Microbiology Labs: Methods of Culturing Microorganisms
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover important terms and concepts related to microbiology lab methods and cell biology, particularly focusing on microbial culturing techniques, cell structures, and staining methods.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Inoculation
The introduction of a tiny sample (inoculum) into a container of nutrient medium for culturing microorganisms.
Incubation
The process where inoculated media is placed in a temperature-controlled chamber to promote growth.
Sterile
The complete absence of viable microbes.
Aseptic
Refers to the prevention of infection/contamination.
Culture
The observable growth that happens in or on a medium.
Inspection
The staining of the bacteria to observe features under a microscope.
Isolation
The process of separating individual bacterial cells to grow discrete colonies.
Colony
Groups of cells large enough to be seen without a microscope.
Glycocalyx
Sugary substances covering the cell, made of polysaccharides and/or polypeptides.
Capsule
A neatly organized and firmly attached type of glycocalyx.
Slime layer
An unorganized and loose type of glycocalyx.
Peptidoglycan
A polymer that makes up the bacterial cell wall, contributing to cell shape and rigidity.
Gram-positive bacteria
Bacteria with a thick cell wall that stain purple in a Gram stain procedure.
Gram-negative bacteria
Bacteria with a thin peptidoglycan layer that stain colorless or red in a Gram stain.
Differential Staining
A technique used to distinguish different types of bacteria based on their cellular structure.
Basic dye
A dye that is positively charged and binds to the negatively charged components of cells.
Acidic dye
A dye that is negatively charged, staining the background instead of the cell.
Simple stain
A staining technique that uses a single dye to color all cells the same color.
Gram Stain
A staining method that classifies bacteria based on their cell wall characteristics.
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, compared to prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells
Cells that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, including bacteria and archaea.
Bacillus
rod shaped
coccus
spherical shaped
spiral
vibrio, spirillum, spirochete
strep-
in a chain
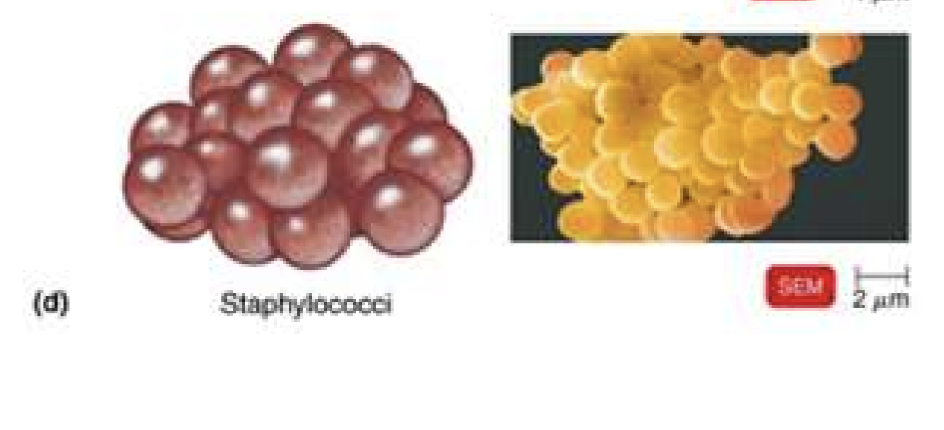
staphyl-
cluster
tetrad
4 cell arrangement
sarcinea
4 cell arrangement
dipplococci, diplobaci
2 cell arrangement
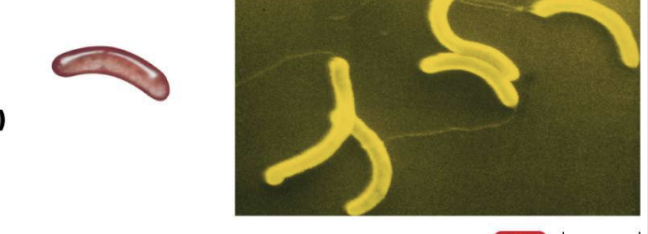
vibrio
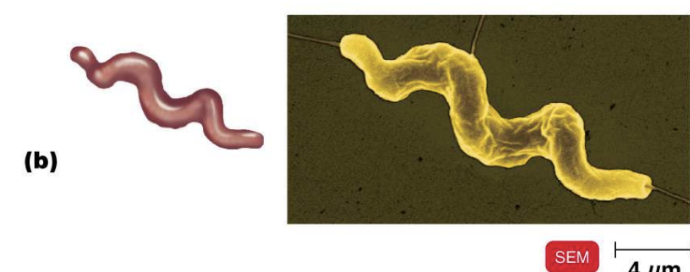
spirillum

spirochete

dipplococi

streptococci
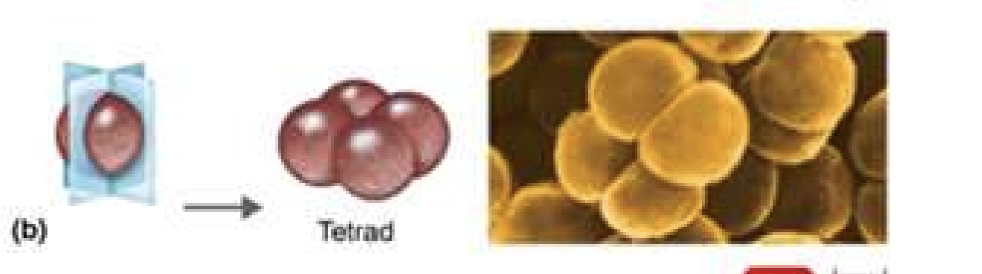
tetrad
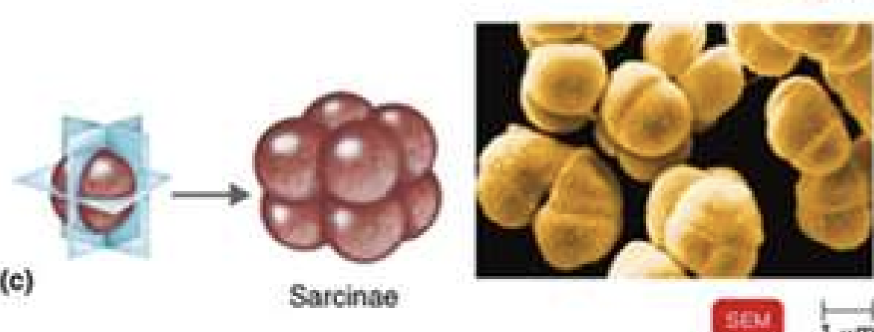
sarcinae
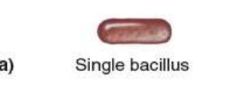
single bacillus
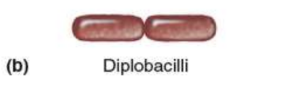
diplobacilli
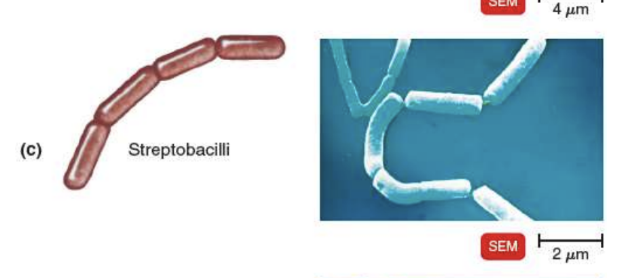
streptobacili
coccobacillus
star shaped bacteria
what structures are found in all bacteria?
• Cell wall
• Plasma membrane
• Cytoplasm (containing simple cytoskeleton structure)
• Nucleoid containing DNA
• 70s Ribosomes
what structures are external to the cell wall?
Glycocalyx
Flagella
Axial filaments
Fimbriae
Pili
Functions of the glycocalyx
Protect bacteria from phagocytosis
Enables adherence
Prevent dehydration
Source of nutrient
flagella
Thread-like structures that enable bacterial motility and movement by rotating.
flagella: flagellin
protein subunits that make up the filament of bacterial flagella.
flagella: hook
the structure connecting the filament and the motor that allows for the rotation of the flagellum.
flagella: basal body
the structure that anchors the flagellum to the cell membrane and drives its rotation.
taxis
a movement response of microorganisms towards or away from chemical or physical stimuli, facilitating adaptation and survival.
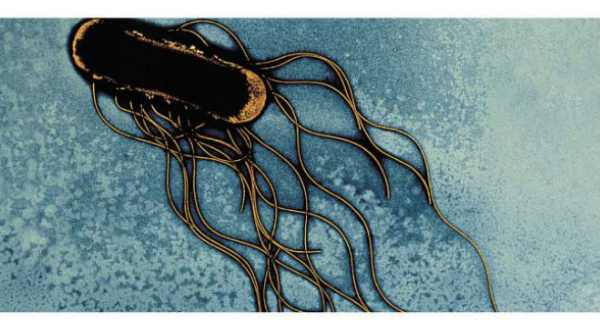
peritrichous
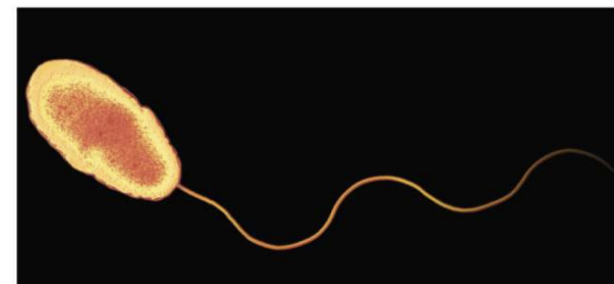
monotrichous and polar
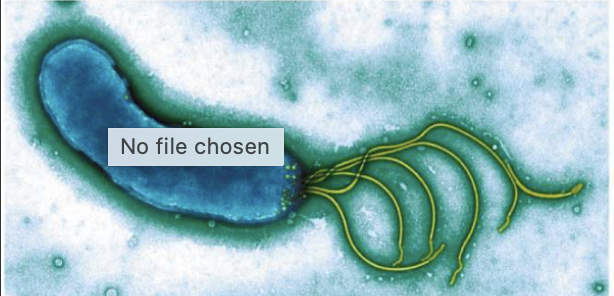
lophotrichous and polar
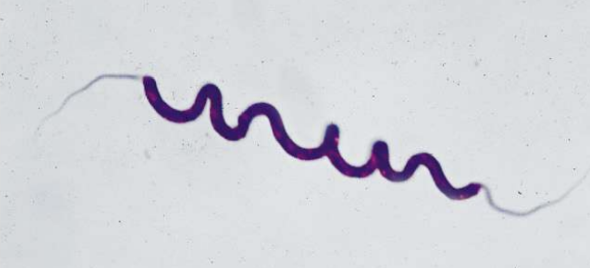
amphitrichous and polar
what is the functions of bacterial
Prevents osmotic lysis
Maintains the cell’s shape
Contributes to bacteria pathogenicity
Differential Stain