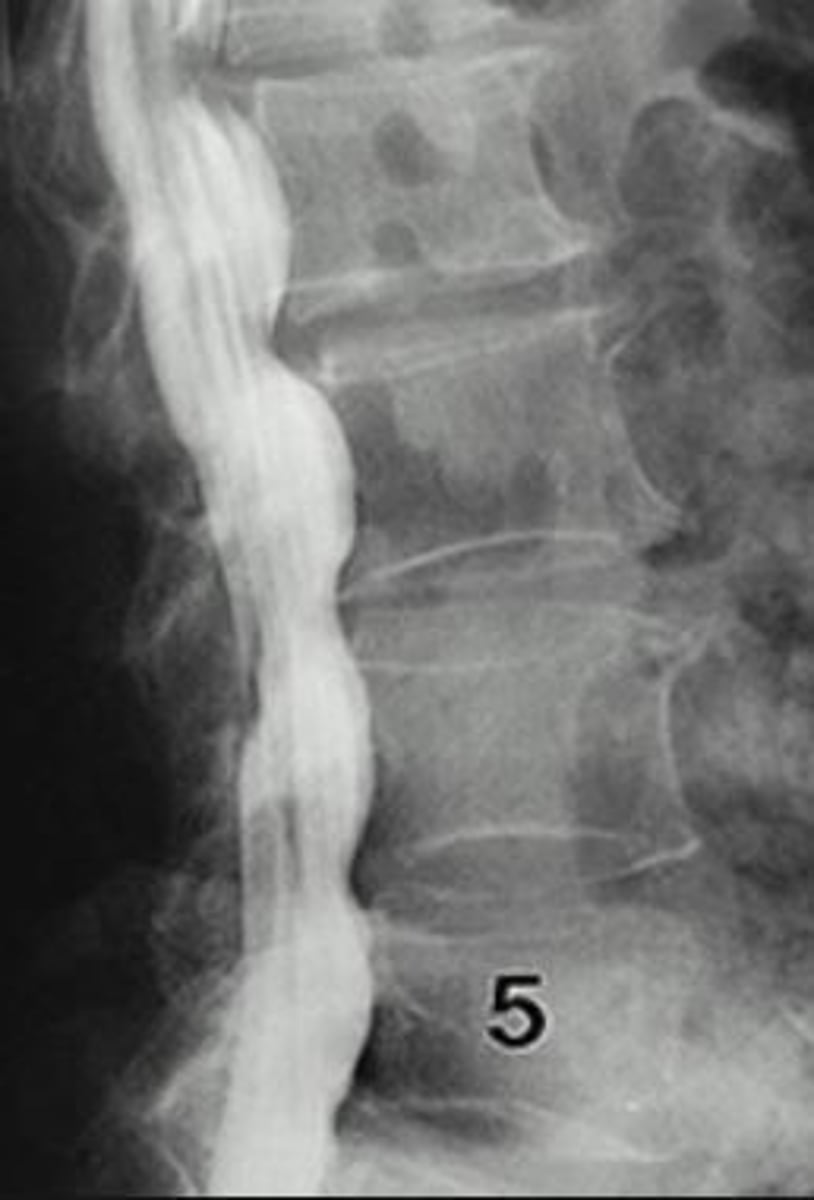
What is the most common indication for a myelogram?
herniated nucleus pulposus
What are the contraindications for a myelogram?
blood in CSF, arachnoiditis, increases intracranial pressure, recent lumbar puncture
True/False: a myelogram require a large pillow or sponge to help flex the PTs spine
true
Which is done first: collecting CSF or injecting contrast?
collecting CSF
What happens to the PT after the myelogram?
you transport them to CT
Why must you keep the PTs head elevated 30-40 degrees after a myelogram?
prevent contrast media passing into cerebral ventricles
What space is the contrast injected for a myelogram?
subarachnoid space
What level is the contrast medium injected for a myelogram?
L3-L4 & C-1-C2
How many ccs of contrast is injected for a myelogram?
9-15 ccs
What is sialography?
radiographic examinations of salivary glands & associated ducts w/ contrast