anatomy unit 4 skeletal system notes
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
bone
strong but not very flexible
Protect
Assisting in the movement of the body
Providing a framework and shape
Storing minerals
Producing red and white blood cells.
Cartilage
weaker but very flexible
Reducing friction at the joints
Support
Acting as shock absorbers
Maintaining the shape & flexibility of ears and nose
Articulating Cartilage
- on ends of the bone to protect bone from grinding together.
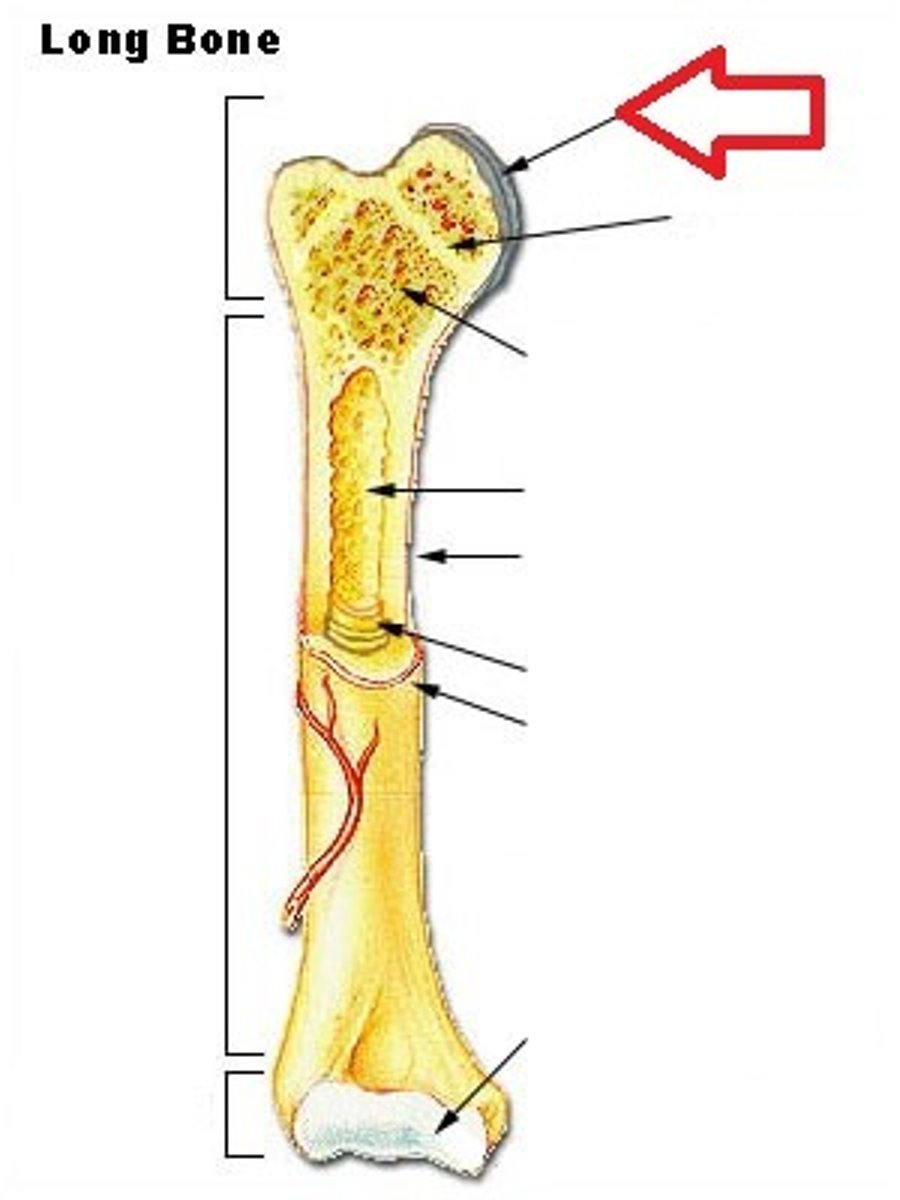
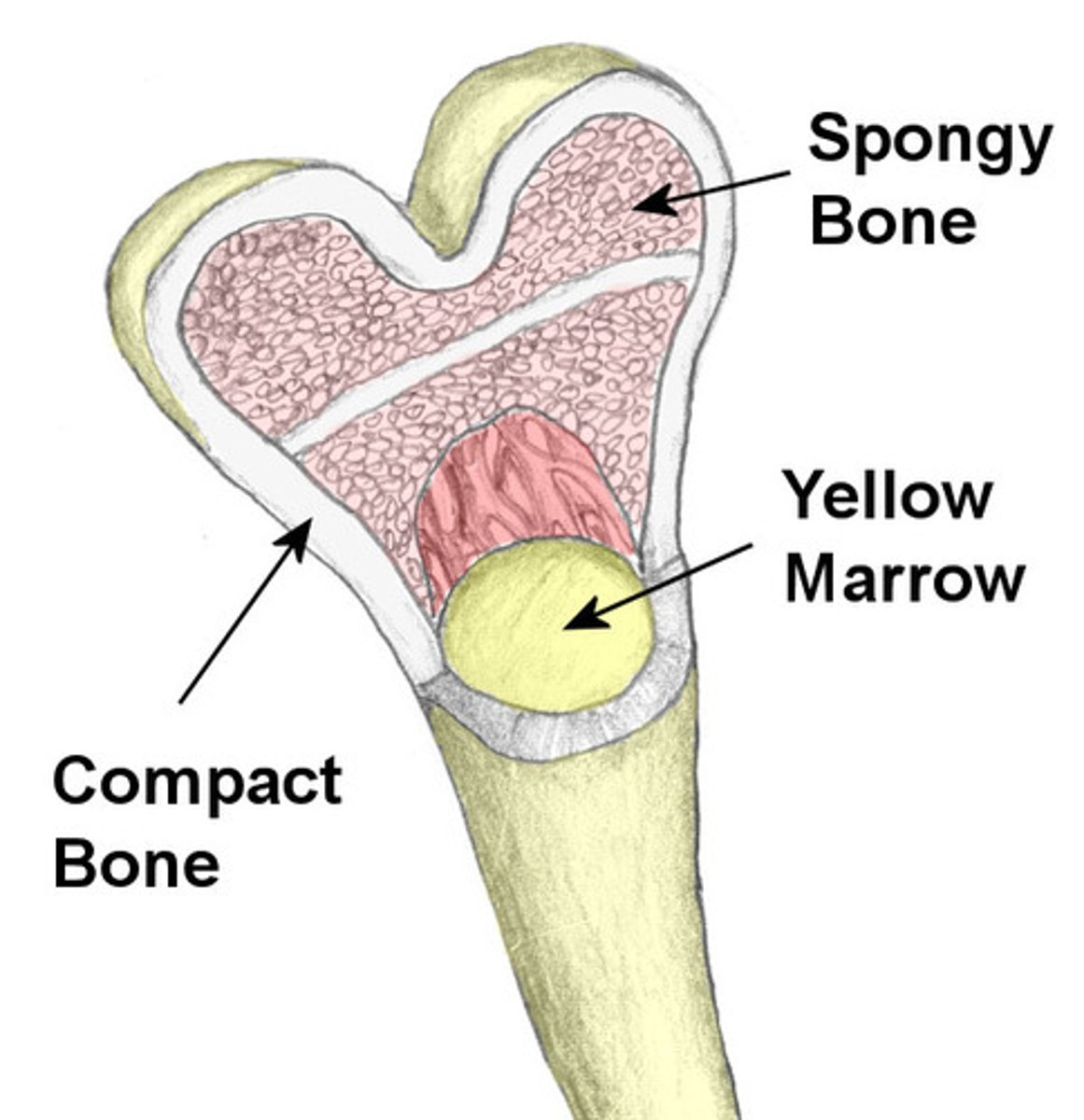
Spongy Bone
- lighter calcified webbing on inside of bones at either end
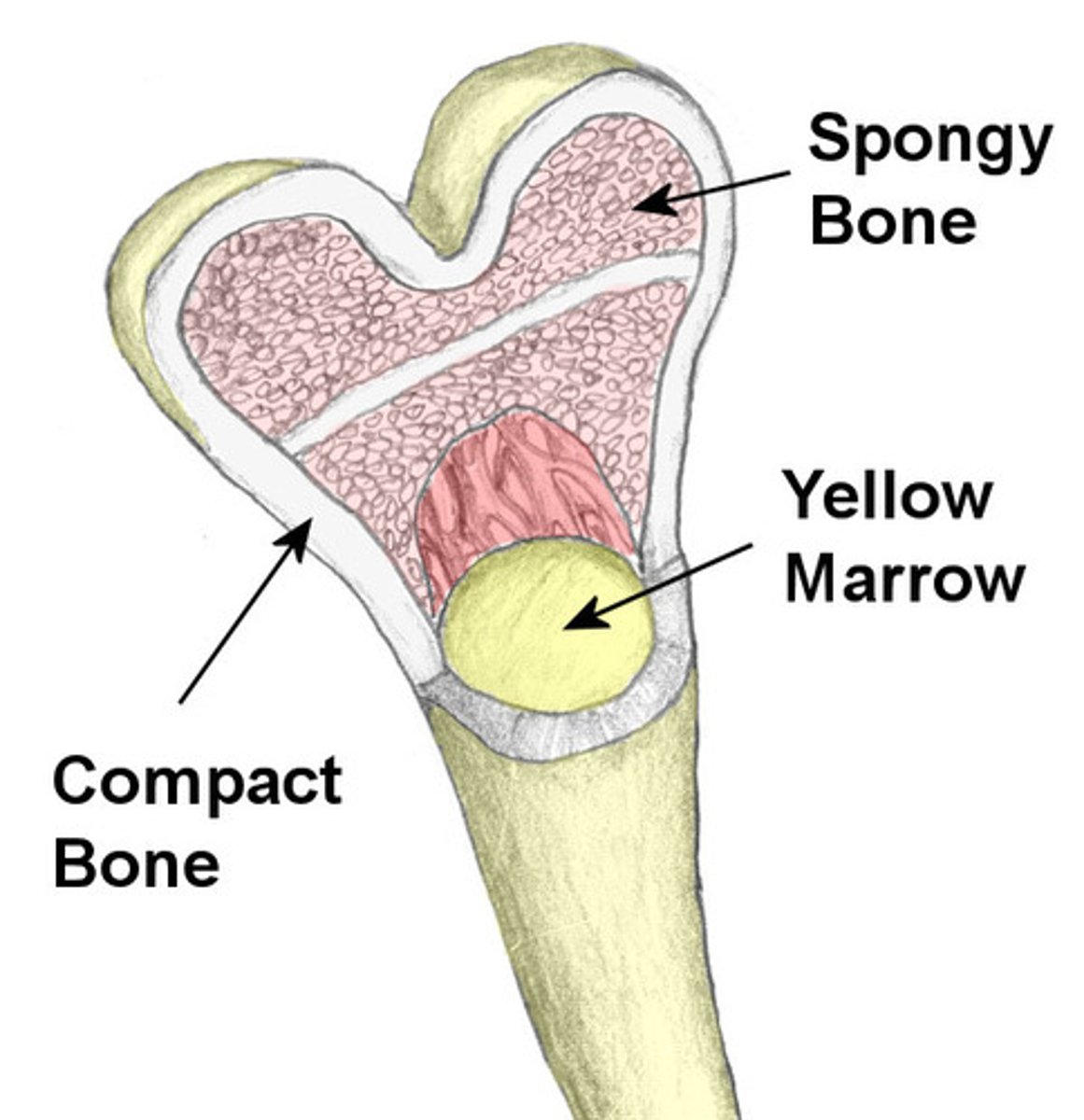
Compact Bone
hard and dense with a large calcified matrix
Periosteum
protective outer coating around the bone.
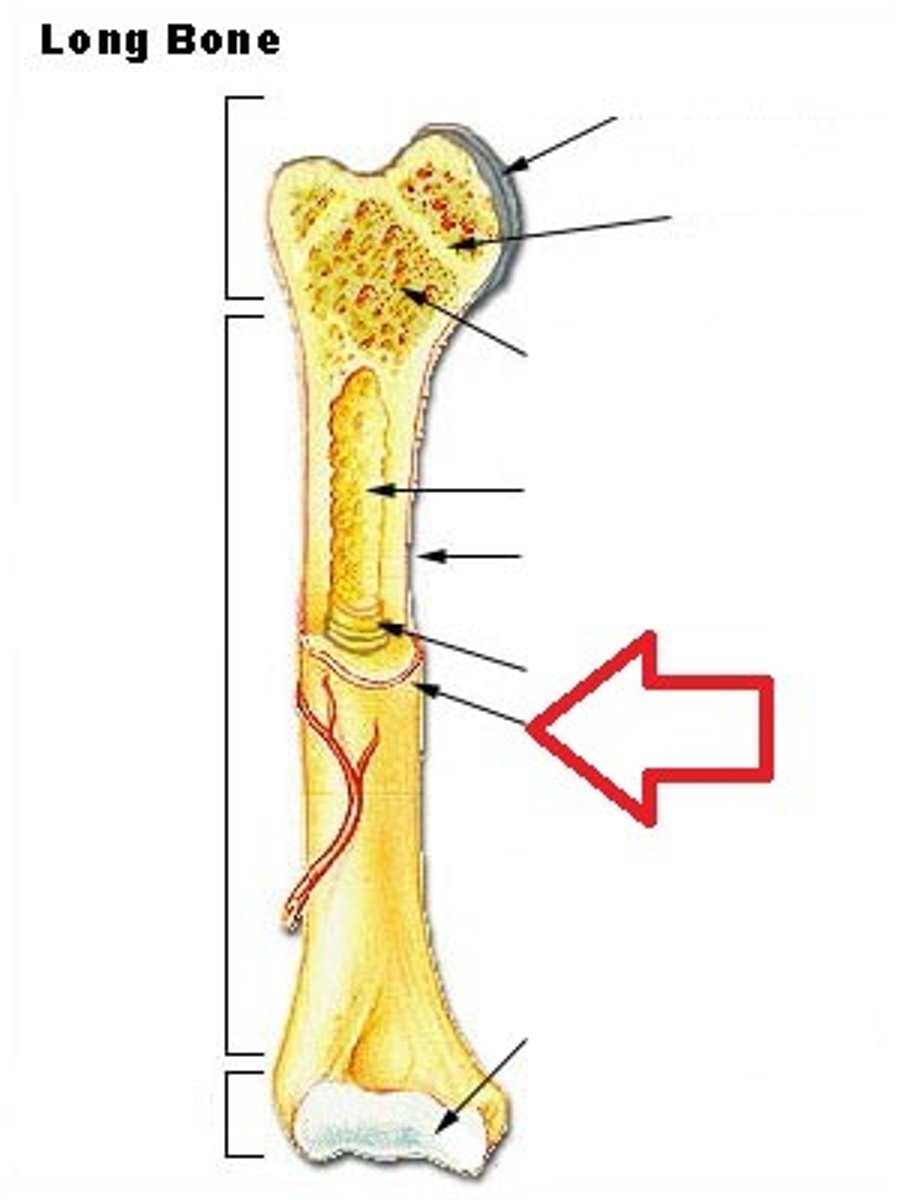
Endosteum
protective coating lines the inside of the medullary cavity.
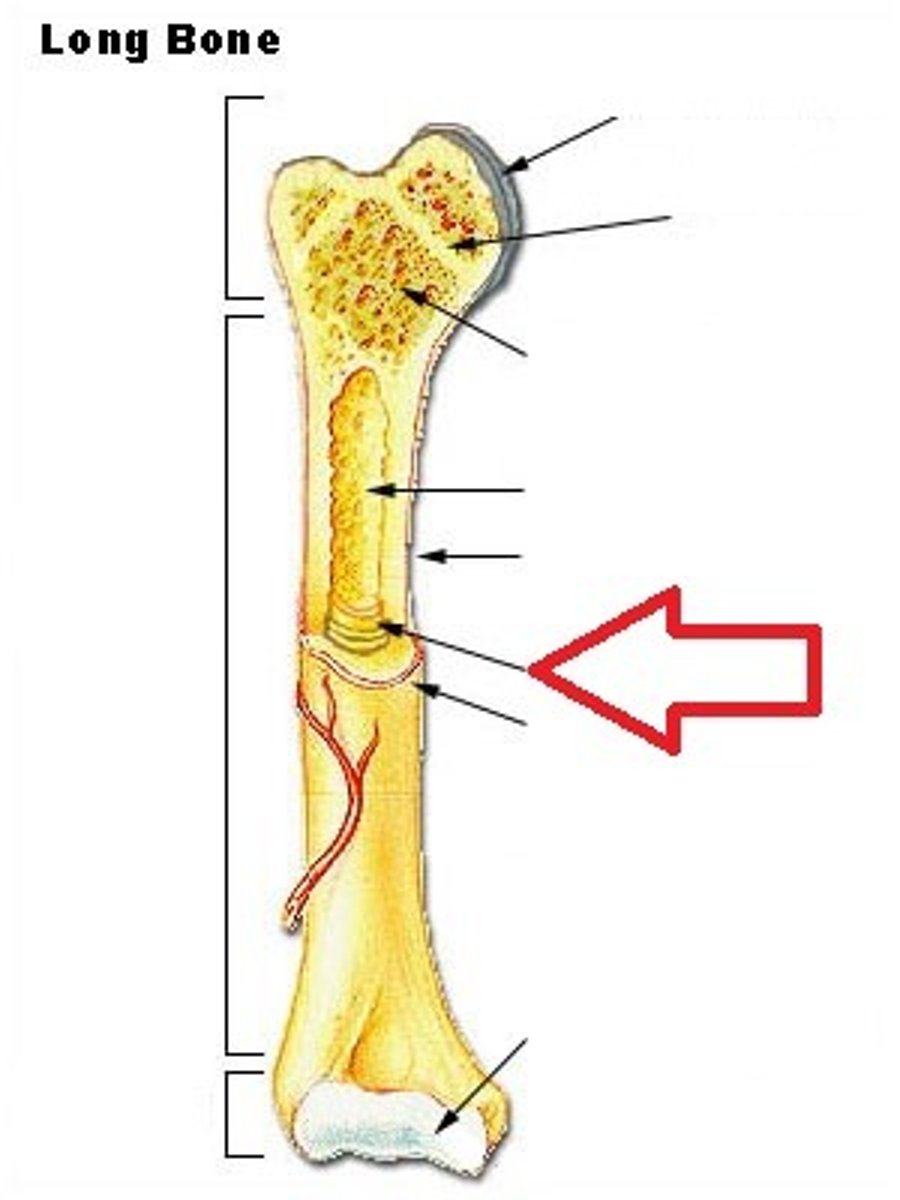
Medullary Cavity
a cavity inside the body of the bone.
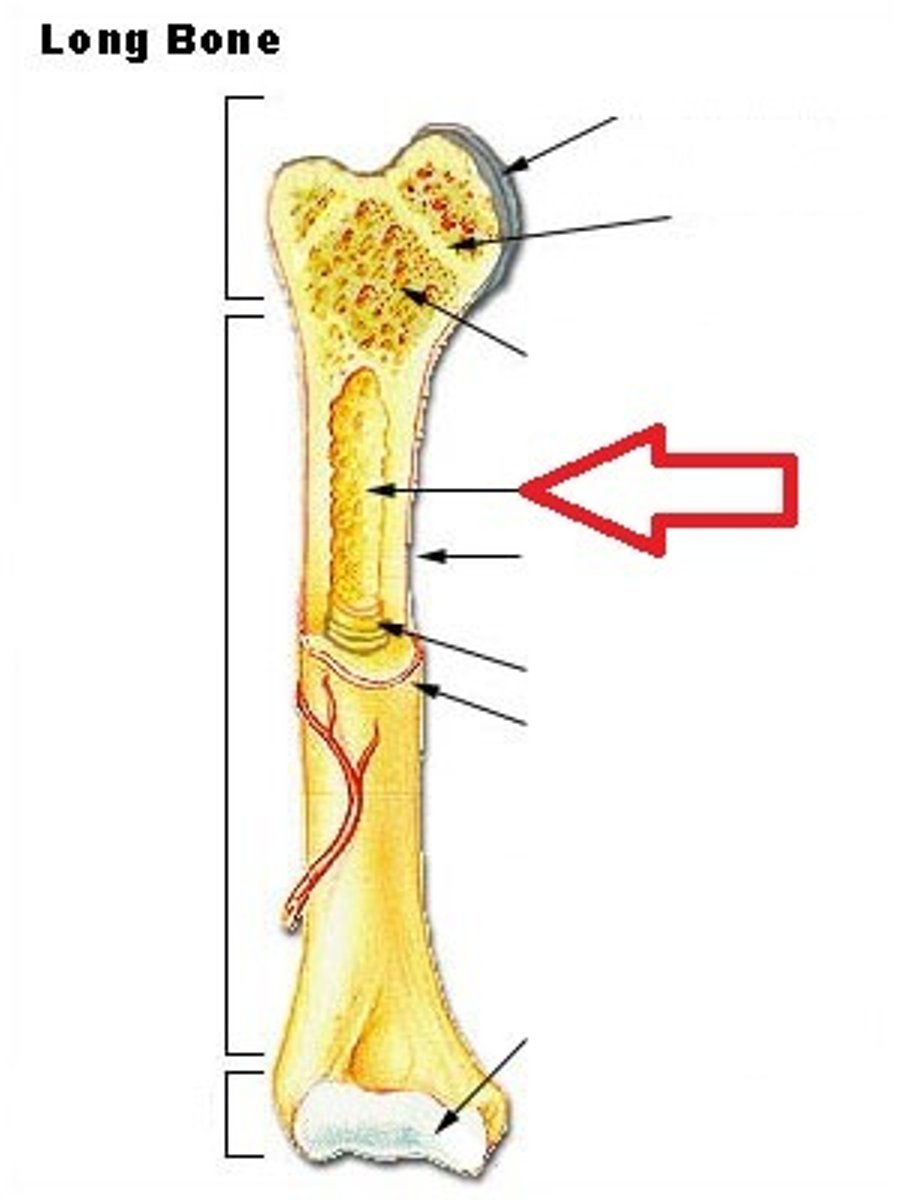
Bone Marrow
sits inside the Medullary cavity. There are two types.
Epiphyseal Line
a line left over from a growth plate/ epiphyseal plate
Red Marrow
creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
At birth, all bone marrow is red. With age, more and more of it is converted to the yellow type; only around half of adult bone marrow is red.
Yellow Marrow
mainly made of fat (adipose) cells.
Osteocytes
mature bone cells, are found in tiny cavities within the bone matrix.
Osteoblasts
bone-forming cells
Osteoclasts
bone-destroying cells
Lacunae
hardened calcified bone matrix (rings) made by the osteocytes.
Haversian system
matrix plus central (Haversian) canals, brings blood vessels and nerves to all areas of the bone.
Intramembranous and Endochondral
Two different types of ossification (bone formation)
Intramembranous ossification
Formation of flat bones; the bone is formed from connective tissue rather than from cartilage.
Endochondral ossification
occurs in long bones and most of the rest of the bones in the body; it involves an initial hyaline cartilage model that continues to grow.
skeletal system functions
Support
Movement
Protection
Blood cell production
Calcium storage and endocrine regulation
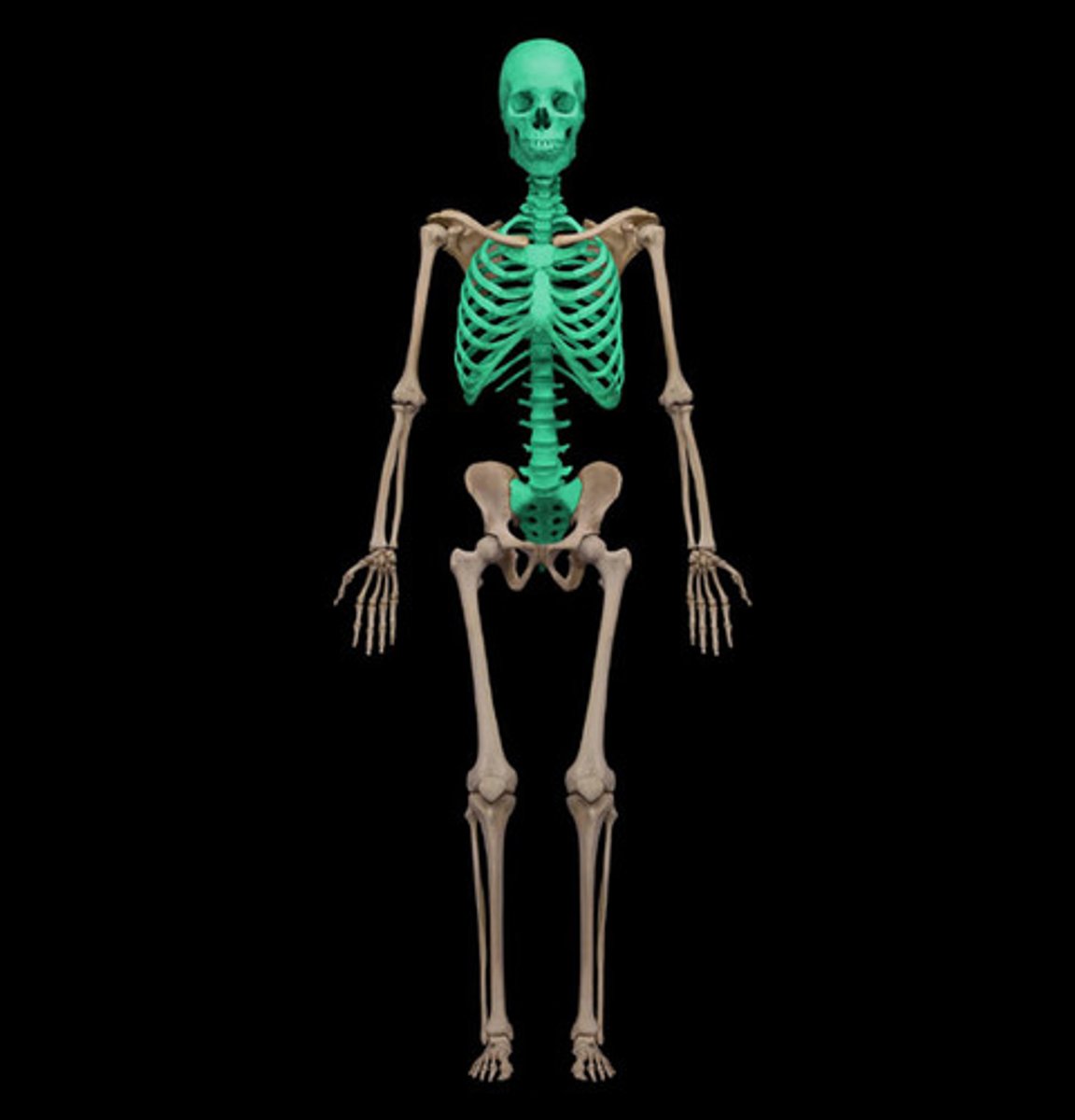
Axial Skeleton
consists of just the bones of the skull, ribs, and vertebrae
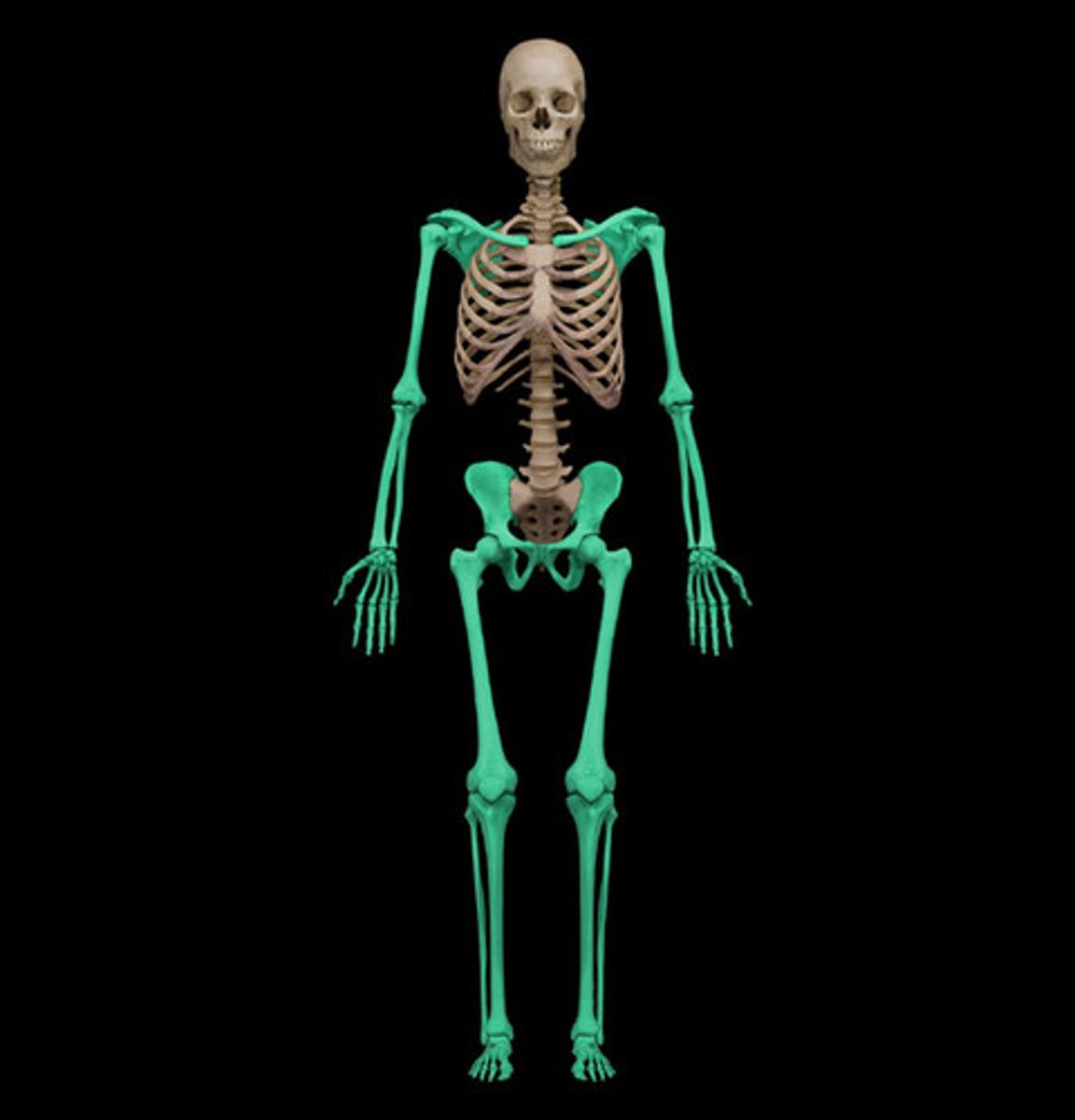
Appendicular Skeleton
consists of the bones from the arms and legs, including the shoulders and hips.
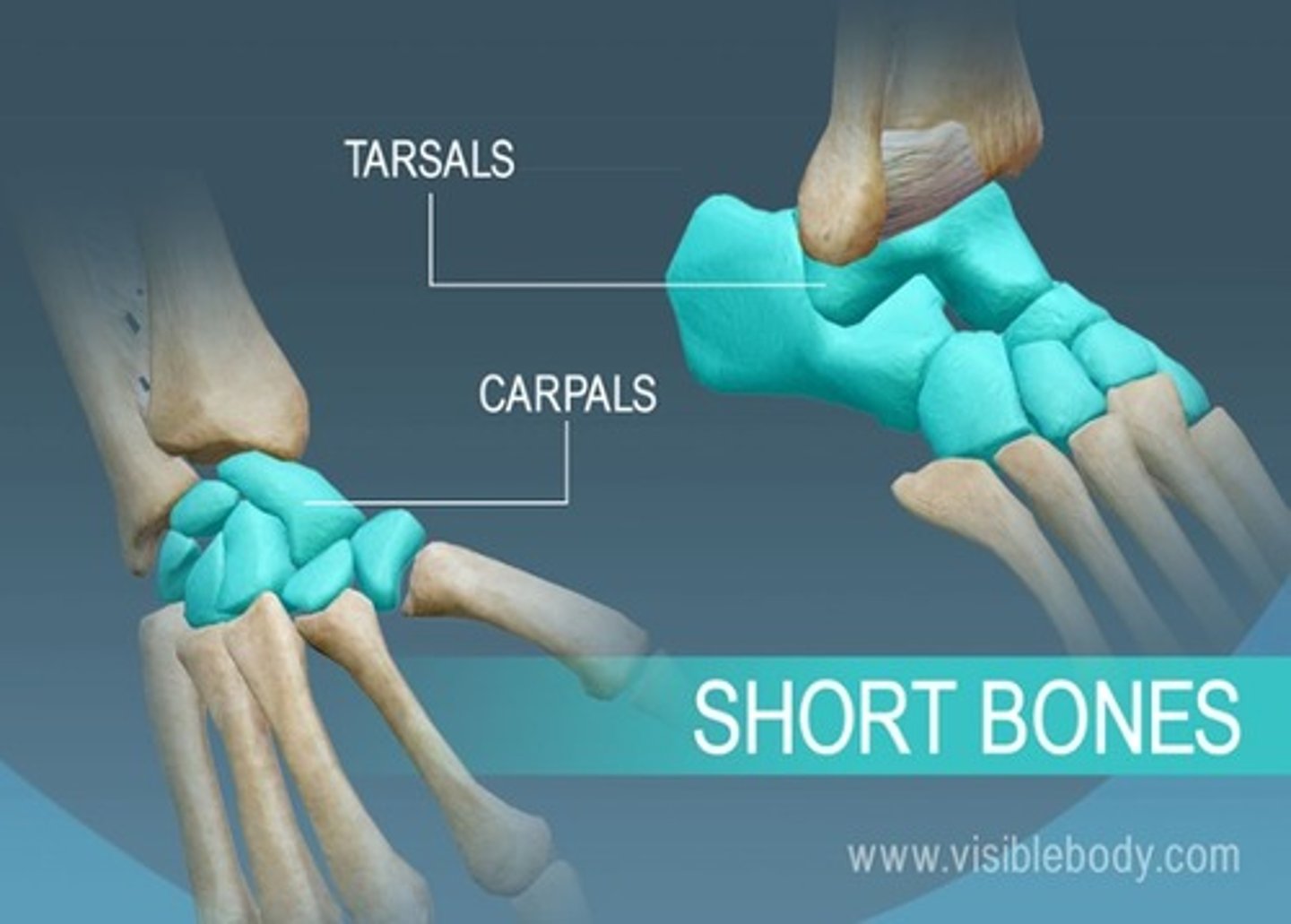
Short bone
bones that are as wide as they are long.
Examples: tarsals and carpals.
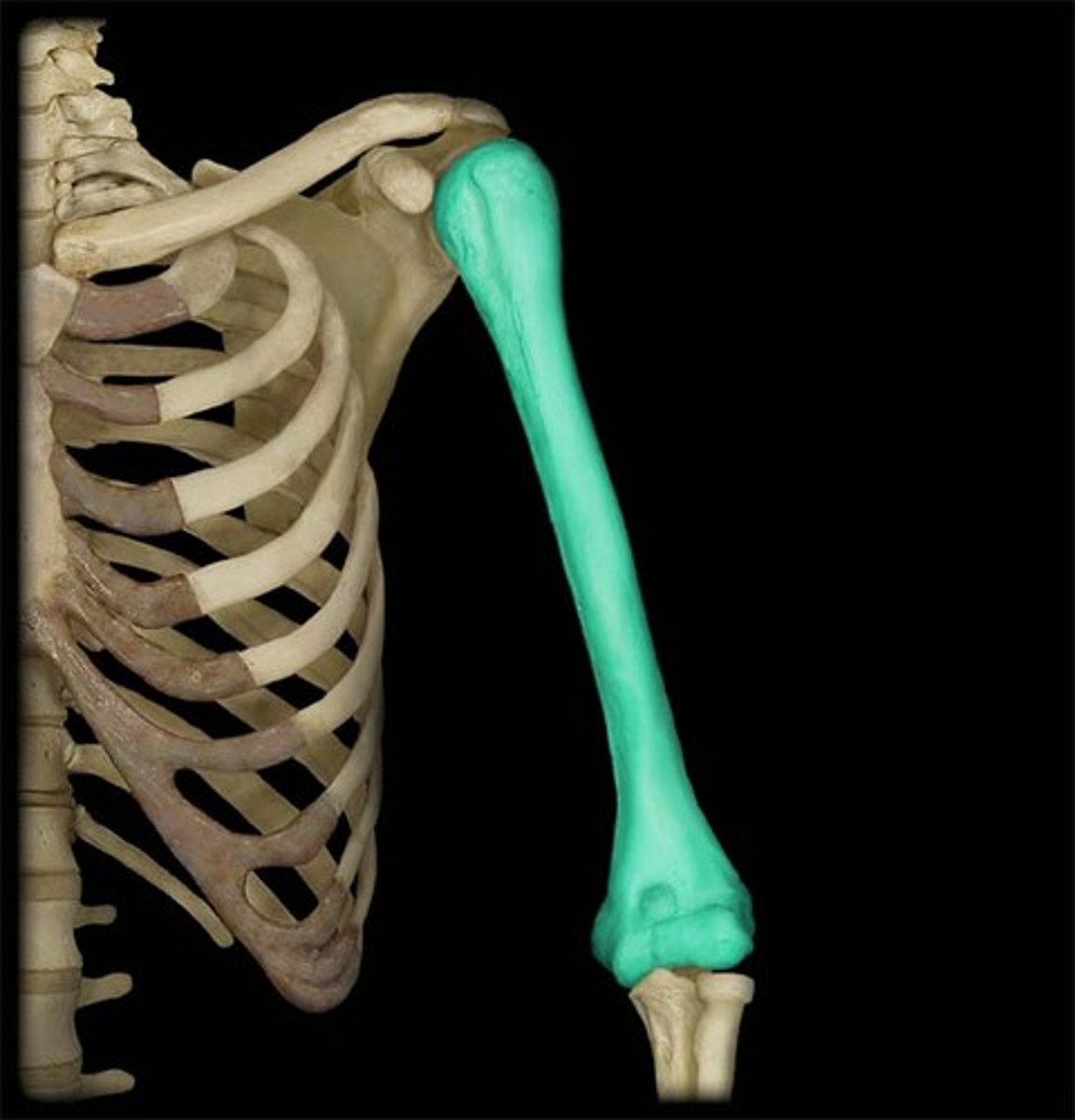
Long bone
bones that are longer than they are wide.
Examples: Femur, fibula, tibia
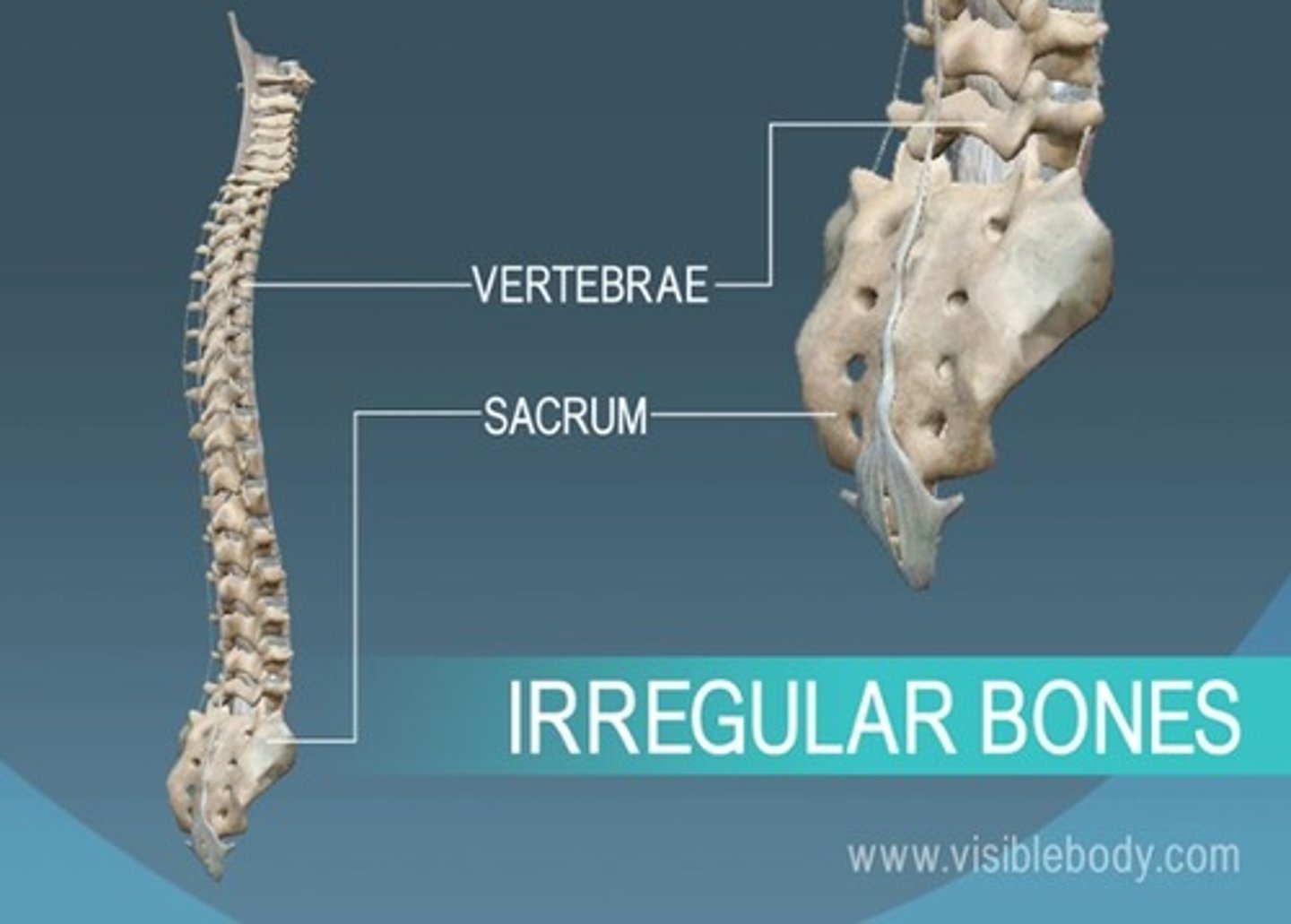
Irregular bone
cannot be grouped as any other type of bone.
Examples: vertebræ, sacrum, coccyx, temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible, palatine, inferior nasal concha, and hyoid.
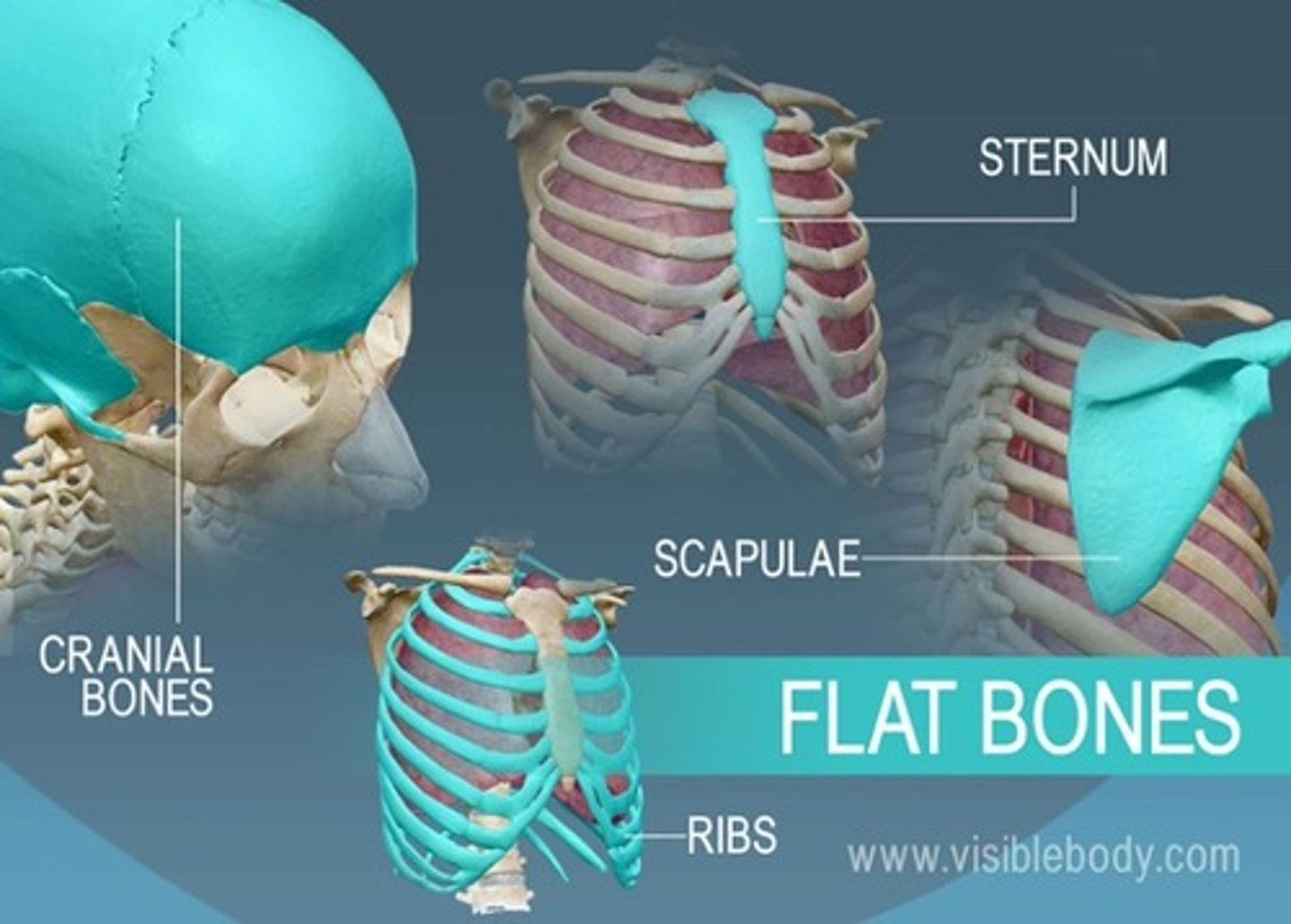
Flat Bones
function is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment.
Examples: occipital, parietal, frontal, nasal, lacrimal, vomer, scapula, hip bone, sternum, and ribs.
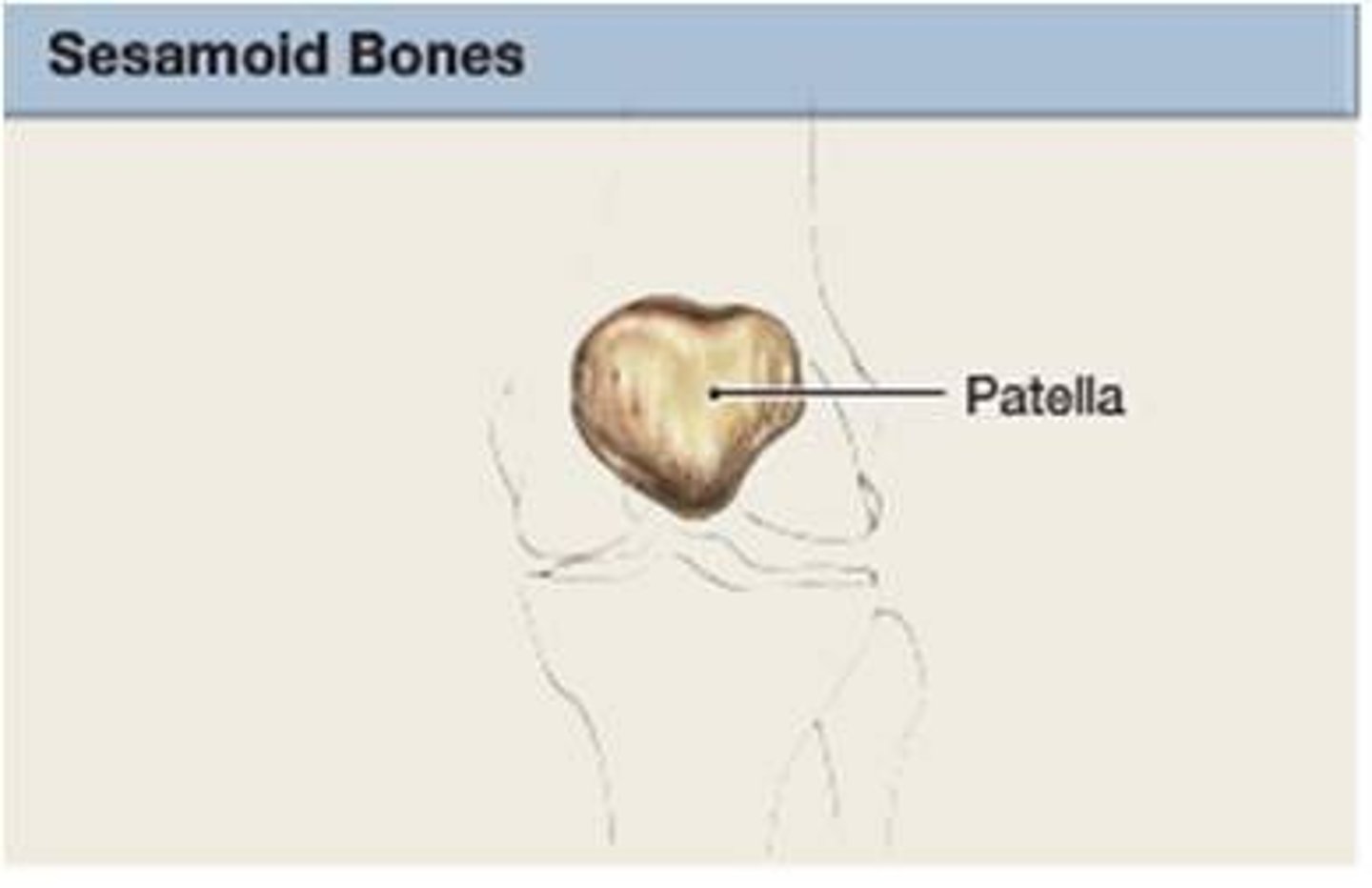
Sesamoid
found in locations where a tendon passes over a joint, such as the hand, knee, and foot.
body, head, neck, process, spine, condyle, fissure, fossa, foramen
types of bone markings
Body
the main portion of the bone
Head
A large rounded projection that forms part of a joint at one end.
Neck
- located at the base of the "head" of the bone.
Process
raised area or projection
Spine
Similar to a crest but raised higher; a sharp, pointed, slender projection.
Condyle
Rounded bump or large rounded prominence.
Fissure
Long, crack-line hole for blood vessels and nerves
Fossa
a shallow depression
Foramen
large hole through a bone
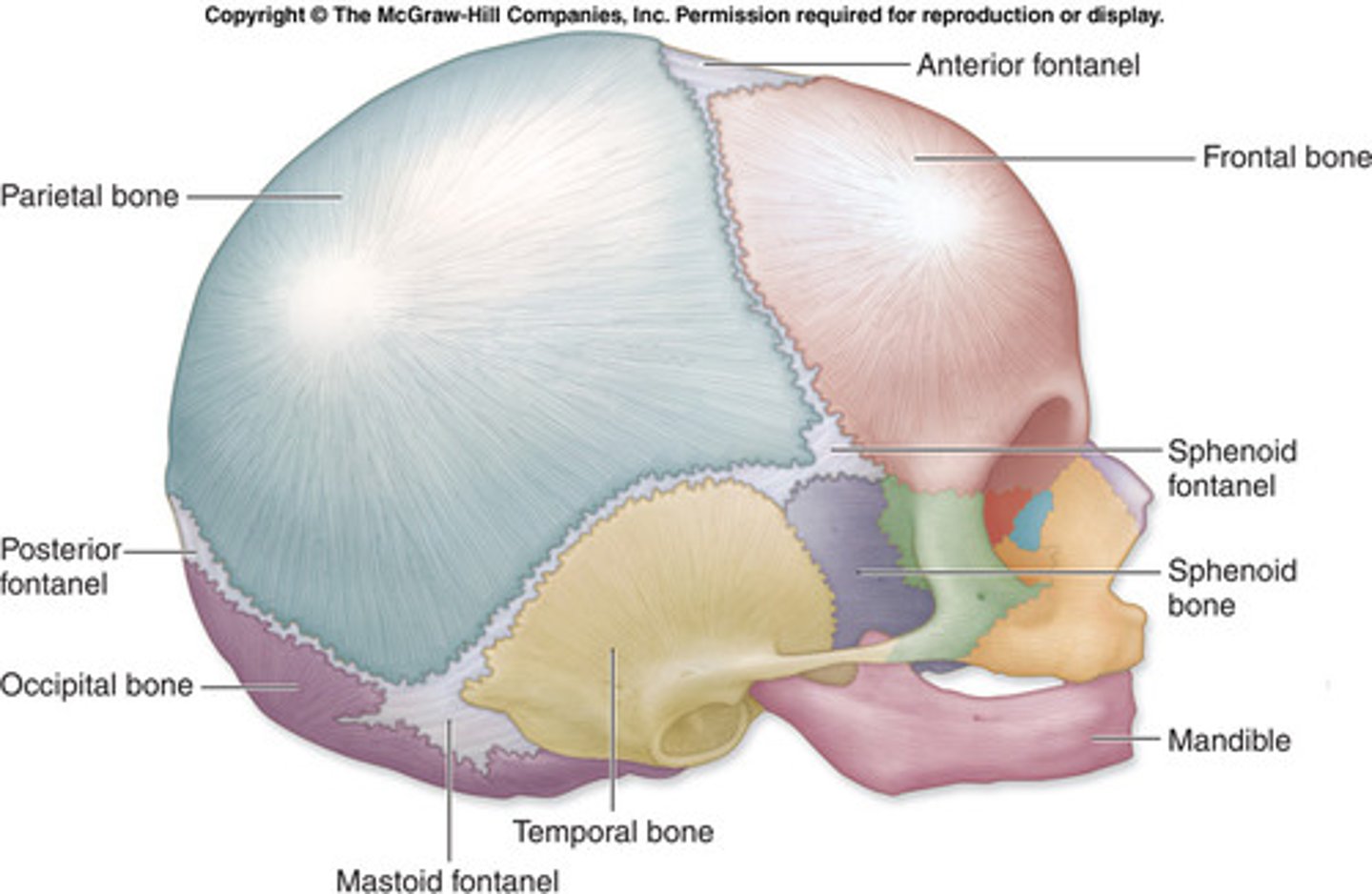
adult vs baby skull
baby skull: more elongated, larger orbits relative to size of skull, very large sutures, no teeth
Fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
main types of joints
Fibrous Joints
- the bones are united by fibrous tissue.
Cartilaginous Joints
the bone ends are connected by cartilage.
Synovial Joints
the articulating bone ends are separated by a joint cavity containing synovial fluid.
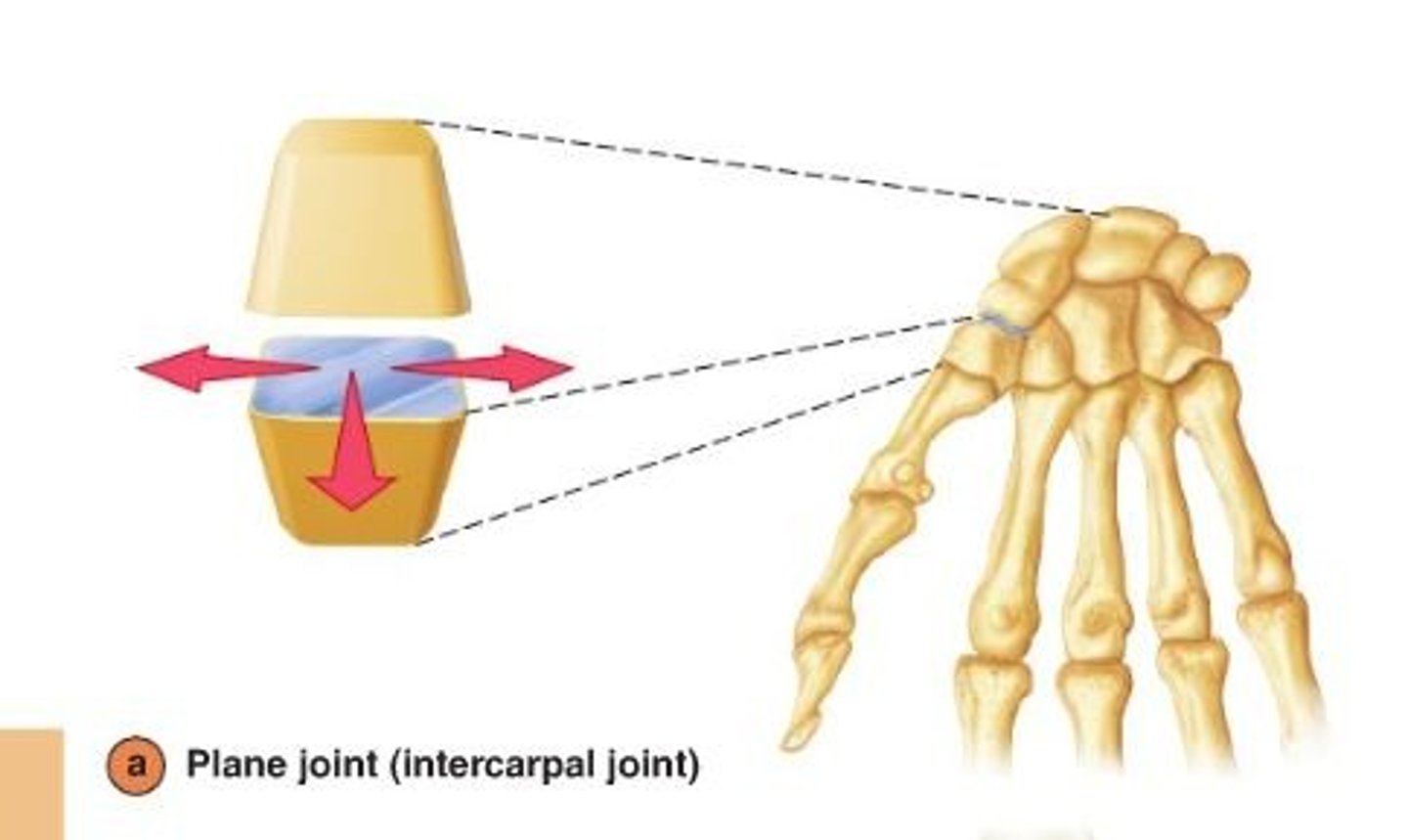
Plane Joint
in between the carpals of your wrist and the tarsals of ankles -- Glide across one another, provides a little bit of flexibility.
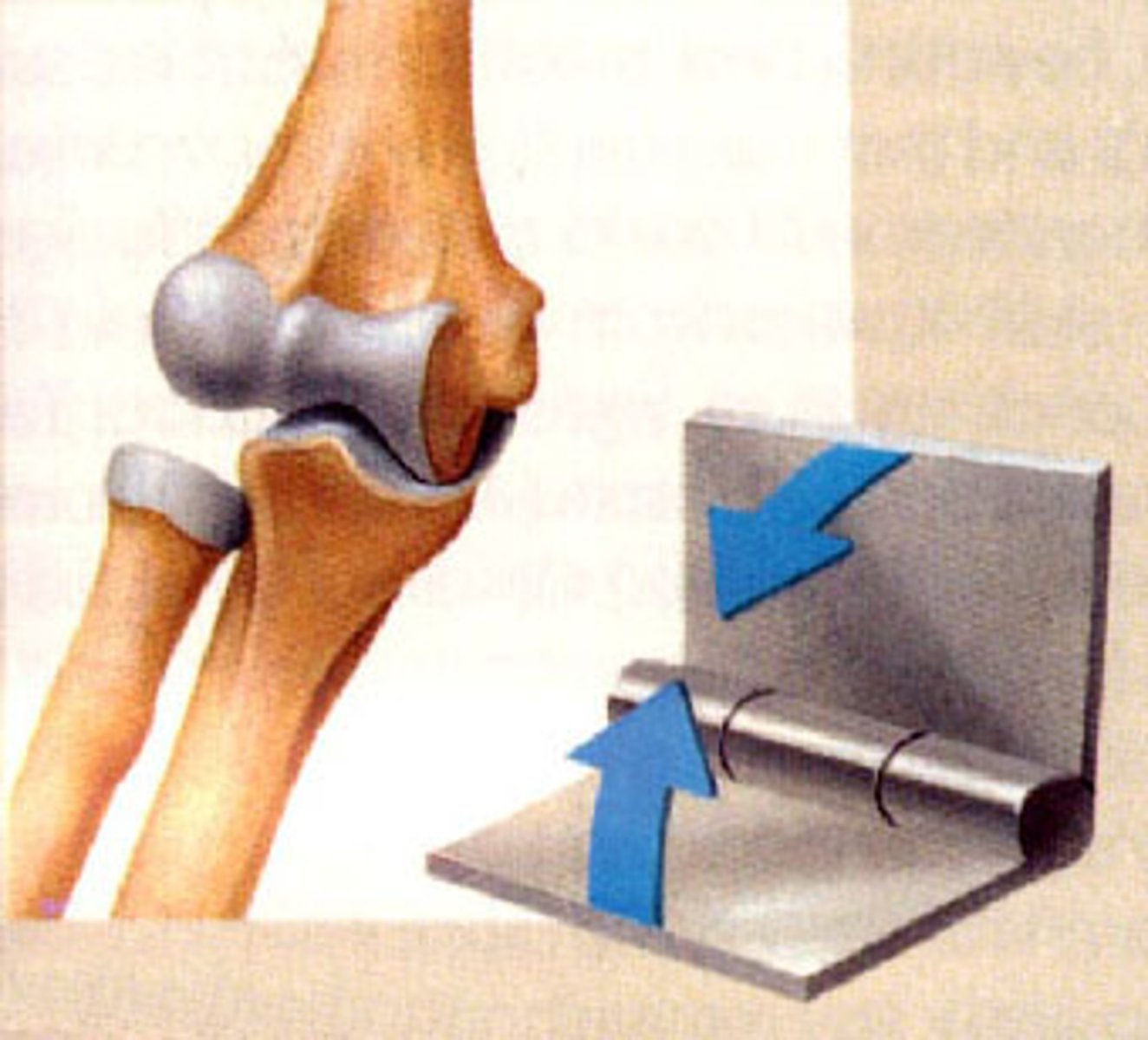
Hinge Joint
elbow (ulna and humerus), knee (tibia and the femur), ankle(tibia and talus)-- Bend/straighten a limb.
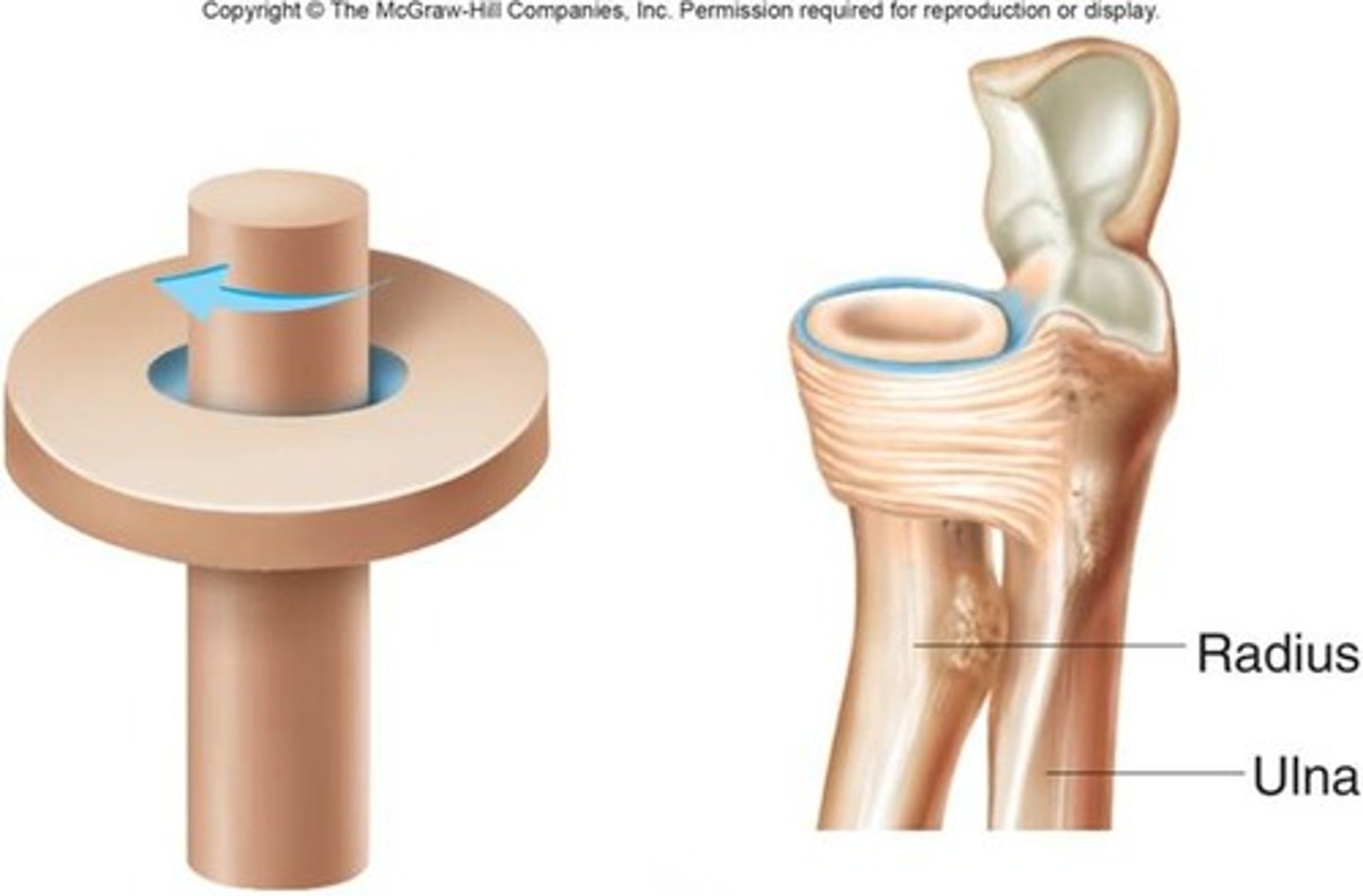
Pivot Joint
Elbow (radius and humerus), Neck (Axis(C2) and Atlas(C1)), Ankle (Fibula and Talus) -- Twist
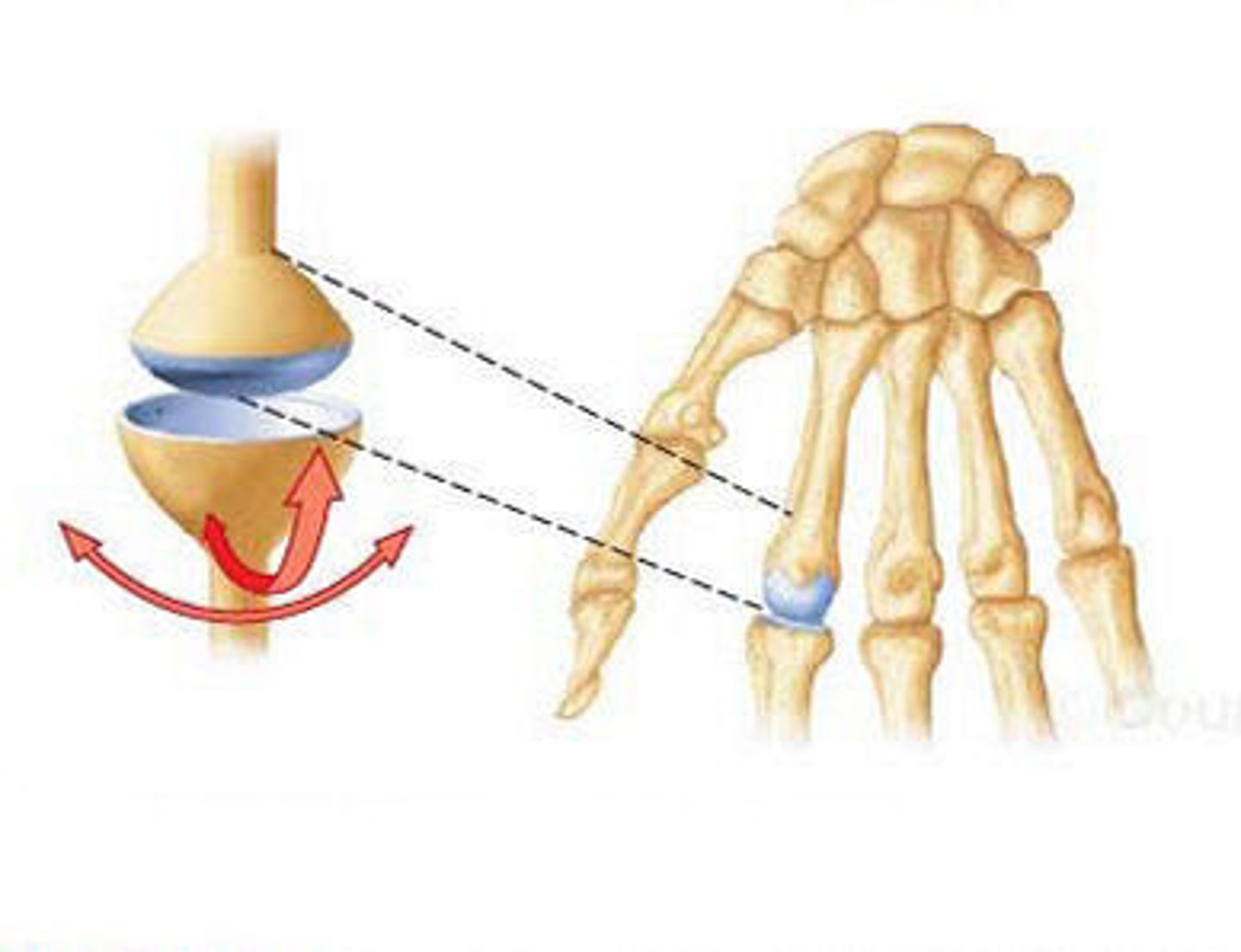
Condyloid Joint-
Fingers (phalanges and metacarpals) and toes (phalanges and metatarsals) ---
Modified ball-in-socket (limited to 2 planes)
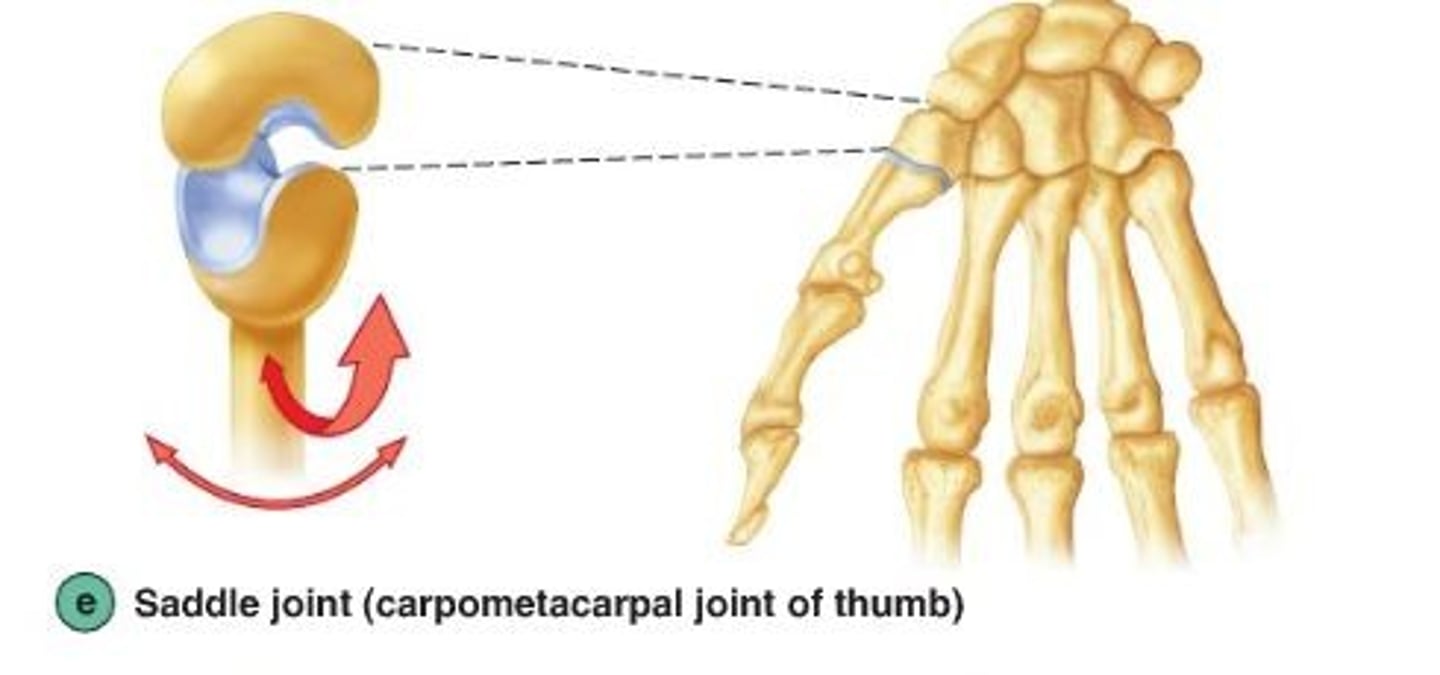
Saddle joint
Thumb (metacarpal and the carpal)-- rocking back-and-forth in two different directions.
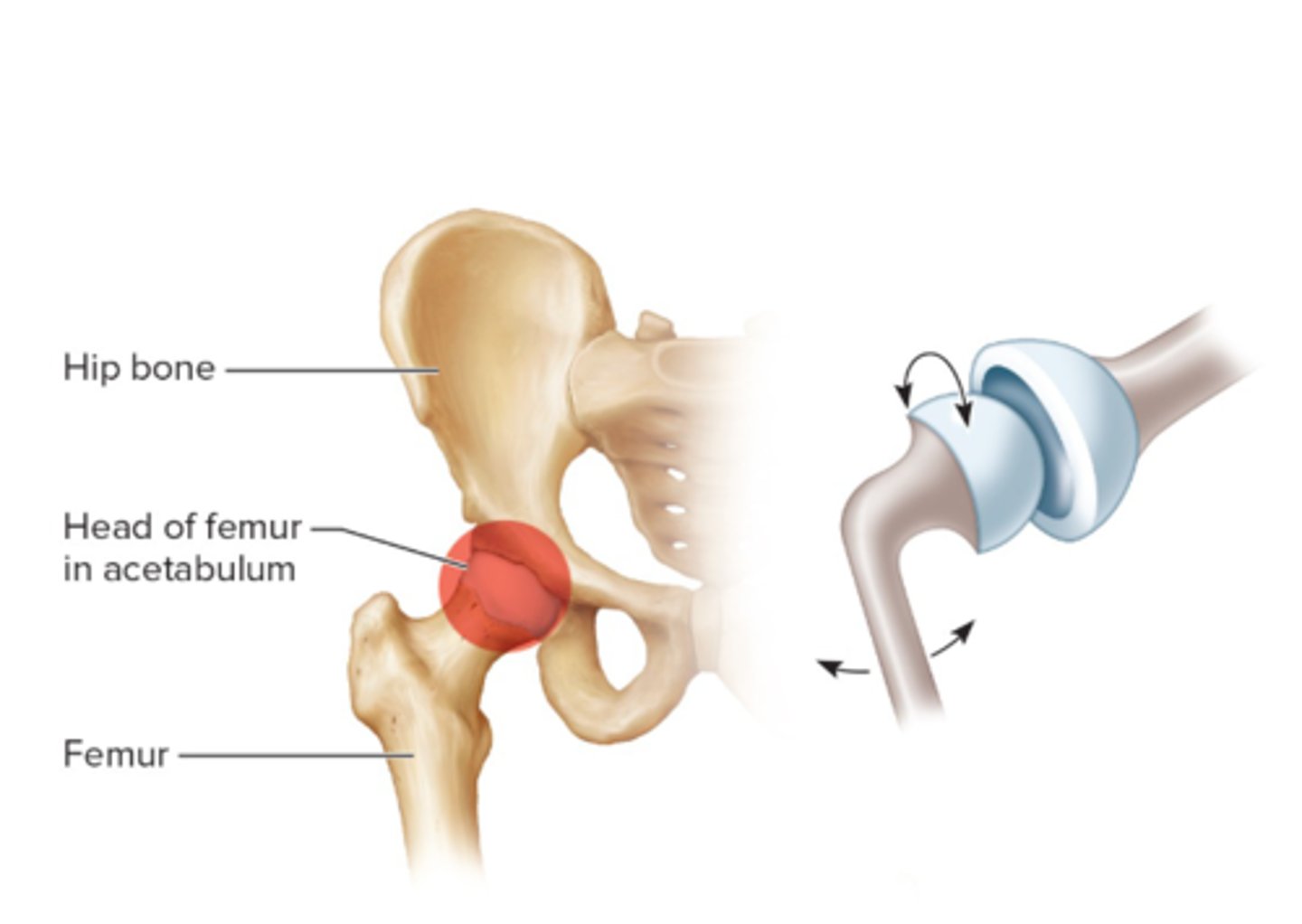
Ball-in-socket joint
Shoulder (Scapula and humerus) and the hip (femur and hip bone)--
greatest amount of movement and flexibility, movement in 3 planes.
Oblique Fracture
an oblique fracture is generally caused by a slanted blow to the bone. Most frequently found in the long bones of the arm and leg.
Spiral Fracture (Torsion Fracture)
Tension is exerted upon one part of the bone, while compressive forces are exerted upon the other. When these forces have exceeded the limit tolerable by the bone, fracture occurs.
Transverse Fracture-
A transverse fracture, which is broken straight across the bone, is the result of a sharp, direct blow or may be a stress fracture caused, for example, by prolonged running.
Complex/Comminuted Fracture
a closed fracture in which the soft tissue surrounding the bone is severely damaged. Several bone fragments.
Displaced Fracture
fracture in which the two ends of the broken bone are separated from one another. (Any type of fracture can also be displaced.)
Open (Compound) Fracture
An open fracture is a broken bone that penetrates the skin. Open fractures are typically caused by high-energy injuries such as car crashes, falls, or sports injuries.
Reactive Phase , reparative phase, remodeling phase
Phases of healing
Reactive Phase
Fracture and inflammatory phase
Hematoma formation
Reparative Phase
Cartilage Callus formation
Bony callus of spongy bone
Remodeling Phase
Remodeling to original bone shape