Google Data Analytics Certification
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Database
Collection of data stored in computer system
Data life cycle
Plan → capture → manage → analyze → archive → destroy
Plan
What data do we need? How will it be managed? Who’s responsible for it? What are the optimal outcomes?
Capture
Collecting data from variety of sources and brought into the organization
Manage
Where to store data? What tools to keep it secure? Actions needed for proper maintenance?
Analyze
Data is used to solve problems, make decisions, support business goals
Archive
Storing data in a place where it’s available, but may not be used again
Destroy
Important for protecting company’s private information and private data about customers
Steps of data analysis
Ask→ Prepare → Process → Analyze → Share → Act
Ask
Define problem and make sure we understand stakeholder expectations.
Defining problem involves looking at current state and identify how it’s different from the ideal state.
Who are the stakeholders? Maintain strong communication with stakeholders.
Stakeholder
People who help make decisions, influence actions and strategies, and have specific goals they want to meet.
Prepare
Collect and store data that will be used for analysis process.
Process
Find and eliminate errors/inaccuracies that can get in the way of results
Cleaning data, transforming it into more useful format, combining datasets, removing outliers
Fix typos, inconsistencies, or missing/inaccurate data
Veryfing and sharing data cleansing with stakeholders
Analyze
Using tools to transform/organize info to make useful conclusions, make predictions, and drive informed decision-making
Share
Interpreting results and sharing them with others to help stakeholders make effective data-driven decisions.
Data visualization is key
Act
Business taking all insights you have provided and uses them to solve the original business problem.
Formula
Set of instructions that performs a specific calculation using the data in a spreadsheet.
Function
Preset command that automatically performs a specific process or task using the data in a spreadsheet.
Query language
Programming language that allows you to retrieve and manipulate data from a database.
Database
A collection fo data stored in a computer system.
Query
Request for data/info from a database
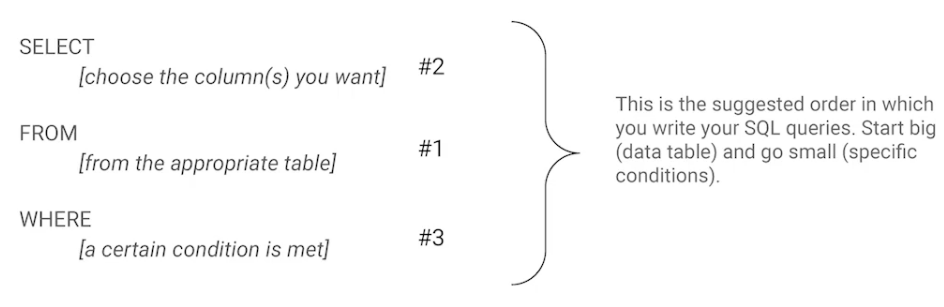
Issue
Topic/subject to investigate
Business task
Question/problem data analysis answers for a business
Fairness
Ensuring that your analysis doesn’t create or reinforce bias
Structured thinking
Process of recognizing the current problem or situation, organizing available info, revealing gaps/opportunities, and identifying options
Making predictions problem type
Using data to make informed decision about how things may be in future
Categorizing things problem type
Assigning info to different groups or clusters based on common features
Spotting something unusual problem type
Identifying data that’s different from norm
Identifying themes problem type
Grouping categorized info into broader concepts
Discovering connections problem type
Finding similar challenges faced by different entities and combining data and insights to address them
Finding patterns problem type
Using historical data to understand what happened in the past and is therefore likely to happen again
Closed-ended questions
Only answered with yes or no, doesn’t really provide useful insights
SMART questions
Specific - simple, significant, focused on single topic or a few closely related ideas
Measurable - can be quantified and assessed
Action-oriented - encourage change
Relevant - matter, important, have significance to the problem you’re solving
Time-bound - specify the time to be studied
Data-inspired decision-making
Explores different data sources to find out what they have in common
Report
Static collection of data given to stakeholders periodically
Pros:
High-level historical data
Easy to design/use
Pre-cleaned and sorted data
Cons:
Continual maintenance
Less visually appealing
Static
Dashboard
Monitors live incoming data
Pros:
Dynamic, automatic, interactive
More stakeholder access
Low maintenance
More visually appealing
Cons:
Labor-intensive design
Can be confusing
Long time to fix bugs
Potentially uncleaned data
Pivot table
Data summarization tool used in data processing, used to summarize, sort, reorganize, group, count, total, or average data stored in database
Metric
Single, quantifiable type of data that can be used for measurement
Can help calculate customer retention rates
Metric goal
Measurable goal set by company and evaluated using metrics
Mathematical thinking
Looking at problem and logically breaking it down step-by-step so you can see the relationship of patterns in data, using that to analyze the problem
Small data
Specific
Short time period
Day-to-day decisions
Ex:) How much water you drink a day
Big data
Large and less specific
Long time period
Usually need to be broken down
Big decisions
Operator
Symbol that names type of operation or calculation to be performed
Cell reference
A cell or range of cells in a worksheet that can be used in a formula
RowNum like A1
Common errors
#ERROR! - Formula can’t be interpreted as input (parsing error)
#N/A - data in formula can’t be found
#NAME? - formula/function name isn’t understood
#NUM! - formula/function can’t be performed as specified
#VALUE! - general error that could indicate problem with formula or referenced cells
#REF! - formula is referencing a cell that is no longer value or has been deleted
Problem domain
Specific area of analysis that encompasses every activity affecting or affected by the problem
Scope of work (SOW)
An agreed-upon outline of the work you’re going to perform on a project
Before communicating…
Who is my audience?
What do they already know?
What do they need to know?
How can I communicate that effectively to them?
First-party data
Data collected by an individual or group using their own resources (preferred)
Second-party data
Data collected by a group directly from its audience and then sold
Third-party data
Data collected from outside sources who did not collect it directly (less reliable)
Nominal data
Qualitative data that’s categorized without a set order
Ordinal data
Qualitative data with a set order or scale
Internal data
Data that lives within a company’s own systems
More reliable
Easier to collect
External data
Data that lives and is generated outside of an organization
Structured data
Data that’s organized in a certain format such as rows and columns
Easily searchable
Analysis-ready
Good for databases
Easily visualized
Ex:) Relational databases, spreadsheets
Unstructured data
Data that’s not organized in any easily identifiable manner
Ex:) Audio and video files
Data model
Used for organizing data elements and how they relate to one another. Works well for structured data.
Keeps data consistent
Maps out how data is organized
Data elements
Pieces of info
Ex:) names, account numbers, addresses
Wide data
Every data subject has a single row with multiple columns to hold the values of various attributes of the subject
Easily identify and compare different data between columns
Long data
Each row is one time point per subject so each subject will have data in multiple rows
Good for storing and organizing data when there’s multiple variables for each subject at each time point
Less columns, only need to add one more column for new variable
Observer (experimenter/research) bias
Different people observe things differently
Interpretation bias
Interpreting ambiguous situations in a positive or negative way
Confirmation bias
Searching for, or interpreting info in a way that confirms preexisting beliefs
Identifying good data
Reliable
Original - validate with original source
Comprehensive - contains all info needed
Current
Cited - makes info more credible
Data ethics
Well-founded standards of right and wrong that dictate how data is collected, shared, and used
GDPR
General Data Protection Regulation of the EU
Ownership
Individuals own the raw data they provide and they have primary control over its usage, how it’s processed, and how it’s shared.
Transaction transparency
All data-processing activities and algorithms should be completely explainable and understood by the individual who provides their data.
Consent
An individual’s right to know explicit details about how and why their data will be used before agreeing to provide it.
Currency
Individuals should be aware of financial transactions resulting from the use of their personal data and the scale of these transactions.
Privacy
Preserving a data subject’s info and activity any time a data transaction occurs.
People should have…
Protection from unauthorized access to our private data
Freedom from inappropriate use of our data
The right to inspect, update, or correct our data
Ability to give consent to use our data
Legal right to access our data
Openness
Free access, usage, and sharing of data
Open data standards:
Availability and access
Reuse and redistribution
Universal participation
Data anonymization
Process of protecting people’s private or sensitive data by eliminating personally identifiable info.
Data interoperability
Ability of data systems and services to openly connect and share data.
Relational database
Database that contains a series of related tables that can be connected via their relationships.
Primary key
An identifier that references a column in which each value is unique.
Used to ensure data in a specific column is unique
Uniquely identifies a record in a relational database table
Only one allowed in a table
No null/blank values
Foreign key
A field within a table that’s a primary key in another table (how one table can be connected to another)
Column or group of columns in a relational database table that provides a link between the data in two tables
Refers to field in a table that’s the primary key of another table
More than one allowed in a table
Descriptive metadata
Describes a piece of data and can be used to identify it at a later time.
Structural metadata
Indicates how a piece of data is organized and whether it is part of one, or more than one, data collection
Administrative metadata
Indicates the technical source of a digital asset
Metadata repository
Database specifically created to store metadata. Make it easier and faster to bring together multiple sources for data analysis
Data governance
A process to ensure the formal management of a company’s data assets
External data
Data that lives and is generated outside an organization
Naming conventions
Consistent guidelines that describe the content, date, or version of a file in its name.
Data security
Protecting data from unauthorized access or corruption by adopting safety measures.
Mentor
Professional who shares their knowledge, skills, and experience to help you develop and grow.
Sponsor
Professional advocate who’s committed to moving a sponsee’s career forward with an organization.
Data integrity
Accuracy, completeness, consistency, and trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle
Types of insufficient data
Data from only one source
Data that keeps updating
Outdated data
Geographically-limited data
Ways to address insufficient data
Identify trends with available data
Wait for more data if time allows
Statistical power
Probability of getting meaningful results from a test.
Hypothesis testing
A way to see if an survey or experiment has meaningful results.
Statistically significant
Results are real and not an error caused by randomness (usually at least 0.8 power)
Confidence level
Probability that your sample size accurately reflects the greater population. Independent from margin of error (doesn’t need to add up to 100%)
Margin of error
Max amount that the sample results are expected to differ from those of the actual population.
Dirty data
Data that’s incomplete, incorrect, or irrelevant to the problem you’re trying to solve.
Clean data
Data that’s complete, correct, and relevant to the problem you’re trying to solve.
Data engineers
Transform data into a useful format for analysis and give it a reliable infrastructure.
Data warehousing specialists
Develop procedures and processes to effectively store and organize data.