core studies 2.0
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
Piliavin Aim
To investigate the affects on helping behaviour on a New York subway.
Piliavin Sample
New York subway. Around 4500 passengers. 45% black & 55% white.
Piliavin IV's
Cane or Bottle. Black or White. Model help- 70 or 150 seconds.
Piliavin Procedure
Males played to role of the ill or drunk. Other male took the role of the helper. Victim fell over after the train had moved off. After 70 or 150 seconds the helper came and helped the victim. 2 females recorded the results.
Piliavin Results
Ill- received help 95% of the time.
Equally helped (race). Drunk- received help 50% of the time. Black victims less likely to receive help. No evidence of diffusion of responsibility.
Piliavin Conclusions
An ill victim is more likely to receive help. Men are more likely to help other men. The longer the incident continues for, the less likely people are to help.
Levine Aim
To investigate helping behaviour a range of different cultures.
Levine Sample
Opportunity samples. 23 cities. Around 1,200 participants.
Levine 3 situations
Dropped pen. Walking with a limp and drops magazines. Blind person crossing the road.
Levine 4 measures
Population size= UN demographic yearbook. Economic prosperity= purchasing power parity. Pace of life= walking speed over 60 feet. Cultural values.
Levine Procedure
Experimenters were students. They were trained on exactly what to do. Observed helping behaviour. Participants were scored as helping if they intervened in any way.
Levine Results
Most amount of help 93% in Rio De Janeiro. Least amount of help 40% in Kuala Lumpur. Economic prosperity was found to correlate significantly with helping behaviours. Richer= Less likely to help.
Levine Conclusions
Helping behaviours in non-emergency situations is not universal but varies between cities. Significant differences between helping behaviours in simpatico and non-simpatia cultures.
Moray Aim
To test factors that would enable an unattended, dichotically presented message to be noticed.
Moray Sample
Experiment 2= 12 participants. Experiment 3= 28 participants (2 groups). Undergraduates.
Moray Procedure 1
Short list of simple words were repeated in the unattended ear. Repeated 35 times. After 30 seconds participants were given a recognition test.
Moray Procedure 2
Participants showed 10 short passages of fiction. Some passages were prefixed with the participants name. Messages were read monotone.
Moray Procedure 3
2 groups shadowed one of two simultaneous dichotic messages. Some messages had digits interpolated in them. Group 1 asked told they would be asked questions about the content. Group 2 asked to remember all the numbers.
Moray Results
Mean no. of words recognised: shadowed= 4.9 / 7 Rejected= 1.9 / 7
Moray Conclusions
Almost none of the content from rejected message can generate the block. A short list of words presented as the rejected message has no trace of being remembered. Names can penetrate the block. It's difficult to make neutral material important enough to break the block set up.
Simons & Chabris Aim
To investigate the effect of several factors on inattentional blindness.
Simons & Chabris Sample
228 participants. Undergraduates. Volunteer sampling. Given a candy bar for taking part.
Simons & Chabris IV's
Transparent/Opaque. Gorilla/Woman with umbrella. Easy/Hard.
Simons & Chabris Procedure
2 teams of 3 passing a ball, (black or white). Participants were told to watch 1 team. Had to count the amount of passes. Hard= Ariel and bounce passes. 44-48 seconds, the unexpected event happened.
Simons & Chabris Questions
'Did you notice anything unusual in the video?' 'Did you notice anything other than the 6 players?' Asked for proof.
Simons & Chabris Results
36 participants data was discarded. Umbrella woman was noticed more, (100%). Gorilla was noticed more by participants attending the black team, (83%).
Simons & Chabris Conclusions
Individuals have a sustained inattention blindness for dynamic events. Failure to notice an ongoing unexpected event,
if engaged in primary monitoring. Levels of inattention blindness depends on the difficulty of the task.
Kohlberg Aim
To investigate development in moral reasoning in early adulthood.
Kohlberg Sample
75 American boys. 10-16 & 22-28 years. Followed at 3 year intervals.
Kohlberg Stages
1- Punishment avoidance. 2- Exchange favours. 3- Good boy/girl (pleasing others). 4- Law and order. 5- Social contract. 6- Ethical principals orientation.
Kohlberg Procedure
Participants were presented with hypothetical moral dilemmas.
Short stories. Age 10- 'is it better to save the life of 1 important person or many unimportant people?' Taiwanese boys asked a question more familiar to their culture.
Kohlberg Results
Participants showed progress through stages with increased age. Not all participants progressed through all stages. Taiwanese boys aged 10-13 tended to give stage 2 responses. Stage 6 was rarely used by age 16 in US.
Kohlberg Conclusion
Each stage of moral development comes one at a time, and in the same order. The six-stage theory is not significantly affected by social, cultural and religious conditions.
Lee Aim
To investigate cross-cultural differences in moral evaluations of lying.
Lee Sample
120 Chinese children. 108 Canadian children. Ages 7 ,9 and 11.
Lee Procedure
Social and physical story conditions. 2 prosocial, 2 antisocial. Teacher asks who did it. 7 point rating chart.
Red stars= good. Blue circle= neither. Black cross= naughty. The words good and naughty were altered within subjects.
Lee Results
Chinese children rated truth telling less positively and lying less negatively. Antisocial lies rated more negative with age.
Lee Conclusion
Moral reasoning can be influenced by cultures. The influence of socio-cultural factors becomes stronger as we age.
Blakemore & Cooper Aim
To investigate whether brain development occurs due to experiences rather than nature.
Blakemore & Cooper Sample
2 laboratory raised kittens.
Blakemore & Cooper Procedure
Kittens raised in the dark. From 2 weeks old, they spent 5 hours a day in a cylinder.
Horizontal stripes Vertical stripes Kittens couldn't see their bodies. Routine stopped after 4 months. Taken for several hours a day into a well lit room. Visual reaction was observed.
Blakemore & Cooper Results
They showed no visual placing when brought up to a table. Within 10 hours, kittens could jump from chair to floor. Behavioural blindness:
Raised in horizontal lines could not detect vertically aligned objects, (vice versa).
Blakemore & Cooper Conclusion
Visual experiences in the early life of kittens can modify their brains and have perceptual consequences. The visual cortex may adapt itself to the nature of its visual experience during maturation.
Neural plasticity.
Maguire Aim
To investigate whether changes could be detected in the brains of London taxi drivers and to further investigate the functions of the hippocampus in spatial memory.
Maguire Sample
16 male taxi drivers. 16 matched non-taxi drivers. Ages 32 to 62.
Maguire Procedure
Stage 1- MRI scan of 50 healthy brains. Analysed to establish comparison of average hippocampus.
By VBM. Stage 2- MRI scan of 16 taxi drivers brains and 16 non-taxi drivers. Control- The expert conducting the analysis didn't know who's brain was on the MRI.
Maguire Results
Increased volume of grey matter in posterior hippocampus of taxi drivers. Volume of R.P.H increased with length of time as a taxi driver.
Maguire Conclusion
The structure of the brain changes in response to environmental demand. The mental map of the city of London is in stores in the posterior hippocampus.
Gould Sample
1.75 million army recruits. Review article that looks at the history of Yerke's intelligence testing.
Gould Procedure
Army alpha:
Written test for literate recruits. Army beta: Pictorial test for those who are illiterate. Individual examination: Individual spoken task for those who failed army beta. Recruits who were illiterate should have been immediately put in army beta...Some sat Army alpha and scored low.
Gould Results
Levels of literacy were much lower than Yerkes anticipated. Average mental age of white males= 13.04. Average mental age for black males= 10.41. Showed the poor, blacks and feeble-minded had been interbreeding. Lighter the skin colour= more intelligent.
Gould Conclusion
IQ tests are culturally and historically biased.
Don't measure natural intelligence. Inappropriate and poorly administered IQ tests can lead to tragic consequences.
Hancock Aim
To examine how features of language are used in crime narratives by psychopaths.
Hancock Sample
52 male murderers.
14 psychopathic. 38 non-psychopathic. Ages 14 to 50. Volunteer sampling.
Hancock Procedure
Participants were interviewed using open ended interviews. Asked to describe their offences in as much detail as possible. Psychopathy was measured using psychology checklist-revised. The narrative was transcribed. Text analysis:
Wmatrix linguistic analysis tool, (speech). Dictionary of affect in language, (tone of words).
Characteristics of a psychopath
Superficial charm, Pathological lying, Manipulation, Impulsivity, Juvenile delinquency.
Maslow's hierarchy
(level 1) Physiological Needs, (level 2) Safety and Security, (level 3) Relationships, Love and Affection, (level 4) Self Esteem, (level 5) Self Actualization
Hancock Results
Psychopaths included more rational cause and effect descriptors, (because or since). Focused on material needs. Psychopaths' language was significantly less fluid. Used more past tense verbs.
Hancock Conclusion
Psychopaths:
More likely to describe cause and effect relationship when describing their murder. More likely to view their crime as a logical outcome of a plan. Focus more on physiological needs... food, drink and money.
Difference between Yerkes and Gould
Yerkes is the original study and the one that tested the army recruits and found that white people had the mental age of 13 and those with darker skin had a lower mental age Gould is the one criticising the study
gould aim
To investigate the fundamental problems involved in the attempts to measure intelligence.
Milgram Aim
To measure the level of obedience to an authority figure, when asked to administer electric shocks to another person.
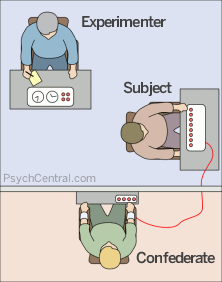
Milgram Sample
40 males aged between 20-50. newspaper article. $4.50.
Milgram Procedure
Participants were 'randomly' allocated to be the teacher. Asked to give an electric shock every time the learner got a question wrong. Increased by 15volts each times.
Milgram Results
100% reached 300v. 65% reached 450v. Signs of extreme stress.
Milgram Conclusions
People obey those of high authority. People will shift the blame to the experimenter.
Bocchiaro Aim
To investigate the rates of obedience, disobedience and whistleblowing in unethical situations.
Bocchiaro Sample
149 participants. (comparison group= 138). Volunteer sampling. Paid $7.
Bocchiaro Pilot studies
8 pilot studies, conducted to ensure the study was ethically sound.
Bocchiaro Procedure
Participants were told that a study into sensory deprivation was going to be carried out. They were put into a room with computers, a mail box and committee form. They were asked to write an enthusiastic statement about the study. They completed a personality test.
Bocchiaro Comparison group
These students were asked: 'what would you do?' 'what would they average student do?'
Bocchiaro Results
76.5% obeyed. 9.4% whistleblew.
Bocchiaro Conclusions
People tend to obey authority figures, even if it is unethical. The level of obedience was underestimated. Wanting to be good is taken over by situational factors.
Loftus & Palmer Aim
To investigate the effect of leading questions on eye witness testimony of car crashes.
Loftus & Palmer Sample
Experiment 1= 45 participants. Experiment 2= 150 participants, (3 groups)
Loftus & Palmer Procedure 1
Shown 7 films of car crashes. They were asked to write an account of the incident. Asked questions about the crash. 'How fast were the cars going when they verb'
Loftus & Palmer Verbs used
Hit Contacted Bumped Collided Smashed
Loftus & Palmer Procedure 2
Participants watched a clip of a car crash. Asked questions after the clip. Group 1= 'how fast were the cars going when they Smashed into each other?' Group 2= 'how fast were the cars going when they hit each other?' Control= were not asked about speed.
Loftus & Palmer Results
EXP 1
smashed = fastest speed estimates contacted = slowest All estimates were higher than the actual crashes EXP 2 More P's in 'smashed' said there was broken glass than in 'hit' and the control. Most P's correctly recalled no glass
Loftus & Palmer Conclusions
Misleading post event information can affect memory. Memories are formed of information from event and after event. Eye witness testimony is rarely accurate.
Grant Aim
To investigate that learning context and taking a test in the same environment has a positive effects on performance.
Grant Sample
8 psychology students as experimenters. 39 participants. Ages 17-56.
Grant Procedure
Instructions were read aloud. Participants were given an article to read. Told they would be tested on it. All participants wore headphones. 2 minute break between reading and testing. Short answer test followed by multiple choice test.
Grant Conditions
Reading/Testing: Silent/Silent Silent/Noisy Noisy/Noisy Noisy/Silent
Grant Results
Better results in silent/silent condition= 14.3. Shows reading and testing in the same environment produces Better results.
Grant Conclusions
Studying and testing in the same environment leads to enhanced performance. There are context-dependency effects for newly learned material. Students should study in silent conditions.Moray
Bandura Aim
To investigate if social behaviours can be acquired by observation and imitation.
Bandura Sample
72 children. 37-69 months. Stanford university nursery.
Bandura Procedure 1
Room 1- children sat at a table and watched models set up toys.
Aggressive models verbally/physically abused the bobo doll. Non-aggressive models assembled a tinker toy set quietly.
Bandura Procedure 2
Room 2- children taken into another room and allowed to play with attractive toys.
After 2 minutes the toys were taken away and told they were for other children.
Bandura Procedure 3
Room 3- Bobo doll, mallet, dart gun, tea set, cars and dolls.
Their behaviour was observed.
Bandura Results
Children in the aggressive condition showed more aggressive behaviours. Children imitated models of their own sex more. Male models exerted a greater influence.
Bandura Conclusion
Children imitate behaviours shown by adult models. Children learn behaviours through observation and imitation. Boys and Girls are more likely to learn verbal aggression from same sex models.
Chaney Aim
To test whether positive reinforcement of funhaler could improve medical compliance.
Chaney Sample
32 children. 1.5 to 6 years. Australia. Parents contacted by the phone.
Chaney Procedure
Parents helped in the use of funhaler. Asked to use the funhaler for 2 weeks instead on their normal one. Funhaler incorporates a number of features to distract the child.
Chaney Results
Improved parent and child compliance. 38% more parents found to have medicated their children when using the funhaler. 60% more children took the recommended cycles.
Chaney Conclusion
Improved adherence and satisfactory delivery characteristics.
Funhaler may be useful for management of young asthmatics. Improve measurements of clinical outcome.
Sperry Aim
To investigate the effects of hemispheric deconnection on perception and memory.
Sperry Sample
11 epileptic participants. Had undergone hemisphere deconnection.