Fichas de aprendizaje Ap psych midterm | Quizlet
1/304
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
305 Terms
psychology
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
soft science
science that is not based in principle, but rather theory
Pseudoscience
A fake or false science that makes claims based on little or no scientific evidence.

Aristotle
Interested in sleep, memory, dreams, and emotion. Ideas come from observation. Nurture

Renes Descartes
French, believed in dualism, believed the mind and body communicated through "animal spirits" that flowed through hollow nerves. "I think, therefore I am." Nature

John Locke
person is a Blank state. Nurture

Neuron
The basic building block of the nervous system, composed of dendrites, axon, cell body, and terminal button
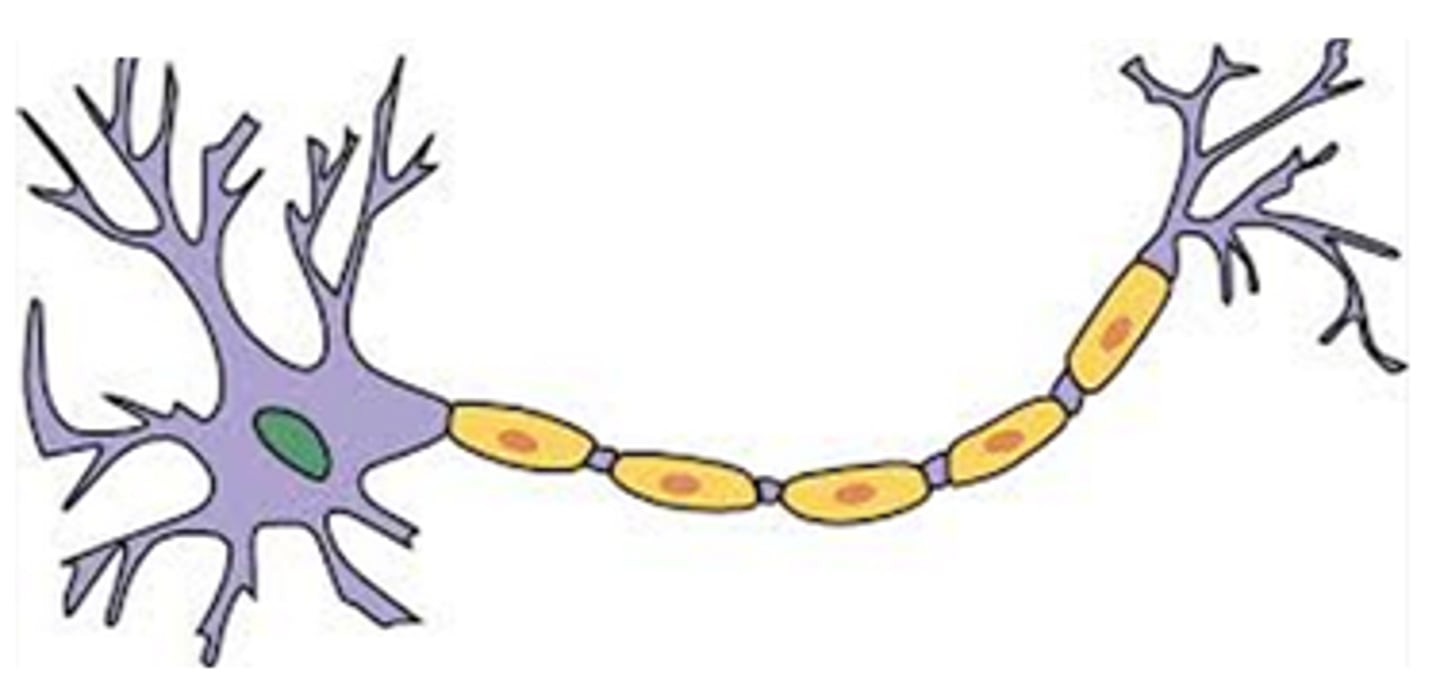
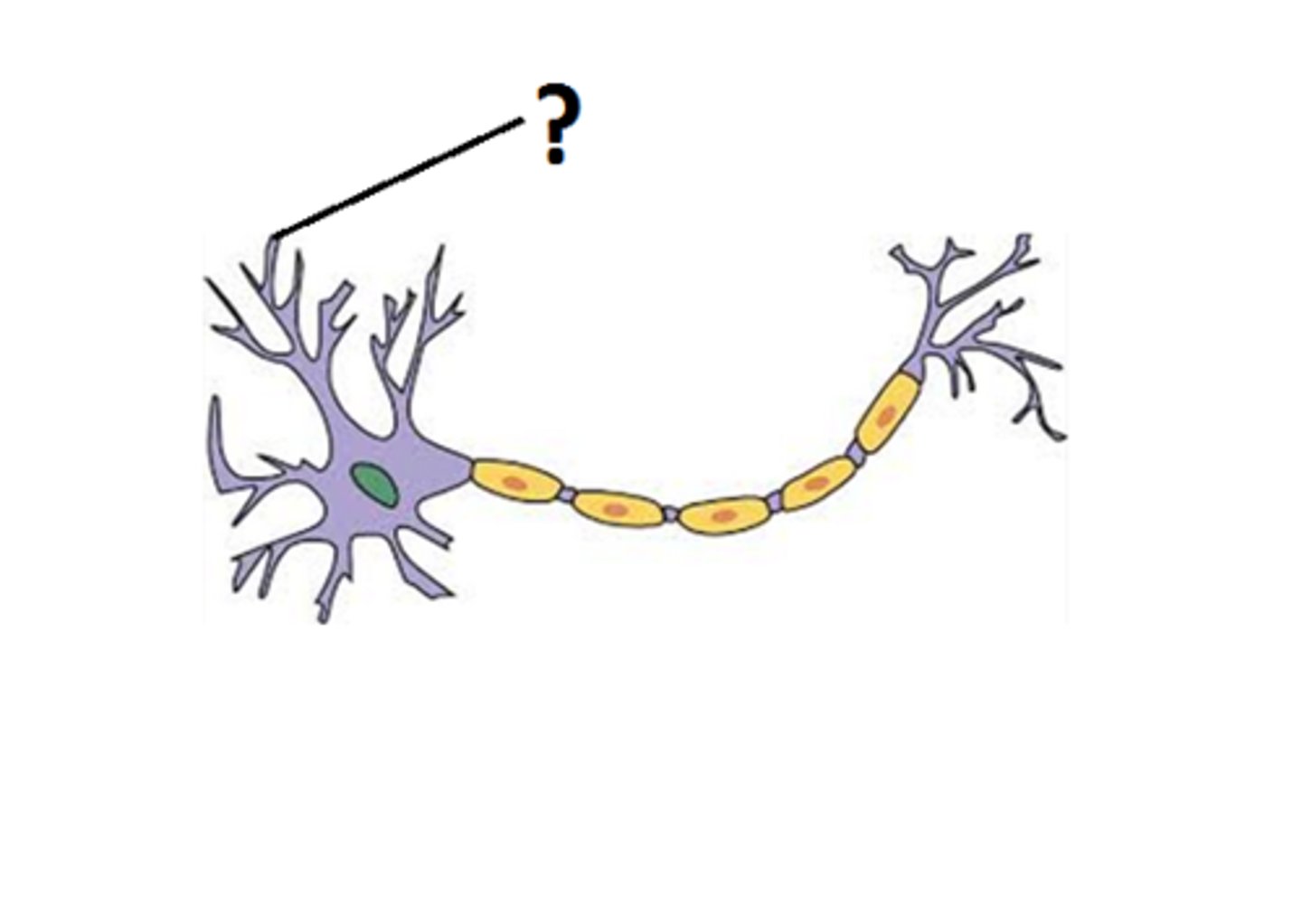
Dendrites
receive messages from other cells
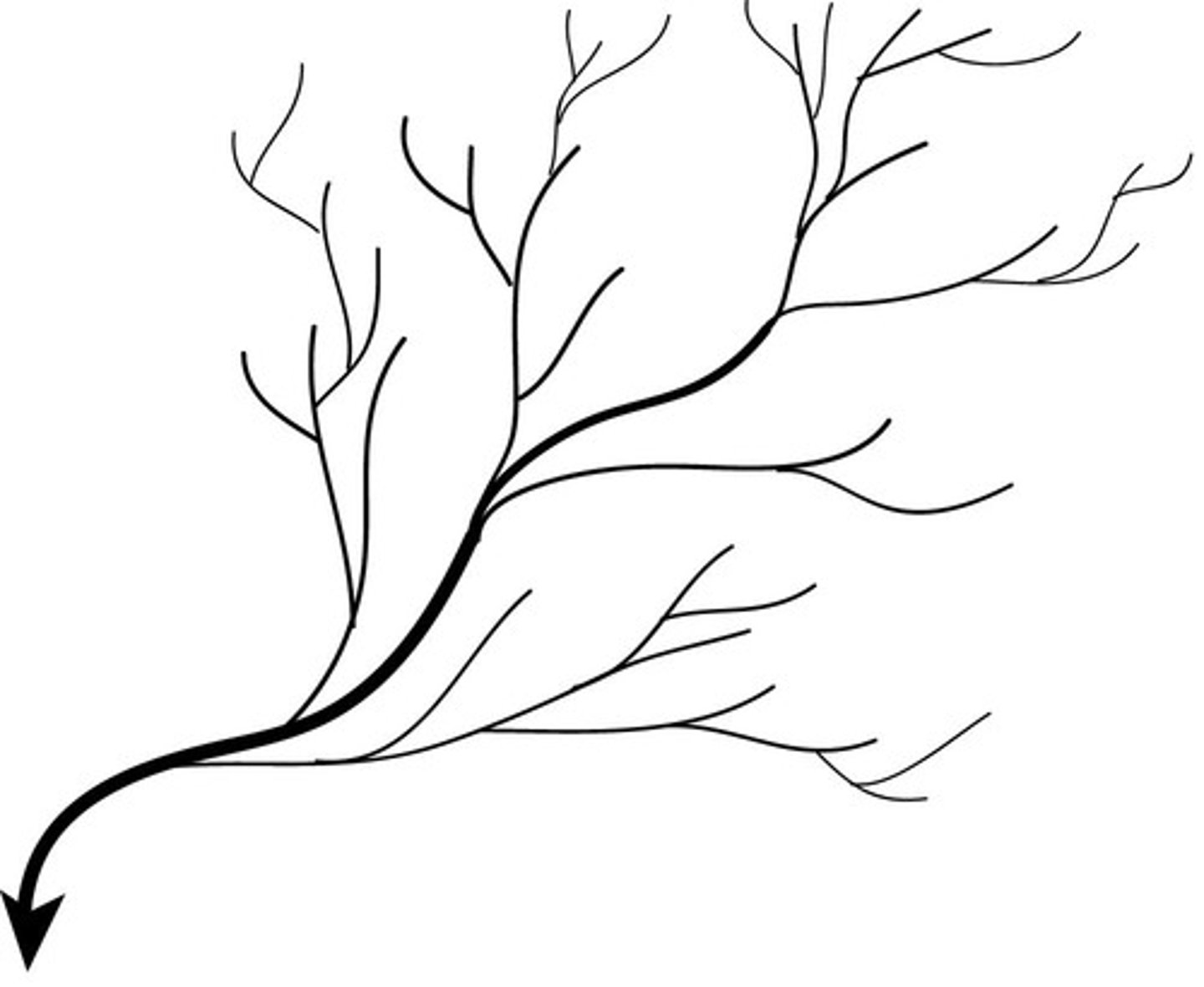
dendritic tree
all the dendrites of a single neuron
dendritic branching
One kind of change to dendrite structure that results in an increase in surface area and thus of available sites
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
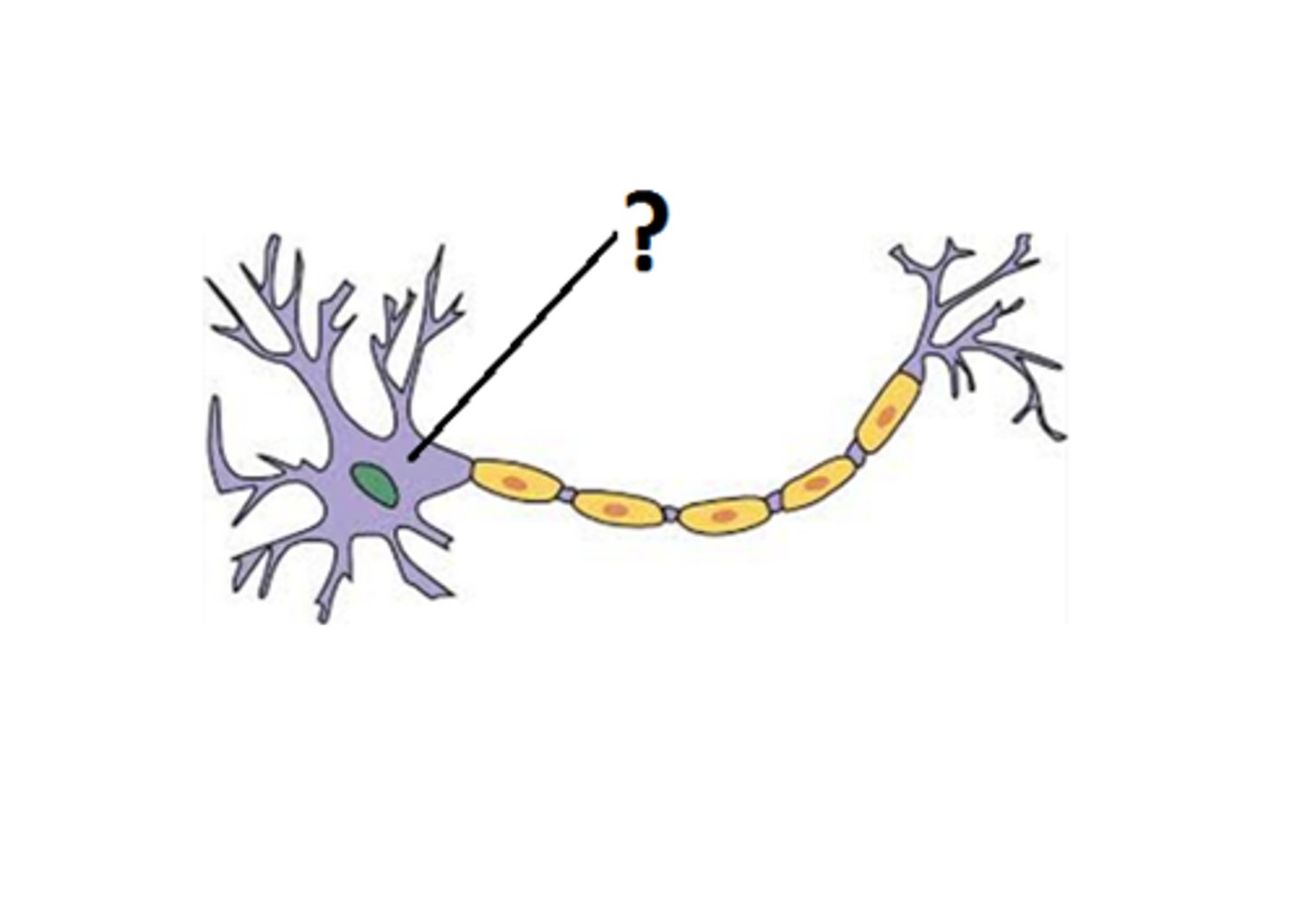
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
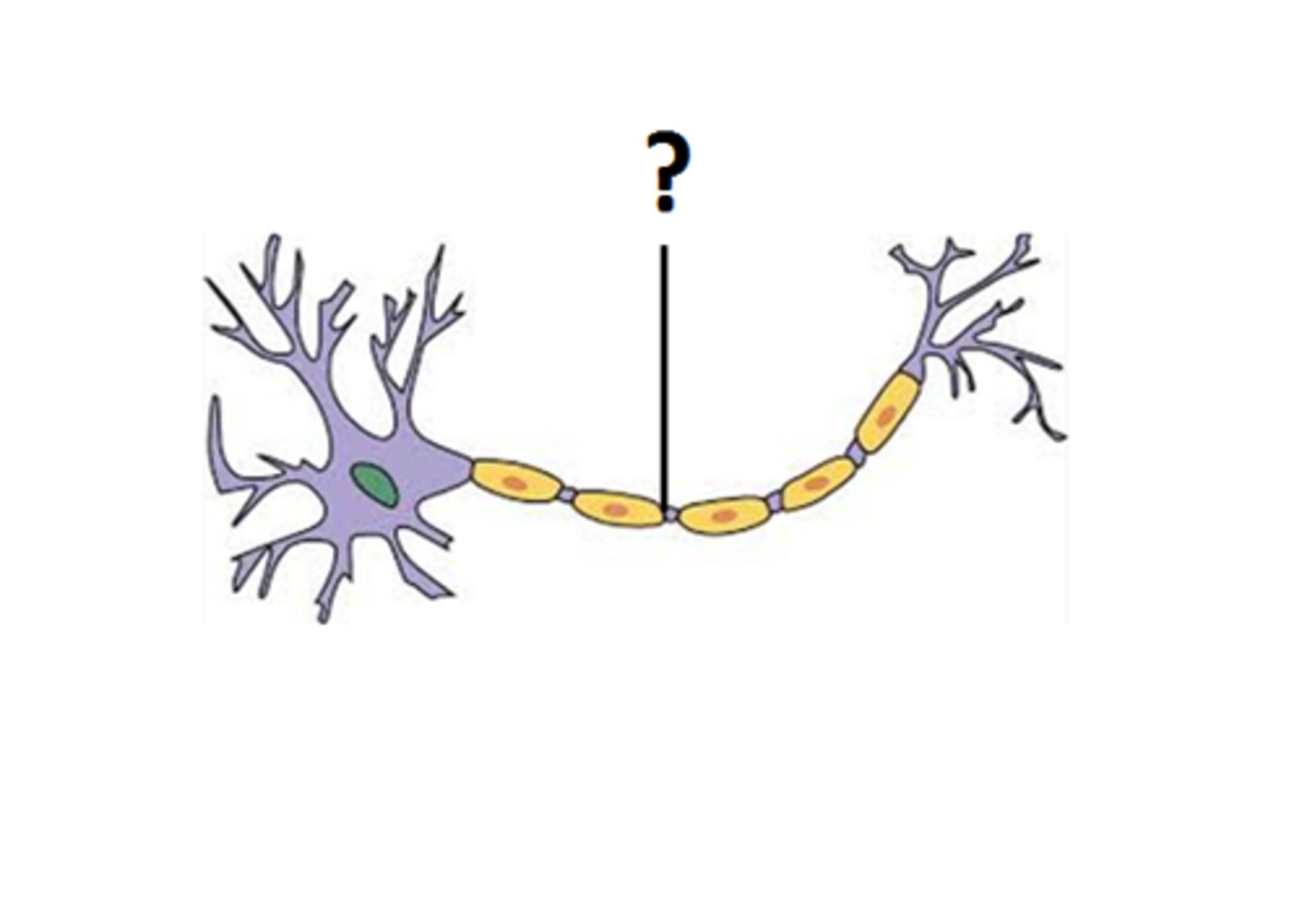
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
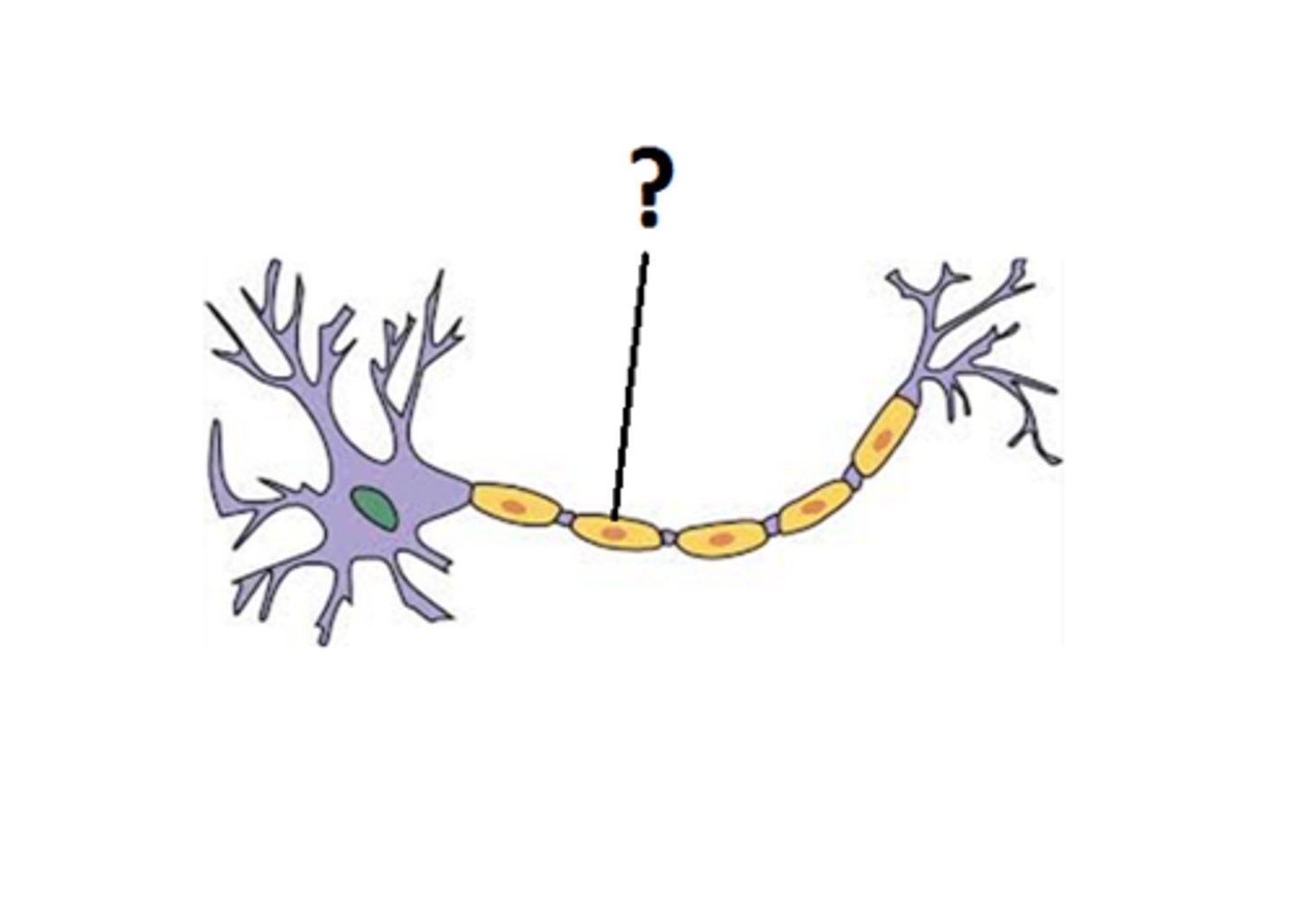
terminal buttons (axon terminals)
ends of axons that secrete neurotransmitters
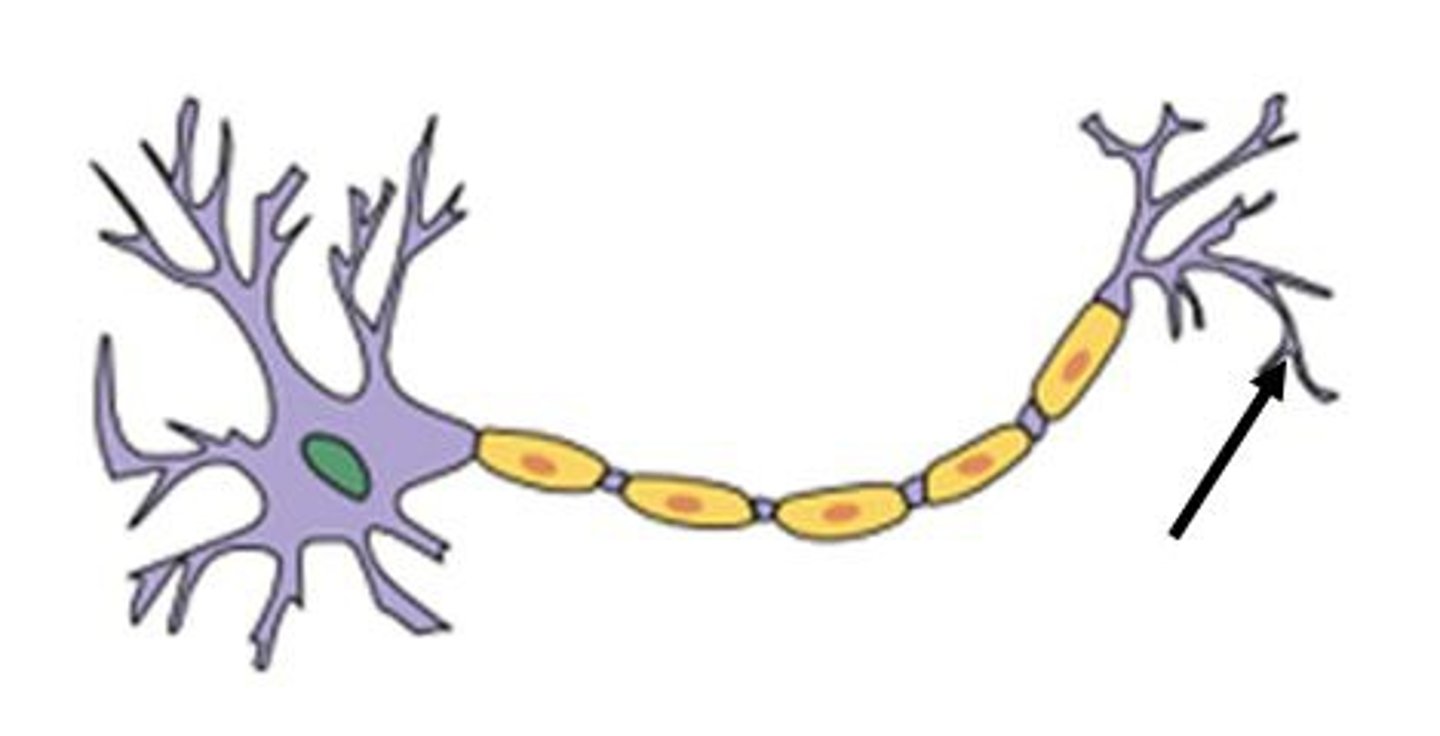
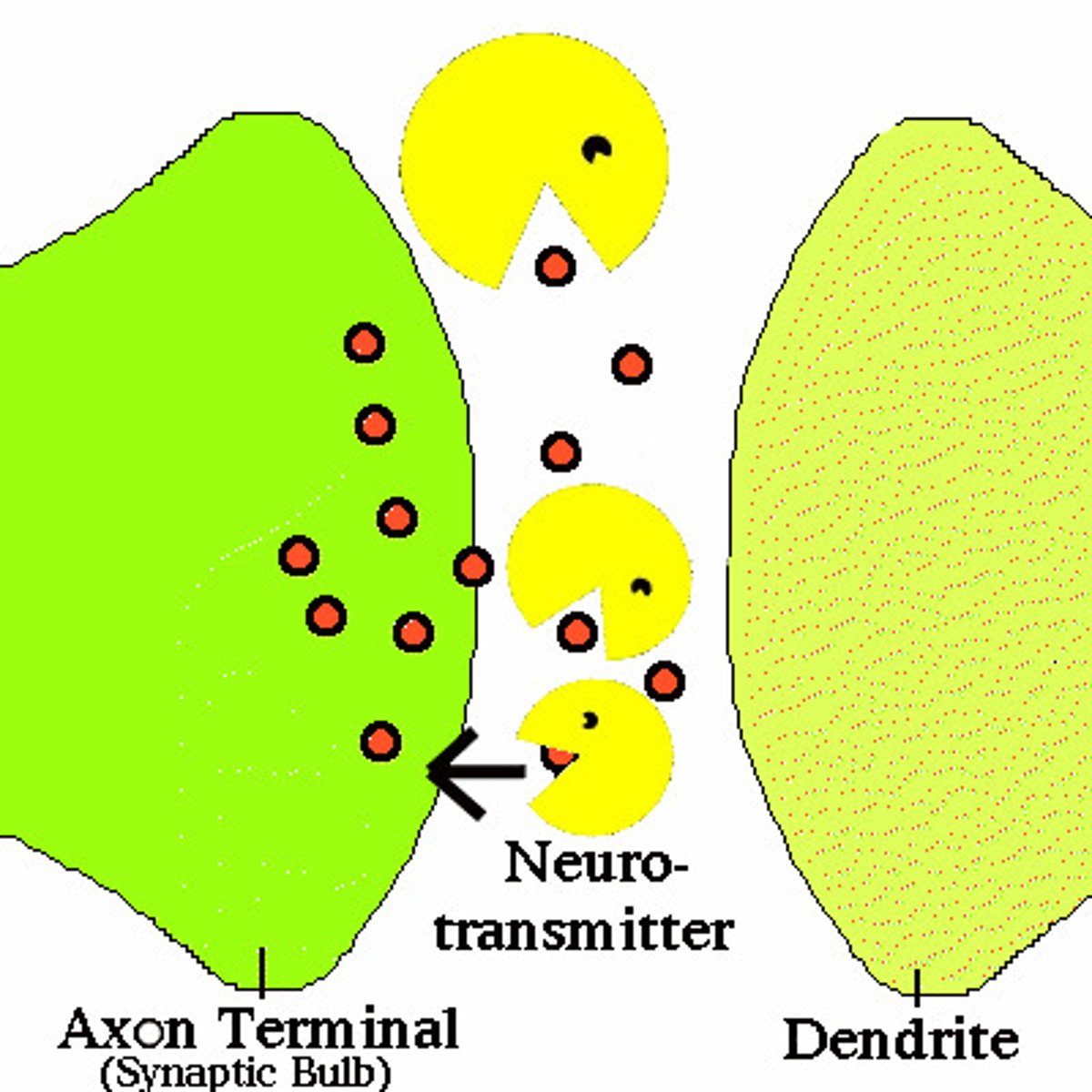
Neurotransmitters
chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons
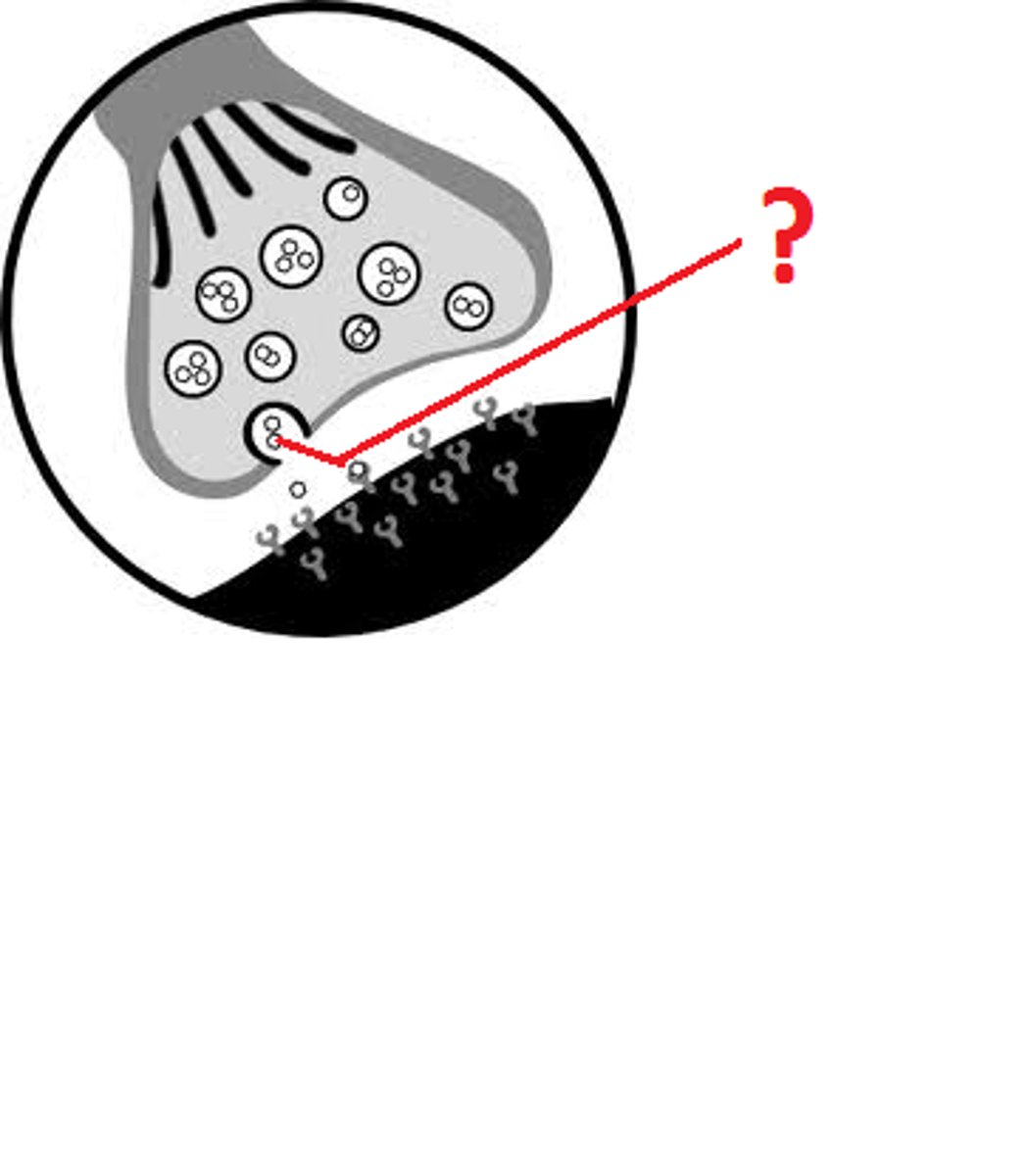
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
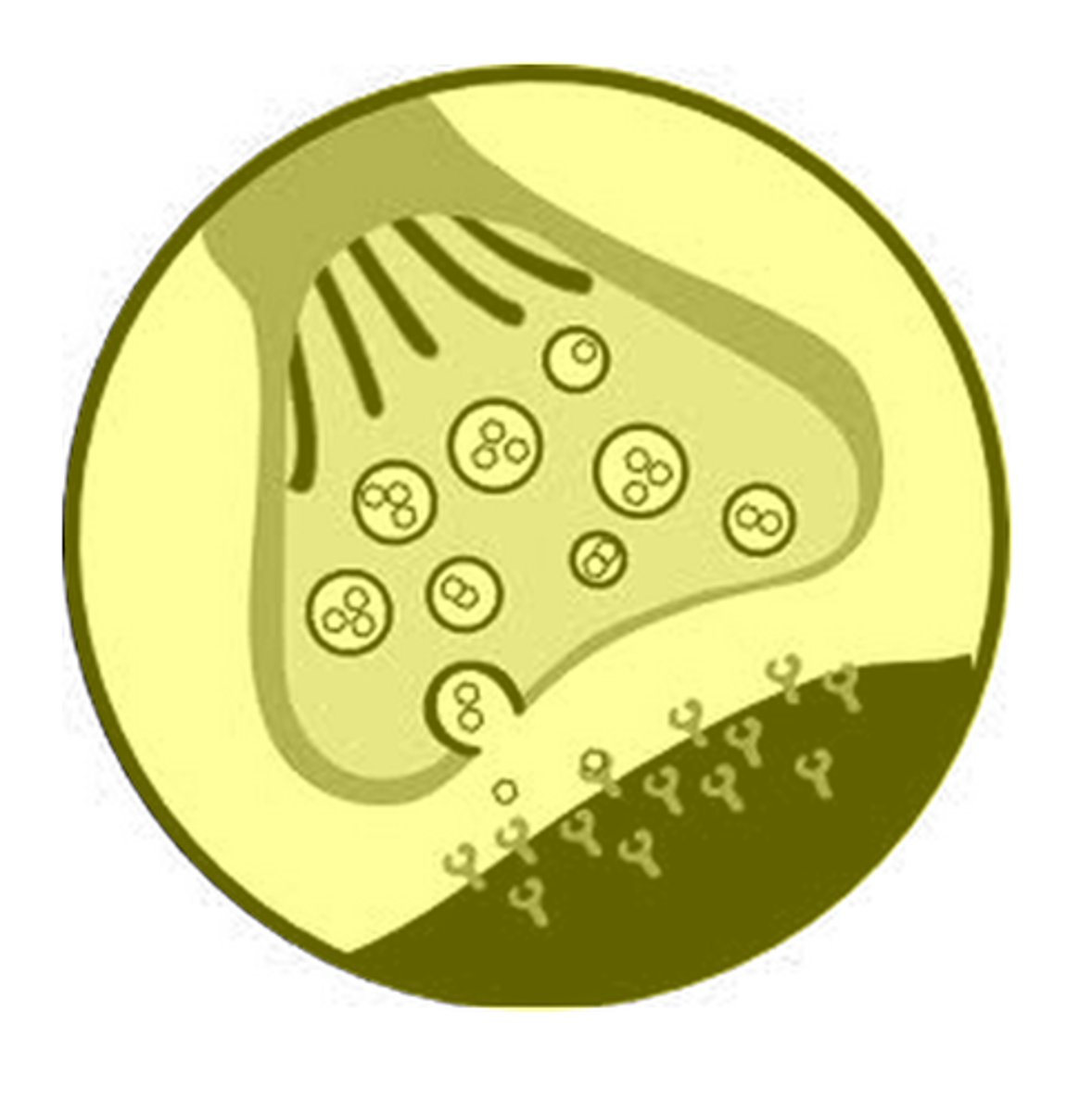
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse

action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
all-or-none principle
Refers to the fact that the action potential in the axon occurs either full-blown or not at all.
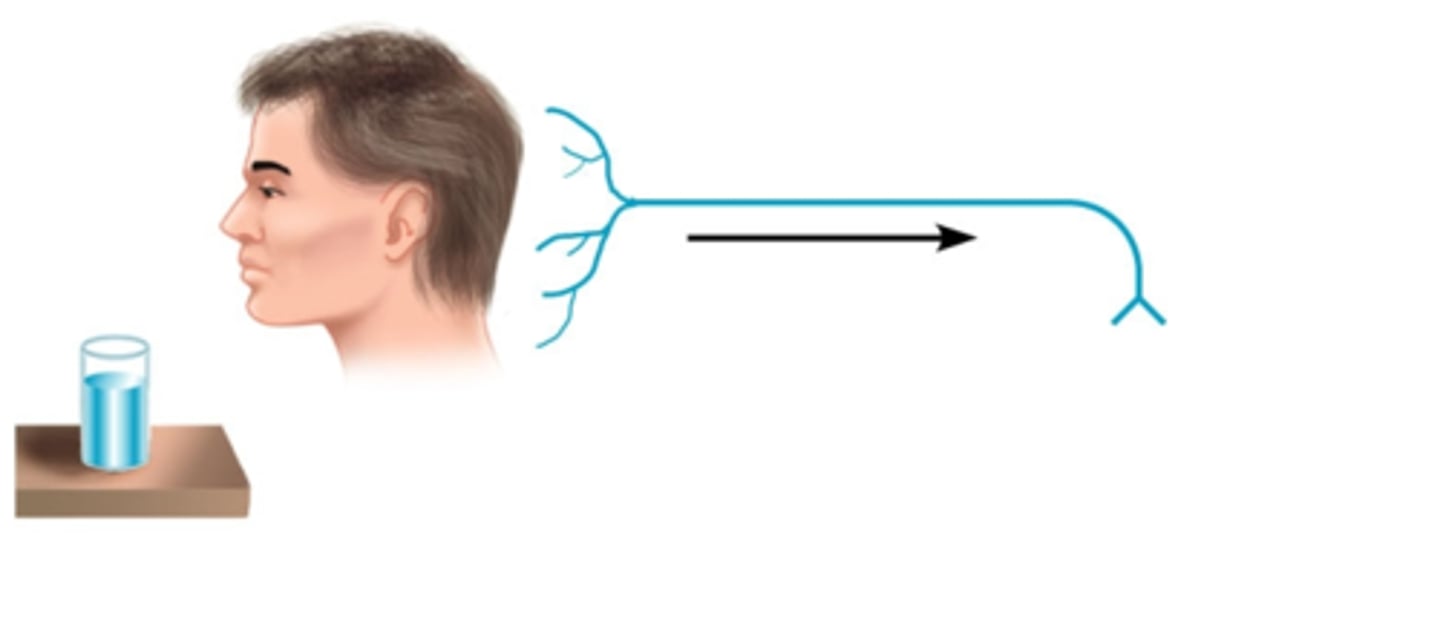
sensory neurons (afferent)
neurons that carry incoming information from the sight, touch, smell, taste, and hearing receptors to the brain and spinal cord
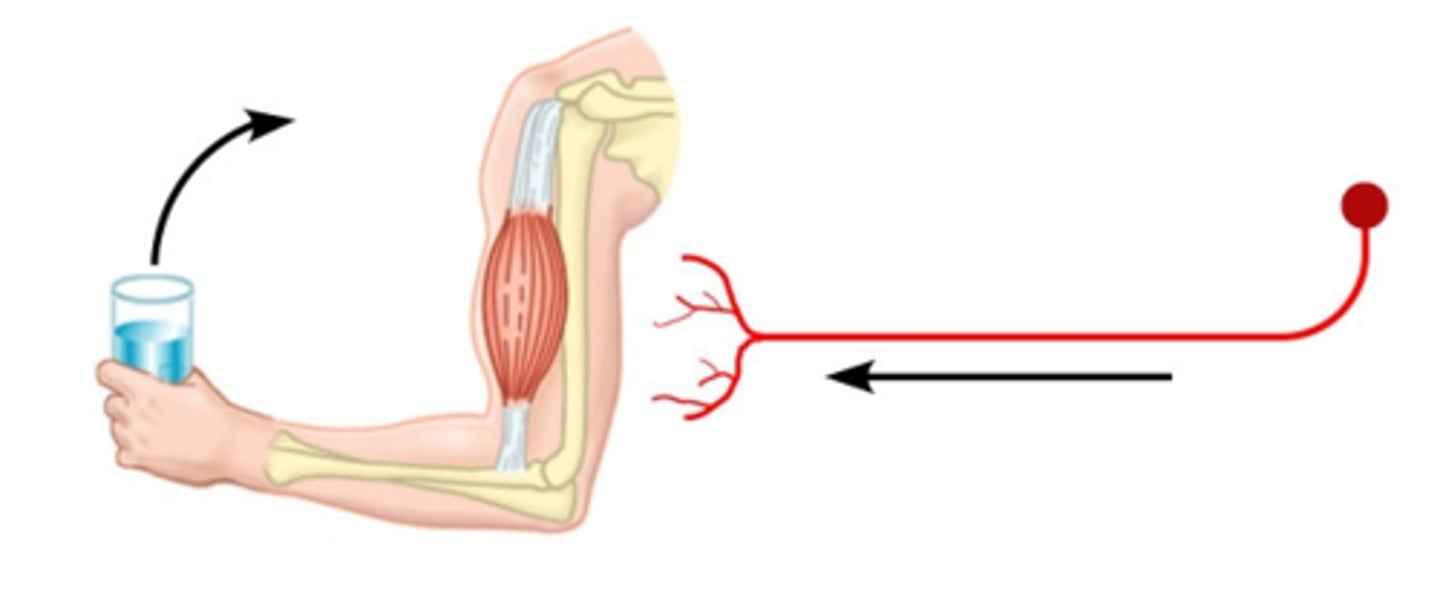
motor neurons (efferent)
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
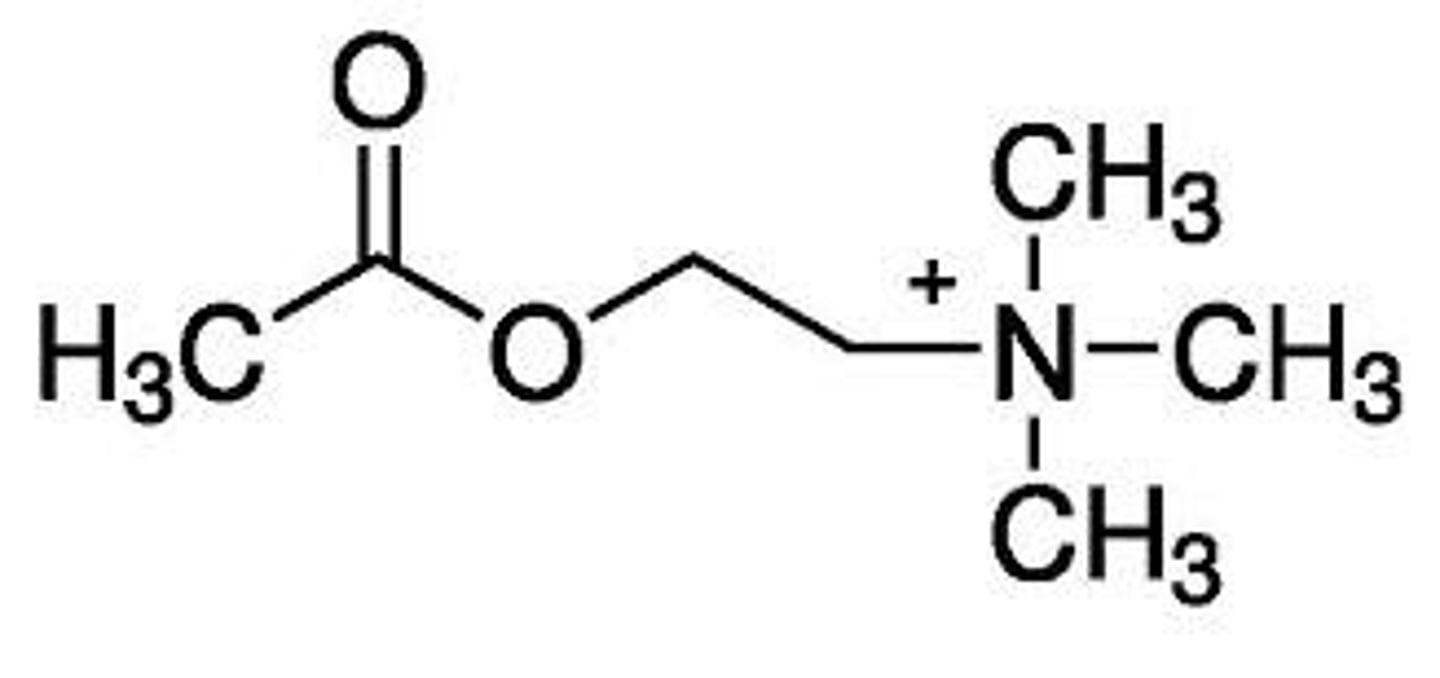
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction, and implicated in Alzheimer disease.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood. Too little may result in depression or agression.

Endorphins
Natural morphine system that affects good feelings, painkilling, control & pleasure. Also associated with the runners' high.
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. Also activates the reward pathway. Too much --> schizophrenia. Too little --> Tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson's disease.

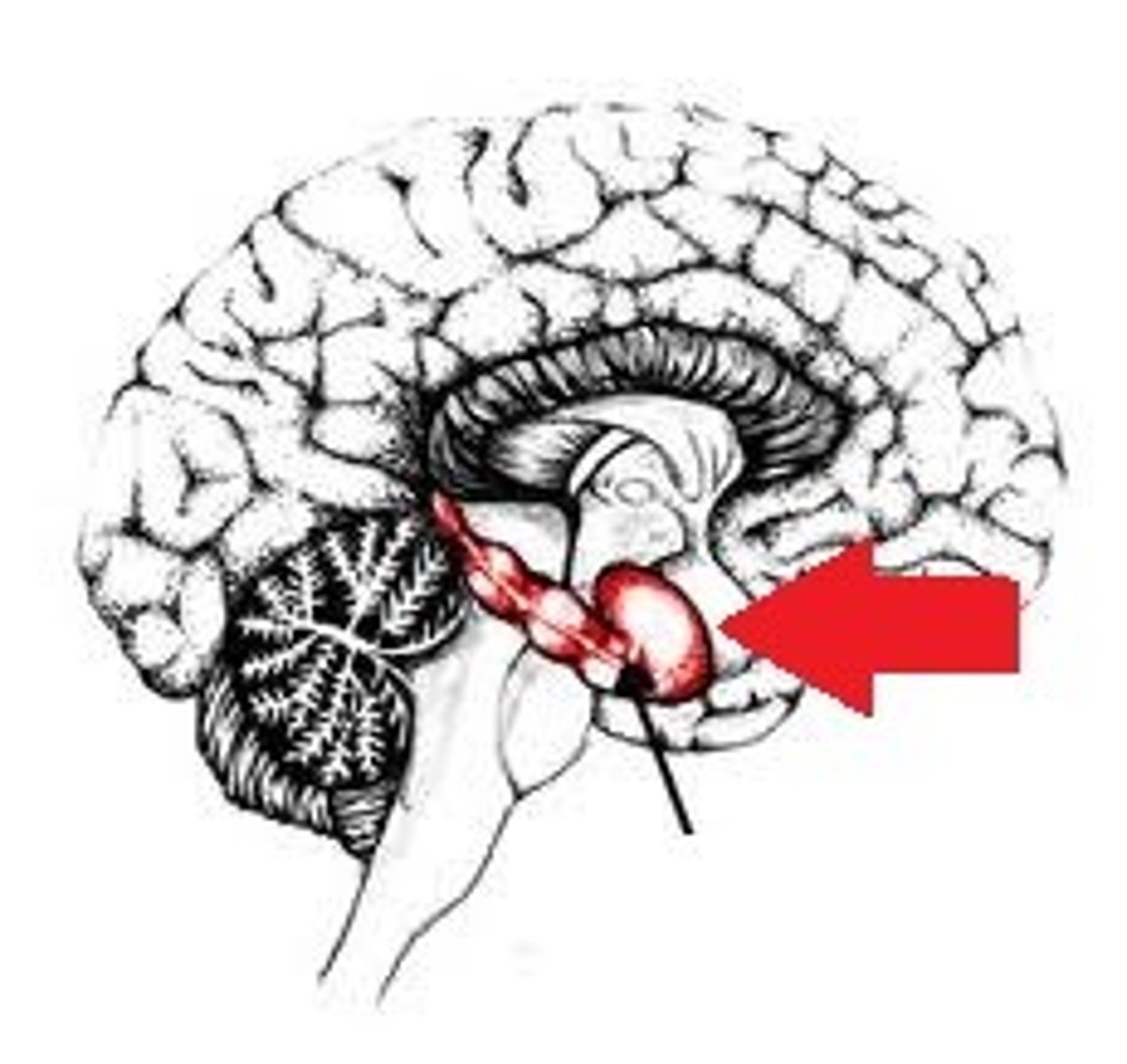
Hippocampus
The sea-horse shaped part of the limbic system involved in forming and retrieving memories, and declarative memory and learning.
cerebral cortex
Gray matter covering outside of cerebral hemispheres. Associated with higher cognitive functions like language, learning, perception, and planning.

frontal lobe
Concerned with motor and higher order executive functions
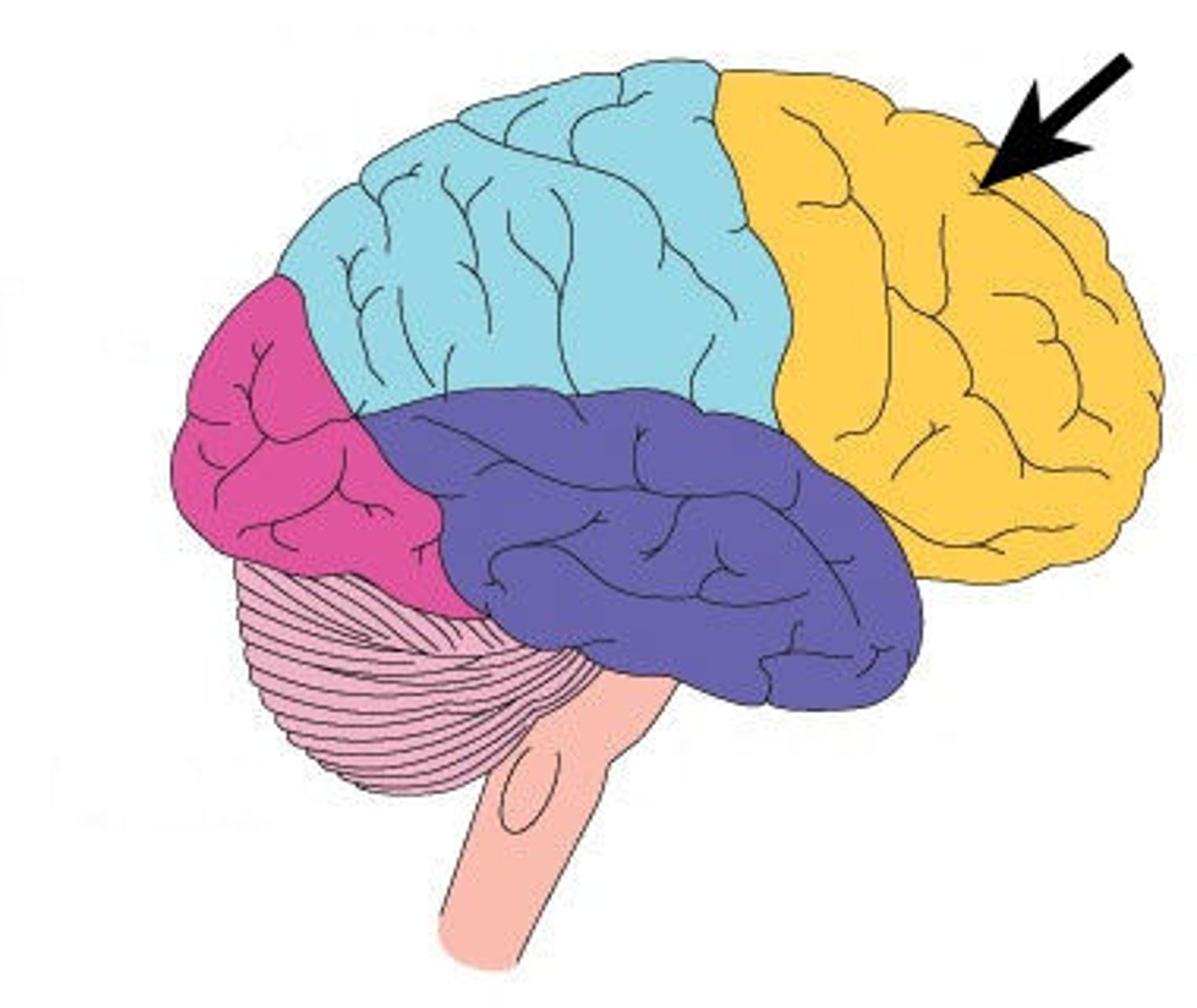
temporal lobe
Part of brain that has auditory projection and auditory association areas. and areas for higher order visual processing.
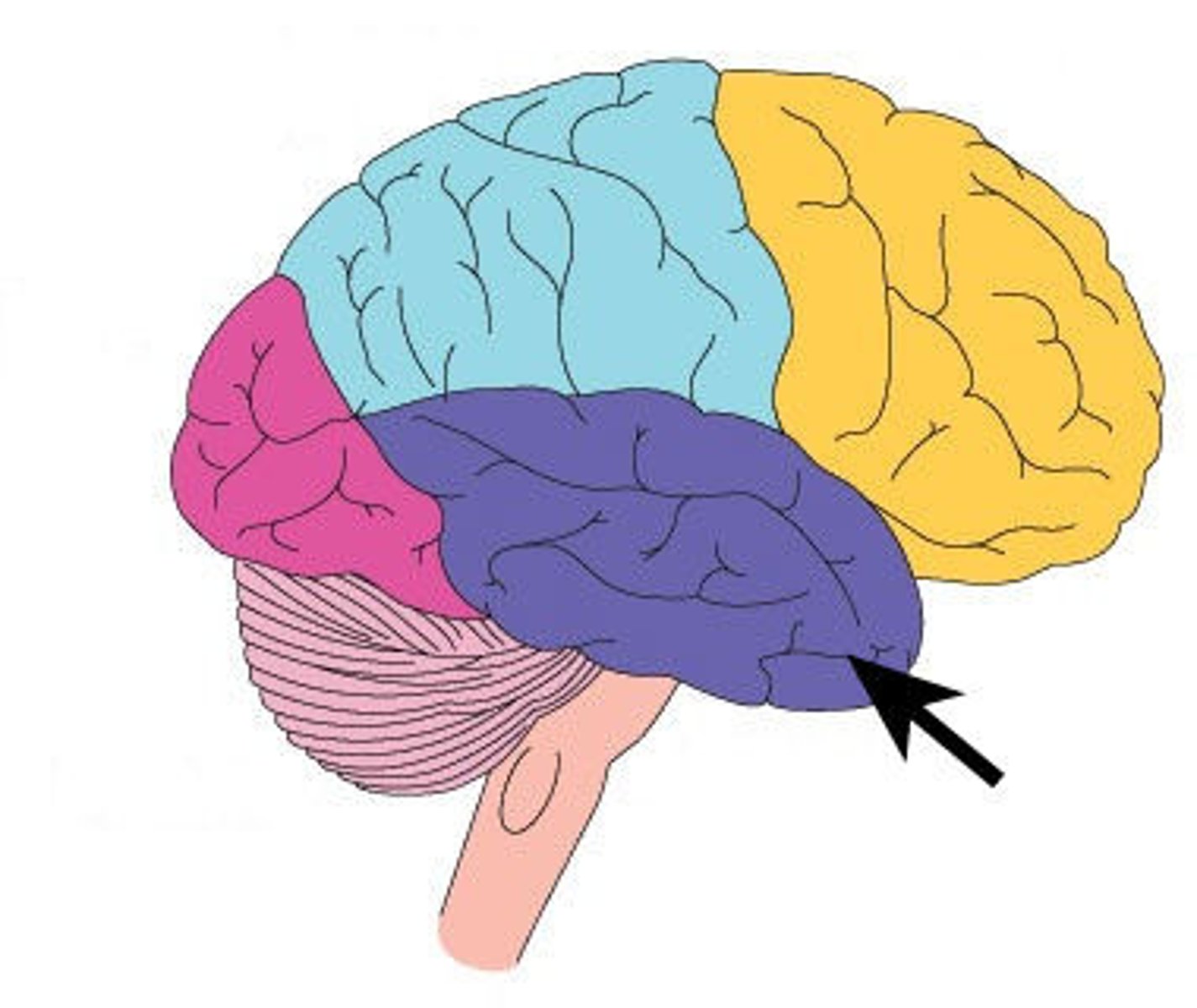
Wernicke's area
controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
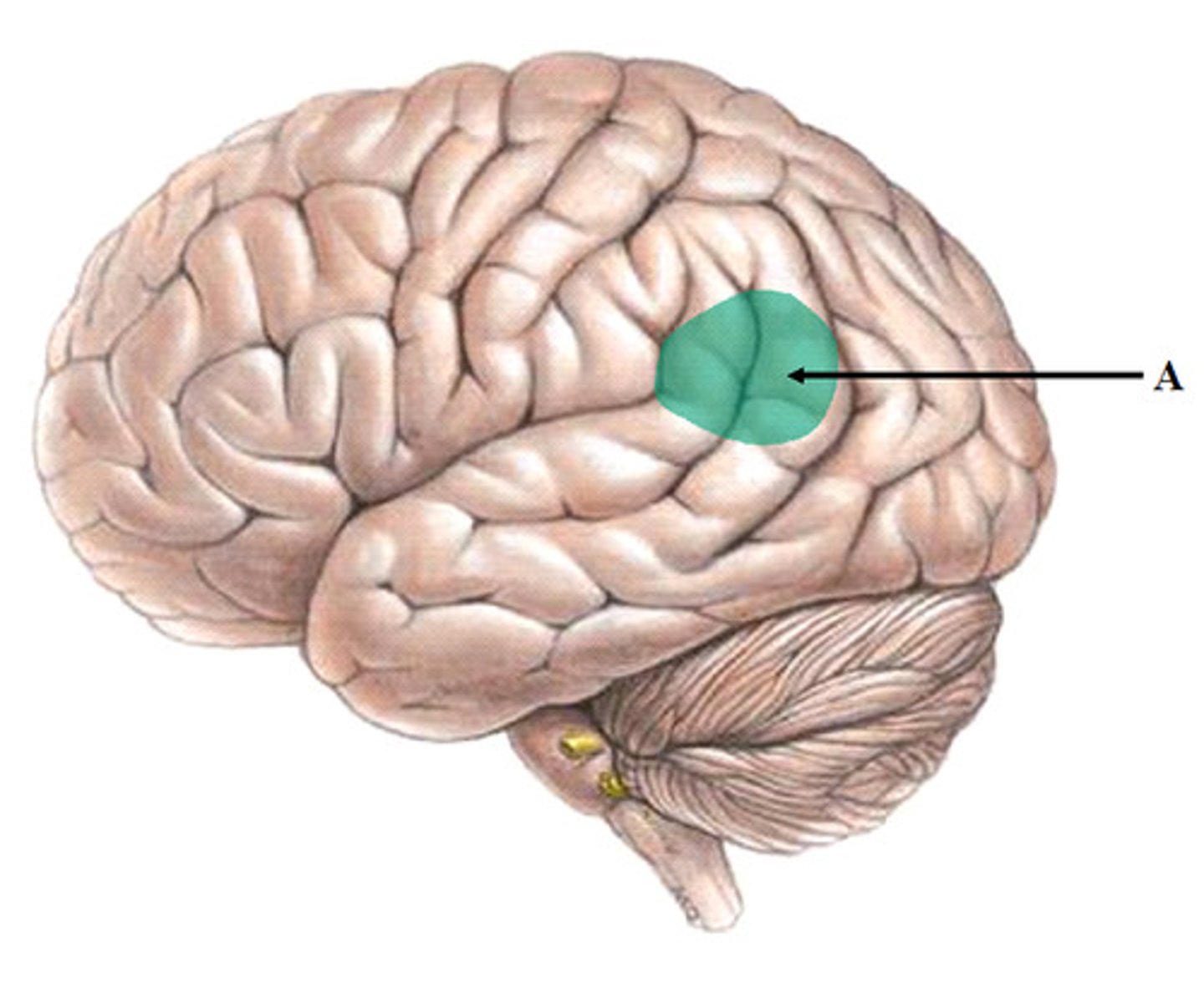
somatic nervous system
Voluntary muscle control. Comprises of sensory and motor neurons that supply the sense organs and skeletal muscles.
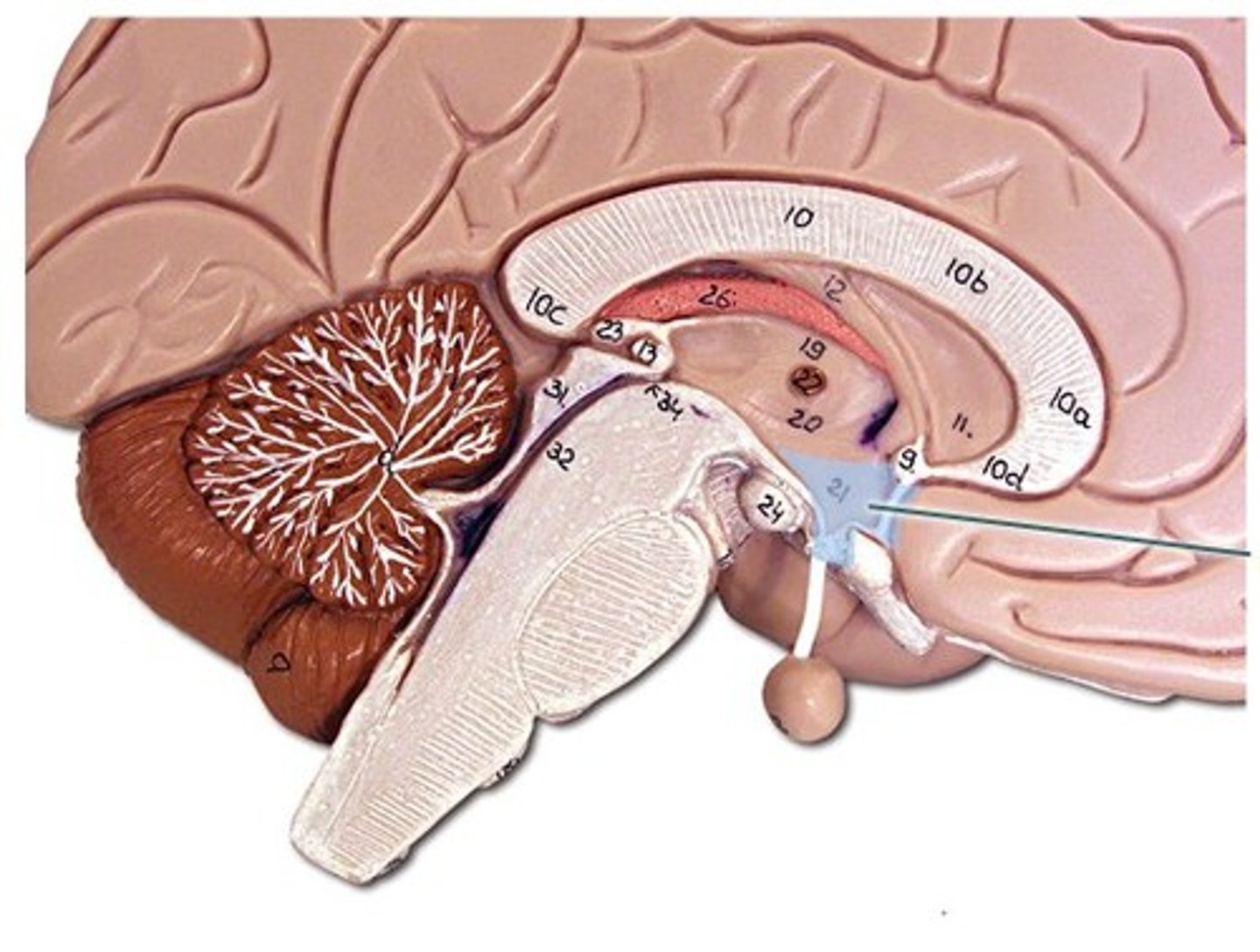
Hypothalamus
Primary control of autonomic functions ( appetite, thirst, sleep, sexuality, heart rate, etc.) Regulates survival behaviors such as eating, drinking, and sleep-wake cycle.
sympathetic nervous system
acts as an integrated whole in affecting a large number of smooth muscle systems. Simultaneously, usually in service of enhancing fight or flight response (dilate pupils, reduce intestine activity, etc)

parasympathetic nervous system
control rest, repair, enjoyment, eating, sleeping, sex activity, social dominance, salivary secretions.

Lesions
damage to normal structure of organ or any part of the organ.
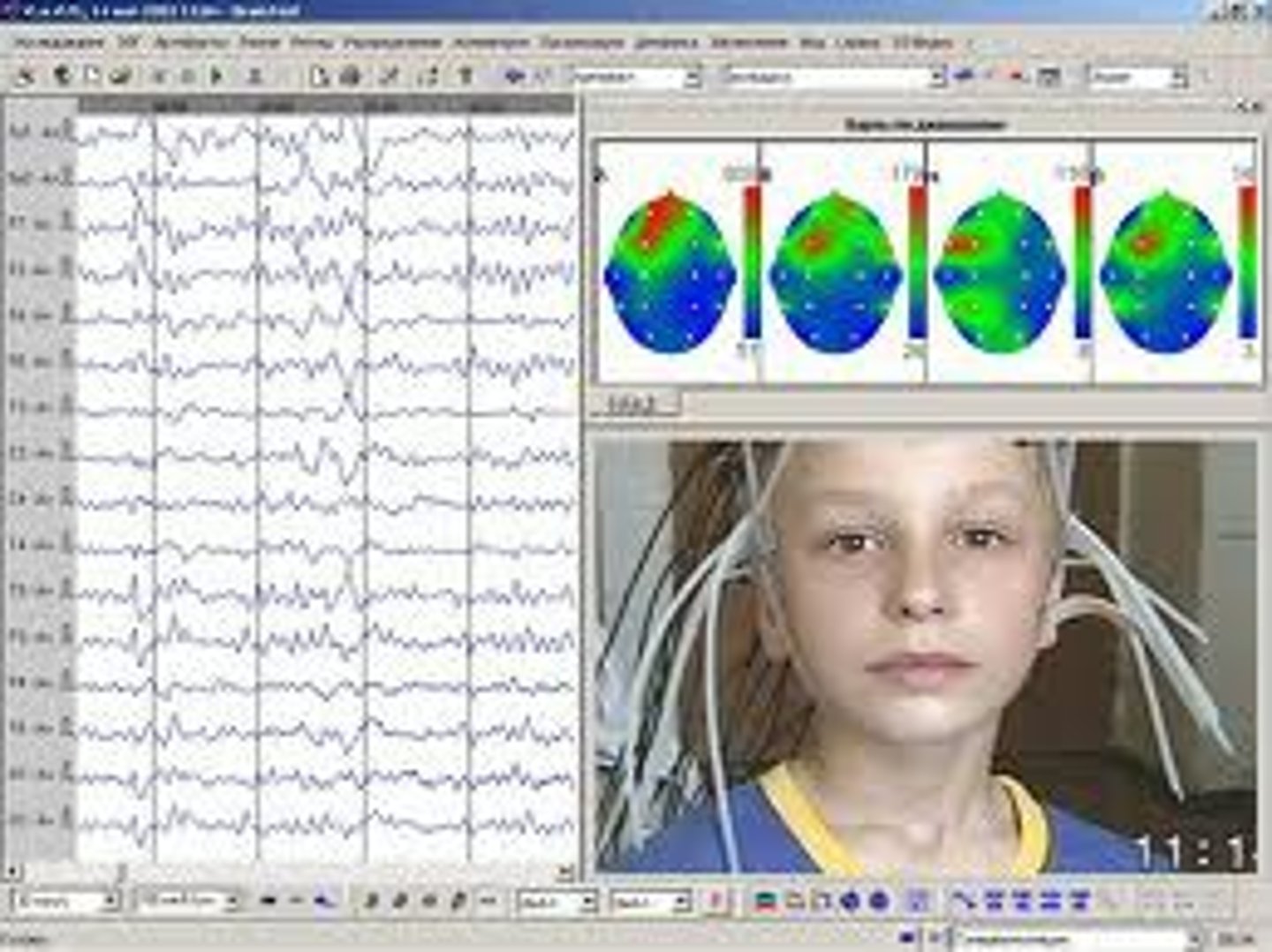
EEG
study brainwaves by amplifying and recording electrical activity through electrodes. Used to study sleep, depth of anesthesia, and diagnose epilepsy.
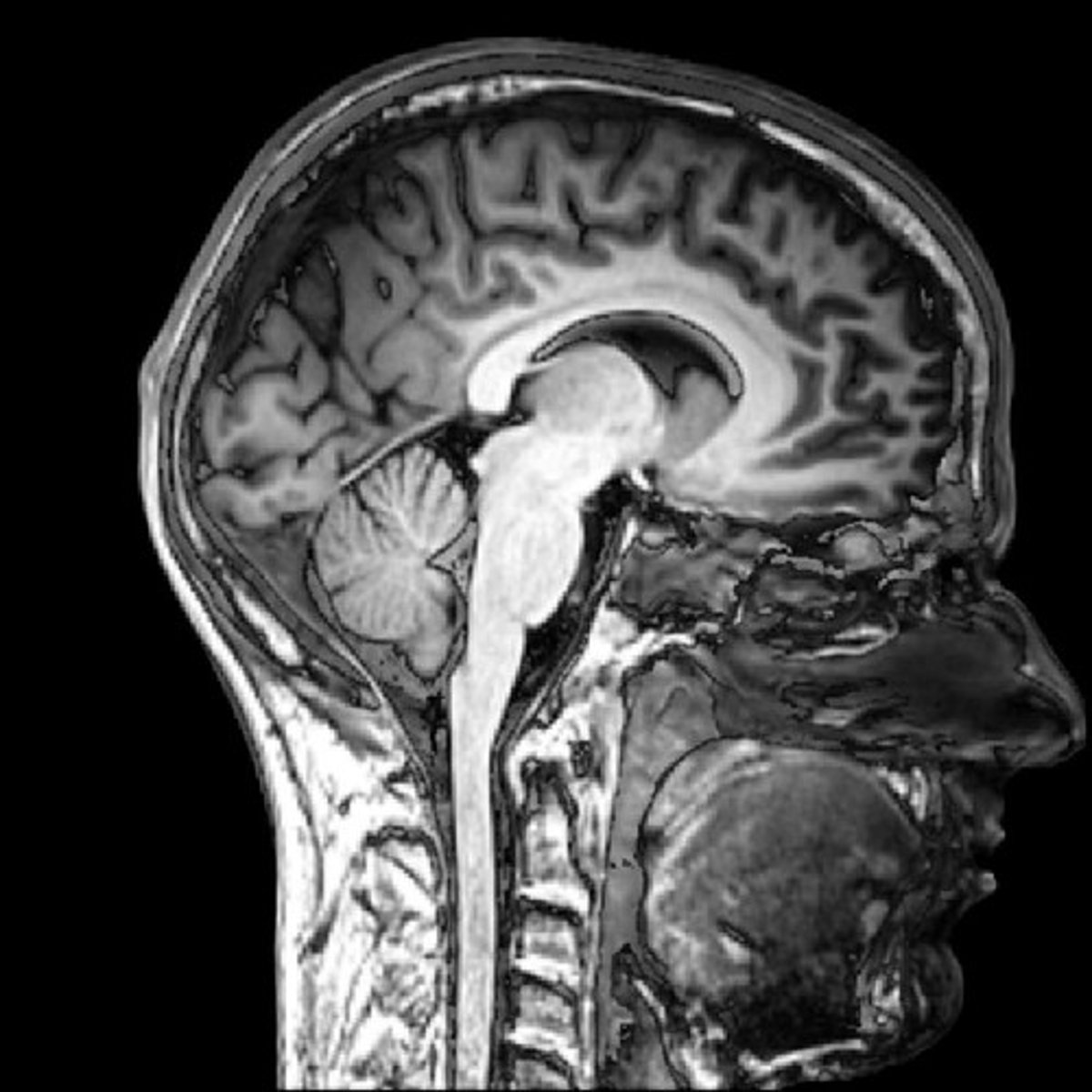
MRI
Uses the response of hydrogen in tissue molecules to strong magnetic impulses to form a 3D picture of body organs and tissues.
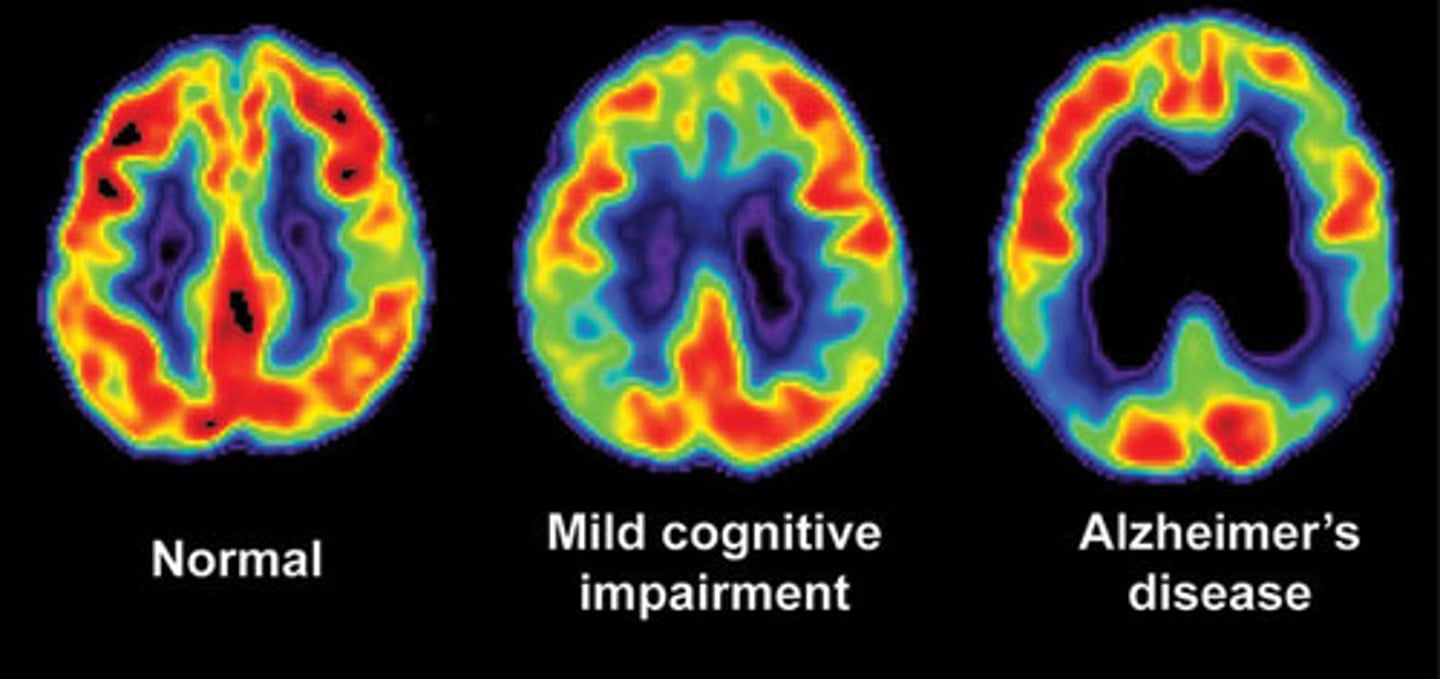
PET
Use radio-labeled tracers to document functional changes that occur during the performance of mental activities. Also Detect disease in other organs.
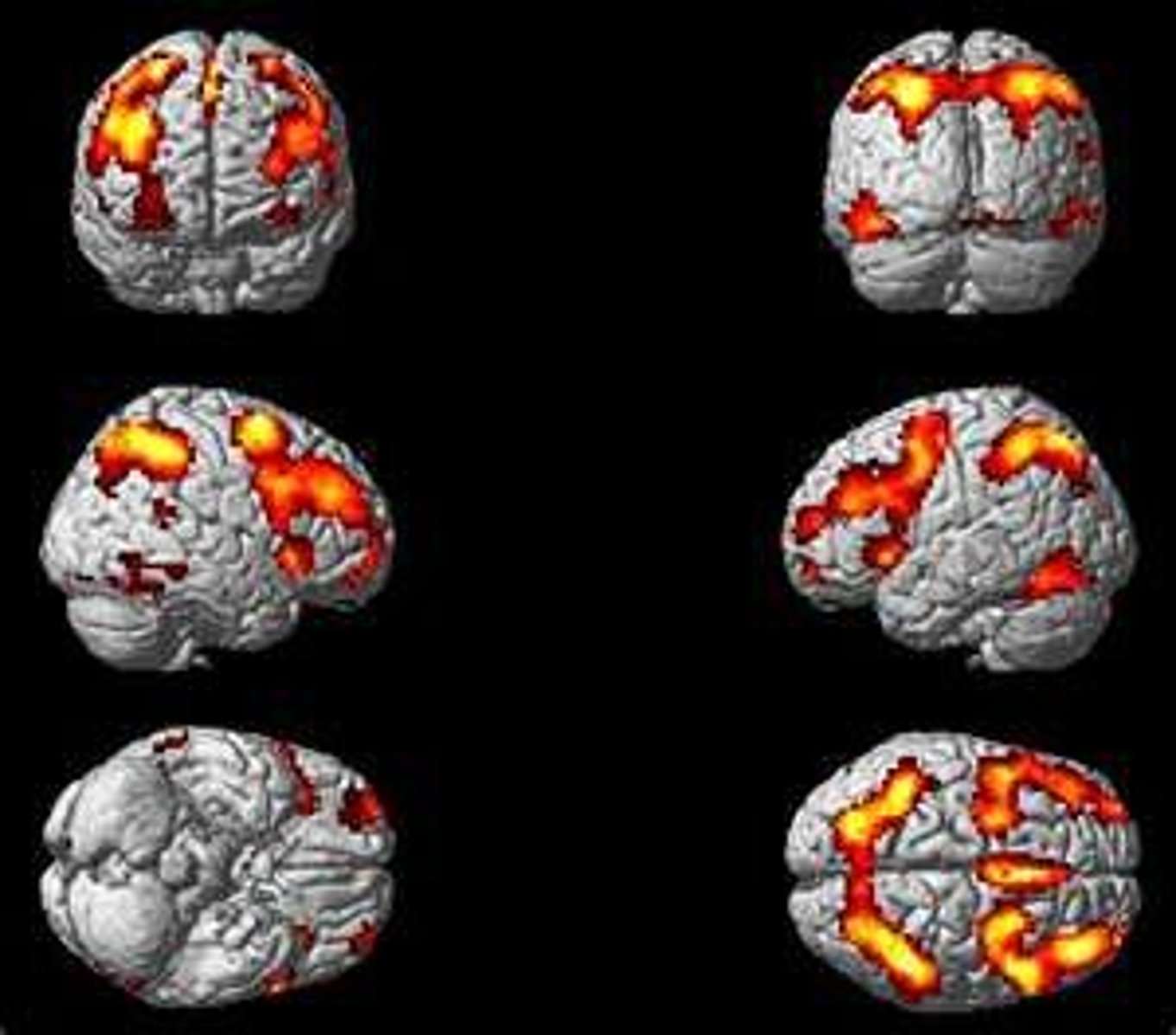
fMRI
Form of MRI that used to localize areas of activation based on correlation of brain activity and blood property changes.
CAT
radiographic technique used to quickly produce 3D images of the brain. X-Ray beam passed through tissue layer-by-layer, slice-by-slice. Can locate abnormalities without exploratory surgery.

Brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain; it is responsible for automatic survival functions like digestion, and vegative functions.
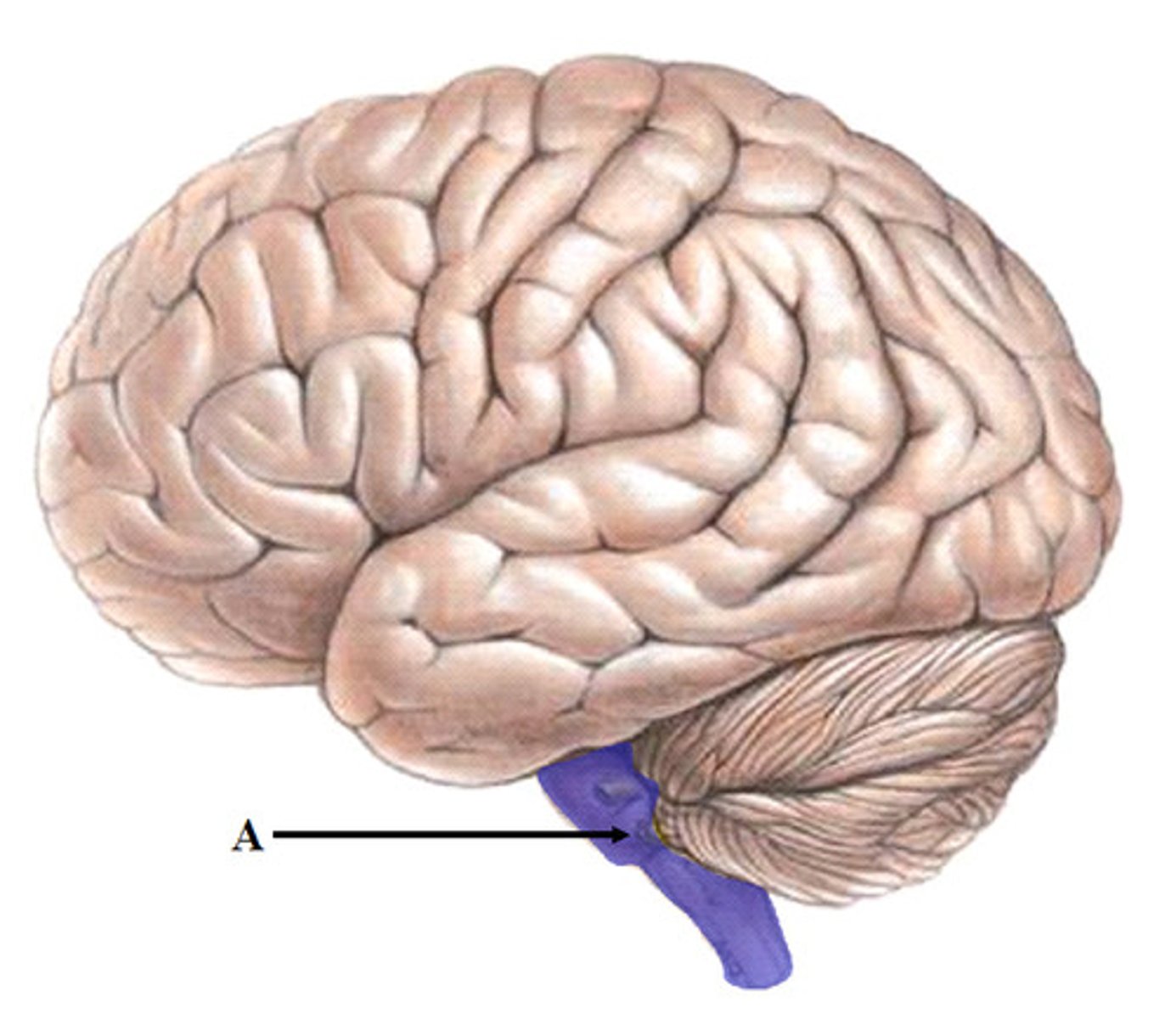
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
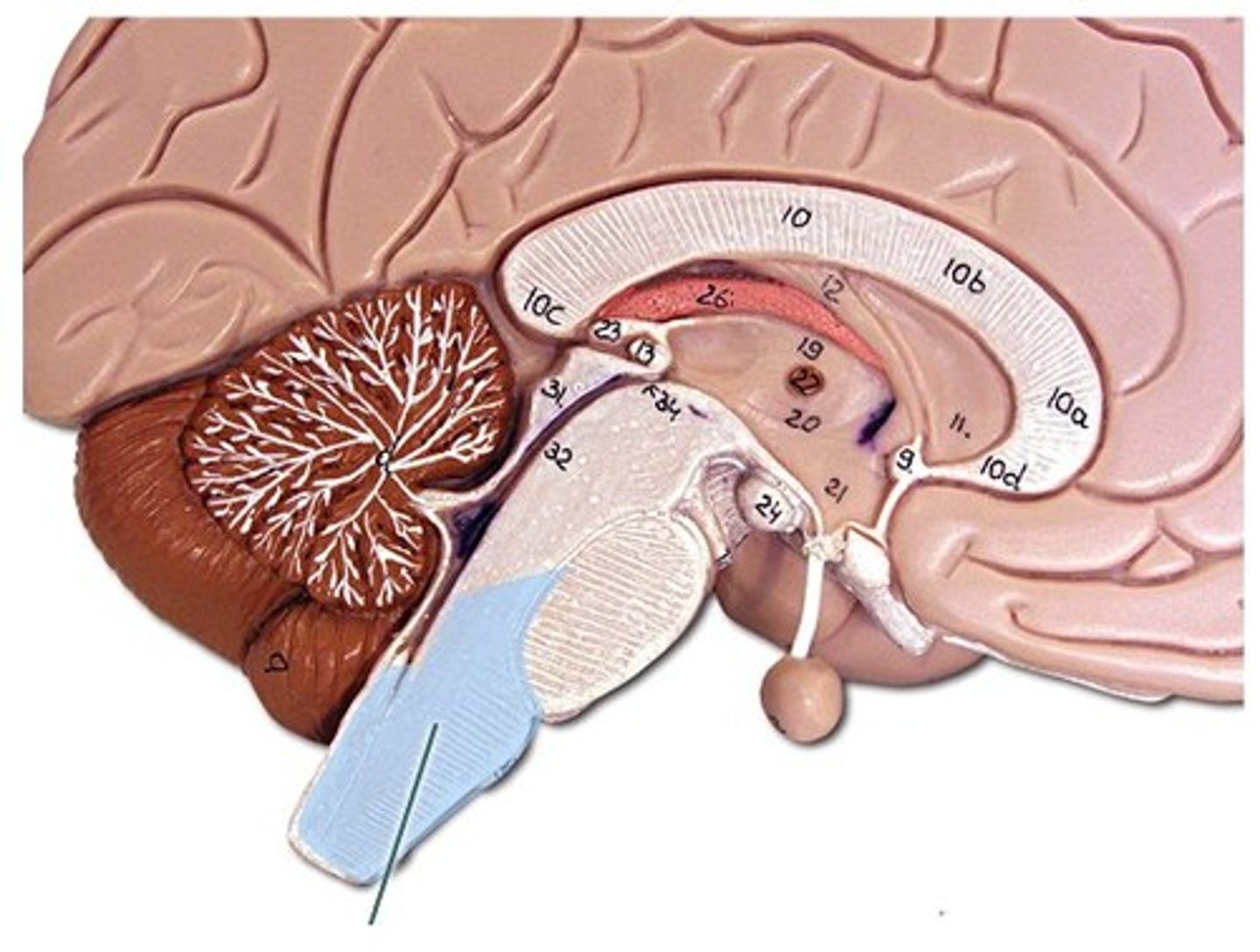
Pons
the part of the brainstem that links the medulla oblongata and the thalamus; serves as a bridge or transmission structure between different areas of the nervous system. Wants to control equilibrium. Responsible for sleep and arousal.
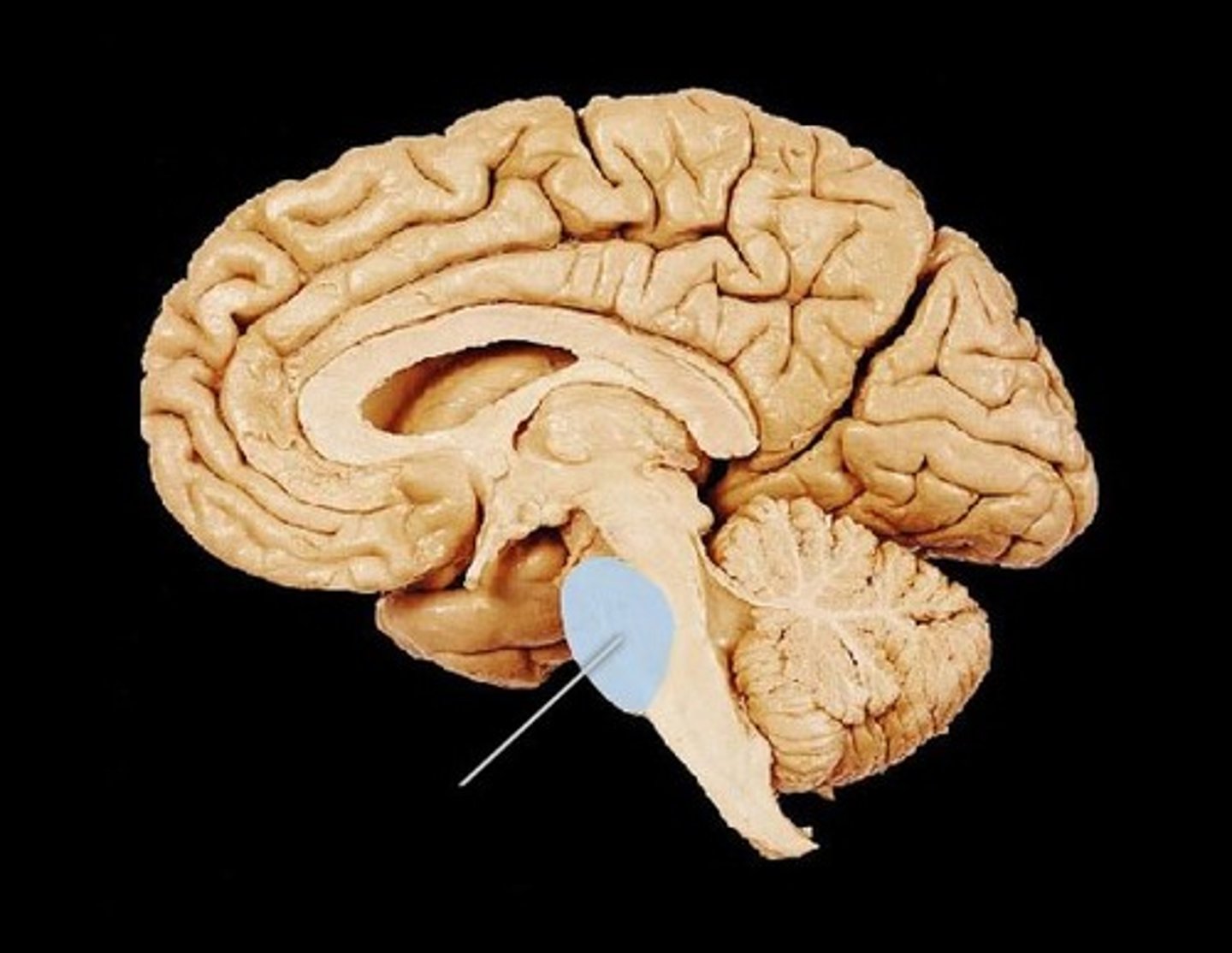
Cerebellum
Portion of hindbrain that modulates muscular contractions to produce smooth and accurately timed ballistic movements. Also helps maintain equilibrium.
glial cells
support, nourish, and protect neurons
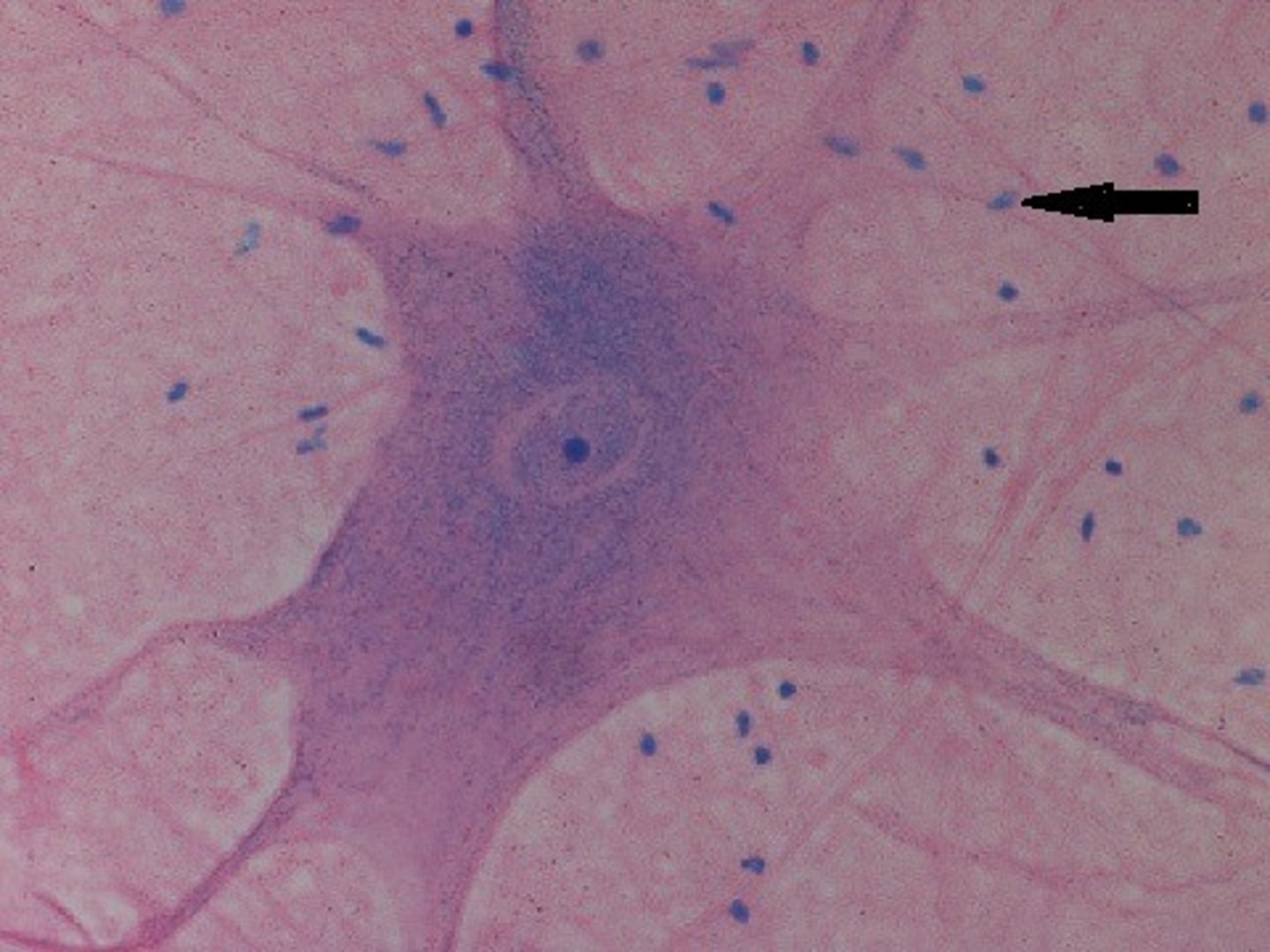
reticular formation
extensive network of nerve cell bodies, and fivers that connected to spinal cord and involved in arousal, alertness, and sleep. If damaged may result in coma.
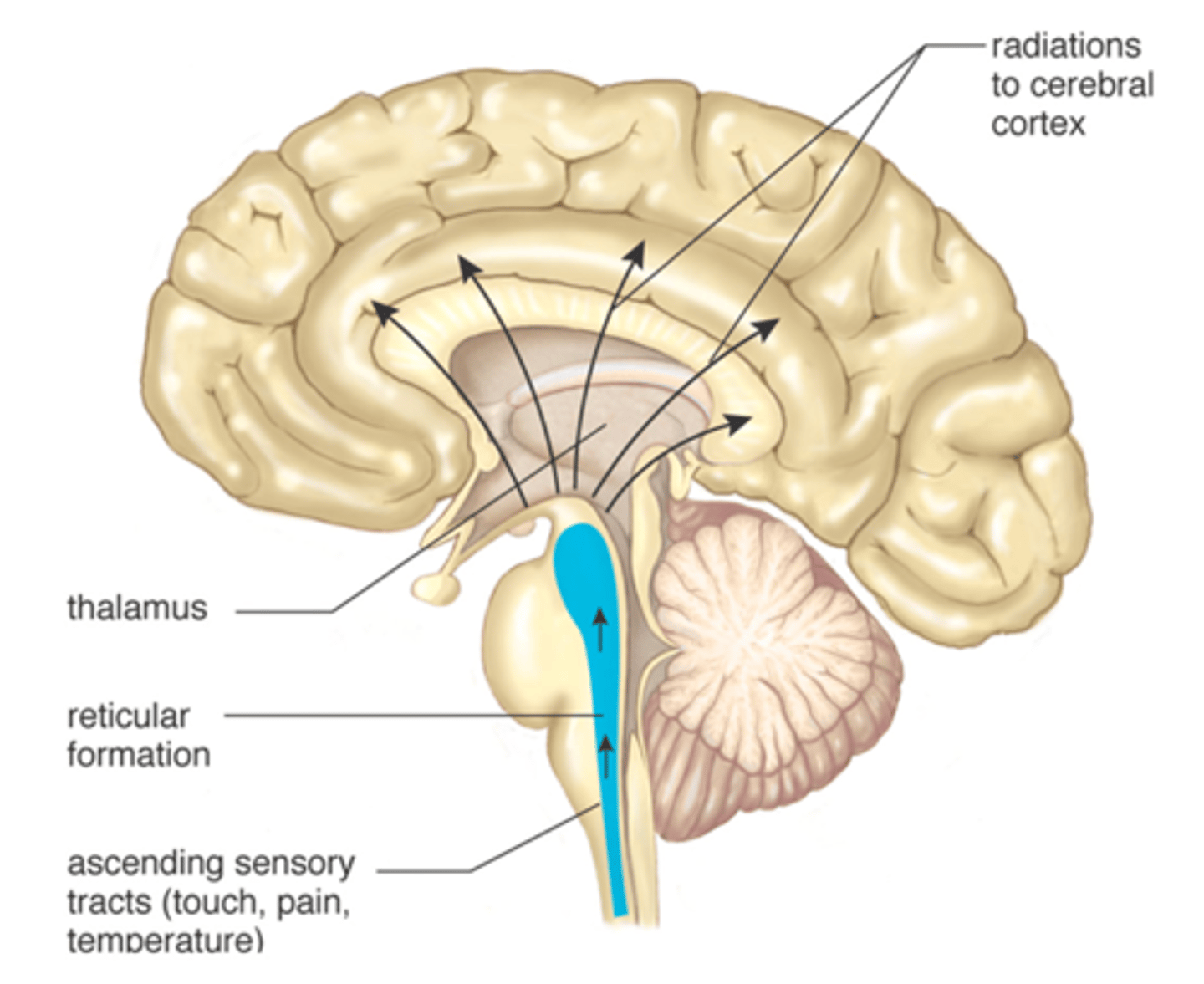
Thalamus
mass of gray matter that consists of sensory, motor, and autonomic, and associated nuclei. Serves as relay for nerve impulses.
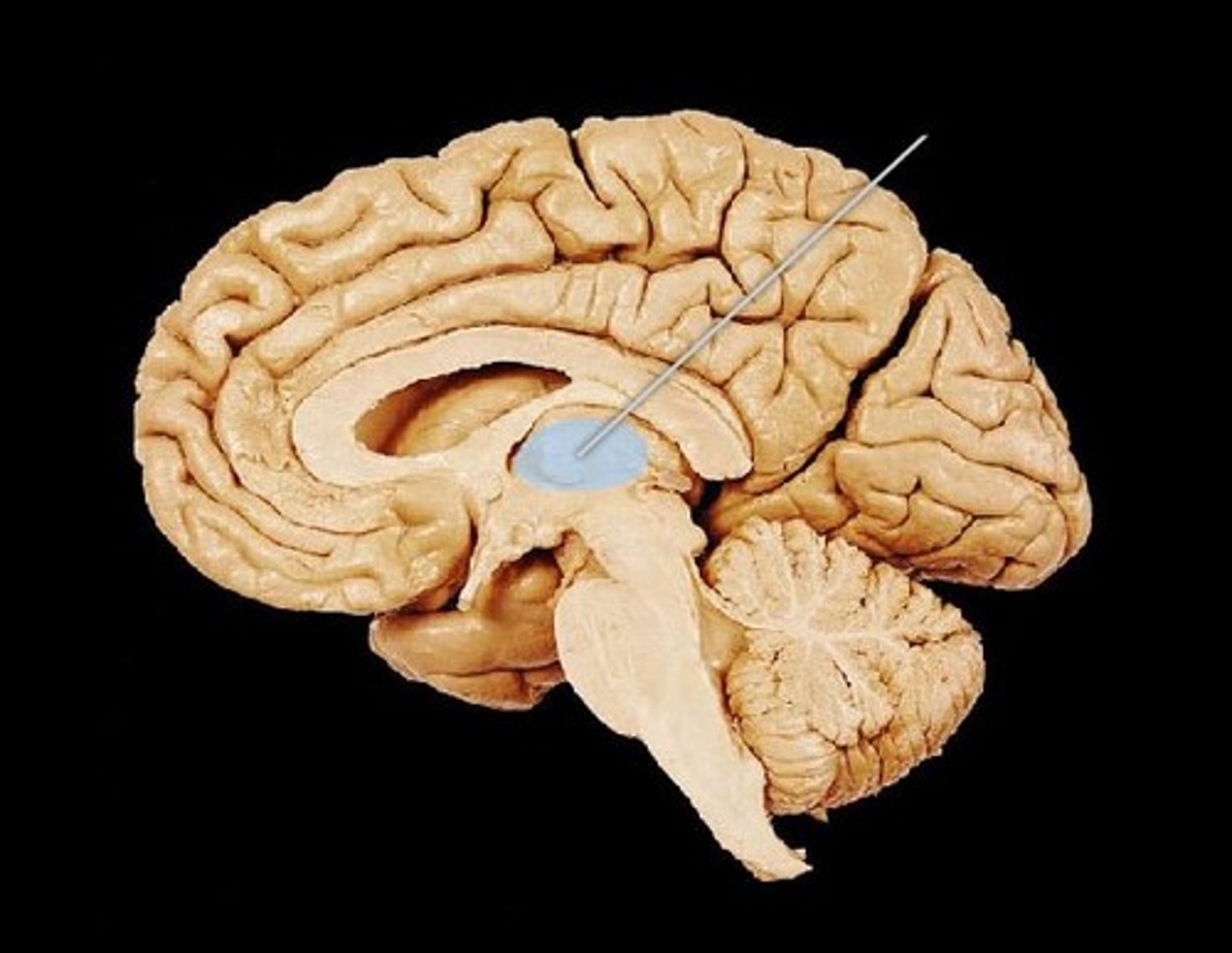
corpus callosum
large tract of nerve fibers running across the longitudinal fissure of the brain, that connects the cerebral hemmispheres.
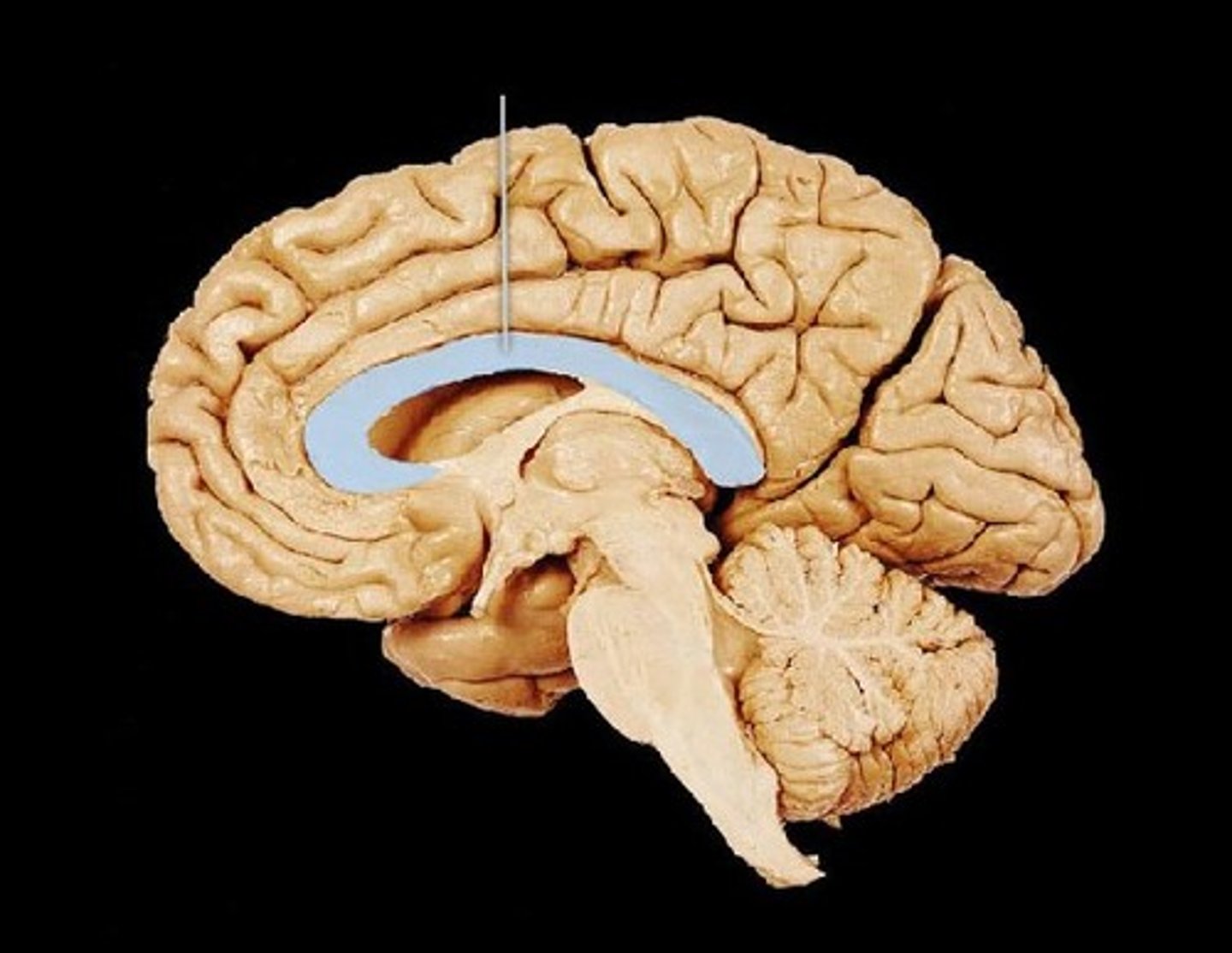
occiptal lobe
posterior subdivision of each cerebral hemisphere. Sort of pyramid and contains several visual areas to process visual stimuli. Portion of it is crucial to face recognition.
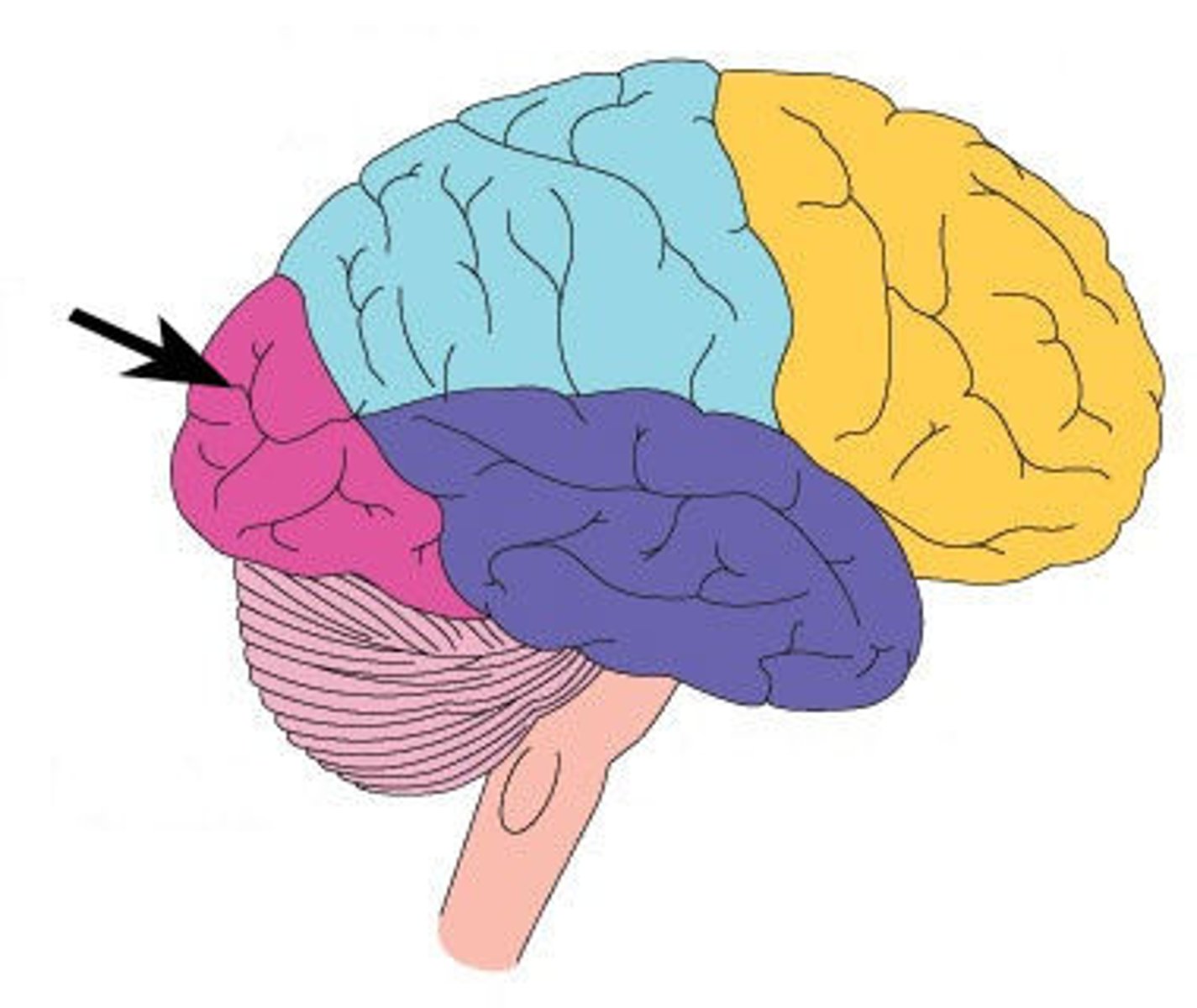
parietal lobe
Participates in sematosensory activities like discrimination of size, shape, and texture of objects.
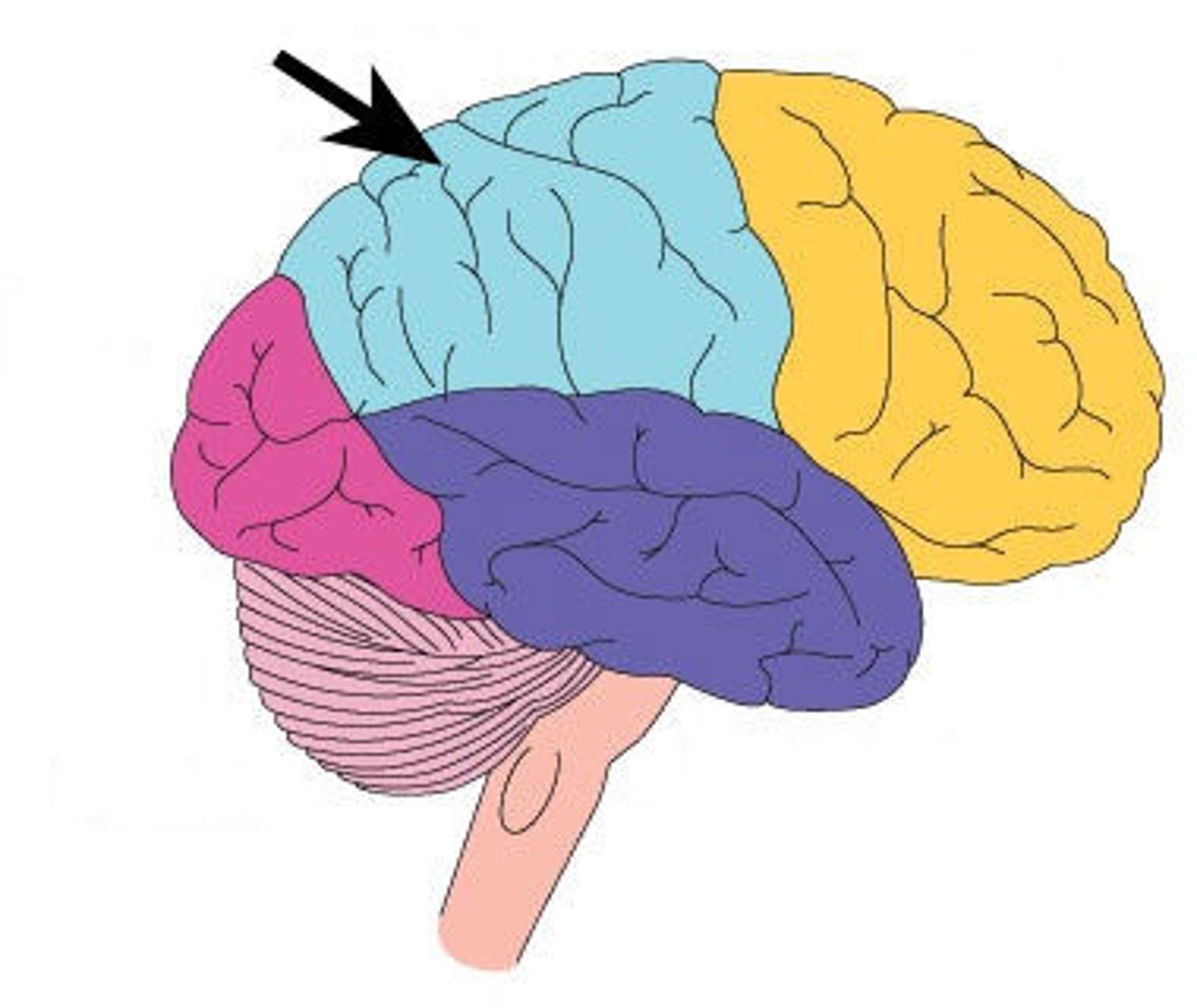
Broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
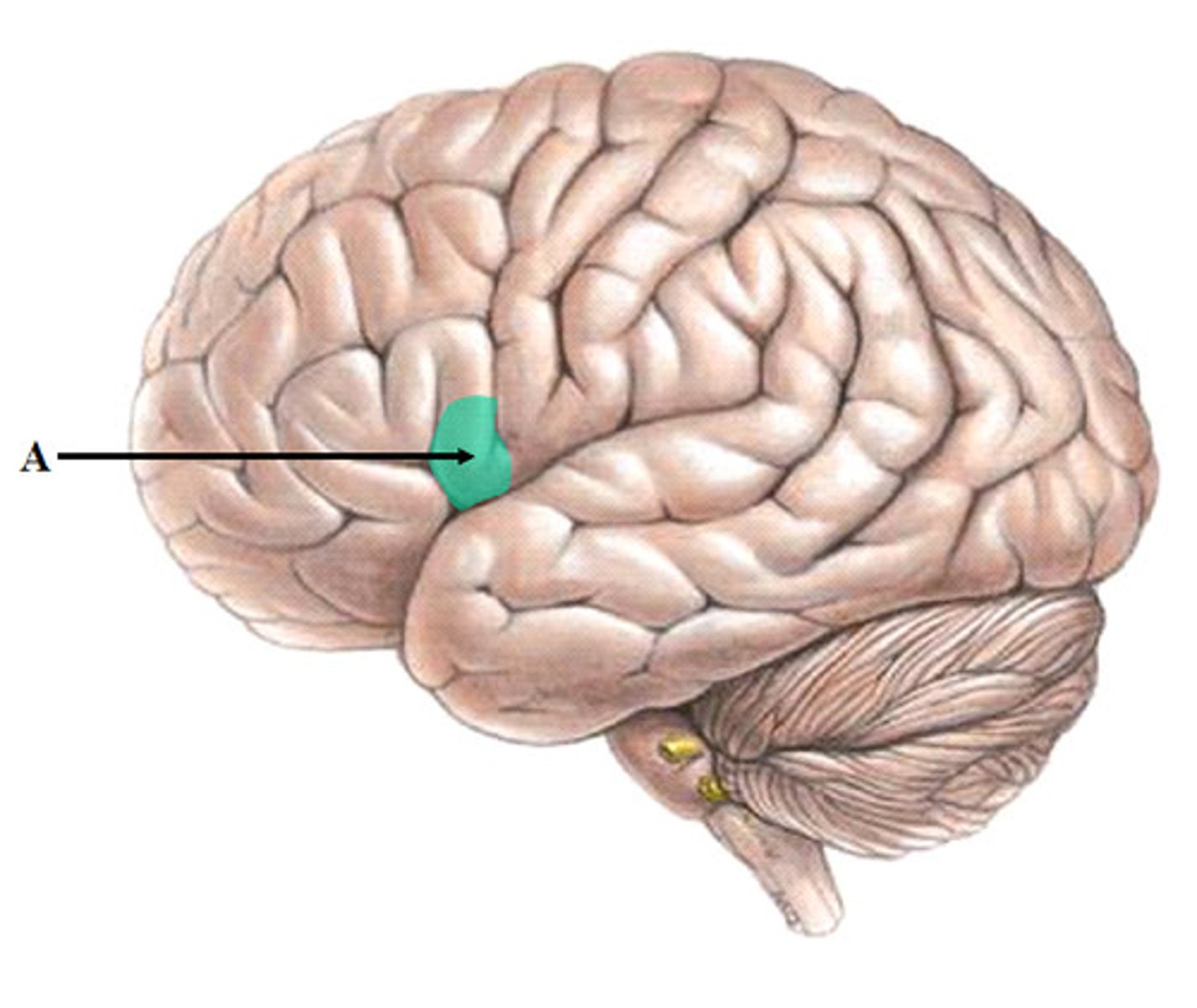
Plasticity
Because the nervous system is ___ it can learn and register new experiences.

aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke's area (impairing understanding).
reuptake
process by which neurotransmitters are taken back into the synaptic vesicles
refactory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired. Must be repolarized and will only respond to stronger than normal stimulus.
agonist
A chemical that mimics the action of a neurotransmitter.
Antagonist
Drug that inhibits the action of another substance

nerve (network)
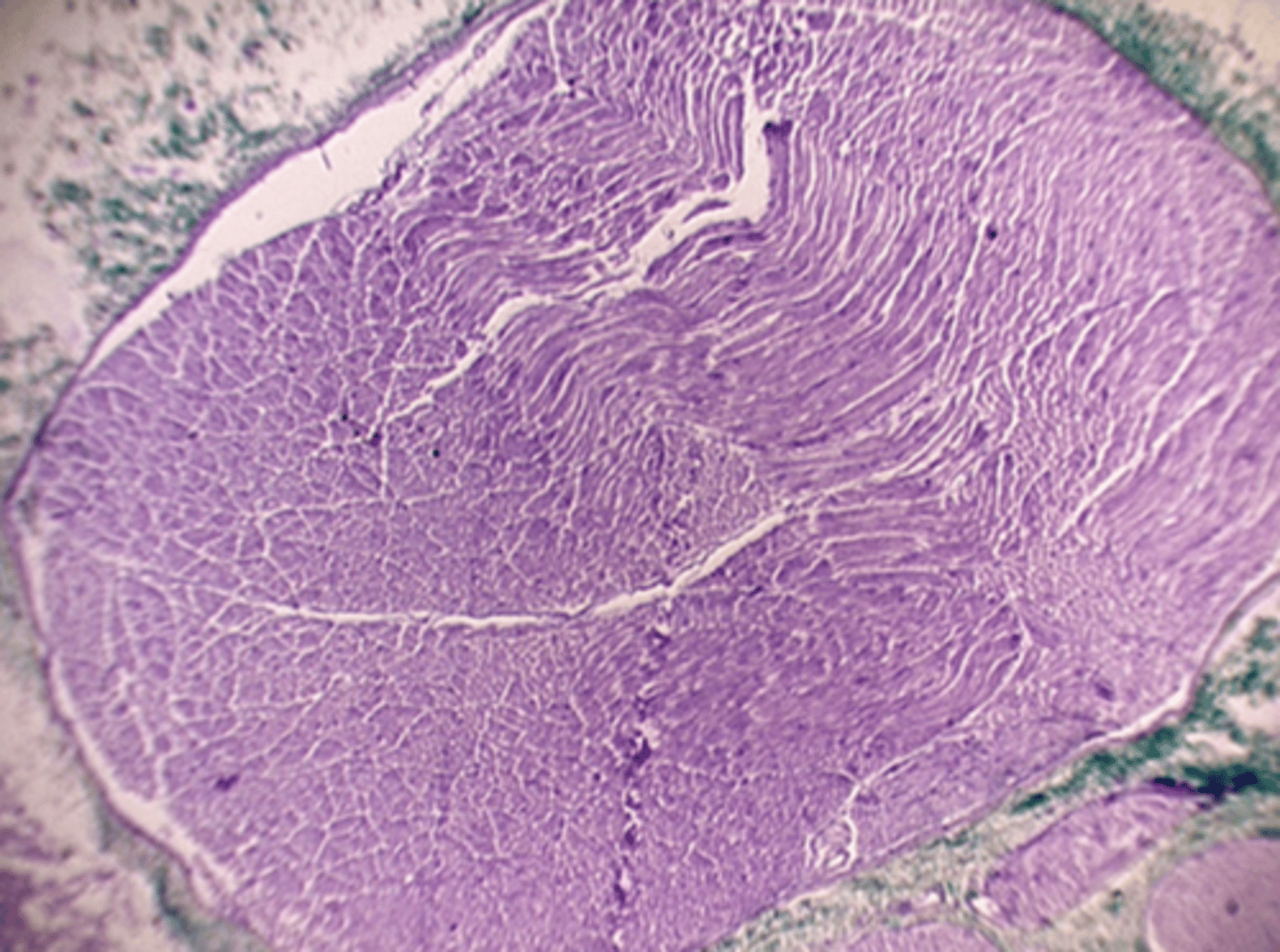
Bundle of axons outside CNS enclosed in a cord like structure.
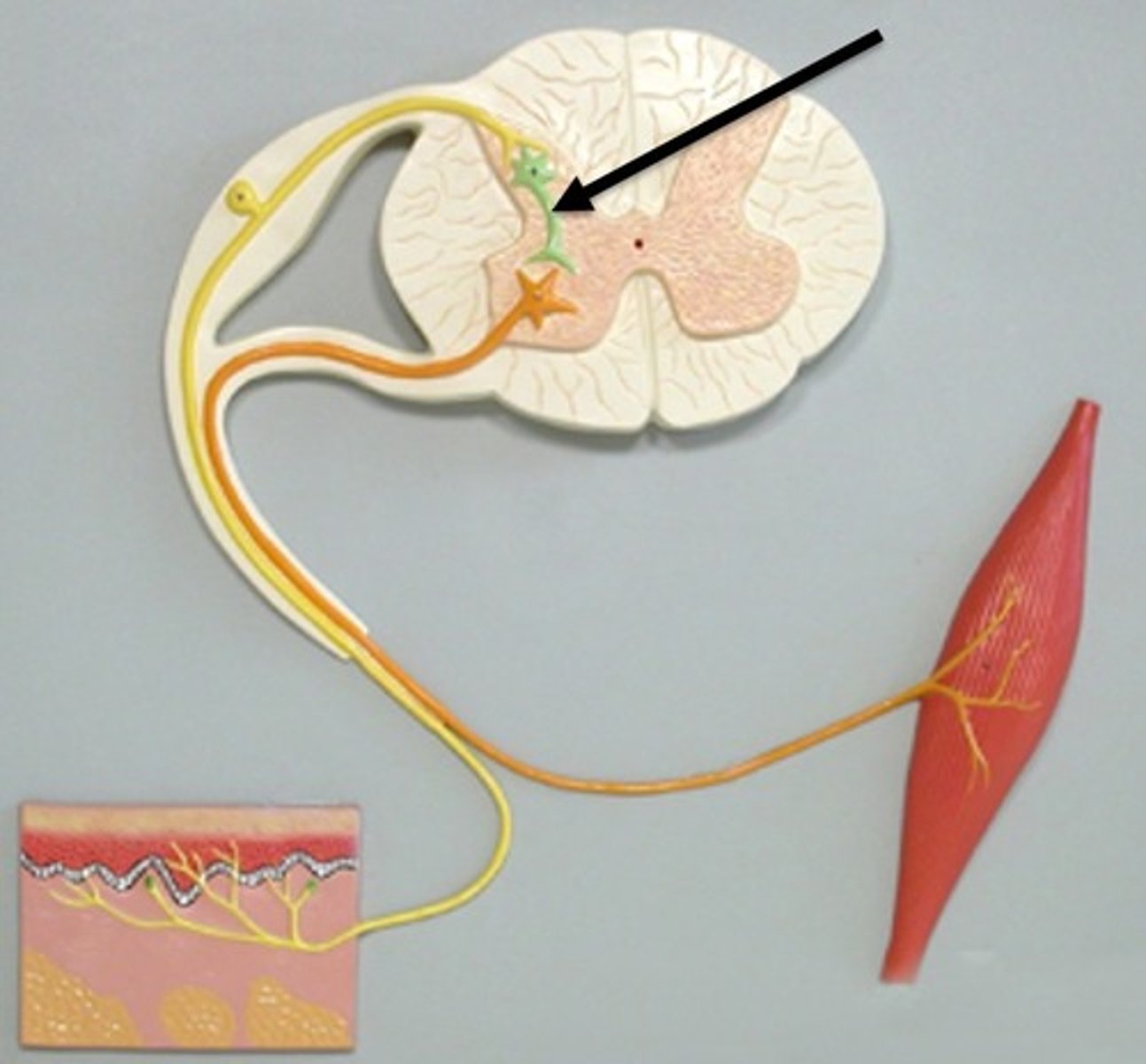
Interneurons
neurons that connect sensory neurons, motor neurons, or others of its kind.
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter that is tied to anxiety. Too little seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
Glutamate
Major excitatory neurotransmitter that is involved in memory. Too much-->over-stimulation to brain, produce migraines or seizures.

Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal The fight or flight system, and can act as a hormone in the endocrine system. Too little--> depress mood.

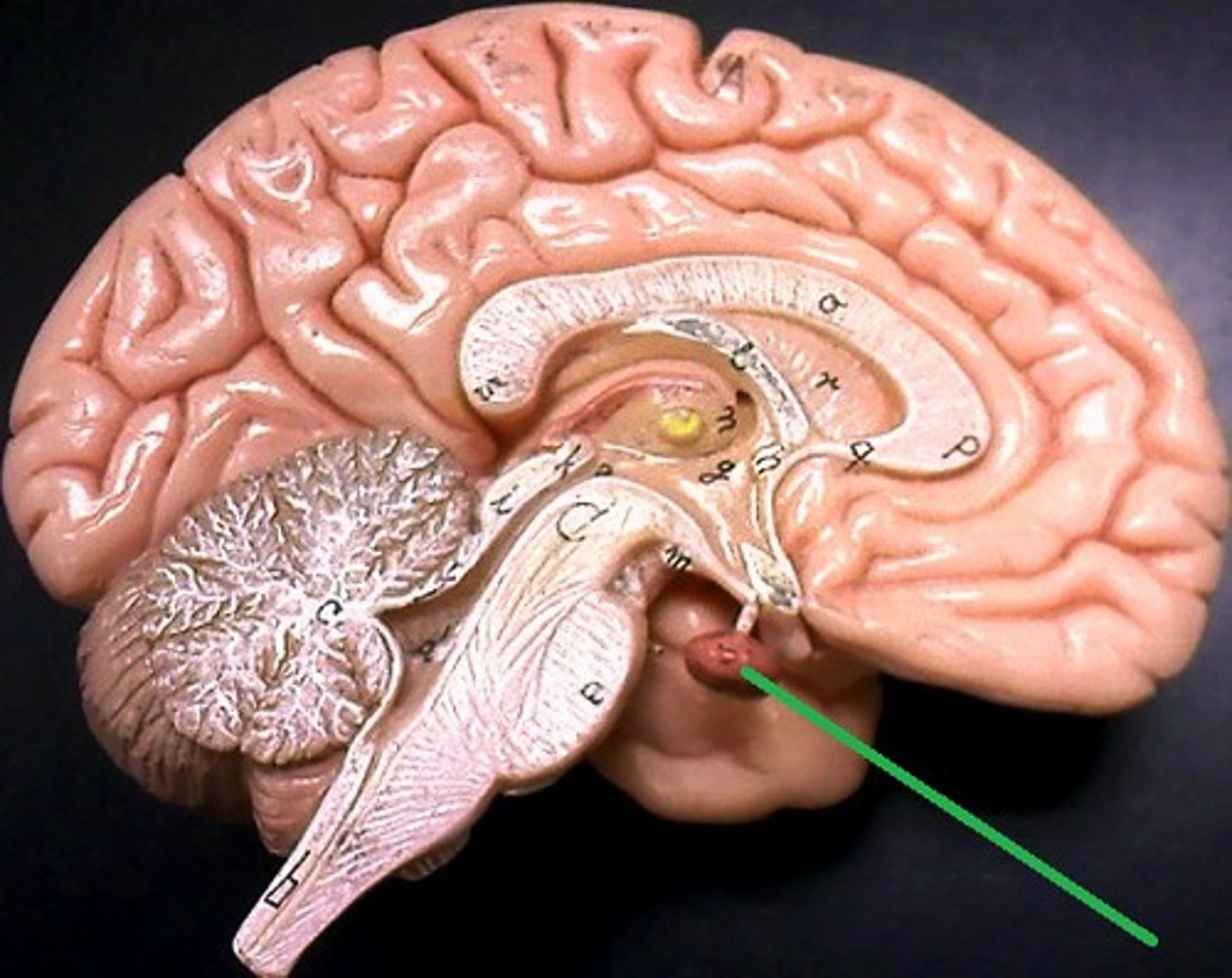
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, this gland regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands. It secretes hormones to regulate the production of other hormones
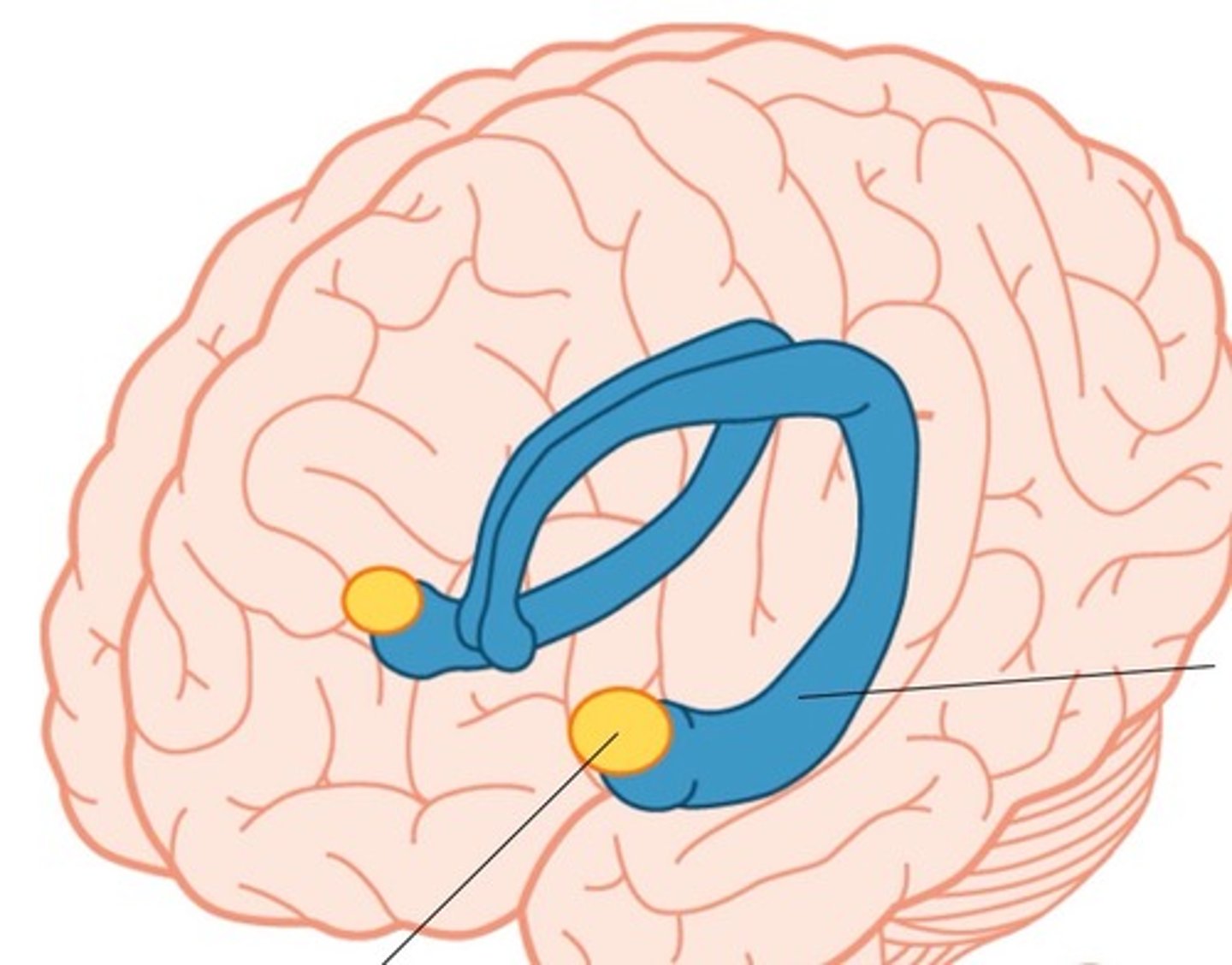
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. They are the synthesizers of information.
Neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons

Amygdala
a key player in the brain's emotional processing and regulation, influencing our emotional responses, memory formation, and social interactions, as well as playing a role in the body's response to stress and threat.
dual processing
decision making has 2 stages 1.) respond or not 2.) choose between alternate responses.

behavior genetics
Study of familial or hereditary behavior patterns, and of genetic mechanisms of behavior traits.

Chromosomes
Strand composed of nucleic acids. Carries the genome, hereditary traits of an individual. Located in cell nucleus.
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
Genes
The basic unit of heredity; these carry all the characteristics that will transfer from parent to child
Genome
all genetic material contained in organism or cell.
identical twins
twins who develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms, also called monozygotic twins.

fraternal twins
twins who develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share a fetal environment. Also called dizygotic twins.

Heritability
Capacity to be inherited.

evolutionary psychology
Views human cognition and behavior in a darwinian context.
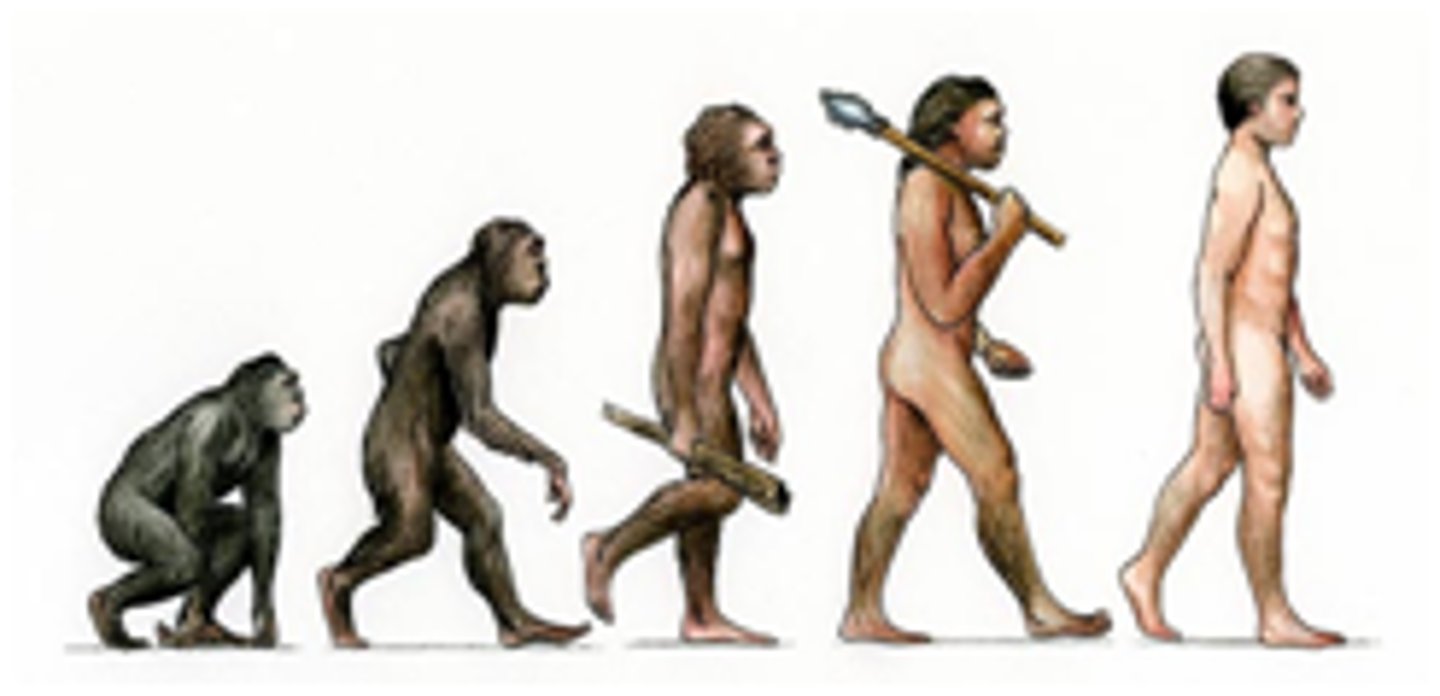
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits. Competition, disease, or climate may eliminate individuals who are less adapted.
Mutation
permanent change in genetic material in an organism

Motivation
a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
instinct
a behavior that an organism inherits

drive-reduction theory
approach to motivation that assumes behavior arises from physiological needs that cause internal drives to push the organism to satisfy the need and reduce tension and arousal

need
Basic requirement for survival

drive
generalized state of readiness precipitating or motivating an activity or course of action. ___ is hypothetical in nature, usually created by deprivation of a needed substance

primary drives
innate drives, such as hunger, thirst, and sexual desire, that arise from basic biological needs

secondary drives
drives that are learned or acquired through experience, such as the drive to achieve monetary wealth

Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.

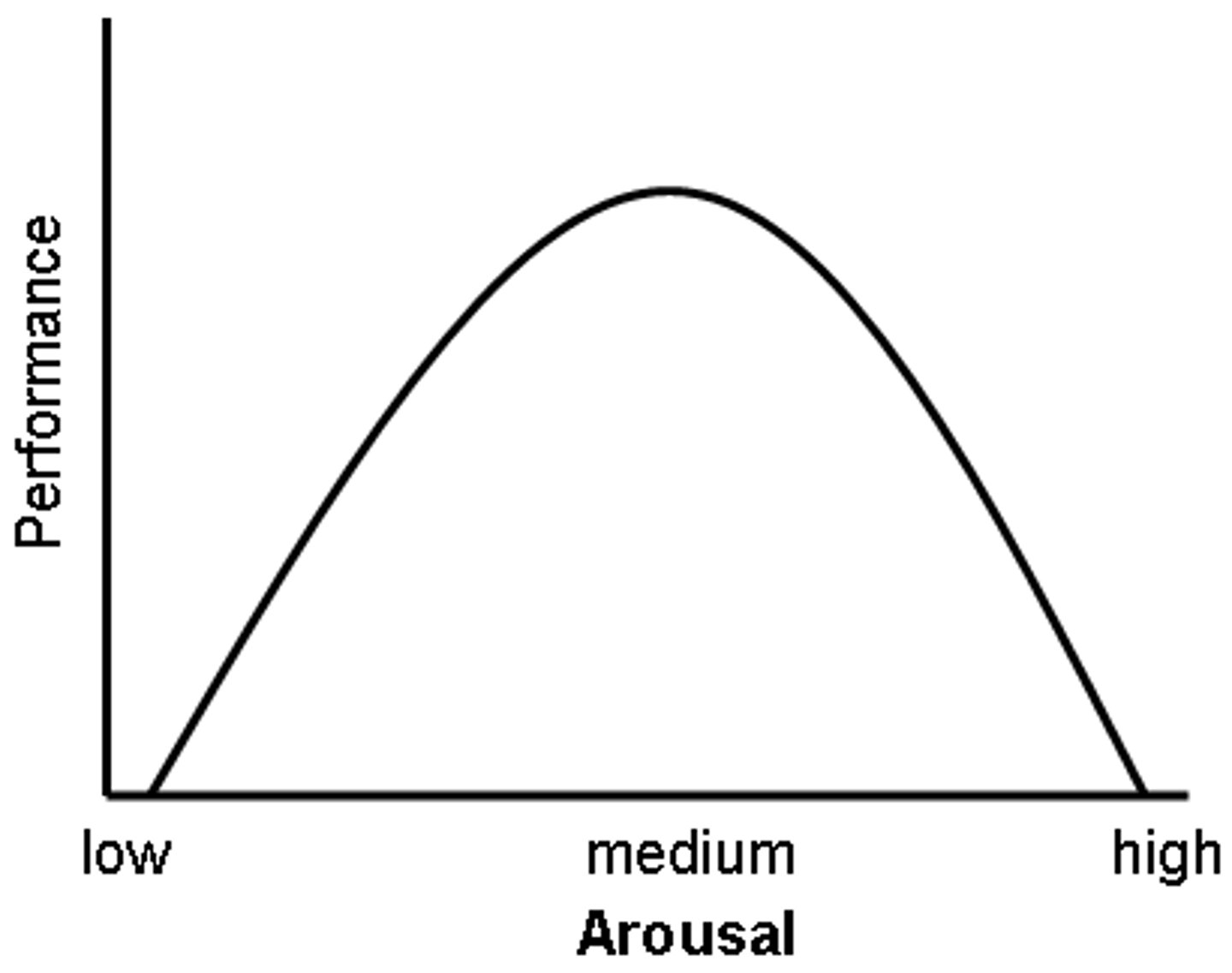
Yerkes-Dodson Law
the psychological principle stating that performance is best under conditions of moderate arousal rather than either low or high arousal
opponent-process theory of emotion
Theory that when a strong emotional response to a particular stimulus disrupts emotional balance, an opposite emotional response is eventually activated to restore emotional equilibrium. That when one emotion is experienced the opposite is repressed. Ex:fear and relief

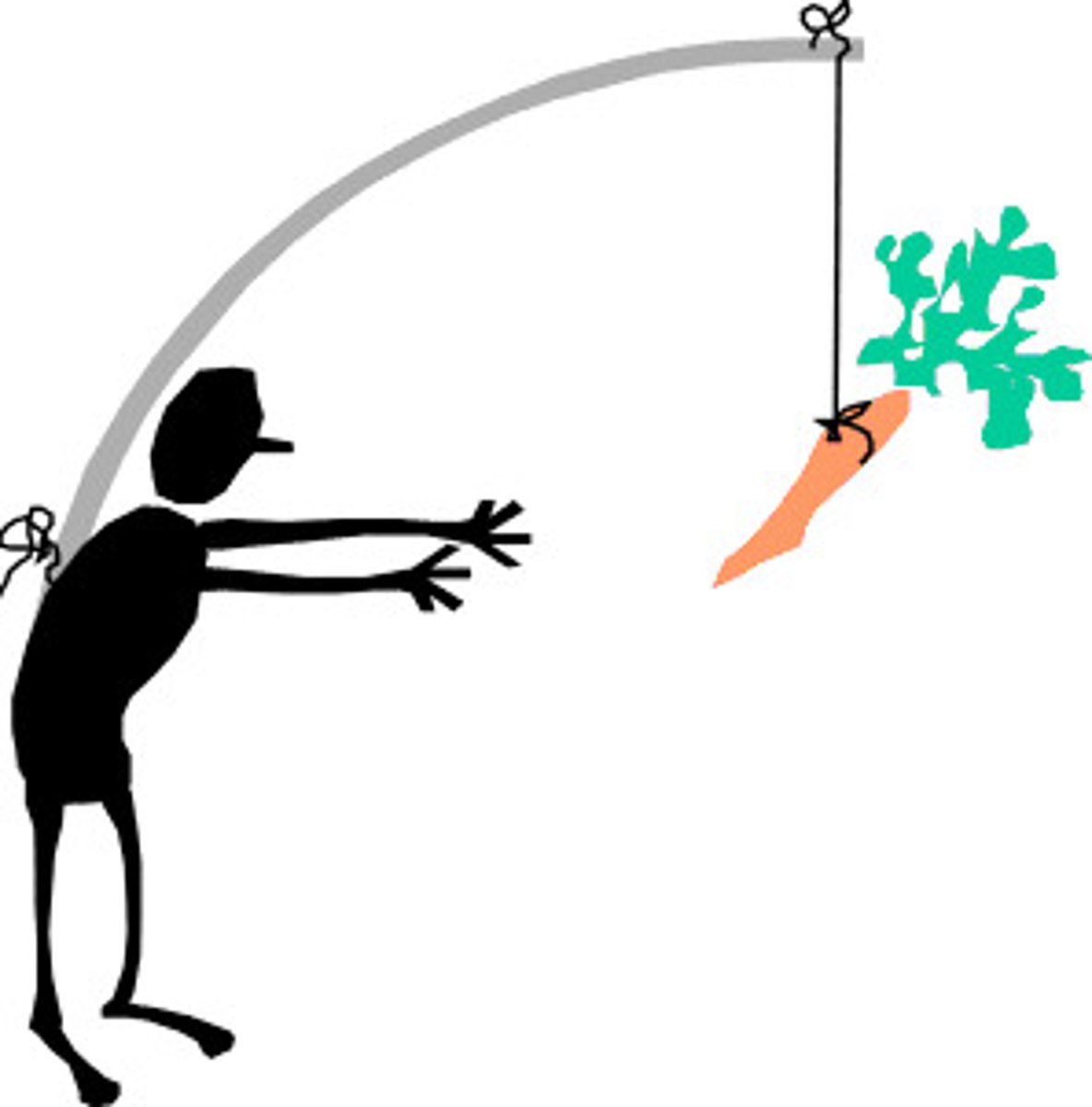
incentive theory
A theory of motivation stating that behavior is directed toward attaining desirable stimuli and avoiding unwanted stimuli.

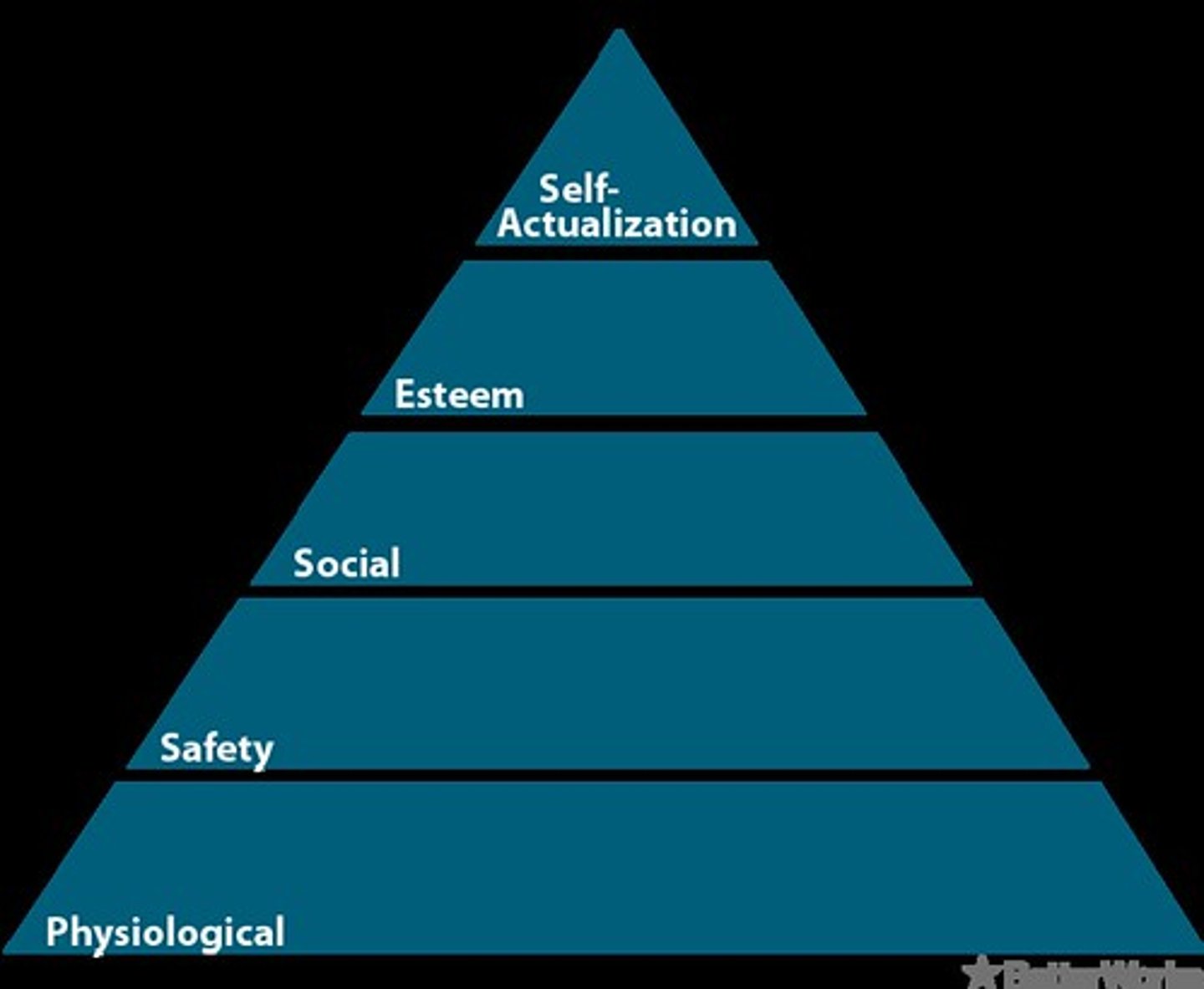
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
(level 1) Physiological Needs, (level 2) Safety and Security, (level 3) Relationships, Love and Affection, (level 4) Self Esteem, (level 5) Self Actualization
lateral hypothalamus
The part of the hypothalamus that produces hunger signals, when stimulated brings hunger, when destroyed stops eating

ventromedial hypothalamus
The part of the hypothalamus that produces feelings of fullness as opposed to hunger, and causes one to stop eating. when stimulated stop eating, when destroyed over eat.

set point theory
belief that hypothalamus plays a role to regulate body weight around a genetically predetermined '____' This ____ is determined by genetics, gender, exercise, metabolism and more.
basal metabolic rate
the body's resting rate of energy expenditure
Bulimia
an eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating, usually of high-calorie foods, followed by vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise

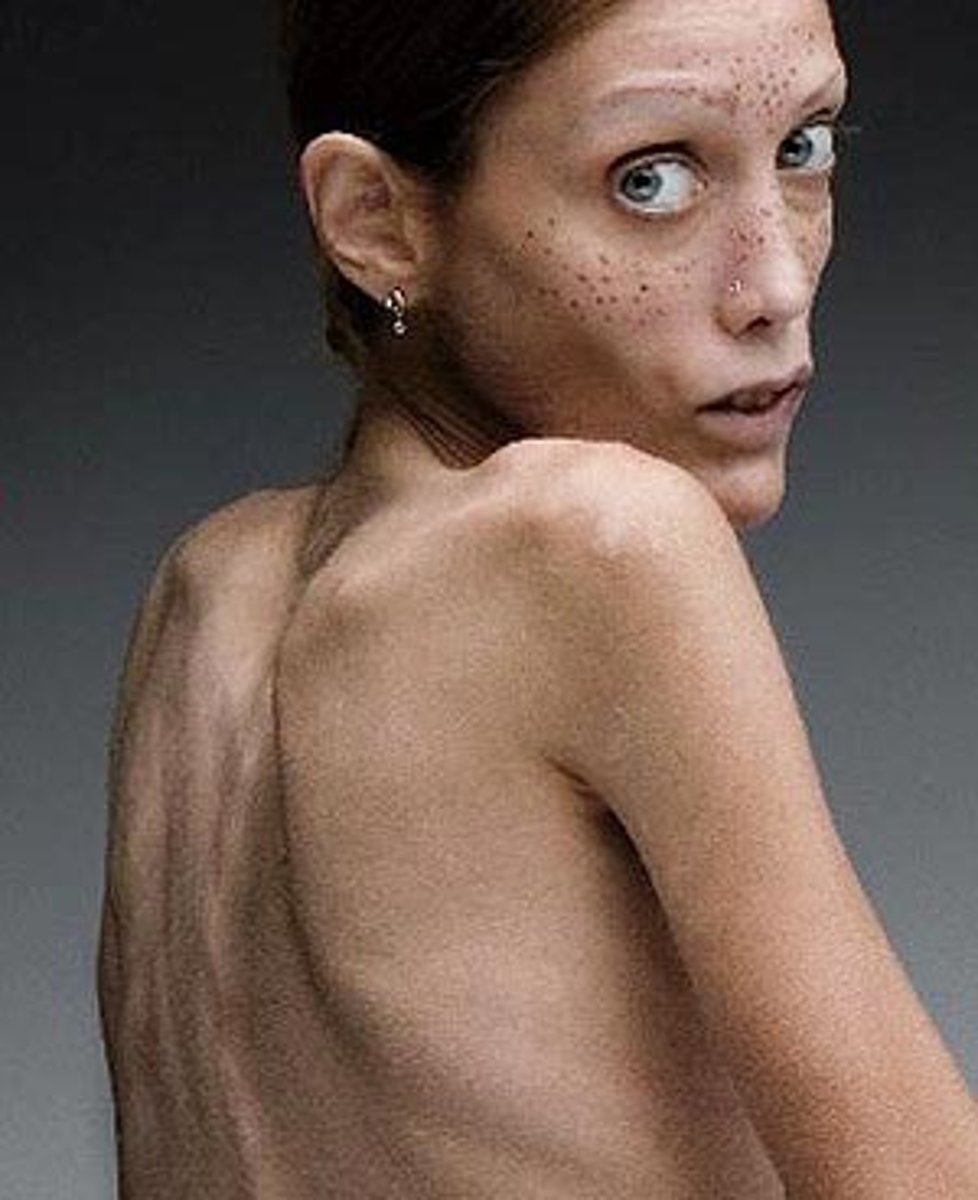
anorexia nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by an obstinate and willful refusal to eat, a distorted body image, and an intense fear of being fat
obesity
having an excess amount of body fat

achievement motivation
a desire for significant accomplishment: for mastery of things, people, or ideas. Top 10 american core value (specifically individualistically)

extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment
