DDT - Diabetic Kidney Disease
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
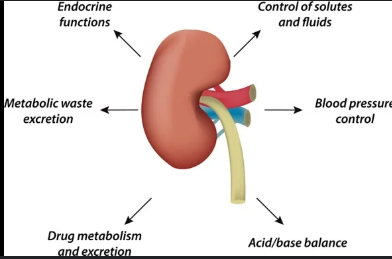
Functions of the kidney?
Water and electrolyte balancing, pH regulation, waste production excretion, vitamin D activation and erythropoietin secretion
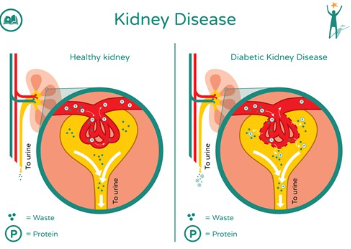
What is diabetic kidney disease?
A slow decline in glomerular filtration rate due to diabetes and linked to retinopathy (damage to the retinas)
Risk factors for DKD (Give 3 answers)
Chronic diabetes, chronic hyperglycaemia, hypertension, sex, family history, obesity, smoking, hyperlipidaemia and certain genes
Ways to diagnose DKD
Monitoring treatments like glucose, insulin, electrolyte and lipid monitoring as well as urine dip. Monitoring the progression of the disease like albumin to creatinine ratio, estimated GFR and renal biopsy.
What are some treatments for Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD)
ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) and ARB (angiotensin II receptor blockers) inhibitors would slow DKD (also help with cardiovascular issues). Alternative anti-hypertensive medication would be used if the previous medications were not successful. Alternatively, statins can be used to help reduce LDL
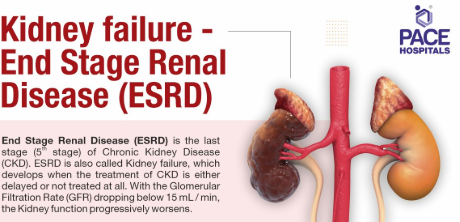
Signs of final stage renal failure
Hyperkalaemia (excessive potassium levels in urine), metabolic acidosis (unable to excrete acid in form of ammonia), hypervolemia (where sodium and water is not excreted properly) and uraemia (failure to excrete urea)
What is AMD and the two types of AMD
AMD is age macular degeneration, which affects vision, and affects the macula region. Wet AMD is neovasculature (excessive blood supply) and blood retina barrier is broken down, but can be treated with antiangiogenic injections. Dry AMD results in retina pigment epithelium and has no treatment.
How does hyperglycaemia result in AMD
Constant changes in cellular metabolism a well as changes I stable macromolecules (molecules vital to biological processes), lead to tissue damage over time. Genetics and certain factors like hypertension can further impact this
What are some ways diabetes can impact fertility?
Diabetes delays puberty, premature menopause which cause a reduction in the reproductive period. Diabetes can also cause irregular periods and greater chances of miscarriage.