Histo & Embryo
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are the layers of the alimentary canal?
Mucosa
Epithelium
Lamina propria
Muscularis mucosae
Submucosa
Meissner’s plexus
Muscularis externa
Inner circular layer
Outer longitudinal layer
Auerbach’s plexus
Serosa/Adventitia
What are the unique histological features of the oral cavity?
No muscularis externa
No serosa/adventitia
Mucosa
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Lamina propria
No muscularis mucosae
Submucosa
Minor salivary glands
Intrinsic glands
Mucus-secreting
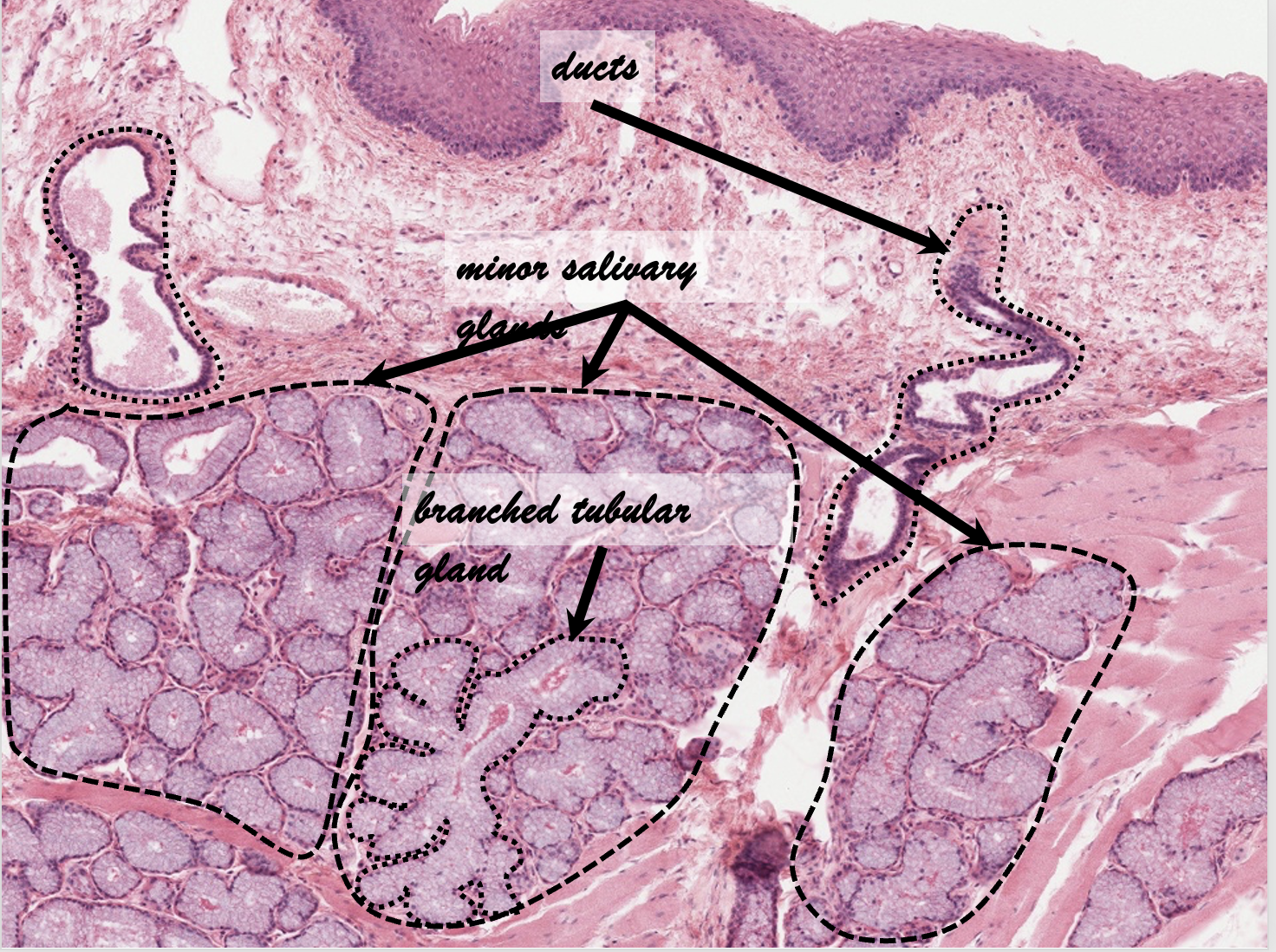
______ are muscular folds of the oral vestibule, surrounding the anterior boundary of mouth interspersed with fibro-elastic connective tissue
Lips are muscular folds of the oral vestibule, surrounding the anterior boundary of mouth interspersed with fibro-elastic connective tissue
What is the function of lips?
•Push food into oral cavity:
–Lips and cheeks help keep food over occlusal surface of teeth
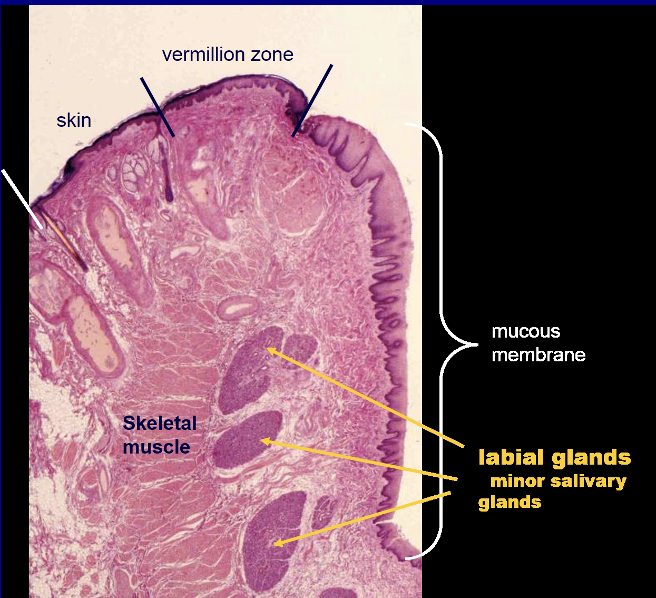
What are the layers of the lips?
Vermillion zone is the external region:
Thin epidermis and high dermal papillae cause it to appear red/pinkish
No sweat glands, hair follicles, or sebaceous glands—prone to excessive dryness and chapping
Internally:
Nonkeratinized with many minor salivary glands
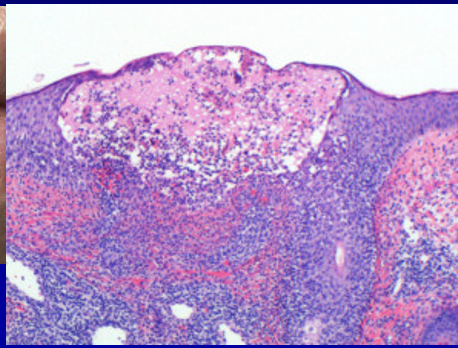
Cold Sores
•Cold sores are painful contagious blisters that generally appear outside the mouth on the lips:
–Caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1
–In the dormant state, this virus resides in the trigeminal ganglion
–Factors triggering the HSV virus include sunlight, sunburn, stress, fatigue, other infections, fever, menstruation, and intestinal upset
Canker Sores
•Canker sores (Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS)) are painful sores inside the mouth:
–Cause is unknown but may be due to a virus, allergic reaction, or an auto-immune condition
–Factors triggering these sores are injury or irritation (e.g., from dentures or sharp teeth), smoking, stress, a diet lacking in vitamin B12, folic acid or iron, and the onset of menstruation
_________ is the largest structure in oral cavity that lies on floor
Tongue is the largest structure in oral cavity that lies on floor
What is the role of the tongue?
•Roles:
–Chewing (mastication)
–Taste (gustation)
–Swallowing (deglutition)
–Speech (articulation)
–Oral cleansing
What is the purpose of the tongue’s extrinsic and intrinsic muscles?
•Extreme mobility due to mass of intrinsic (4) and extrinsic (4) skeletal muscles:
–Intrinsic muscles alter shape of tongue
–Extrinsic muscles move tongue in/out and side to side
–Covered by a mucous membrane
What divides the tongue?
•V-shaped terminal groove (or sulcus) divides tongue into:
–Posterior part (lingual tonsil)
–Anterior part (numerous mucosal projections)
–Foramen cecum is site of origin of thyroid primordium
Intrinsic muscles of the tongue
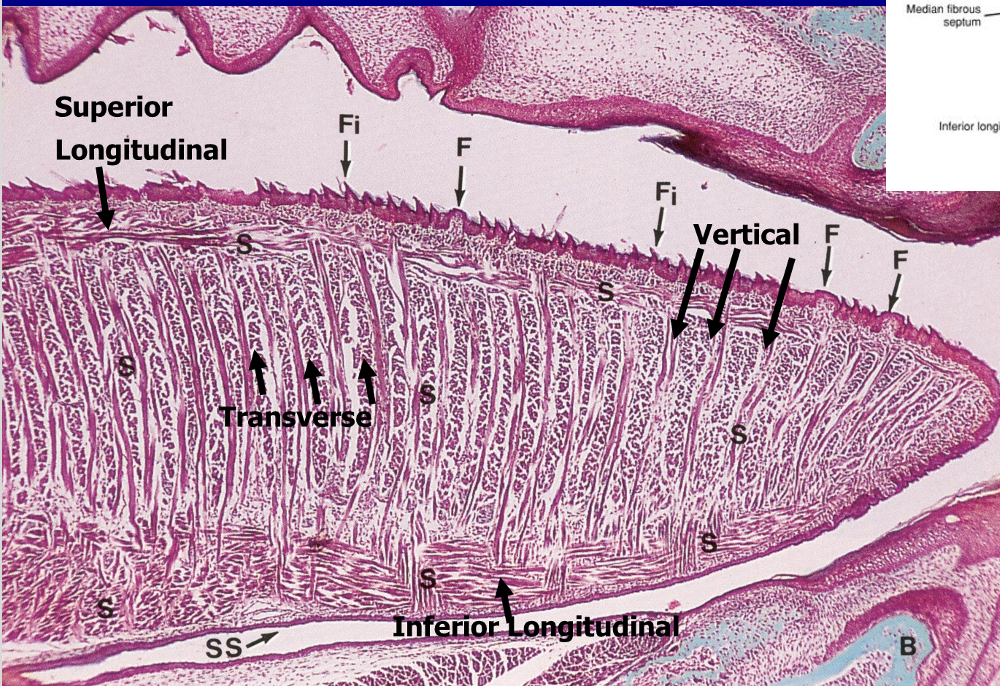
What are histological features of the tongue?
•Epithelium: keratinized SSE
•Musculature: extrinsic & intrinsic
•Papillae
–Filiform
–Fungiform
–Circumvallate
–Foliate
Filiform papillae
–Most abundant type
–Keratinized
–No taste buds
–Mechanical role
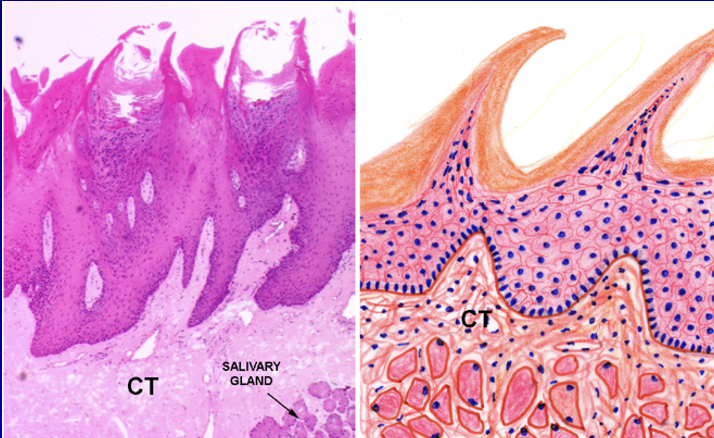
Fungiform Papillae
–Anterior tongue
–Mushroom-shaped
–Taste buds
•Apical surface
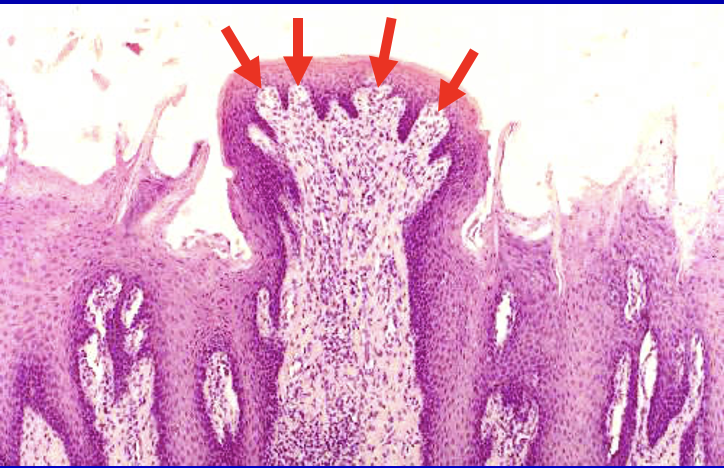
Circumvallate Papillae
–Large, dome-shaped
–8-12
–Moat-like groove
•Taste buds
–Von Ebner’s glands
•Serous lingual salivary glands
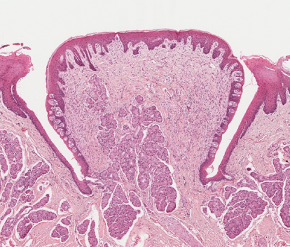
Foliate Papillae
–Parallel ridges
–Taste buds
•Lateral surfaces
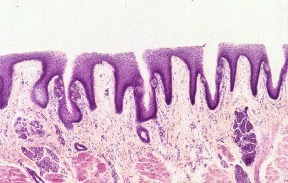
Taste Buds
•Oval-shaped
•Taste pore
–Opening into the surface
•Sensory cells
•Support cells
•Location
–Lingual papillae
–Oral cavity
•Glossopharyngeal arch
•Soft palate
•Epiglottis
Major Salivary Glands
•Functions: produce the saliva
–Lubrication
–Moistens the food
–Digestion of carbohydrates
–Antimicrobial
–Contains IgA
–Source of Ca and phosphate
•Structure
–Secretory part
–Ductal system
–Capsule and septa
–Stroma
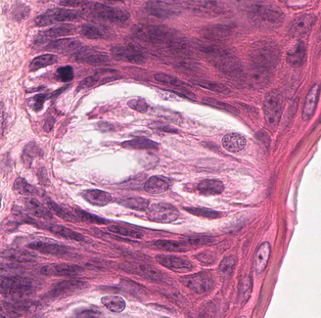
Salivary Glands: Serous Acini
•Protein-secreting
•Cell structure
–Euchromatic nucleus
–Abundant RER
–Apical secretory granules
•Rounded
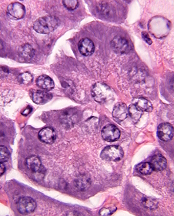
Salivary Glands: Mucous Acini
•Mucus-secreting
•Cell structure
–Heterochromatic nucleus
–“Frothy” appearance
•Tubular
Types of salivary gland ducts
•Intralobular ducts
–Within lobules
•Interlobular ducts
–Between lobules
•Main ducts
–From glands to oral cavity
Intralobular Ducts
–Intercalated ducts
•Cuboidal epithelium
•Basally-placed nucleus
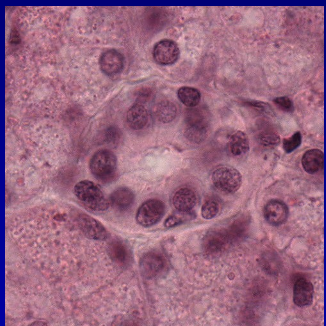
Intralobular Ducts
–Striated ducts
•Columnar epithelium
•Basal membrane infoldings
•Mitochondria
•Ion transport
•Hypotonic saliva
•Centrally-placed nucleus
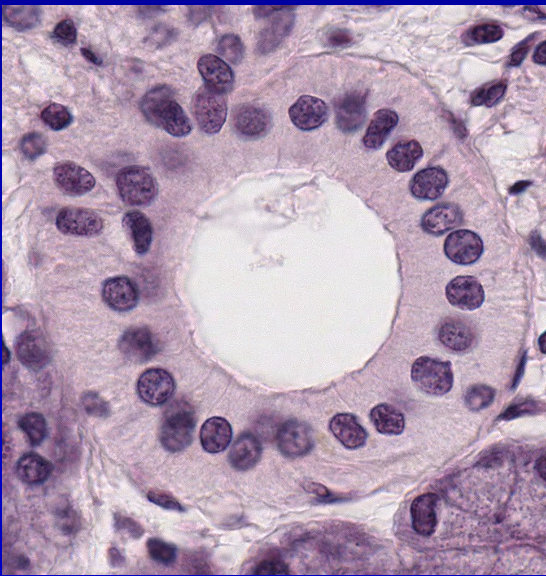
Parotid Gland
–Largest
–Serous gland
–Long duct
Submandibular Gland
–Floor of the mouth
–Mixed gland
•Mostly serous
Sublingual Gland
–Floor of the mouth
–Mixed gland
•Mostly mucous
Pleomorphic Adenoma
•Benign tumor
•Rather common
•Composed of
–Ductal cells
–Myoepithelial cells
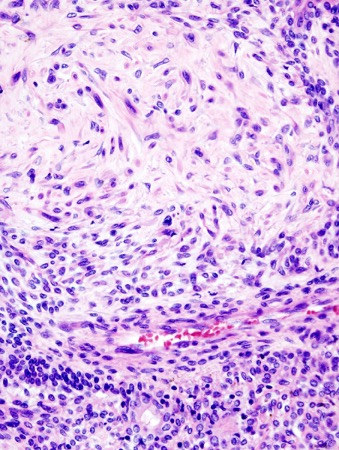
__________ is a calcification that is formed usually in the submandibular gland
Salivary calculus (sialolithiasis) is a calcification that is formed usually in the submandibular gland
Salivary calculus (sialolithiasis)
•Salivary gland stones can form in any of the salivary glands
•Etiology is unknown, but factors associated with a higher risk include:
–Blood pressure drugs and antihistamines reduce the amount of saliva produced
–Being dehydrated makes saliva more concentrated
–Not eating enough food causes a decrease in saliva production
•Sialoliths are the most common disease of the salivary glands in patients between 30 to 60 years of age:
–Men are more likely to get salivary stones than women
•Main symptom is pain in your face, mouth, or neck that becomes worse just before or during meals
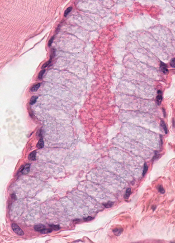
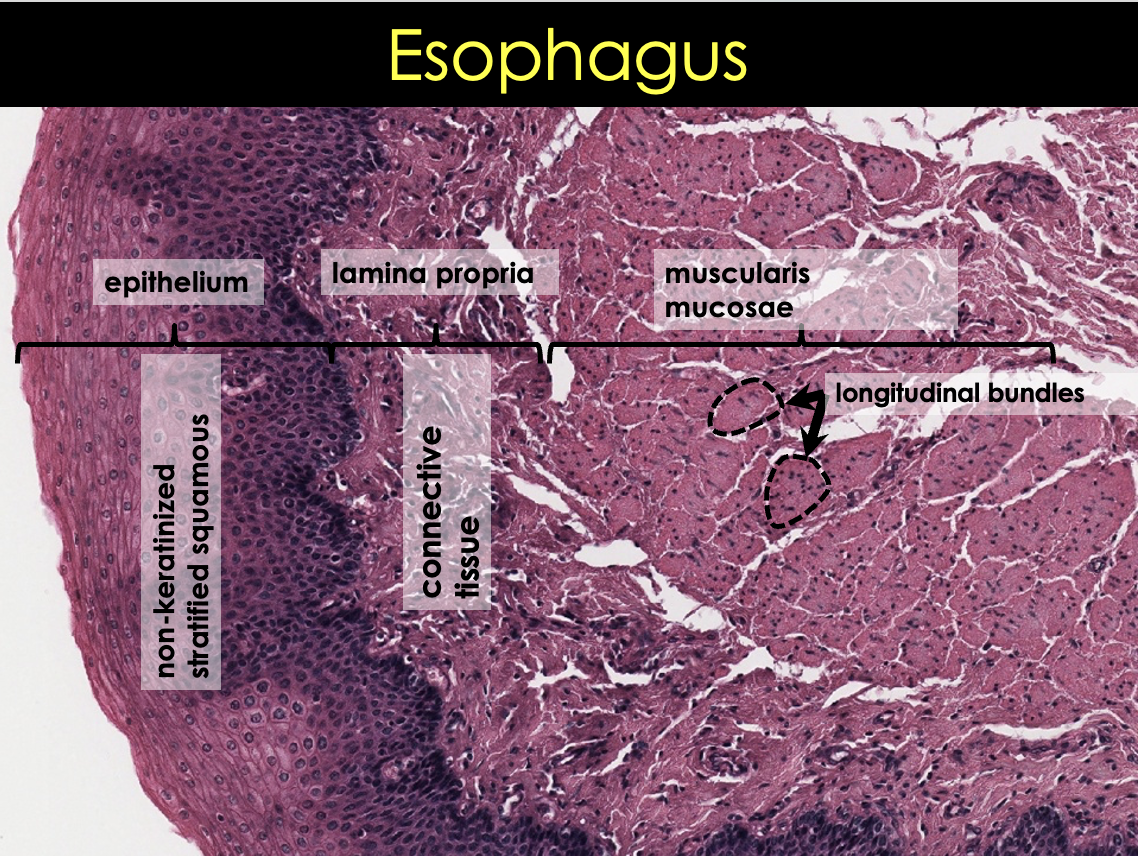
Histological layers of the esophagus
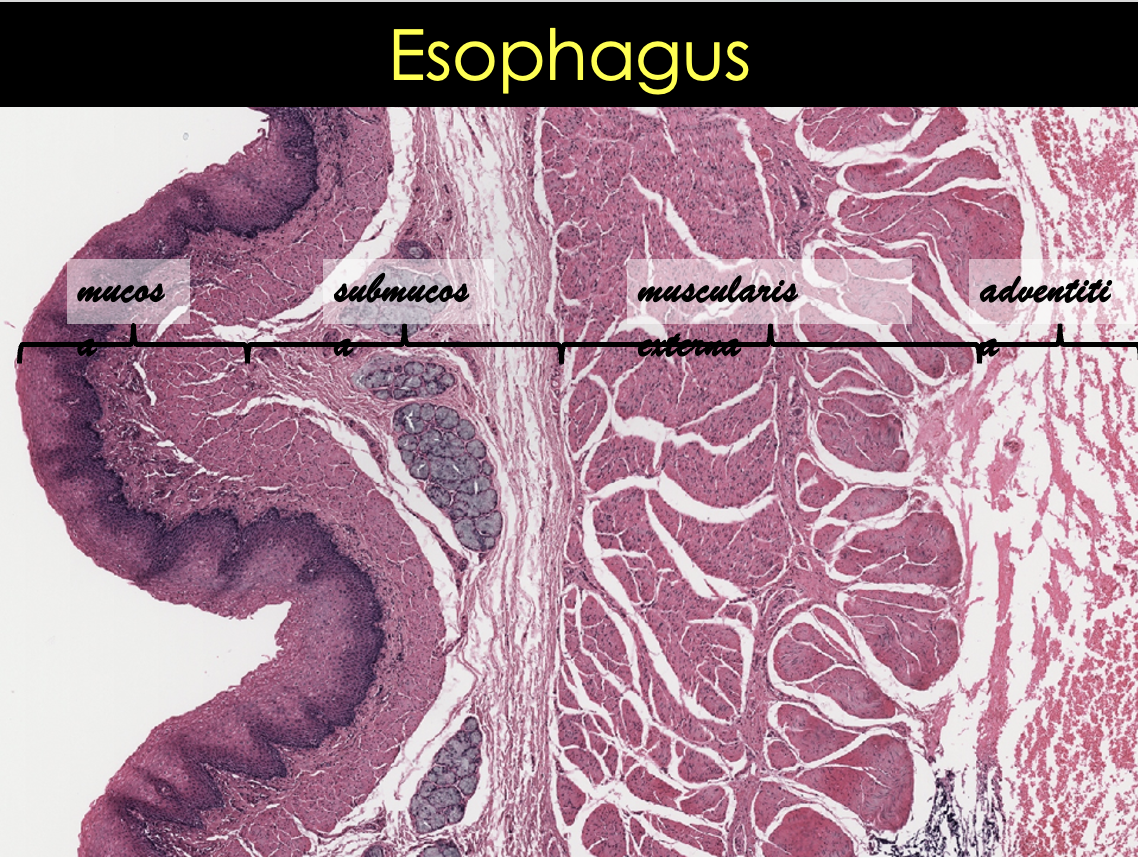
What are the three layers of esophageal mucosa?
Epithelium
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Lamina propria
Connective tissue
More fibrous
Muscularis mucosae
Different from the rest of GI
Longitudinally oriented bundles
Smooth muscle
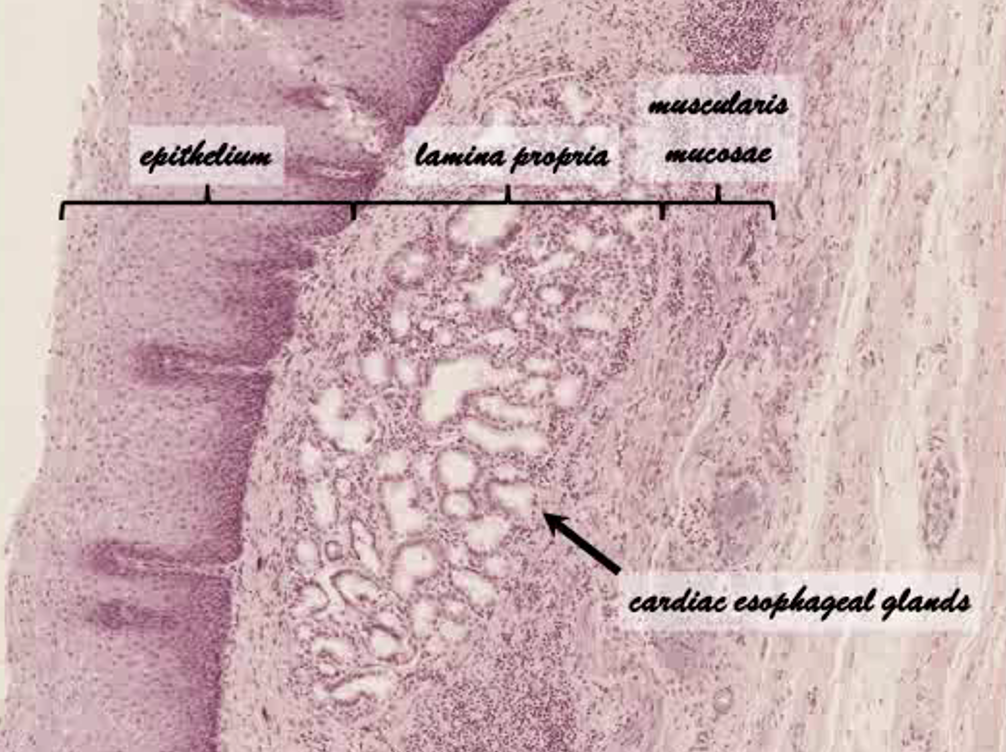
What region of the esophagus is this?
Terminal/Distal esophagus
What and where are the esophageal mucosal glands?
–Esophageal glands proper
•Small
•Compound tubuloalveolar glands
•Most of esophagus
Esophageal submucosa
–Dense irregular connective tissue
–Blood vessels
–Nerve fibers and ganglion cells: Meissner’s plexus
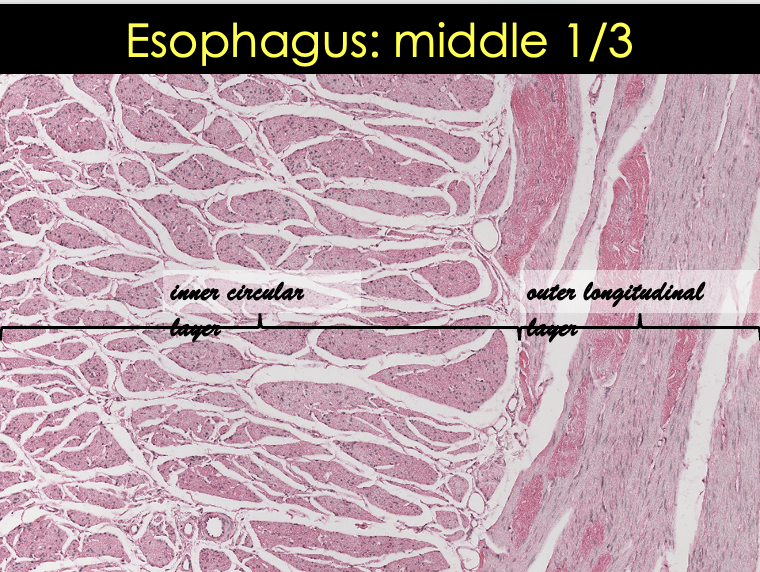
Describe the muscularis externa layers in the different sections of the esophagus
Upper esophagus
Skeletal muscle
Middle 1/3
Skeletal muscle
Smooth muscle
Lower esophagus
Smooth muscle
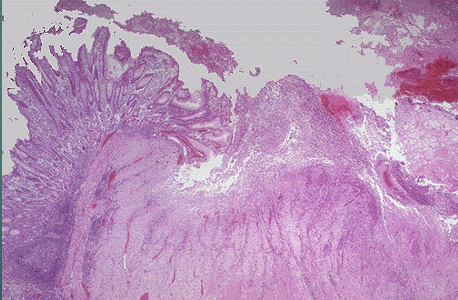
![<p>Esophagus Middle 1/3 Slide [ 2 images ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fe18ca7a-ee8a-423d-9585-26a61ef64015.png)
Esophagus Middle 1/3 Slide [ 2 images ]
Barret’s Esophagus
Metaplasia of esophageal epithelium
Stratified squamous to simple columnar
Caucasian males > 50 years
Results from Gastroesophageal reflux
Common precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma
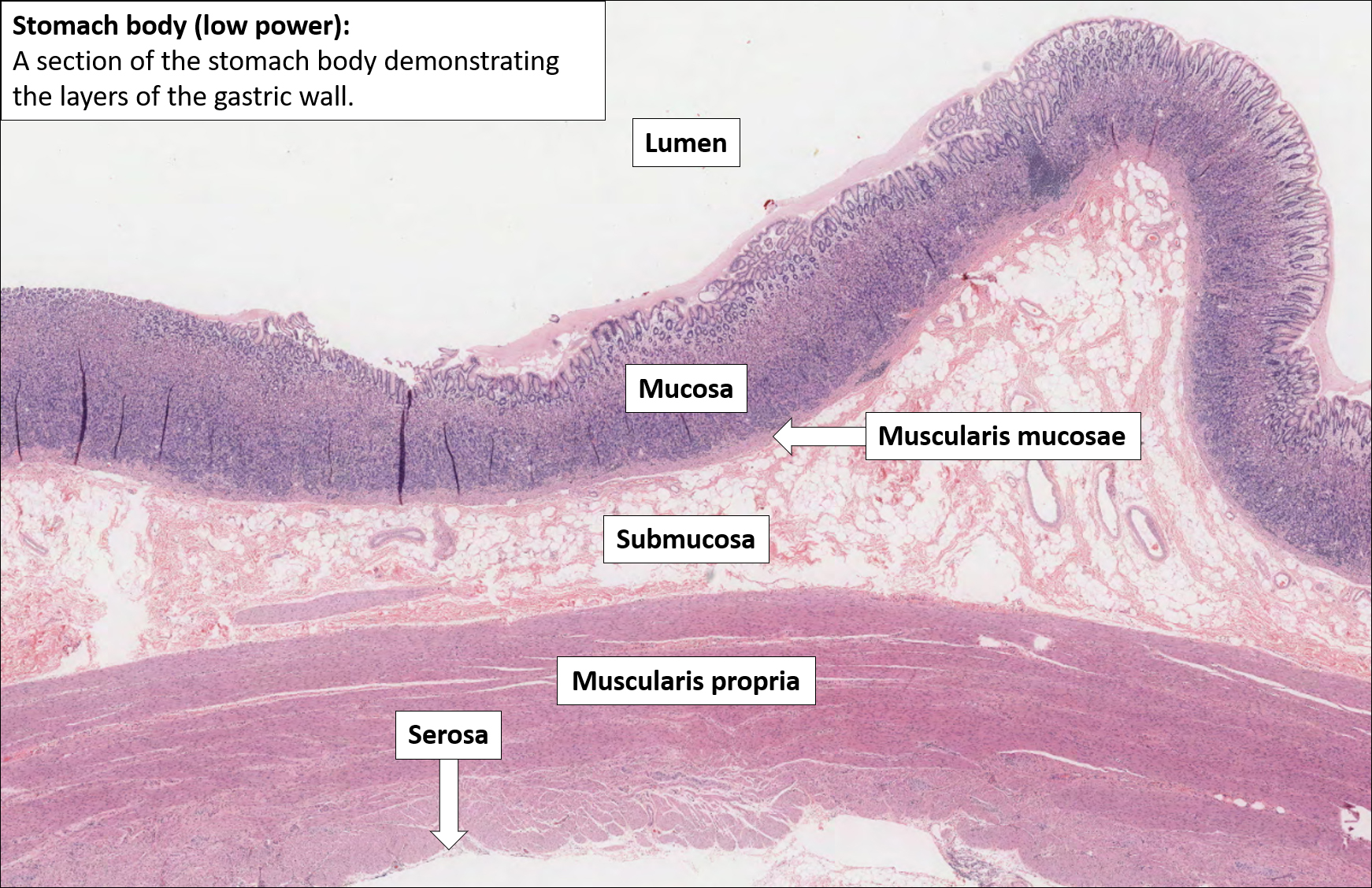
Layers of the stomach
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa
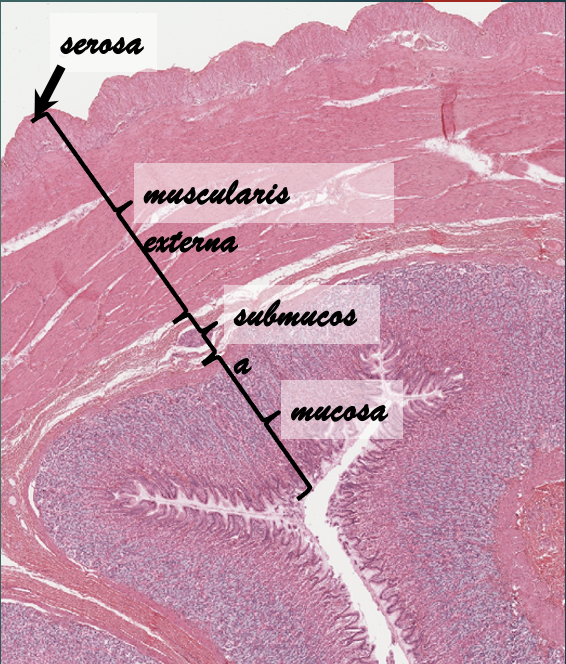
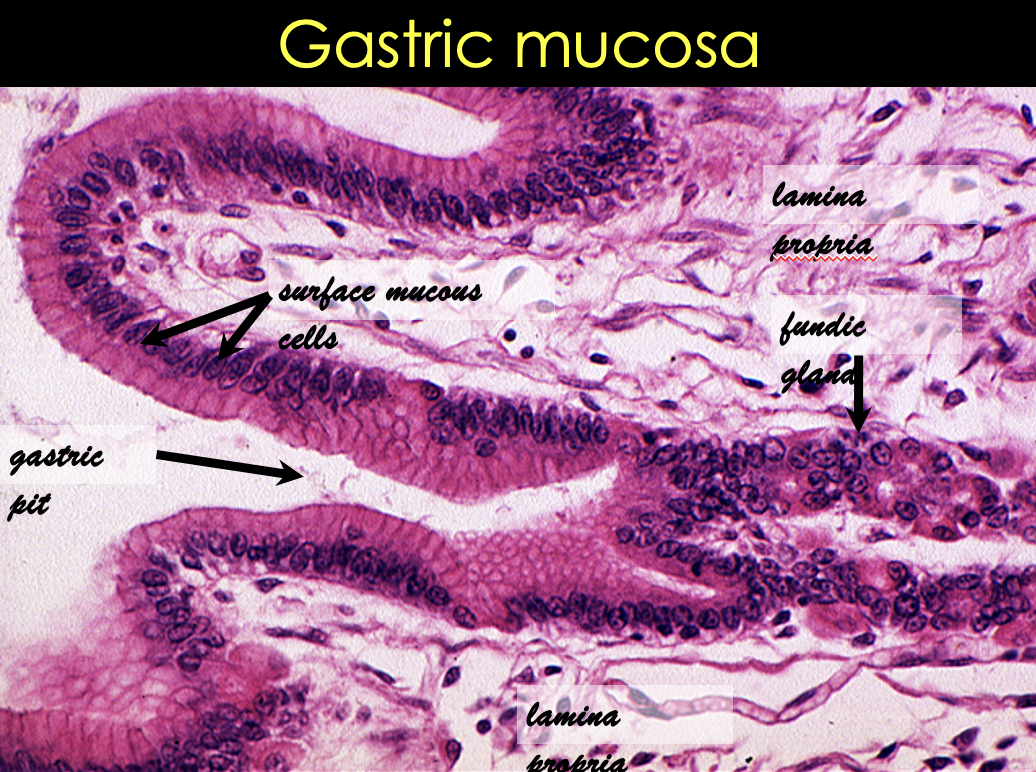
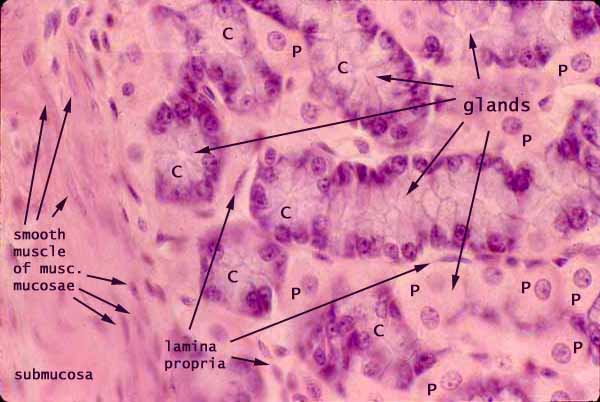
What comprises the surface epithelium of the gastric mucosa?
Simple Columnar
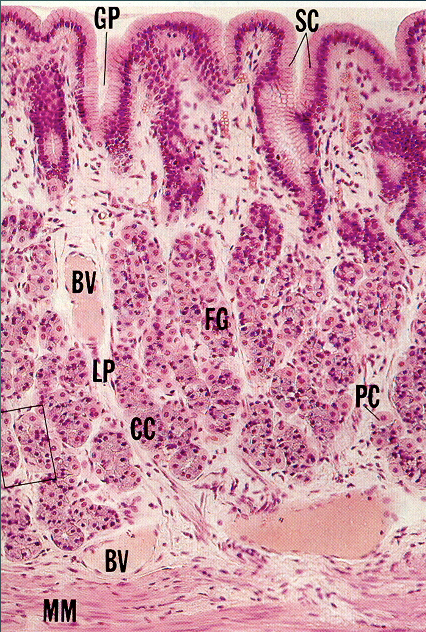
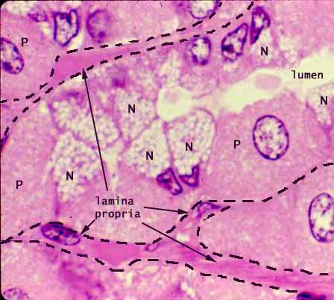
What is contained within the lamina propria?
fundic glands
cardiac glands
pyloric glands
lymphoid tissue
Gastric Mucosa Histological Slide
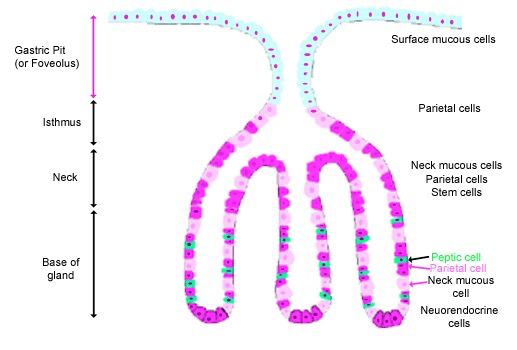
Fundic Gland Anatomy
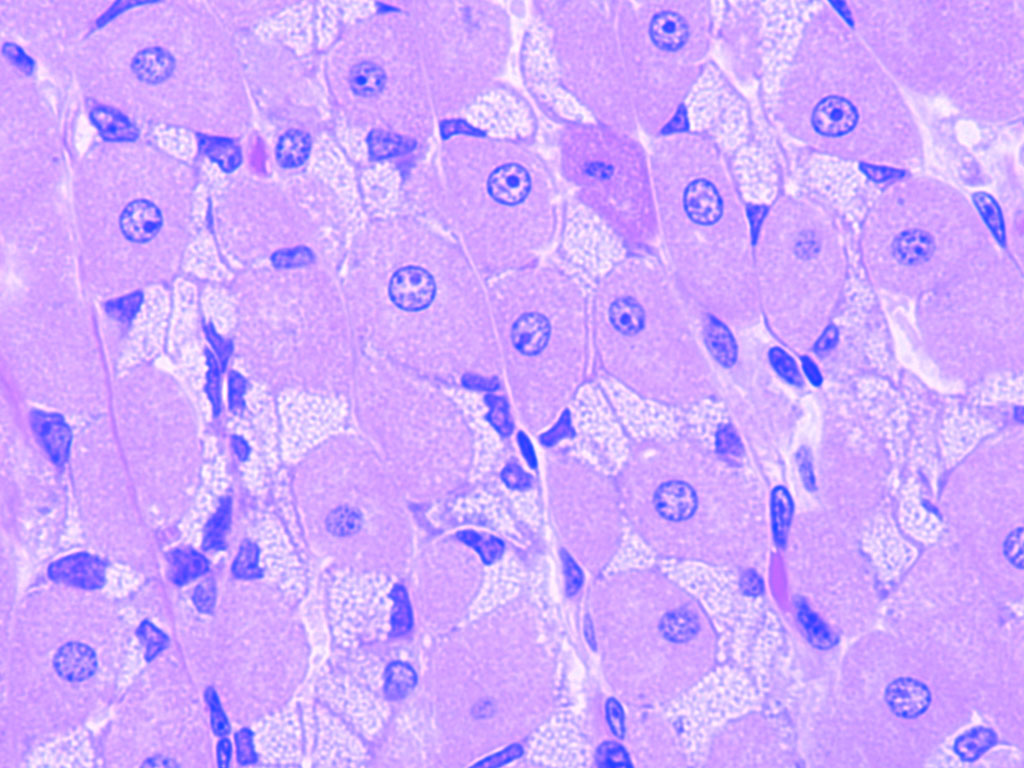
What cells are within fundic glands?
Parietal
gastric chief
mucous neck
progenitor
enteroendocrine
Parietal Cell (Location, Properties)
Location: neck and base of fundic gland
Large, pyramidal shape
Numerous mitochondria
Stain with eosin
Secrete
HCl
Intrinsic factor (B12)
Apical part of the cell
Actively secreting cell
Intracellular canaliculi with microvilli
Resting cell
Tubulovesicular system: membrane storage
Gastric Ulcer
Epithelial protective barrier
Impaired
HCl destroys cells
Penetrates deep if untreated
Peritonitis
What can happen in patients with chronic gastritis?
Deficiency of parietal cells
No intrinsic factor produced
Hemoglobin formation inhibited
Pernicious anemia
Gastric Chief Cell (Location, Properties)
Location
Base of the gland
Secrete
Pepsinogen
Pepsinogen -> pepsin
Cell structure
Abundant RER
Protein synthesis
Basophilia
Apical secretory granules
Mucous Neck Cell (Location, Properties, Structure)
Location
Neck of the gland
Secrete
Soluble mucus
Cell structure
Small cell
Heterochromatic nucleus
Mucinogen granules
“Frothy” cytoplasm
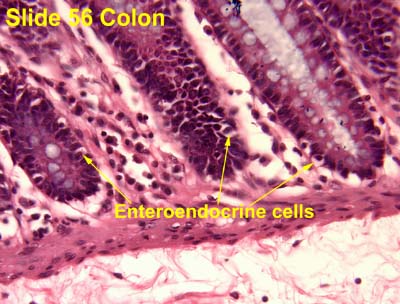
Enteroendocrine Cell (Location, Properties, Structure)
Small cell
Location
Mostly at the base
Secrete
GI hormones
Gastrin, ghrelin
Into lamina propria
Cell structure
Microvilli
On the luminal surface
Numerous secretory granules
At the base of the cell
Progenitor Cell
Undifferentiated cell
Location
Isthmus
Precursors for
Surface mucous cells
Short lifespan: 3-5 days
Gland cells
Long lifespan: 6-8 months
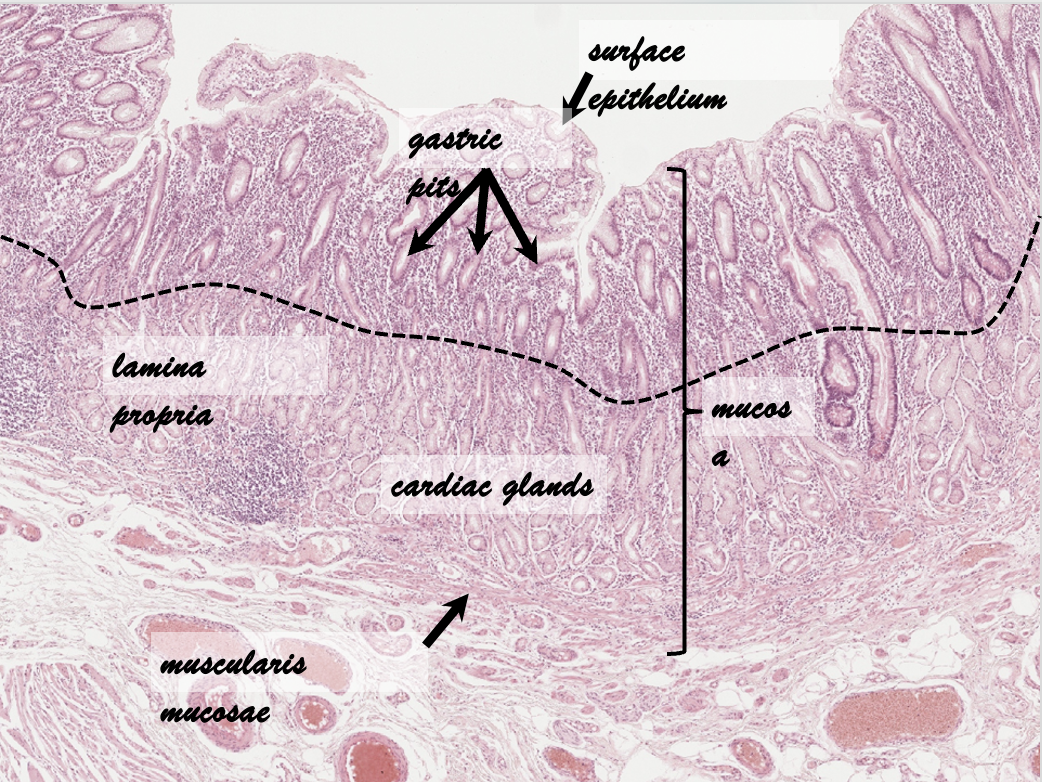
Cardiac Glands (Distribution, Function, Structure)
Distribution
Narrow ring
Around the esophageal orifice
Function
Production of mucus
Protection against acid reflux
Structure
Branched tubular glands
Mucous glands
Basal nucleus
Mucinogen granules
No parietal/chief cells
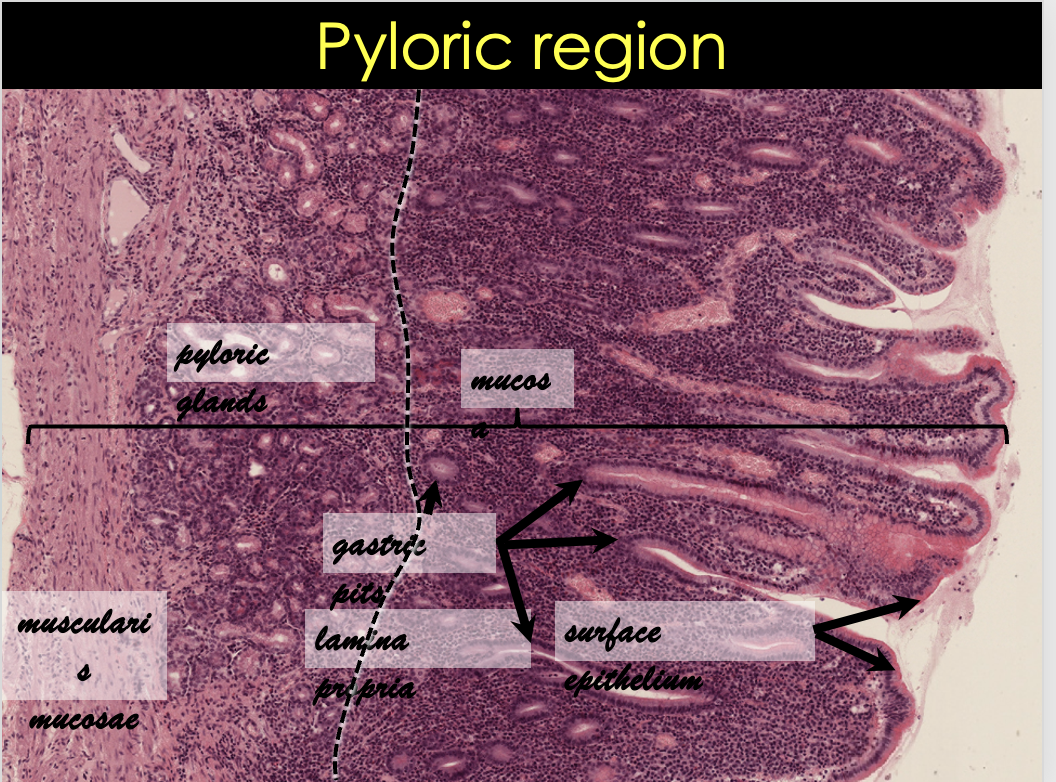
Pyloric Glands (Distribution, Function, Structure)
Distribution
Pyloric antrum
Function
Production of mucus
Structure
Branched coiled tubular
Mucous glands
Basal nucleus
Mucinogen granules
No parietal/chief cells
Lamina propria
Muscularis mucosae
Layers of the Stomach
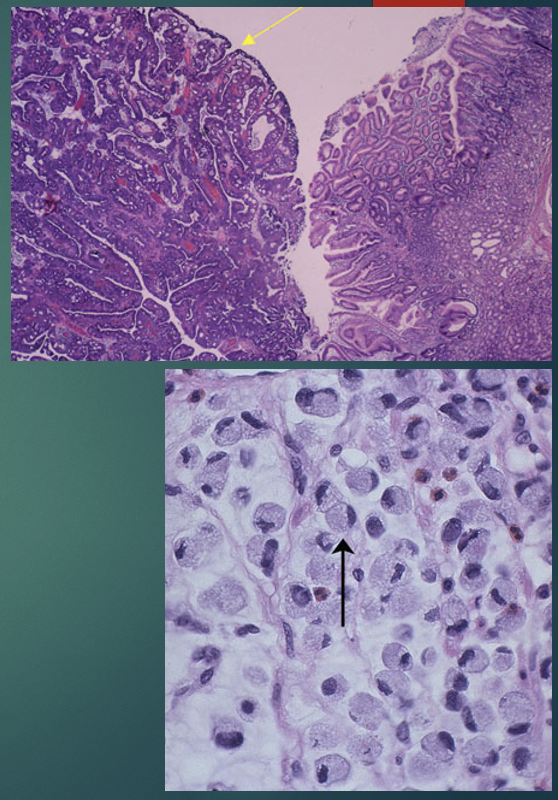
Malignant Tumors of the Stomach
Carcinoma
From surface epithelial cells
Associated with
Intestinal metaplasia
Adenocarcinoma
From glandular epithelium
Stages
Early
Penetrate into submucosa
Good prognosis
Late: poor prognosis
Penetrate into muscularis externa