ATI 2023 Maternal Newborn Proctored Exam
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
FHR can be heard by Doppler at:
10-12 weeks GA
Between 18 and 30 weeks the fundal height should measure what?
It should equal the week of gestation
MSAFP screening is done:
15-22 weeks of gestation
maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) screen. It's usually as part of a set of tests, which screen for genetic problems, called the quad screen.
AFP is a substance made in the liver of an unborn baby (fetus).
Smoking tobacco during pregnancy is associated with :
Low Birth Weight
Pregnant mothers should consume how much water each day?
2 to 3 Liters of water from food and beverage sources.
Regarding kick counts, what are signs that a woman needs further evaluation?
Fetal movements of less than 3 in one hour
No fetal movement for 12 hours
The recommended weight gain during pregnancy is usually:
25-35lbs
3-4 lb in first trimester
1 lb per week in the last two trimesters
Foods high in folic acid are:
Leafy vegetables
Dried peas
Dried beans
Seeds
Orange juice

It is recommended that _____ mcg of folic acid be taken during pregnancy.
600
It is recommended that clients who are lactating consume ____ mcg of folic acid.
500
What vitamin aids in the absorption of Iron?
Vitamin C
The clients bladder needs to be _____ before an ultrasound.
Full
biophysical profile (BPP) normal score is
A biophysical profile (BPP) test measures the health of your baby (fetus) during pregnancy.
8-10
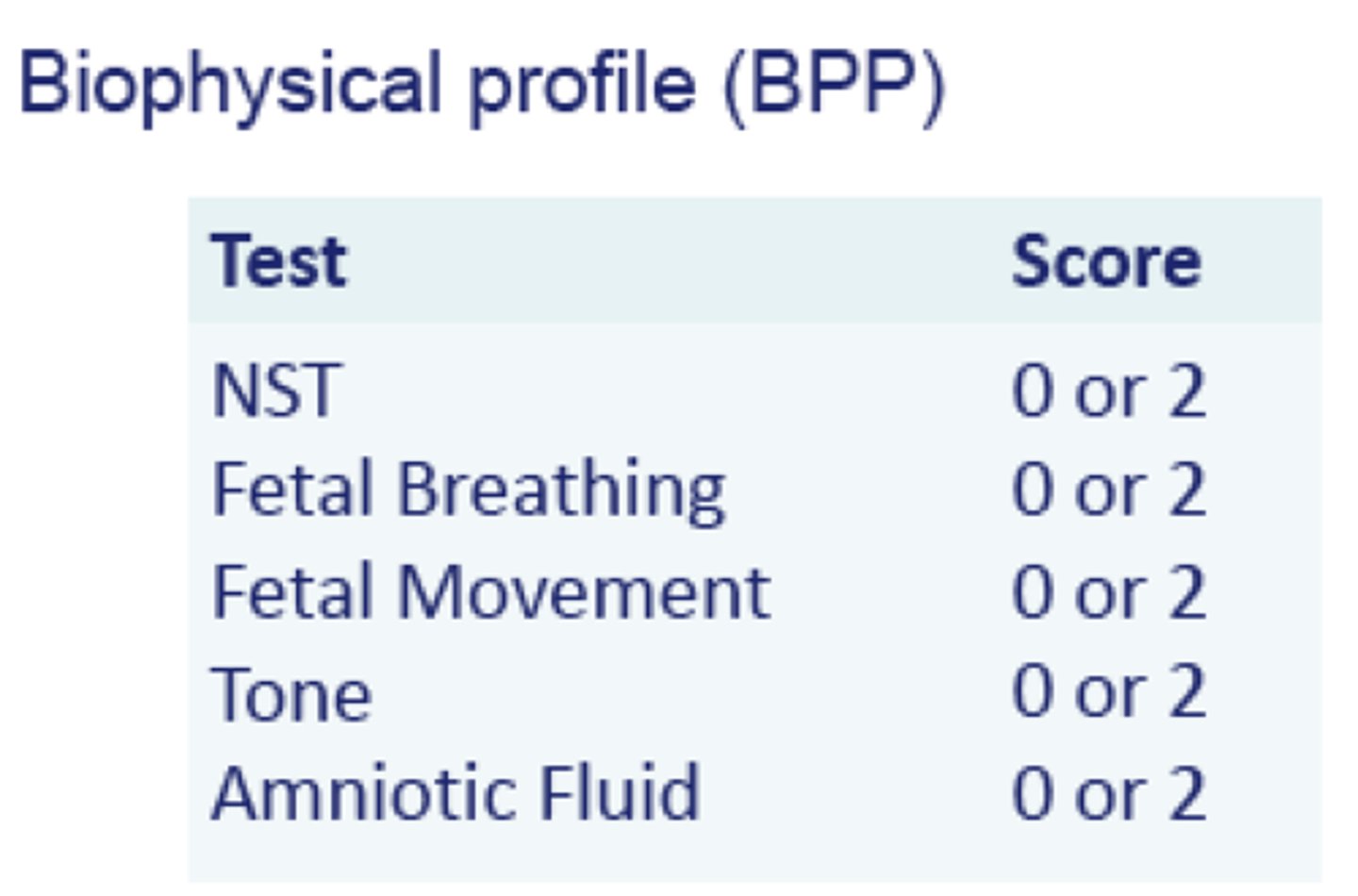
BPP abnormal score is
<4
If a BPP comes back as 6.....
It should be retested
BPP assess for
Fetal well being
non-stress test ( NST)
most widely used technique for antepartum evaluation of fetal well being performed during the third trimester.
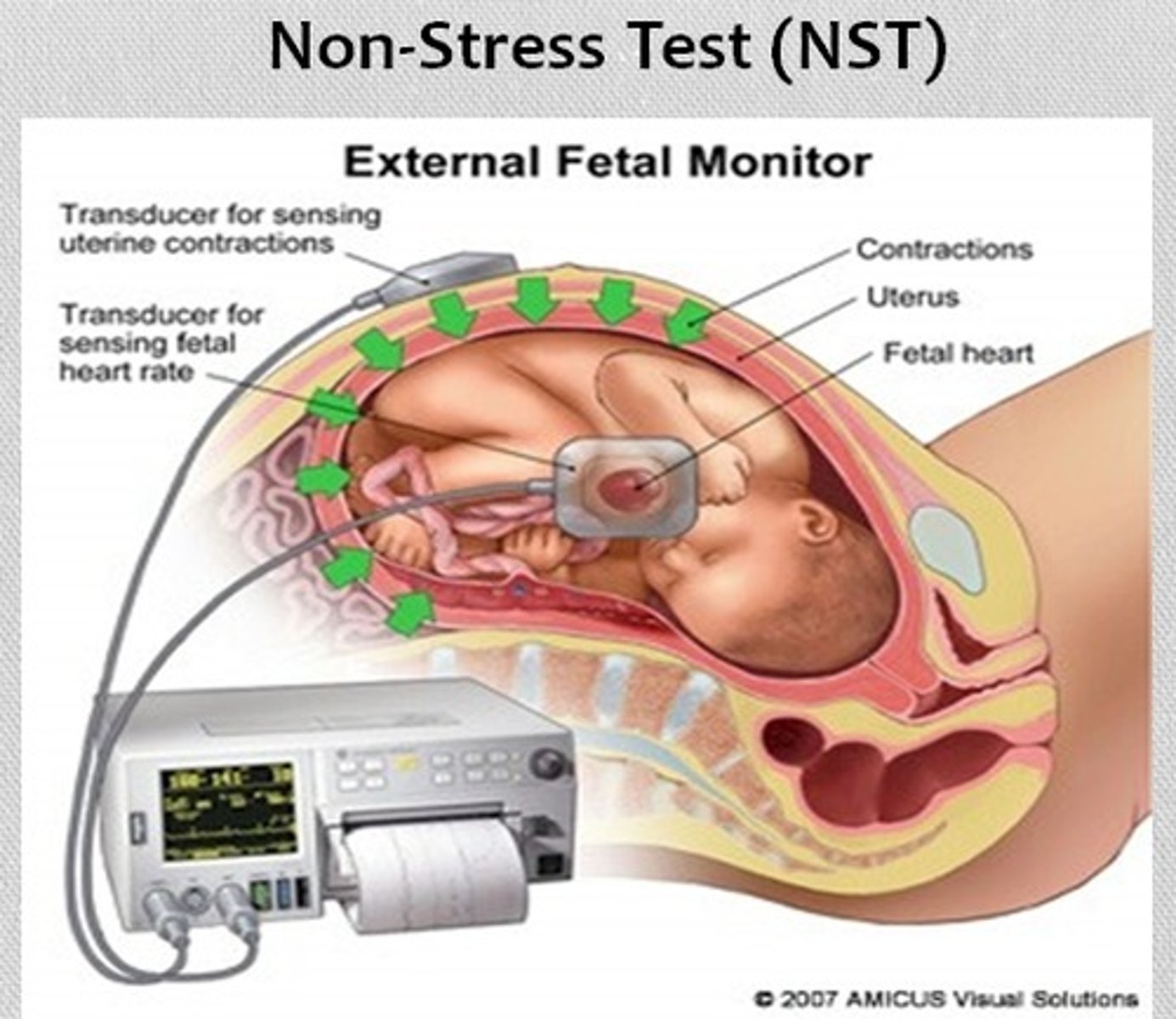
Reactive NST
FHR is a normal baseline rate with moderate variablity
Two accelerations to 15 bpm for at least 15 secs in 20 min period
A non reactive NST would indicate what about the fetus?
The fetal heart rate does not accelerate adequately with fetal movement.
-A BPP or CST will need to be done now
Positive CST is normal or abnormal
abnormal
The contraction stress test — also called a stress test or an oxytocin challenge test — may be done during pregnancy to measure the baby's heart rate during uterine contractions. Its purpose is to make sure the baby can get the oxygen he needs from the placenta during labor.
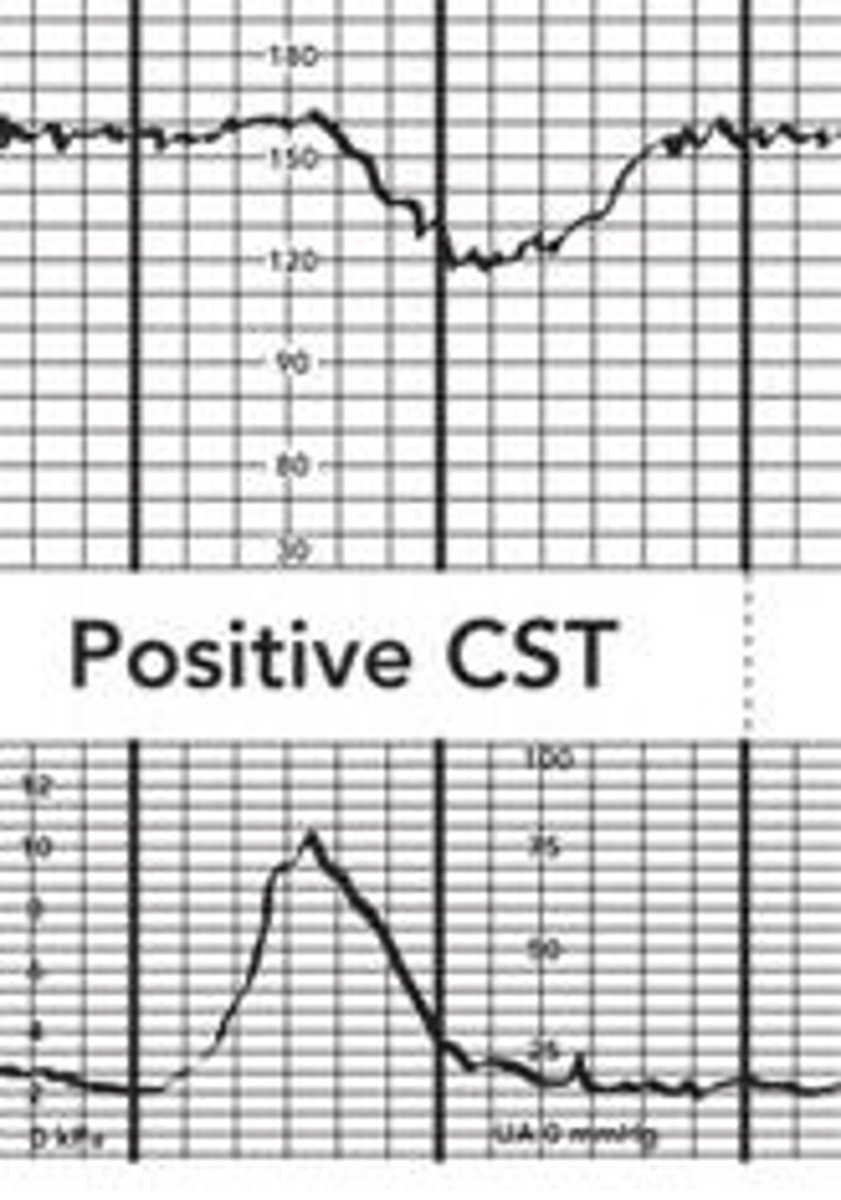
Positive CST is indicated when:
Persistent and consistent late decels on more than half of the contractions.
An amniocentesis may be performed when?
After 14 weeks gestation
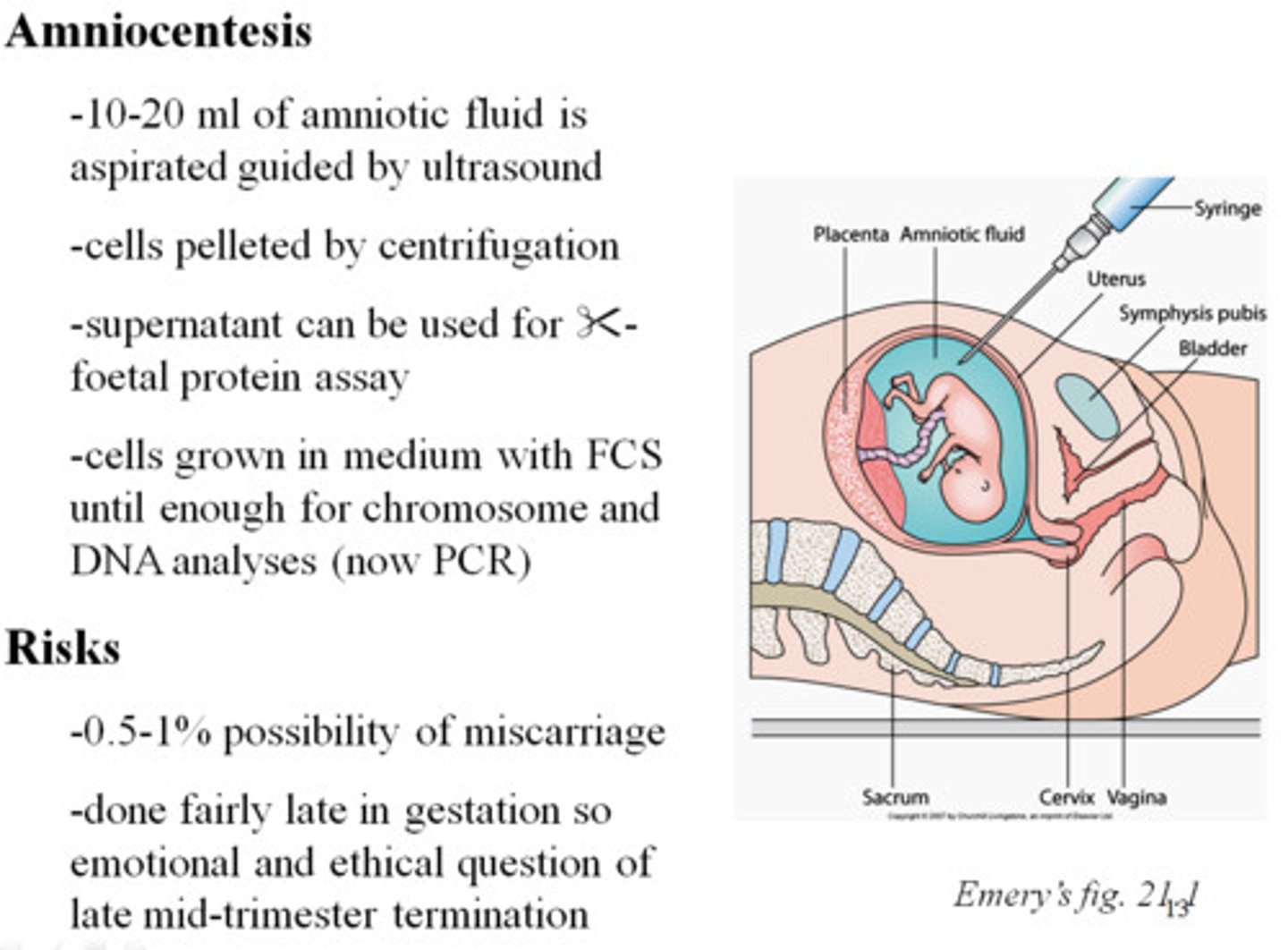
AFP can be measured from the amniotic fluid between:
16 and 18 weeks
alpha-fetoprotein
Presence of PG on a fetal lung test is associated with:
Respiratory distress
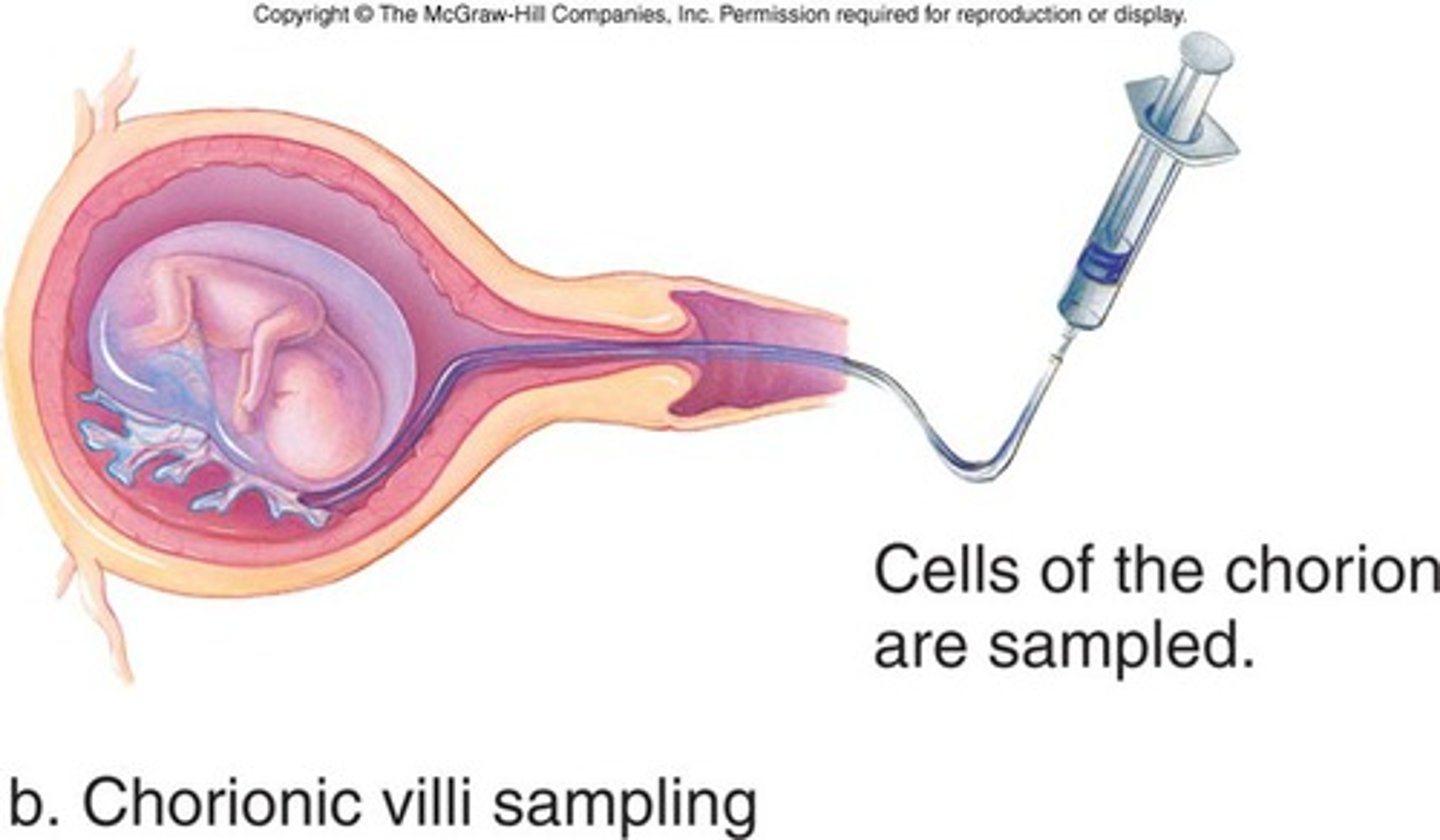
CVS can be done at
10-12 weeks
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test that diagnoses chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, as well as a host of other genetic disorders. The doctor takes cells from tiny fingerlike projections on your placenta called the chorionic villi and sends them to a lab for genetic analysis.
First stage of labor:
1-1.5 cm (onset of labor)
Latent phase of labor:
0-3 cm
mild to moderate contractions
irregular
q 5-30 min
lasts 30-40 sec
Active phase of labor:
4-7 cm
moderate to strong contractions
regular
q 3-5 min
lasts 40-70 sec
Transition phase of labor
8-10 cm
strong to very strong contractions
q 2-3 min
lasts 45-90 sec
Second stage of labor:
Full dilation
Intense contractions
BIRTH!!
Third stage of labor:
Delivery of placenta
Fourth stage:
Maternal stabilization of vital signs
First stage pain:
internal visceral
may be felt as back/leg pain
Second stage pain:
somatic
occurs with fetal descent and expulsion
Third stage pain:
similar to first stage pain
Pain S&S:
Increased BP
Tachycardia
Hyperventilation
Absent or undetectable variability is considered:
Non-reasurring
Minimal variability:
> undetectable but <5/min
Moderate variability:
6-25/min
Marked variability:
>25/min
Accelerations mean:
Healthy fetal/placental exchange
Fetal bradycardia means (less than 60)
Uteroplacental insufficiency
Umbilical cord prolapse
Maternal hypotension
Prolonged umbilical cord compression
Fetal congenital heart block
Anesthetic meds
Fetal tachycardia means:
Maternal infection
Fetal anemia
Fetal heart failure
Fetal cardiac dysrythmias
Maternal use of cocaine or meth
Maternal dehydration
Decrease or loss of variability means:
Meds that depress the CNS
Fetal hypoxemia w/resulting acidosis
Fetal sleep cycle
congenital abnormalities
Early decels mean:
Compression of the fetal head resulting from uterine contraction
Vaginal exam
Fundal pressure
Late decels mean:
UPI causing inadequate fetal oxygenation
Maternal hypotension
placental abruption
Uterine hyperstimulation w/pitocin
Variable decels mean:
Umbilical cord compression
Short cord
Prolapsed cord
Nuchal cord
Oligohydraminos
Fetal descent and cervical dilation are caused by
Frequency, duration, and strength of contractions
What is the sensation the patient will feel when completion of dilation and fetal descent?
She will feel like she needs to take a big ole poooo!
First degree laceration extends through:
skin of perineum
Second degree laceration extends through:
skin of perineum
muscles of perineum
Third degree laceration extends through:
skin of perineum
muscles of perineum
anal sphincter
Fourth degree laceration extends through:
skin of perineum
muscles of perineum
anal sphincter
anterior rectal wall
Third stage:
Signs of placental separation from the uterus are indicated by:
fundus firmly contracting
swift gush from introitus of dark blood
umbilical cord appears to lengthen as placenta descends
vaginal fullness of exam
There is a high risk of _________ surrounding external cephalic version.
Cord prolapse
Regarding BISHOP scoring, when is a woman ready for labor?
A score of
9 for nulliparas
5 or more for multiparas
Mechanical methods to ripen cervix:
balloon caths
hydroscopic dilators and sponges
laminara tents
synthetic dilators and sponges
Methods of induction
prostaglandins applied cervically
admin of IV oxytocin
amniotomy
stripping of membranes
nipple stimulation
Dystocia
prolonged, difficult labor
Before administering pitocin, where should the fetus be?
engaged in the birth canal at a minimum of 0 station.
Discontinue oxytocin if:
contraction frequency more often than every 2 mins
contraction duration longer than 90 seconds
no relaxation of uterus between contractions
uterine resting tone greater than 20 mmHg between ctx
Labor typically begins within ___ hours after ROM.
12
An amnioinfusion can be used to:
Reduce severity of variable decelerations (cord compression)
Dilute meconium-stained amniotic fluid
Caput Succedaneum is:
Normal
Should resolve within 24 hrs
For breast engorgement:
apply cool compresses b/t feedings
apply warm compresses
take warm shower b4 breast feeding
Cold cabbage leaves
may also be applied to breasts to decrease swelling and relive discomfort
Postpartum the mother should not lift anything that is heavier than:
the infant
PP the mom should consume ______ to_______ ml of water each day.
2000-3000
Encourage women who are lactating to add an additional ___ calories/day to their prepregnancy diet.
500
Teach the clent to avoid sexual intercourse until:
episiotomy/laceration is healed
&
vaginal discharge has turned white
Postpartum disorders are:
unexpected events or occurrences that may happen during the PP period
Deep Vein Thrombosis S&S
Leg pain
Chills
Unilateral swelling, warmth, redness
Warm extremity
Calf tenderness
Elevated temp
Cough
Tachycardia
Thrombophlebitis: position arm:
Above the lever of the heart
Thrombosis tx drugs:
Heparin
Warfarin (coumadin)
Pulmonary Embolus S&S
Chills
Apprehension
Pleruitic Chest pain
Dyspnea
tachypnea
hemoptysis
heart murmurs
peripheral edema
distended neck veins
elevated temp
hypotension
hypoxia
DIC risk factors
abruptio placenta
AFE
missed abortion
fetal death in utero
Severe preeclampsia or eclampsia (GHTN)
Septicemia
cardiopulmonary arrest
hemorrhage
hydatiform mole
Post partum hemorrhage is considered to occur if the client loses how much blood?
more than 500 mL after vaginal birth
more than 1000 mL after c/s
Two complications that can occur following PP hemorrhage include:
hypovolemic shock
anemia
PP hemorrhage VS findings:
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Meds given to tx PP hemorrhage
Oxytocin
Methergine
Cytotec
Hemabate
Subinvolution is when:
The uterus remains enlarged with continued lochial discharge and may result in PP hemorrhage
Subinvolution s&s
increased vag bleeding
uterus enlarged and higher than normal in the abd relative to umbilicus
boggy uterus
prolonged lochia d/c with irregular or excessive bleeding
Risk factors for subinvolution of uterus:
Pelvic infection and endometritis
Retained placental fragments not completely expelled from the uterus
Inversion of the uterus
Retained placenta
Uterine atony
Excessive fundal pressure
Abnormally adherent placental tissue
Multiparity
Fundal implantation of the placenta
Extremem traction applied to the umbilical cord
Leiomyomas
Inversion of uterus s&s
pain in lower abd
vag bleeding
dizziness
low BP
pallor
Retained placenta:
Placenta or fragments of the placenta remain in the uterus preventing the uterus from contracting which leads to uterine atony or subinvolution
Med given: oxytocin....if unsuccessful then tocolytic for d&c
APGAR scoring is:
a brief physical exam done immediately following birth to rule out abnormalities.
APGAR of 0-3 indicates
severe distress
APGAR or 4-6 indicates
moderate distress
APGAR of 7-10 indicates
no distres
APGAR
Heart rate scoring
0= absent
1= <100
2= >100
APGAR
RR scoring
0= absent
1= slow, weak cry
2= good cry
APGAR
Muscle tone scoring
0= Flaccid
1= some flexion
2= well-flexed
APGAR
Reflex irritability
0= none
2= grimace
3= cry
APGAR
Color scoring
0= Blue, pale
1= pink body, cyanotic hands and feet (acrocyanosis)
2= Completely pink
Normal newborn weight range:
2500-4000 grams
Low birth weight
less than 2500 grams
Term birth
between 38 weeks and 42 weeks
Grunting and nasal flaring are:
signs of respiratory distress
crackles and wheezing are signs of
fluid or infection in the lungs