Anti Depressants
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
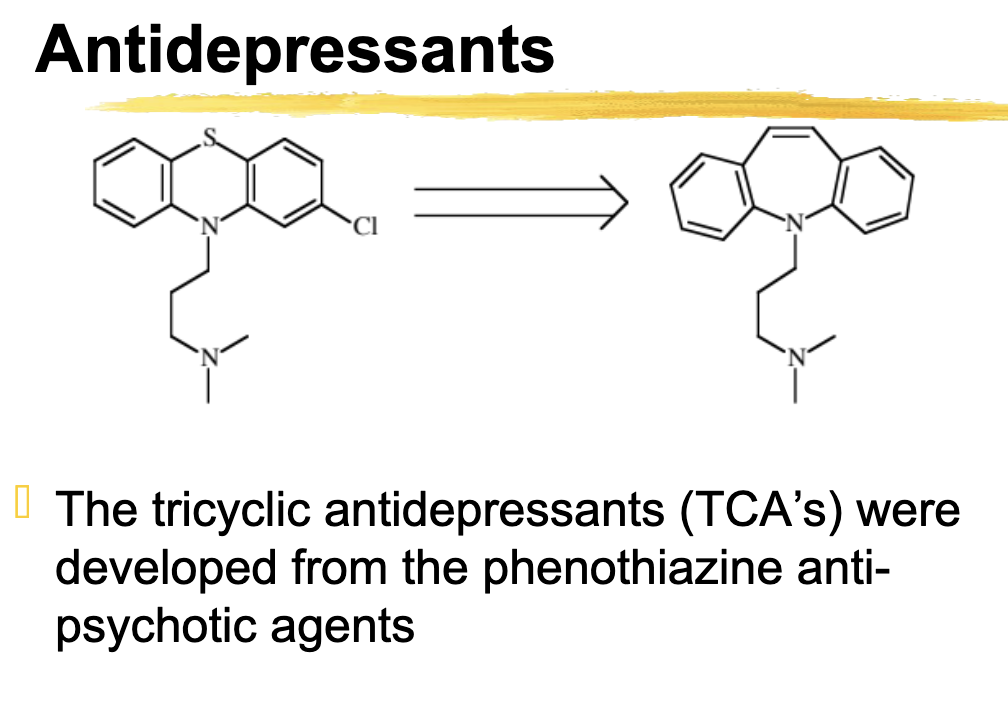
Developed from phenothiazine anti-psychotic agents
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA’s)
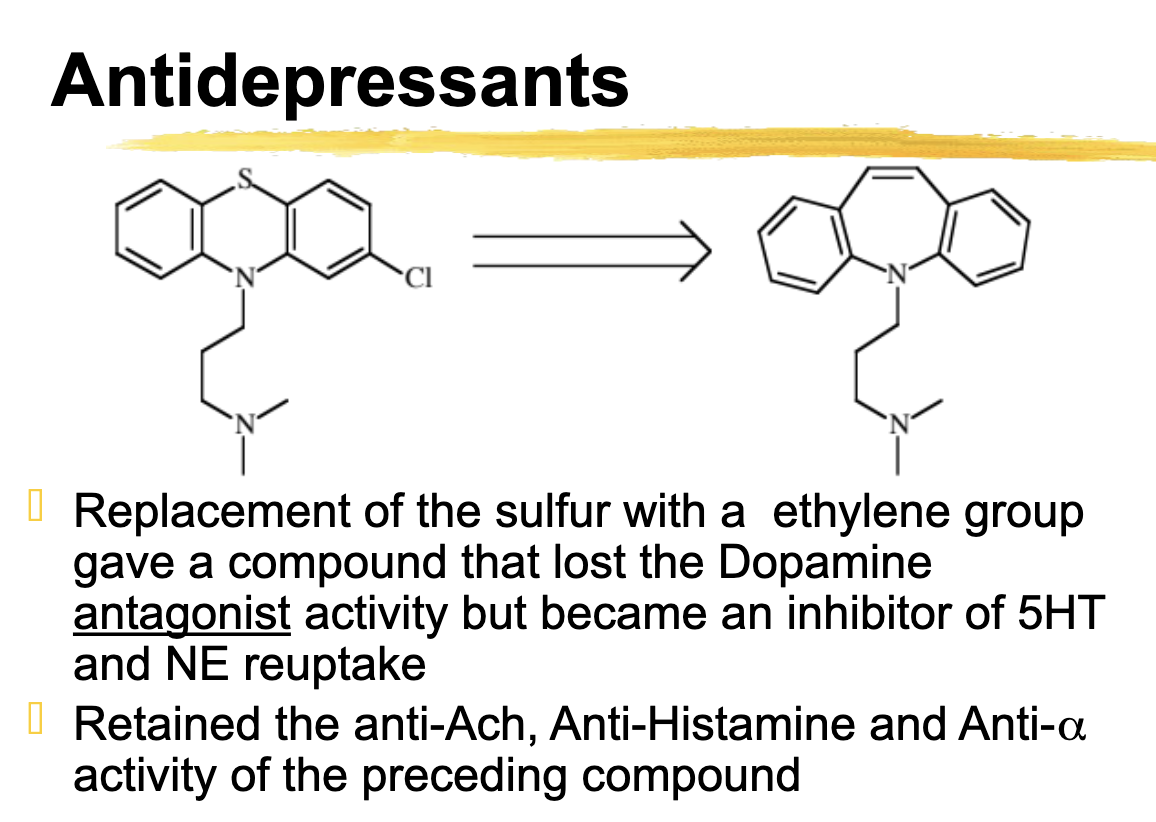
replacement of the sulfur with a ethylene group gave a compound that lost the _______ ______ activity but became an inhibitor of ___ and ___ reuptake
Replacement of the sulfur with a ethylene group gave a compound that lost the Dopamine
antagonist activity but became an inhibitor of 5HT and NE reuptake
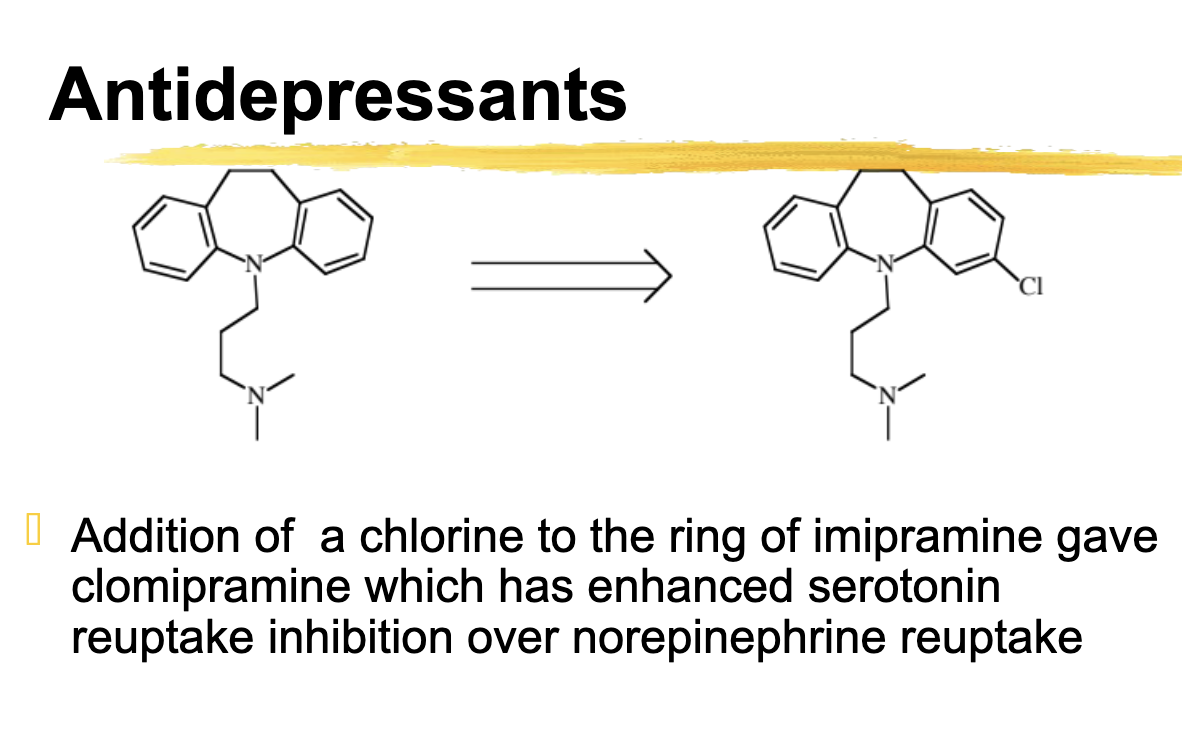
Cl substitution as in clomipramine has what effect on 5HT and NE reuptake
Enhances effect 5HT over NE reuptake
Reducing the double bond in the TCAs resulted in
Increased potency as a reuptake inhibitor and yielded imipramine
Side effects of TCA’s
Anticholinergic
Sedation
Hypotension
Cardiotoxicity

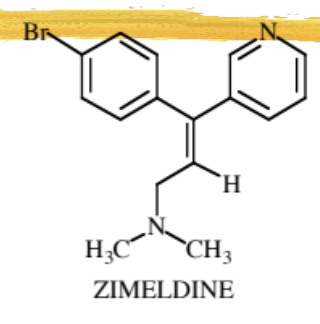
First SSRI
Zimeldine
what group on the antidepressants is important for SSRI activity?
Para electron withdrawing group
Para to the oxygen, EDG/EWG is located located on the ring
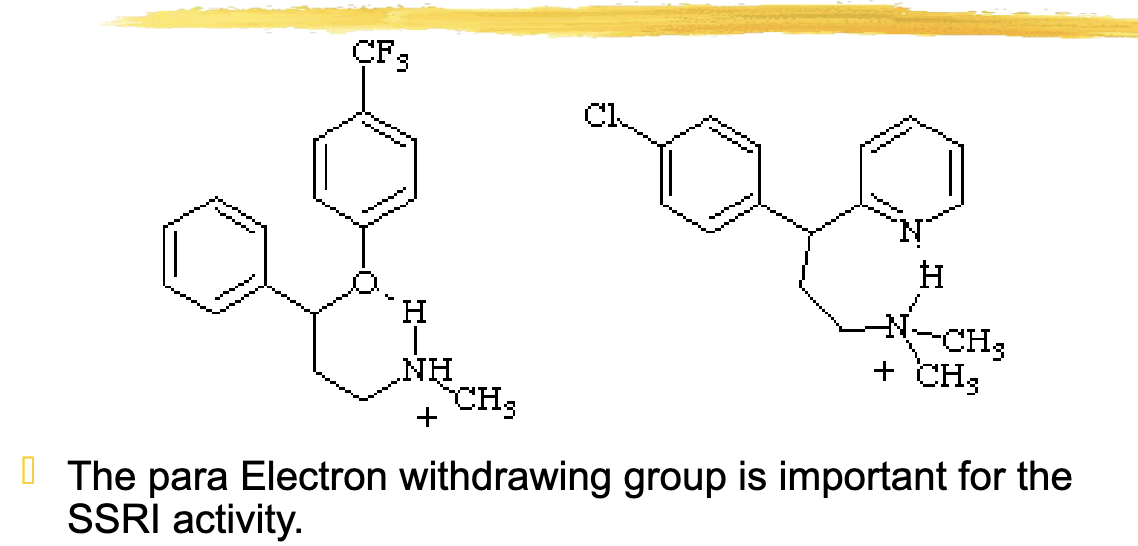
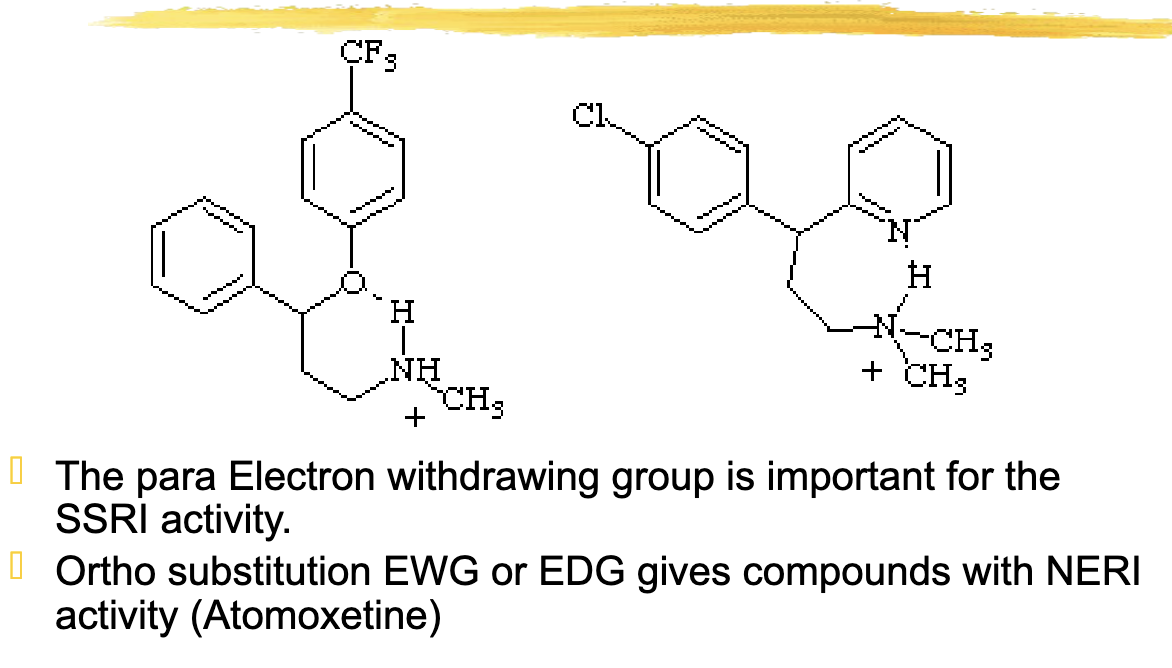
The ortho substitution EWG or EDG gives compounds with
NERI (Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor) activity (Atomoxetine)
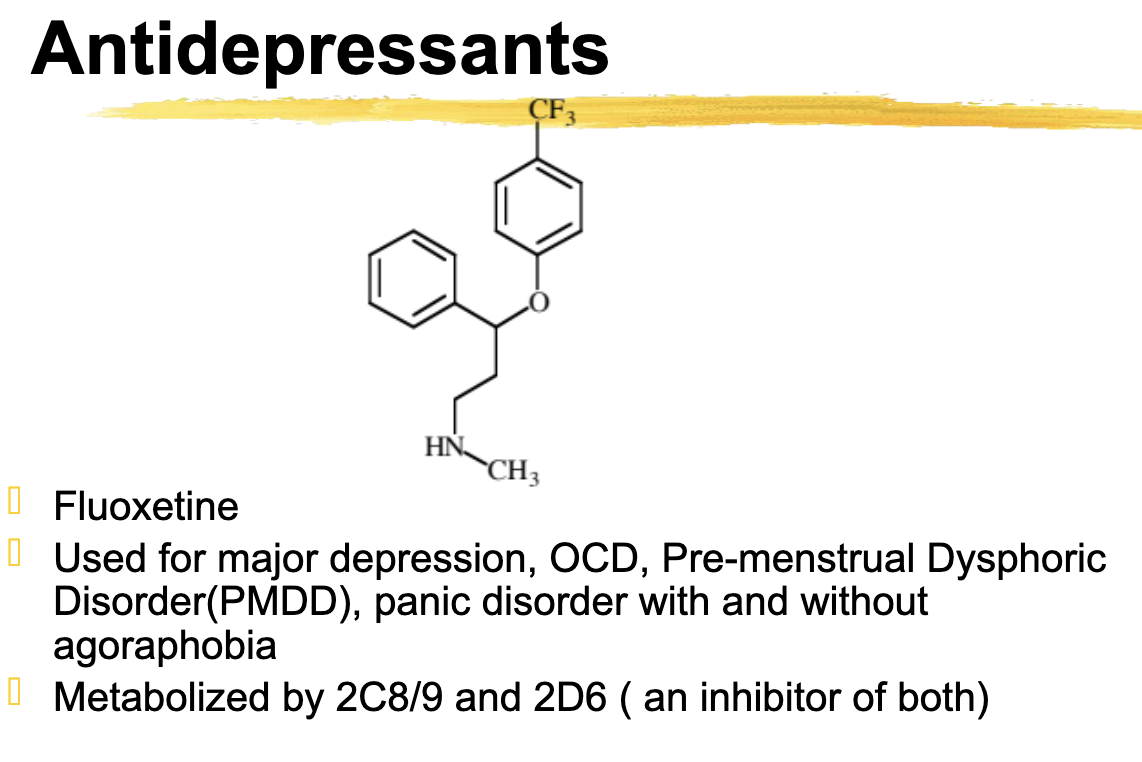
Fluoxetine Use *not tested
Major depression, OCD, Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder, Panic Disorder with and without agoraphobia
Fluoxetine metabolize
Metabolized by 2C8/9 and 2D6
Inhibitor of both
T/F: Fluoxetine is metabolized by 2C8/9 and 2D6 and is an inducer of both
FALSE
Fluoxetine is metabolized by 2C8/9 and 2D6 and is an inhibitor of both
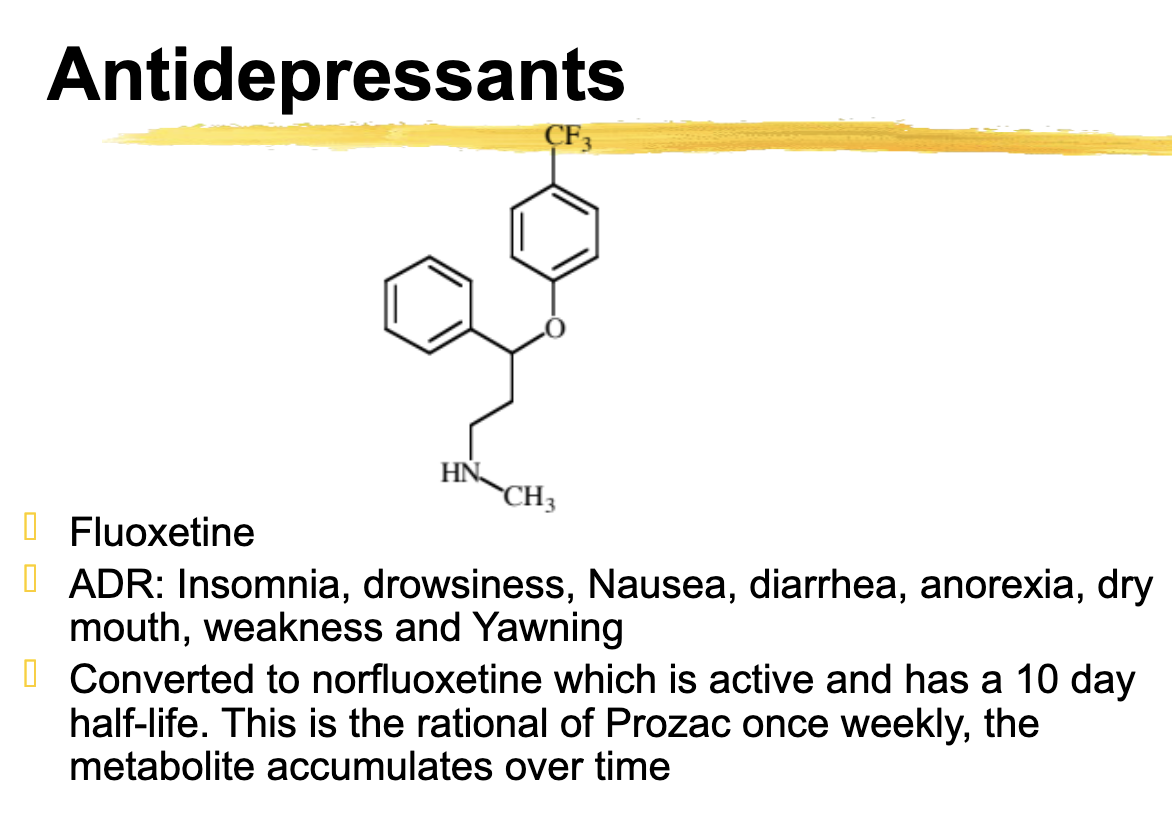
Fluoxetine ADR
Insomnia, drowsiness, Nausea, diarrhea, anorexia, dry mouth, weakness and Yawning
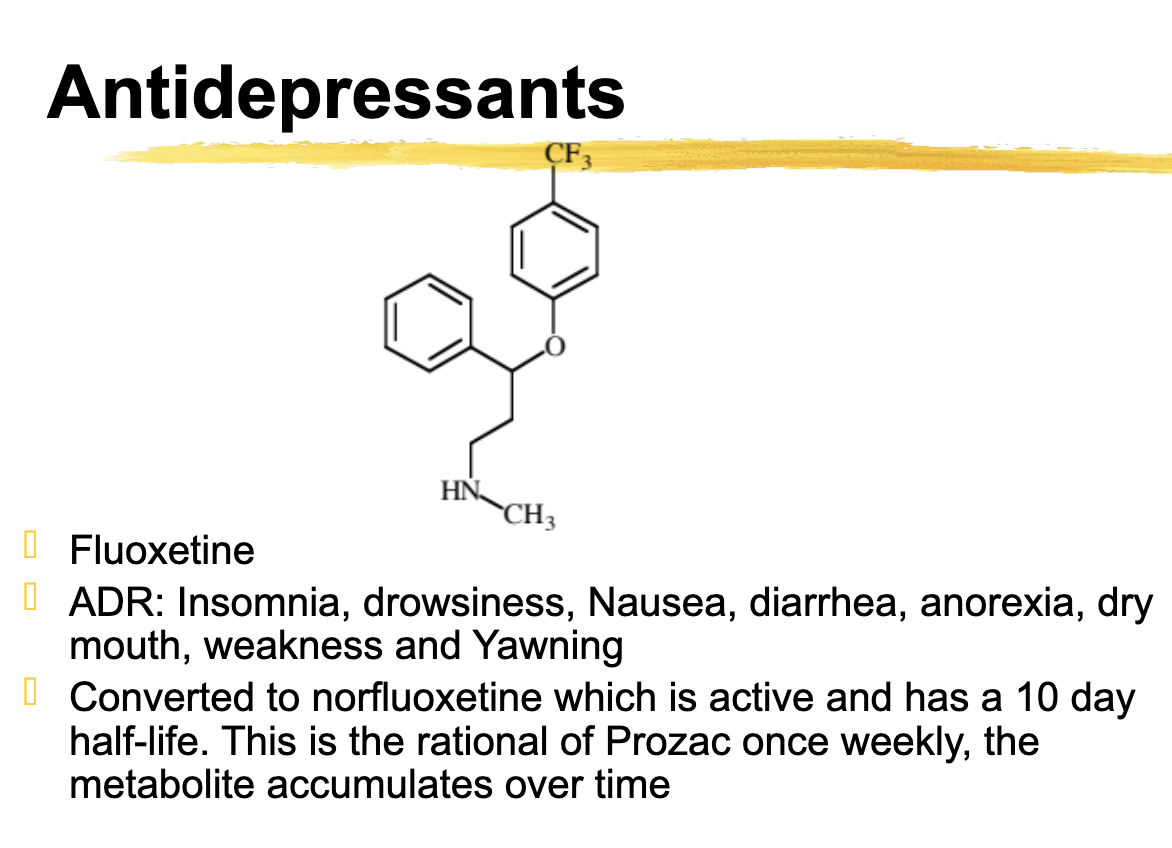
Fluoxetine is converted to ________ which is active and has a 10 day half-life. + How often do you take it
Converted to norfluoxetine which is active and has a 10 day half-life. This is the rational of Prozac once weekly, the metabolite accumulates over time
Fluvoxamine different from fluoxetine
No second aromatic ring and primary amine
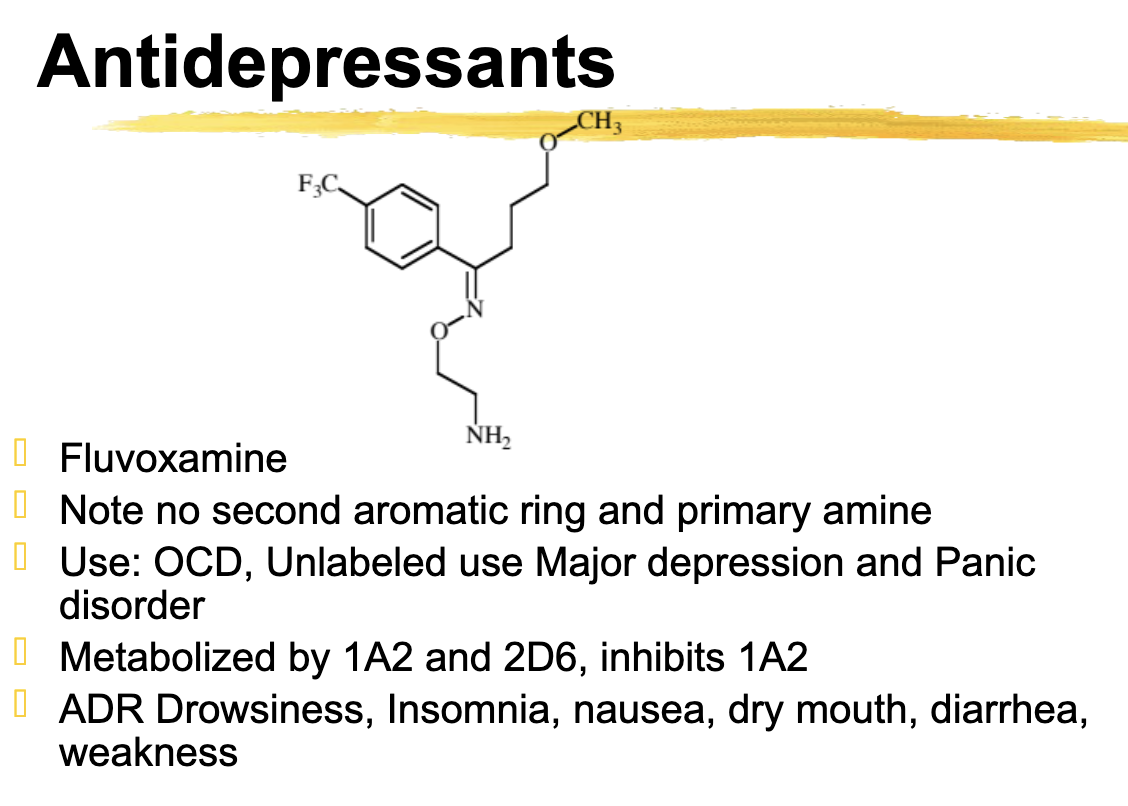
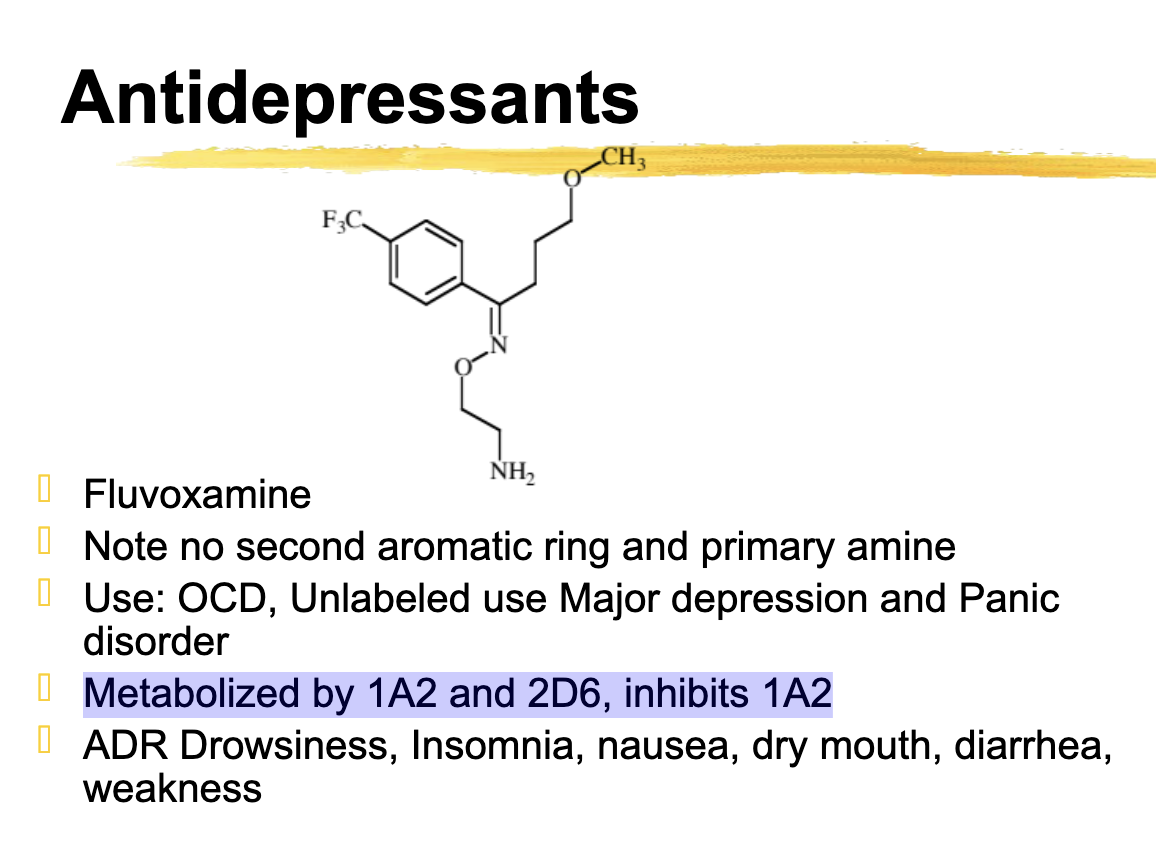
fluvoxamine metabolized
1A2 and 2D6
Inhibits 1A2
Citalopram metabolized
2C19 and 3A4
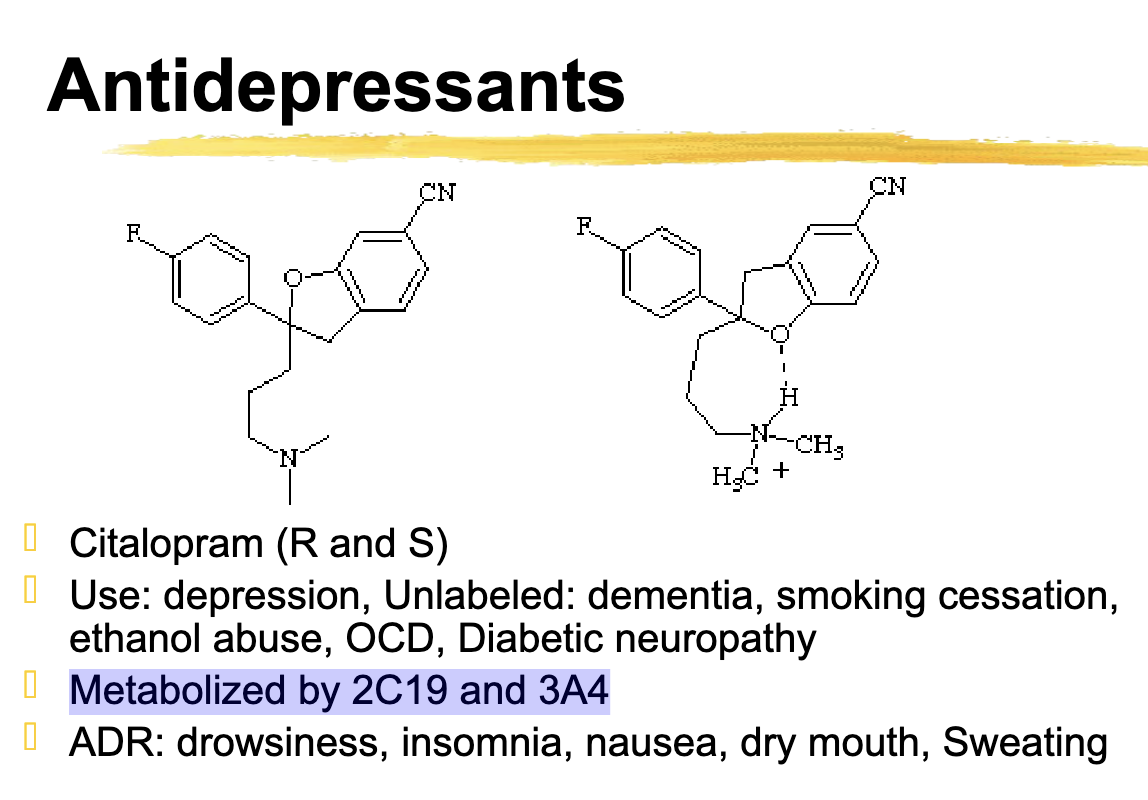
Citalopram ADR
ADR: drowsiness, insomnia, nausea, dry mouth, Sweating
Escitalopram relationship to citalopram
Escitalopram is the S isomer and is the active form of citalopram
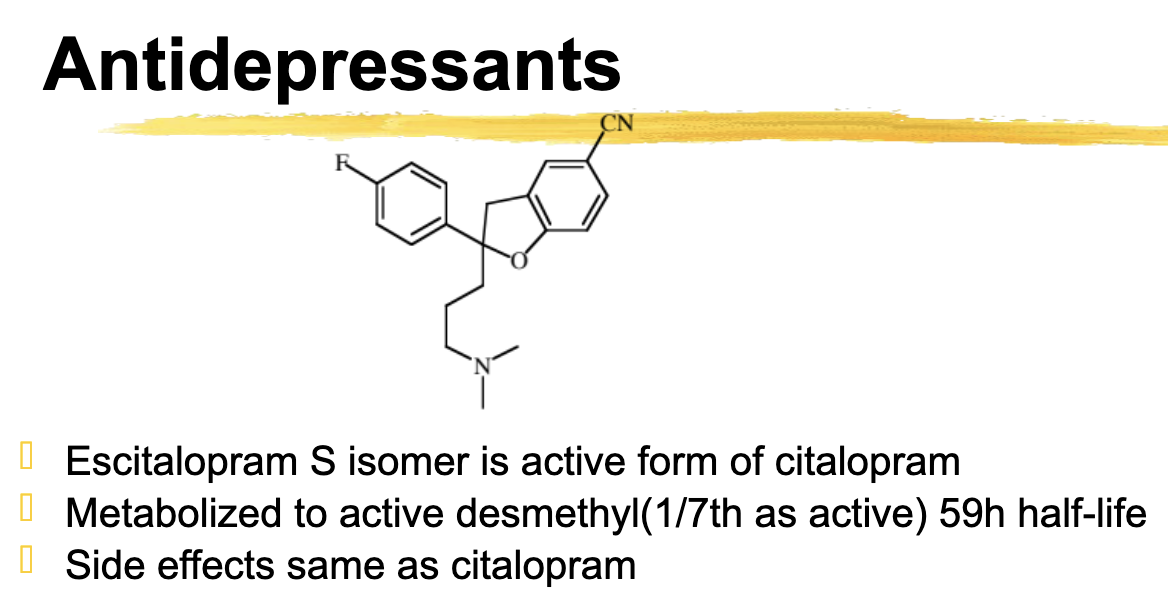
Escitalopram metabolizes
active desmethyl with a long half life (59h)
ADR same as citalopram
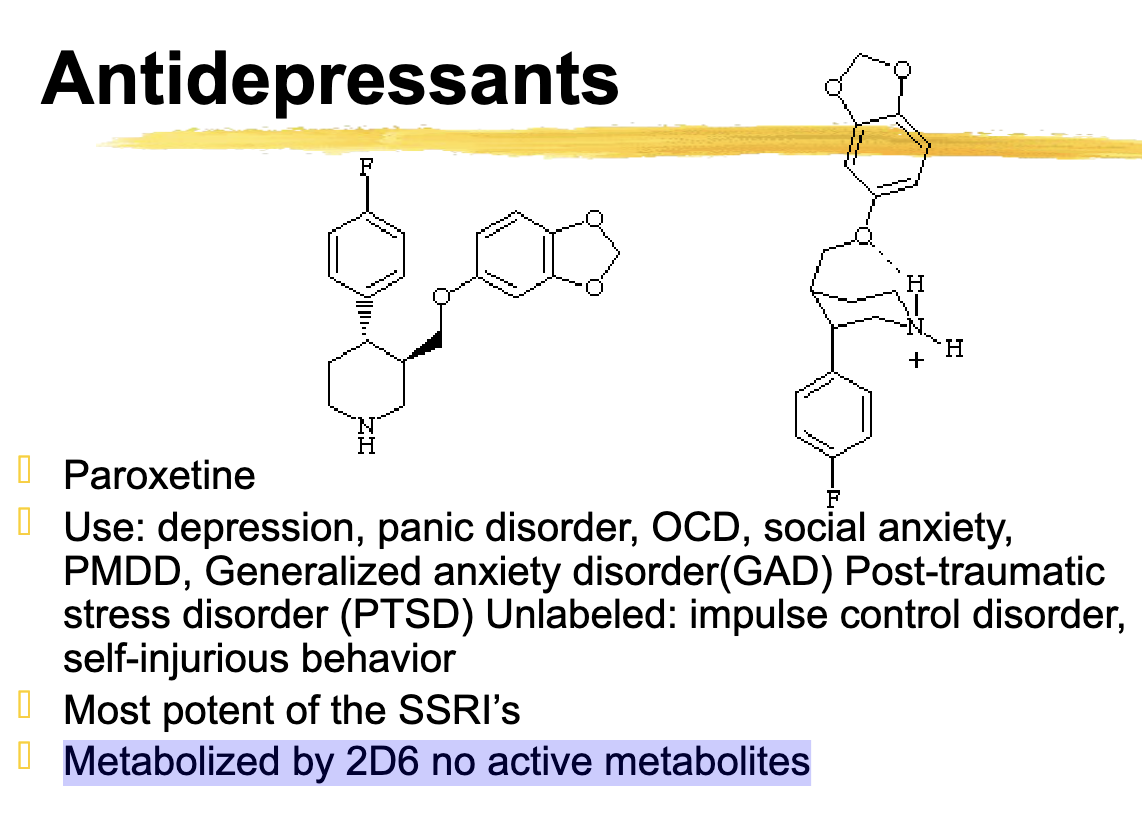
Paroxetine unique SSRI
Most potent of the SSRIs
Paroxetine is Potent
Paroxetine metabolized by
2d6
This will accumulate in poor 2d6 metabolizers
sertraline is structurally similar to
chlorpheniramine
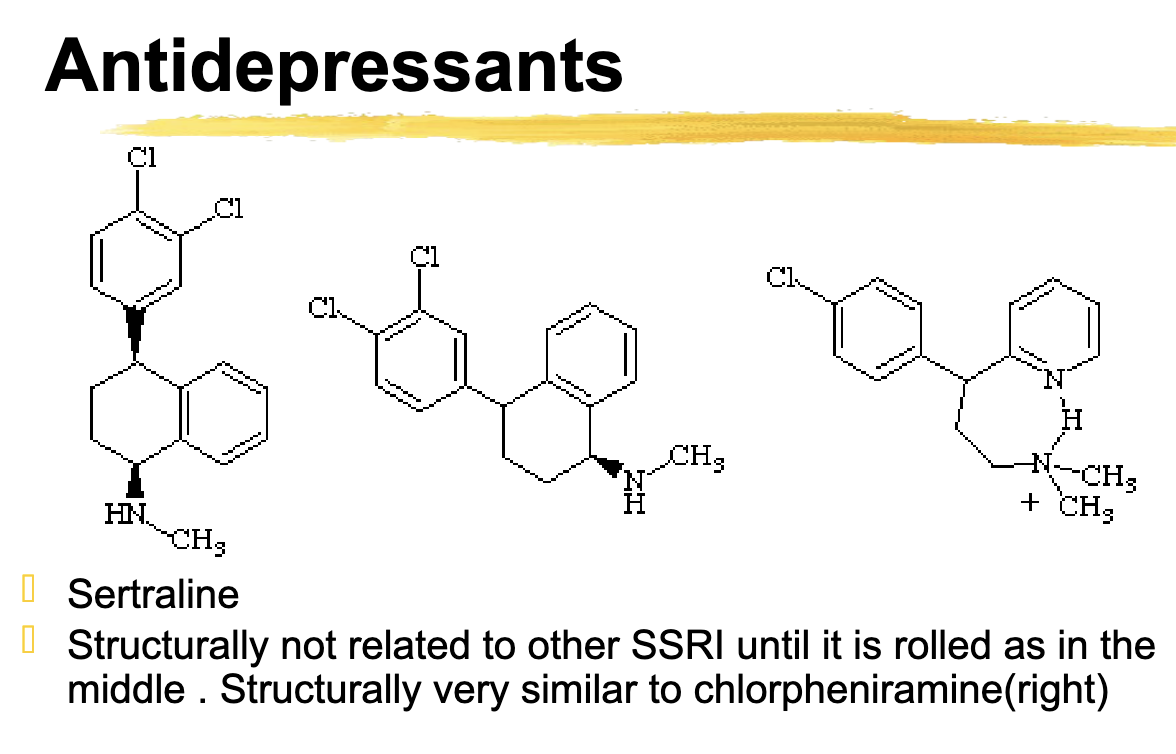
sertraline metabolized by
2c19, 2d6, moderate inhibitor of 3a5. 2c19, 2d6
Which of the following are mixed reuptake inhibitors
Escitalopram
Paroxetine
Duloxetine
Sertraline
Venlafaxine
Venlafaxine and Duloxetine are Mixed
The rest are SSRIs
venlafaxine use
Use Depression, GAD, Social anxiety, Panic disorder
Unlabeled: OCD, Hot flashes, Neuropathic pain, ADHD
venlafaxine metabolized
2D6 and 3A4
Active metabolite O-desmethyl (desvenlafaxine, Pristiq)
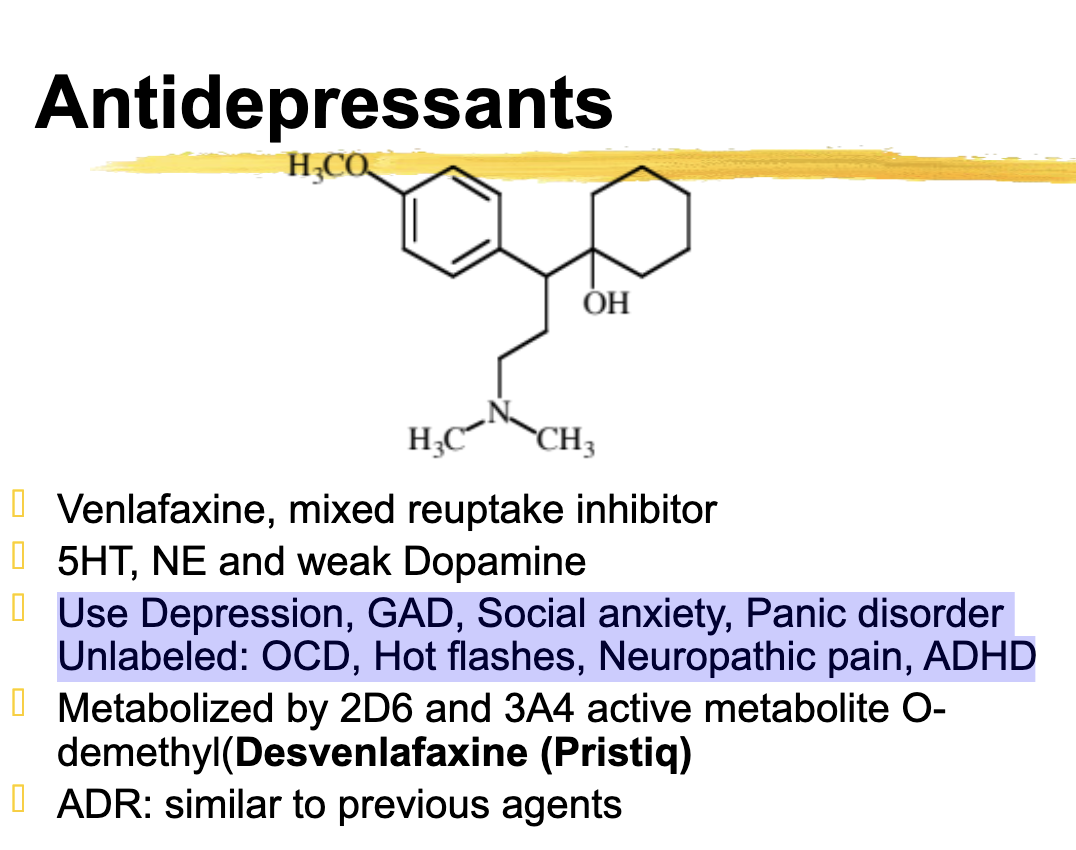
active metabolite of venlfacine
desvenlafacine
Duloxetine use
Use: depression, GAD, diabetic neuropathy, chronic pain, management of Fibromyalgia Unlabeled Stress incontinence
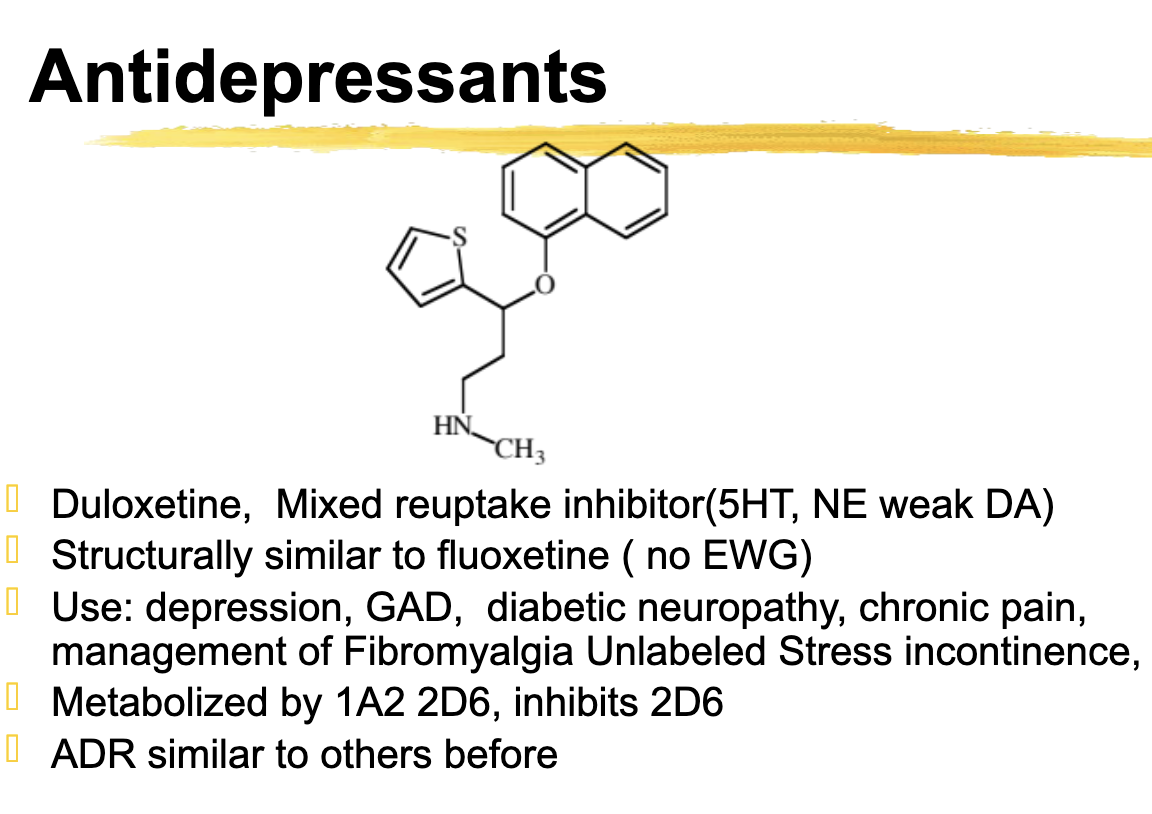
duloxetine metabolized
Metabolized by 1A2 2D6, inhibits 2D6
milnacipran active isomer
+ (positive) isomer is active, used in a racemic mixture
milnacipran type
Selective 5-HT and NE reuptake inhibitor
Milnacipran use
Fibromyalgia only
milnacipran metabolism
CP450 metabolism and NOT an inhibitor of CP450, some glucuronide formation, excreted renally
+ (positive) isomer has a longer half-life than the - (negative) isomer
levomilnacipran moa
selective 5-ht and ne reuptake inhibitor
levomilnacipran use
major depression only
levomilnacipran metabolized
3A4 and hydroxylation and glucuronidation
levomilnacipran adr
Nausea and tachycardia (low incidence), small weight loss
levomilnacipran dosage forms
extended release formulation (beads in capsule)
vilazodone moa
New class 5HT reuptake pump and 5HT1A partial agonist (5HT modulator and stimulator)
vilazodone metabolized
3a4 major
2c19 and 2d6 minor (not inhibitor or inducer)
what increases vilazodone levels
3a4 inhibitors increase plasma levels of vilazone
vortioxetine moa
inhibits 5HT reuptake and agonist/partial agonist at 5HT1A also %HT3 antagonist
vortioxetine metabolized
2D6 (primarily)
3A4, 2C19, and others, glucuronidation
Poor metabolizers have 2x plasma levels
vortioxetine metabolite
carboxylic acid metabolite major
vortioxetine adr
Increase QT and nausea
ortho substitution causes switch from fluoxetine to:
atomoxetine
atomoxetine moa
NERI
atomoxetine use
ADHD
atomoxetine metabolism
2D6 to 4-OH which is equal active and desmethyl which is weakly active
Bupropion moa
DA reuptake inhibitor, metabolite is an NE reuptake inhibitor
Bupropion use
Depression and smoking cessation: Unlabeled ADHD
Bupropion metabolized
2B6 hydroxy bupropion and hydrobupropion
bupropion adr
ADR: insomnia, nausea, dry mouth, Sore throat? Seizure
>300 mg/ day non SR or XL formulation
Trazodone moa
atypical antidepressant
weakt 5ht reuptake inhibition, parent and metabolite m-chlorophenyl piperazine are agonists at 5HT1
atypical antidepressant related to trazodone
nefazodone
What MOI are non-selective
Phenelzine
Tranylcypromine
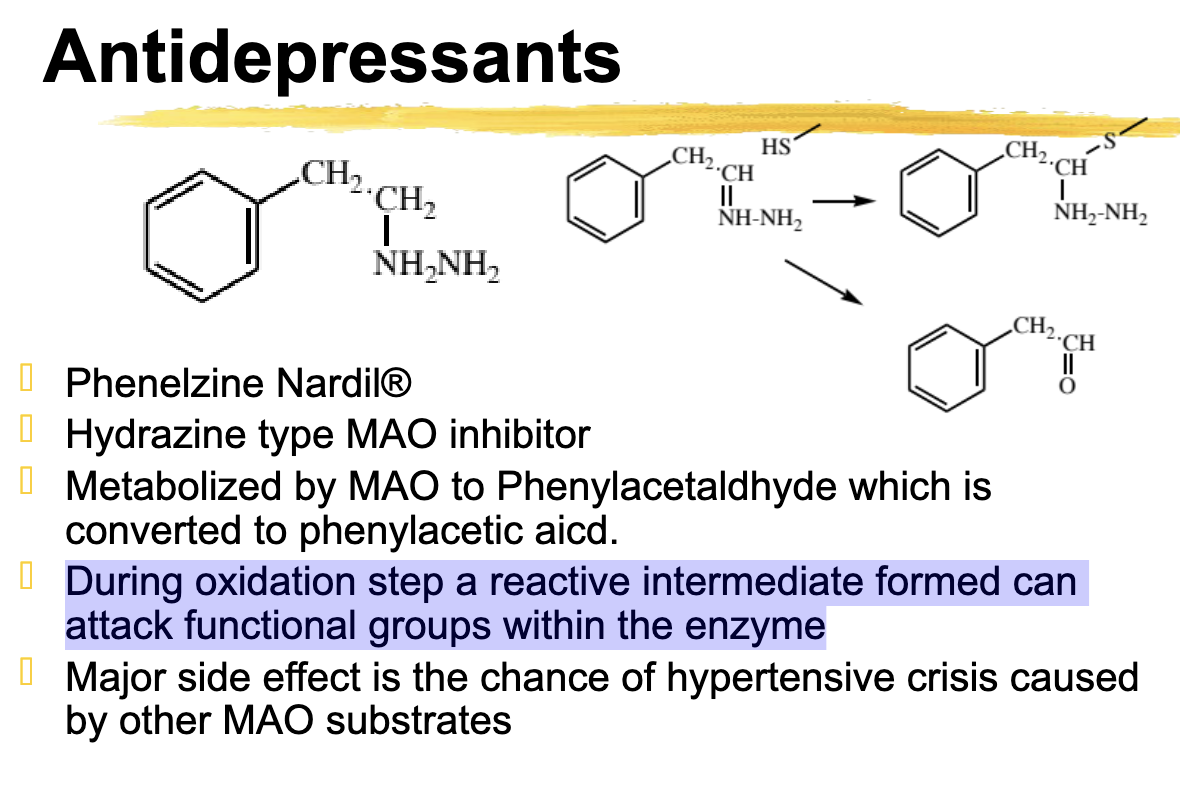
Phenelzine moa
Hydrazine type MAO inhibitor
non-selective for mao (a and B)
tranylcypromine moa
non-selective for MAO (a and B)
tranylcypromine parnate major side effect
chance of hypertensive crisis caused by other MAO Substrates
Selegiline moa
Selective MAO-B
Only in the brain not the periphery
Selegiline is available in
a once daily transdermal patch for depression
Phenelzine metabolized to
Metabolized by MAO to phenylacetaldehyde → Phenylacetic acid
what drug has an oxidation step that forms a reactive intermediate that can attack functional groups within the enzyme?
Phenelzine
Phenelzine is what type of inhibitor
hydrazine type MAO inhibitor
Phenelzine is converted to
phenylacetic acid
Tranylcypromine metabolized
Cyclopropane derivative once oxidized can react with group within MAO and inactivate
phenelzine major adr
hypertensive crisis caused by other MAO substrates
tranylcypromine major ADR
hypertensive crisis caused by other MAO substrates
Toxic effects for all MAOA inhibitors
Hypertensive crisis is the most serious
Avoid tyramine rich foods as they can increase blood pressure due to no presence of MAO
most dangerous foods are aged cheese and yeast products
Can interact with sympathomimetic amines in cold preparations like
ephedrine, phenylpropanolamine, pseudoephedrine, and phenylephrine