Chemistry - static electricity 2024/12/5
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is static electricity?
Static electricity is the buildup of electric charge on the surface of objects, usually caused by friction.
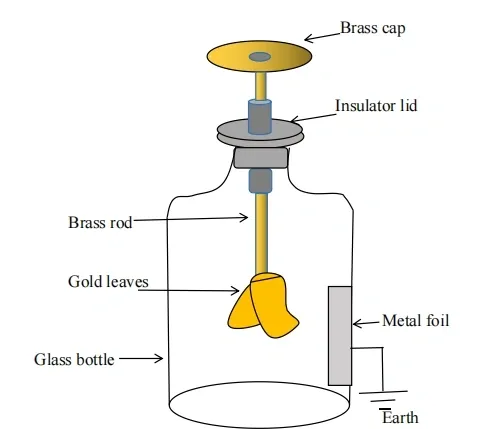
What are the two main ways to detect static charge?
Using a metal leaf electroscope or a pith ball electroscope.
What is a conductor?
A material that allows electrons to flow easily, like metals.
What is an insulator?
A material that does not allow electrons to flow easily, like rubber or glass.
What is charging by friction?
Transferring electrons by rubbing two materials together, often using the electrostatic series chart to predict charge.
What is charging by conduction?
Charging an object by direct contact with another charged object.
What happens when a positive rod touches an electroscope?
Electrons move away from the rod, leaving the electroscope positively charged.
What happens when a negative rod touches an electroscope?
Electrons move into the electroscope, making it negatively charged.
What is charging by induction?
Charging an object without direct contact,
-By bringing a charged object near it and grounding the object to allow electrons to flow.
What happens when a neutral pith ball is near a positively charged object?
If the charged object is positive, the electrons in the pith ball are attracted to the side closer to the charged object
What is grounding?
Connecting an object to the Earth to neutralize its charge by allowing electrons to flow in or out.
What happens when you ground a negatively charged object?
Electrons flow from the object to the ground, neutralizing it.
What happens when you ground a positively charged object?
Electrons flow from the ground into the object, neutralizing it.
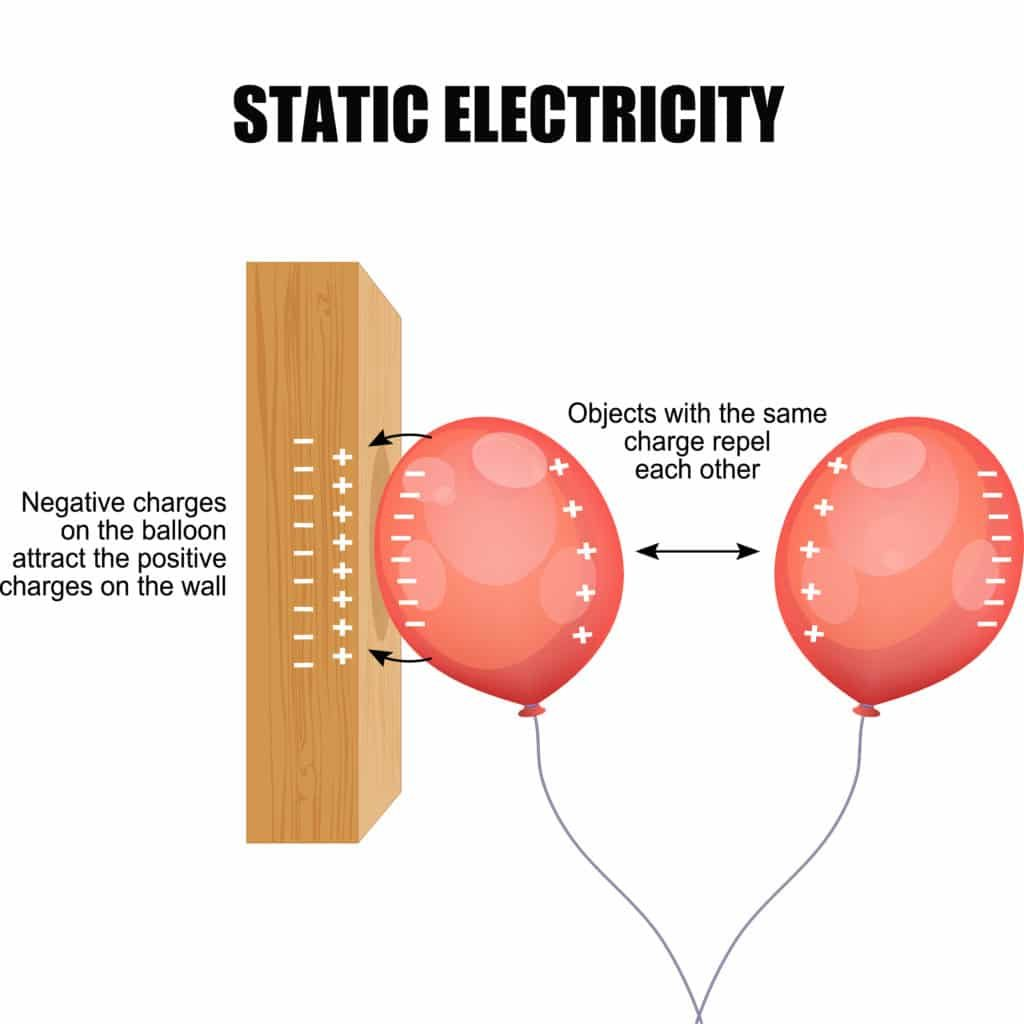
How does a balloon stick to a wall after being rubbed on your hair?
The balloon becomes negatively charged and produce a positive charge on the wall, causing attraction.
What is the purpose of a lightning rod?
To safely redirect lightning strikes to the ground, preventing damage.
How does an electrostatic precipitator work?
It uses static electricity to remove particles like dust from the air by attracting them to charged plates.
How does an electrostatic duster work?
Attracts dust using static electricity
How does an electrostatic paint sprayer work?
Paint particles are given a charge so they stick evenly to the oppositely charged surface.
What is a Electroscope diagram
What is a Pith Ball diagram

What happens when a neutral pith ball is near a negatively charged object?
The electrons in the pith ball move closer to the negatively charged object, attracting them to each other.
Pith Ball Already Charged it shows:
Show repulsion or attraction depending on the charge of the rod.
Balloon on a Wall (Charging by Induction) picture*
Grounding Diagrams
When you rub a balloon with your hair:
Hair:
Becomes positively charged. Electrons are transferred away from your hair to the balloon.
When you rub a balloon with your hair:
Balloon:
Becomes negatively charged. It gains the electrons from your hair.
more electrons than protons is
negatively charged
Fewer electrons than protons
Positive charge