Lec 3 - Visualization of Cells and Tissues
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How is an image formed in light microscopy?
An image is formed by alteration of light waves to generate visible contrast (through a light medium).
How is an image formed in transmission electron microscopy?
Am image is formed by passing an accelerated electron beam through a specimen to a phosphor screen.
Denser samples absorb electrons from the beam, making them appear darker and provide contrast.
How is an image formed in scanning electron microscopy?
An image is formed by scanning a focused electron beam over specimens.
Electrons interact with atoms of the sample surface, generating a scatter that is used to generate a 3D image.
What are the three crucial methods that allow visibility of cells in light microscopy?
Contrast: creating differences in light intensity between specimen and background
Magnification: ability to produce an image larger in scale than actual size
Resolution: ability to distinguish detail
What is cell fixation? Why is it done? What are the three methods of doing this? How do they differ?
A cell sample is treated with agents that kill the cells and fix their proteins, lipids, and DNA in place.
This prevents degradation, provides a temporal snapshot, and allows the observation of specific proteins.
Alcohols and acetone permeates the cell membrane. Aldehydes preserve the membrane.
Why is permeability important in the fixation of cells?
Antibody tracking of particular proteins may be hindered if using a fixative that preserves cell membrane rigidity (aldehydes).
What is the process of the preparation of histological tissue samples?
A tissue is fixed, dehydrated, cleared, infiltrated, and embedded in resin, which is then cut into thin sections by a microtome to be mounted on slides.
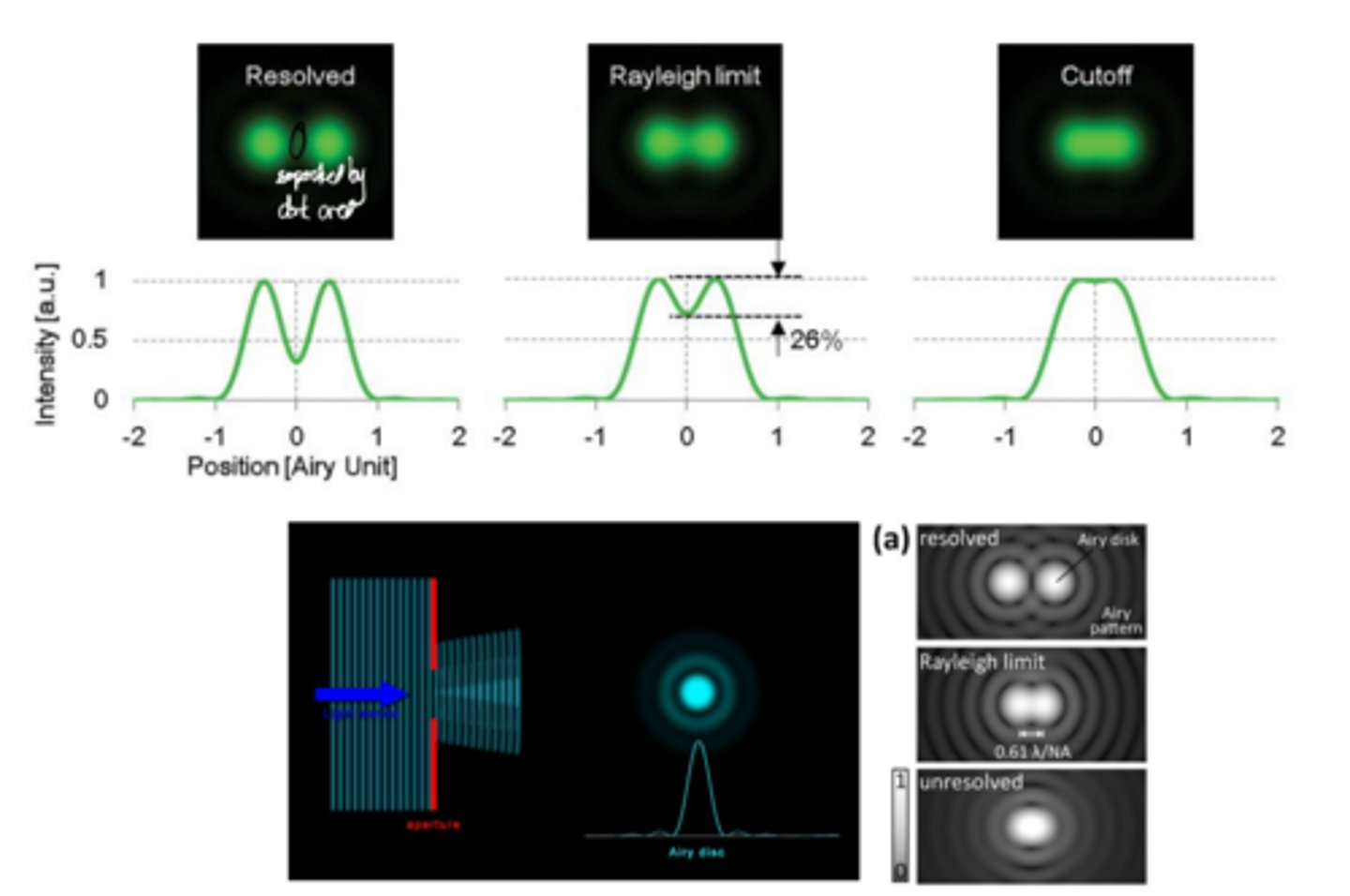
What is the relationship between wavelength and resolution?
As wavelength decreases, resolution increases, and as it increases, resolution decreases.
What is the Rayleigh Criterion?
Two objects can be resolved if the valley between the overlapping brightness maxima is reduced by >20% compared to the maxima.
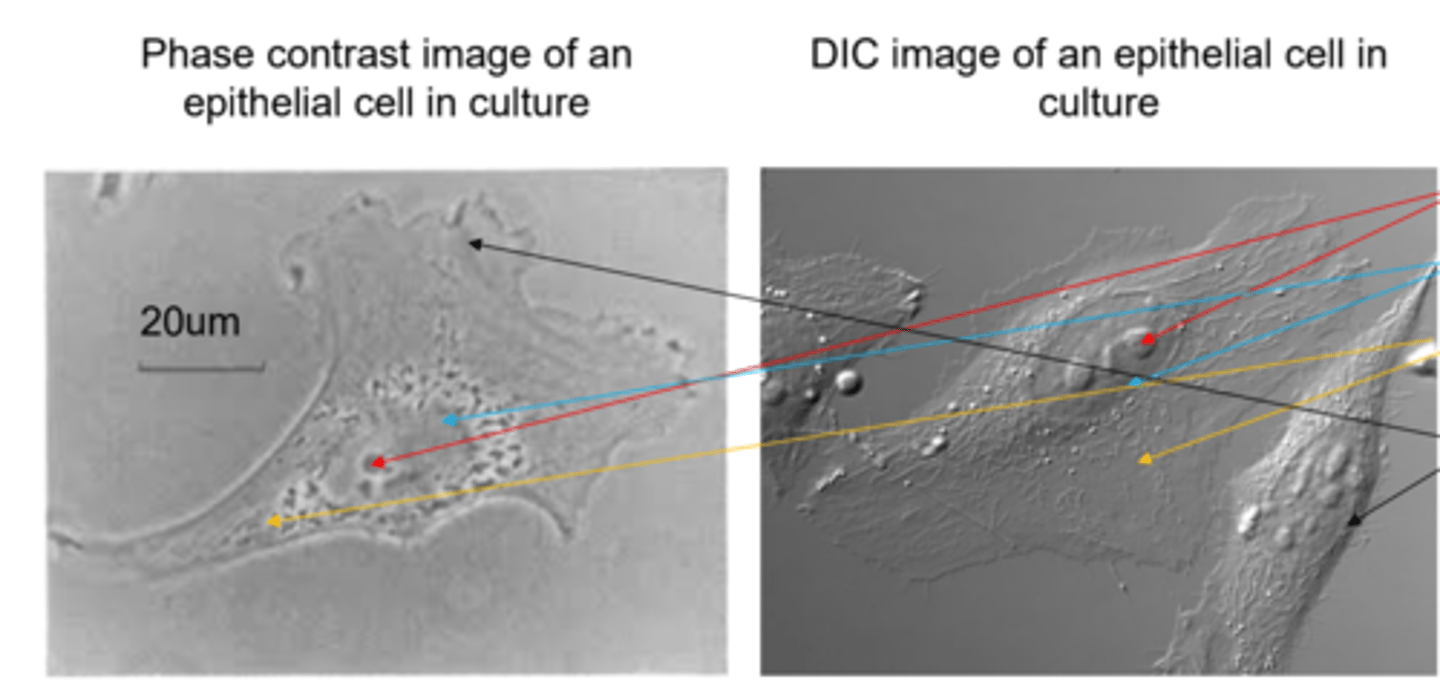
What are the two common microscope components that are used to generate contrast?
Phase optics, and differential interference contrast (DIC) optics
What is PAS staining?
PAS staining, or Periodic acid-Schiff staining, is a histological staining technique used to visualize carbohydrates, glycogen, mucosubstances, and other carbohydrate-rich macromolecules in tissue samples.
It colors than bright magenta or purplish-red.
What is oil red O staining?
Used to stain neutral lipids (triglycerides and cholesterol esters) and colors them red.
What is trichrome staining?
A histological staining technique used to differentiate muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nuclei.
What is the benefits of generating contrast with fluorescence?
Adds specificity in molecules, sensitivity to recognition, spatial, and temporal resolution.
What are the characteristics of samples used in viewing immunological reactants?
Immunofluorescence imaging uses antibodies to recognize proteins, thus requiring a fixed sample
What are GFPs? How are they used in imaging?
Green fluorescent protein can be fused to any protein of interest using recombinant DNA methods and can be expressed in cells and detected
How are phase contrast and DIC methods in light microscopy distinguished?
DIC generates a 3D appearing image; almost appearing metallic
What type of image can be created with transmission electron microscopy?
Generates a finely detailed 2D image, with denser objects appearing darker
Why is depth important to consider in imaging?
The different possible cross-sections of cell can alter the appearance of certain organelles and structures (such as nuclei and mitochondria)
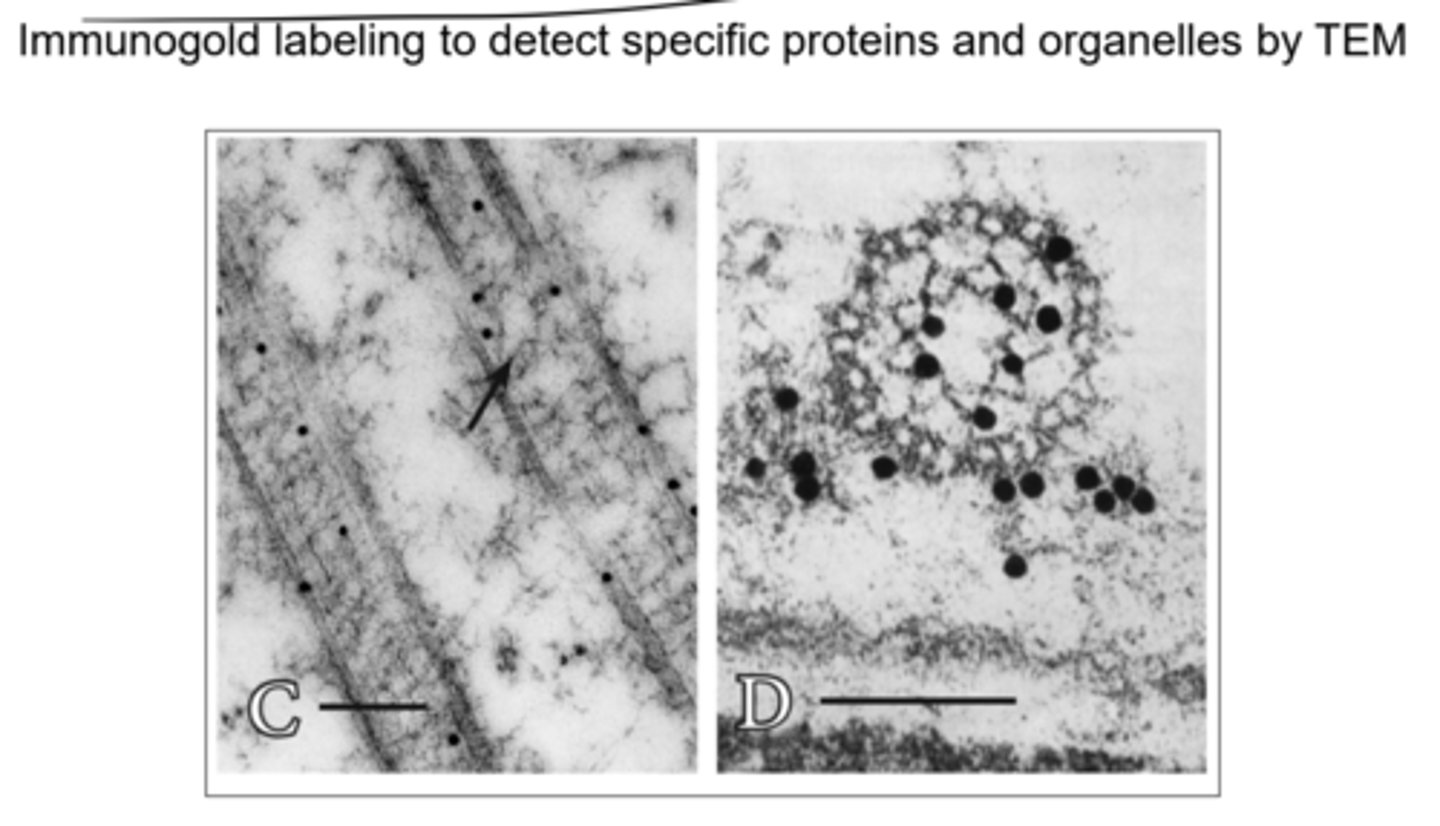
How is immunolabeling similar and different in TEM?
Immunogold, or heavy metal ions, are used to detect particular proteins and organelles
What is visible in scanning electron microscopy?
Reveals surface features of cells
What is visible in freeze fracture etching + scanning electron microscopy?
Allows the 3D view of the interior of cells
Why is electron microscopy have better resolution than light microscopy?
Electrons have a shorter wavelength than light