COA 423: Anatomy
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
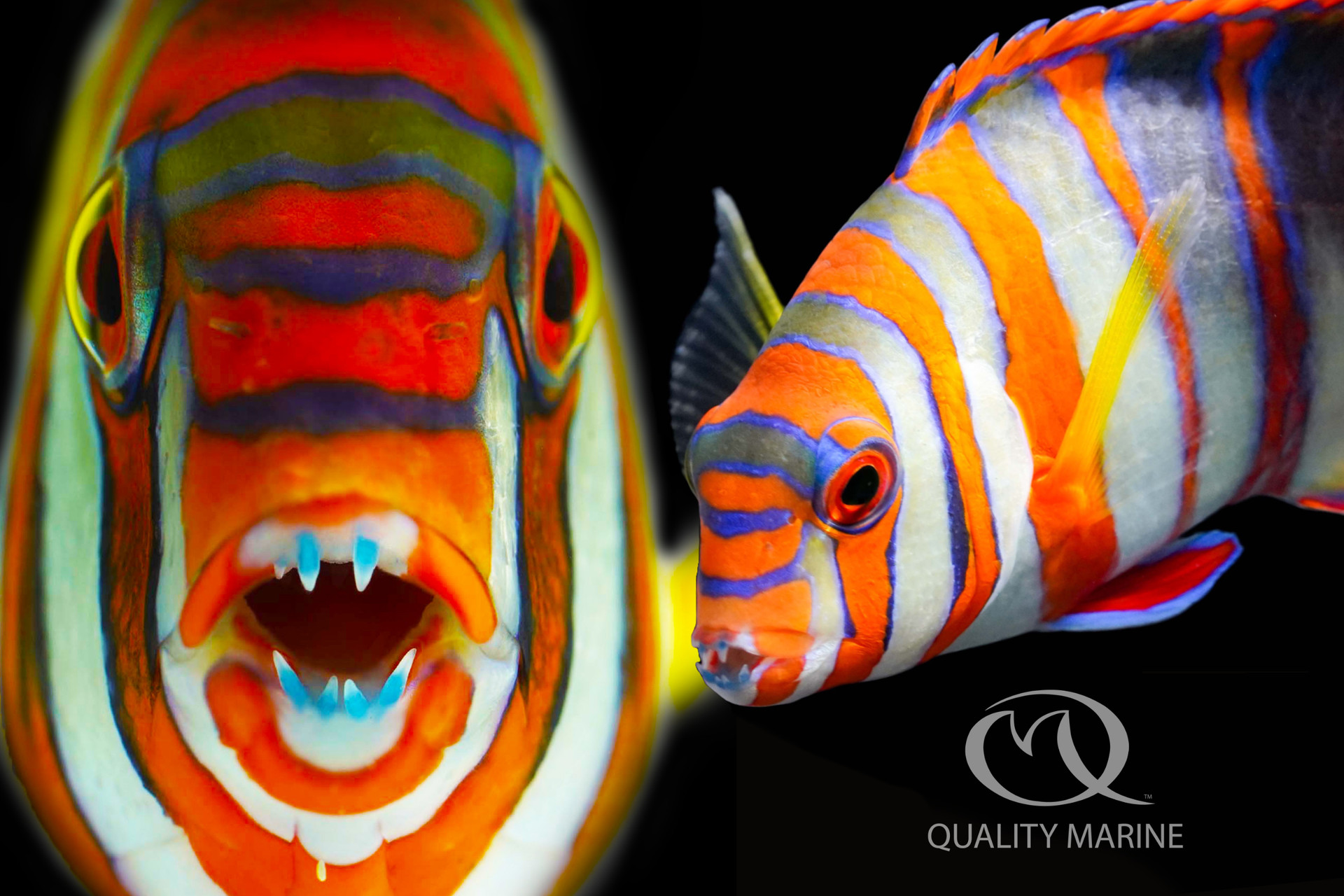
Canineiforms
large conical teeth located at the corners of the mouth:
→ useful in ripping apart exoskeltons and flesh

Villiform
small, fine teeth. Needlelike
→ pierce through skin

Molariform
pavement like crushing teeth, forms plates or individual molars
→ grinds up prey and crushes exoskelton
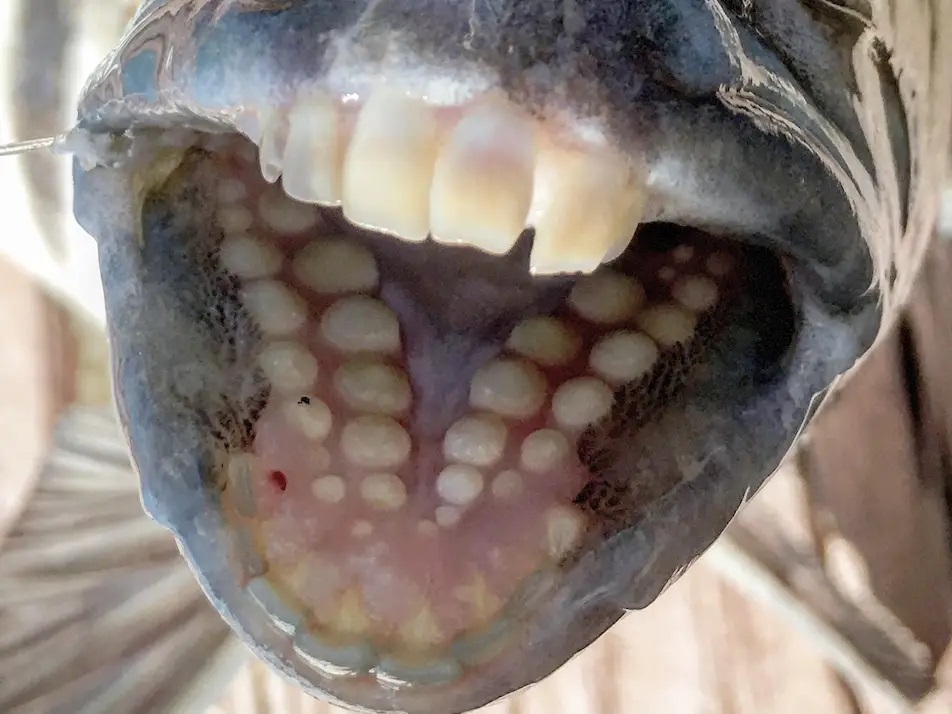
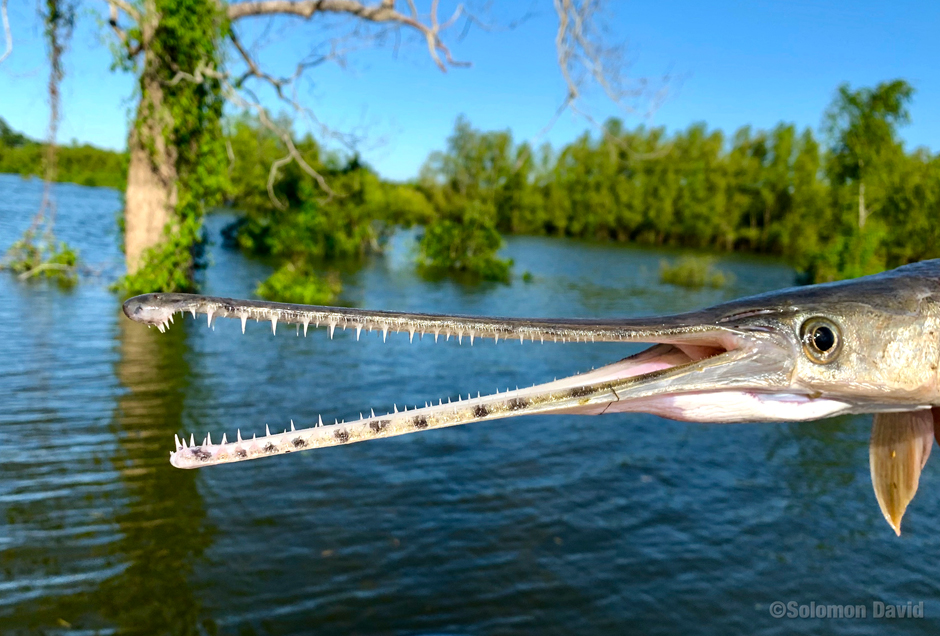
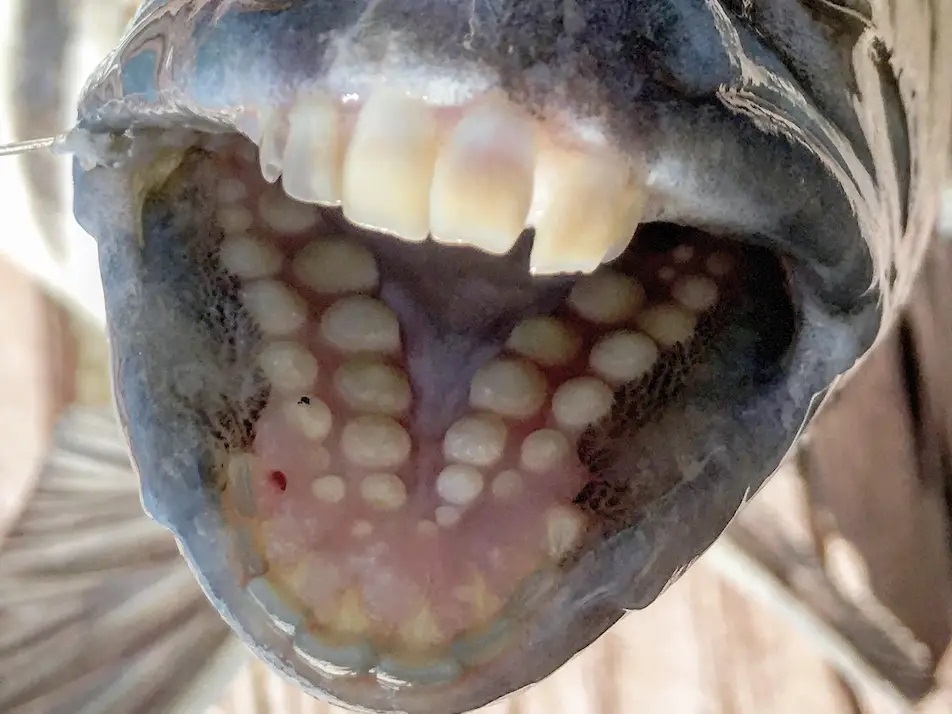
Cardiforms
fine, pointed teeth arranged as in a woold card
→ allows for a piercing grip when prey is swallowed whole
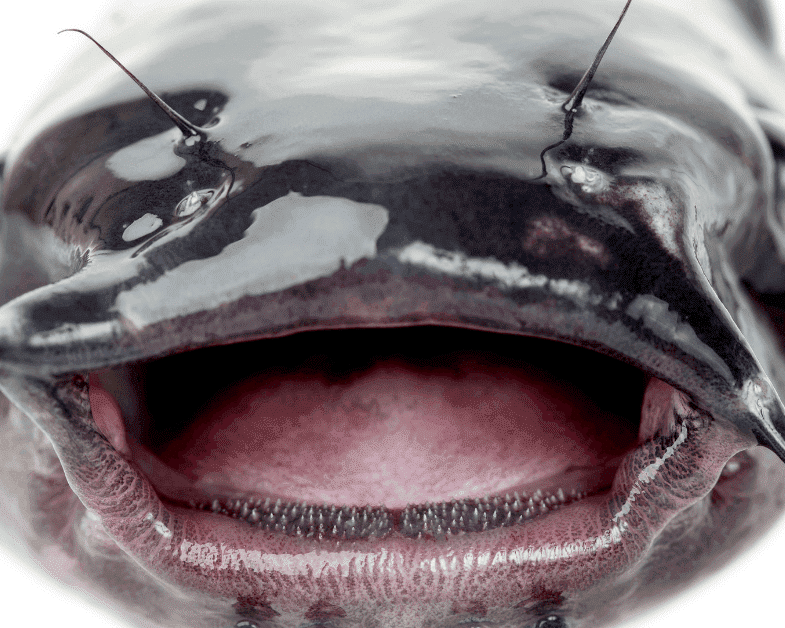
Incisors
Large teeth flattened cutting surfaces
→ primary prey: mollusks and crustaceous
→ can pick aparrt prey
Beaks
teeth morphed into a sharp structured
→ used for scraping plant materials off surface for consumption, or cutting into a hard shell
Flattened Triangular
teeth that are flattended and sharp
→ wide range of prey from squid, small fish, crusteceansm and marine mammals
→ pierce and hold prey in place to be consumed quickly
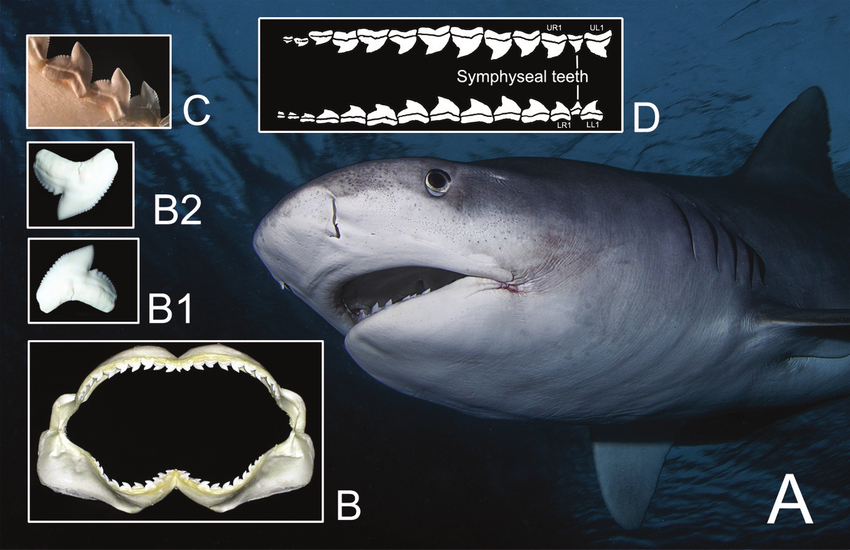
Pharygneal teeth
teeth located on the pharygneal arch that can exhbiti multiple types of teeth for secondary consumption
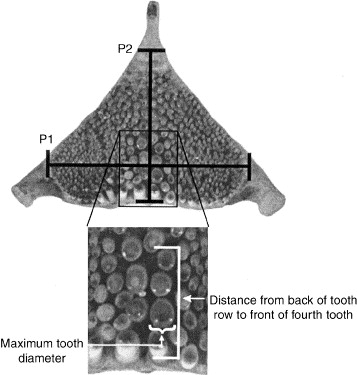
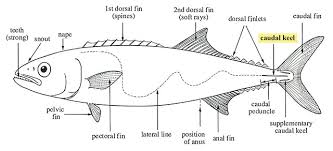
finlets
series of small doesal and anal finlets w/ a paried keel at the caudal fin
Branchicranium
consists of five series of endoskeletal arches (mandibular arch, palatine, hyoid, opercular, and branchial)
Mandibular Arch
forms upper jaw,
in bf: composed entirely of dermal bones
→palatoquadrate cartialge in Chondrichtyes
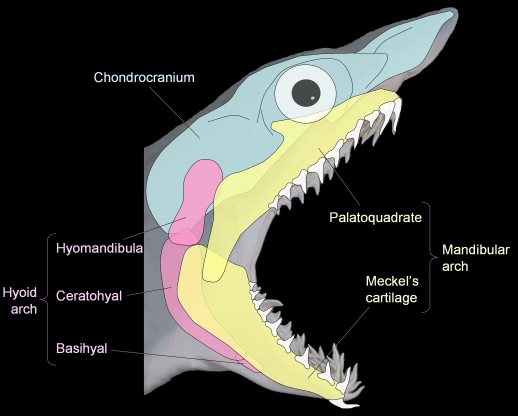
Palatoquadrate cartilage
mandibualr arch name in Chondrichtyes
Characiformes, Siluriformes, Salmoniformes, Myctophiforms, Trout Perches
orders that have adipose fins
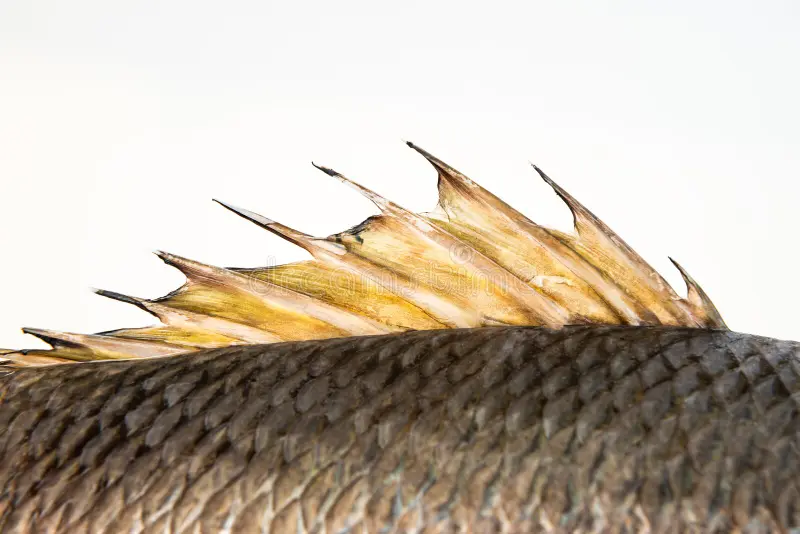
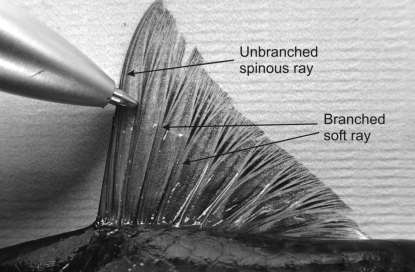
Spines
hard and pointed
unsegmented
unbranched
solid
located in the first dorsal fin in advanced teleosts

soft rays
soft, not pointed segment
segemented
usually branched
bilateral, with left and right halves
usually found on the 2nd dorsal fin in advanced teleosts
Protocercal
caudal tail, primited, undifferentiated that extends around posterior
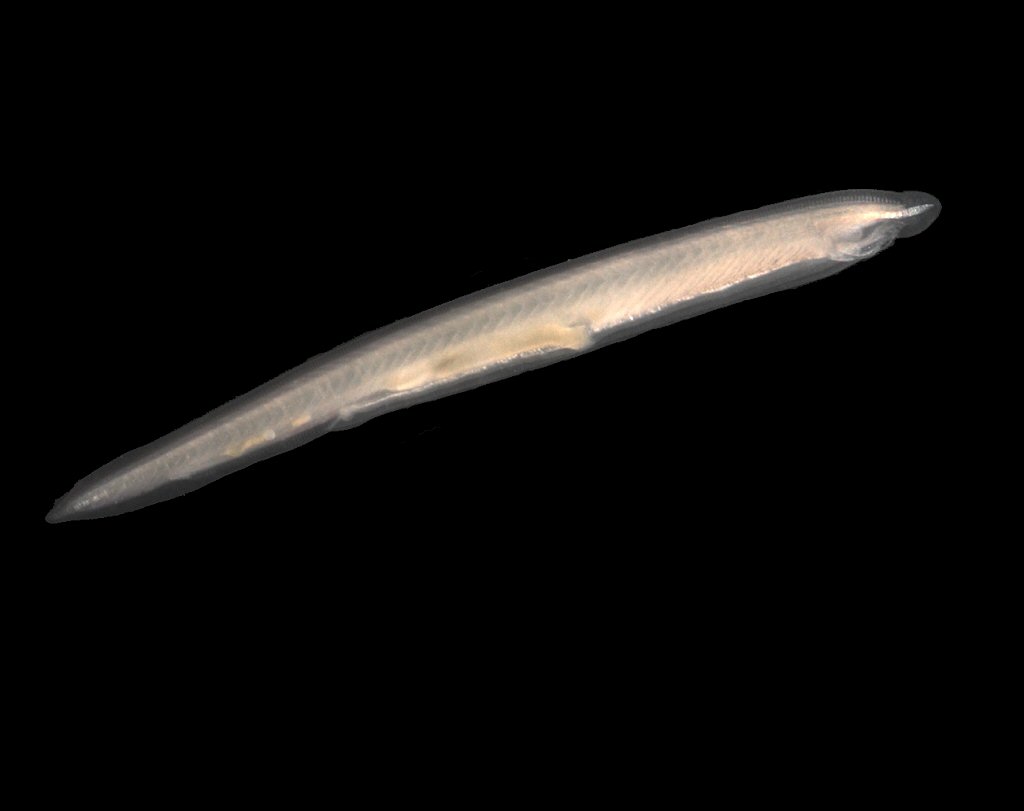

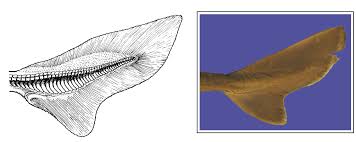
heterocercal tail
unequal lobed, verebral column extends to upper lobe
homocercal
equal lobed, caudal fin rays arranged symmetrically
found in most actinopterygii

leptocercal tail
caudal fin with he spinal column extending horizontally to the end of the tail, r
isocercal tail
caudal tail wehre last vertebra is modified into small plate to which caudal fin rays are attached
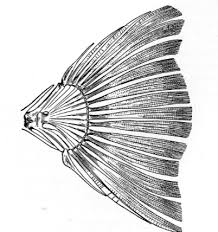
gephyrocercal tail
lack a true tail, modified elements of dorsal and anal fin form tail (Molidae)
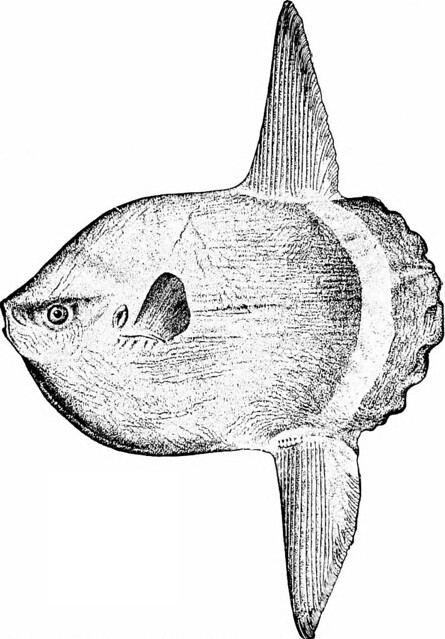
Placoid Scales
Outlayer: vitrodentine, derived from the ectoderm. Largley noncellular
flattened rectangular basal plate in upper part of the dermis, from which a protruding spine projects
do not increase in size, grow in between each other
Belong to: Chondricthyes
Cosmoid Scales
Two basal layers:
→ Isopedine: dense lamellar bone
→ cancellous: spongy bone
covered in noncellular cell like structure (Cosime)
growth by addition of new lamellar bone
arose from fusion of two placoid scales
GROUP: fossilized colecanths, lungfishes
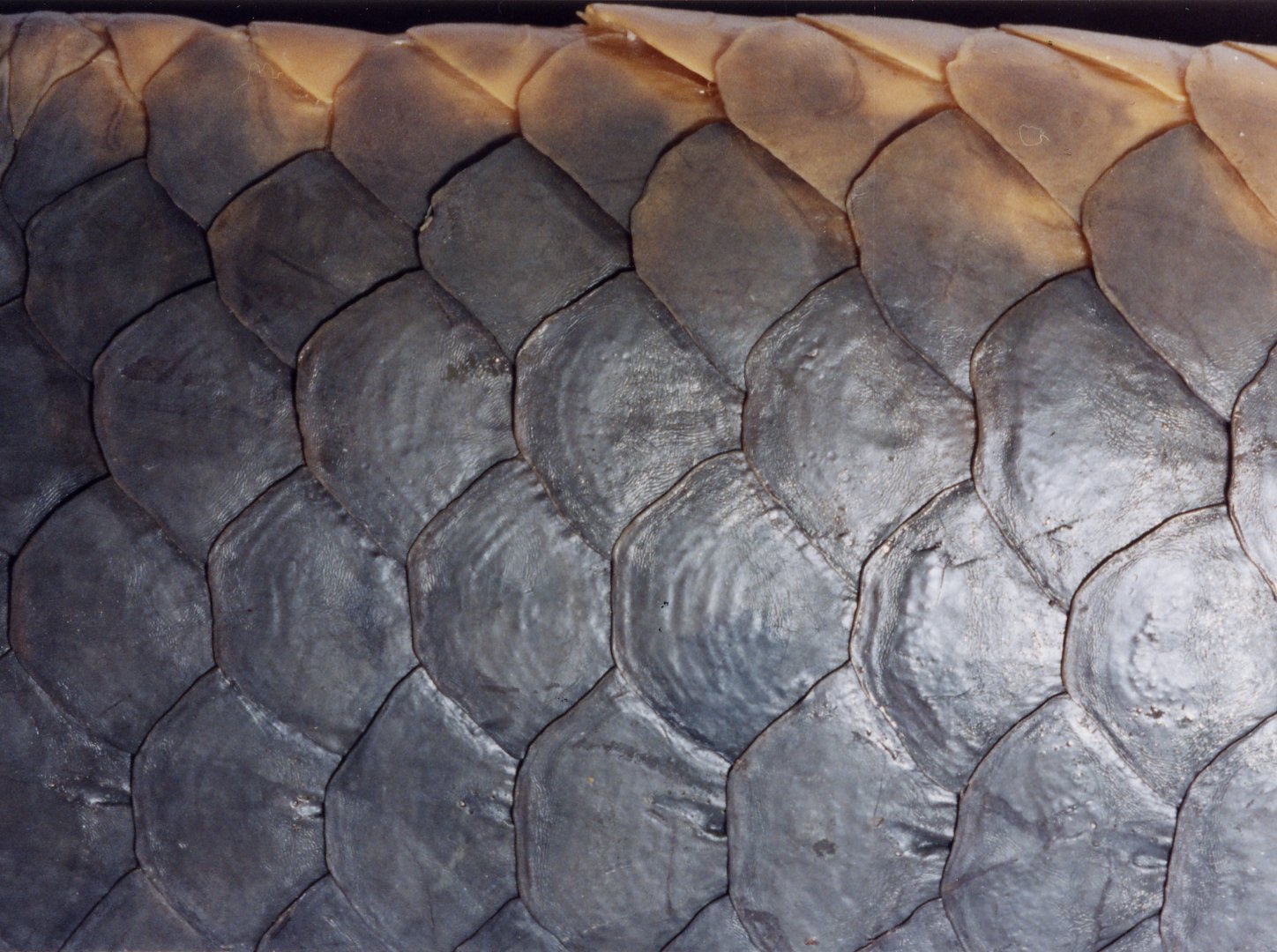

Ganoid
Rhombodial shaped scales with peg and socket joints between them
contains ganoine
coated in dentine layer
GROUP: Chondrostei, Holostei

ganonine
inorganic bone salt secreted by the dermis. Calcified noncellular
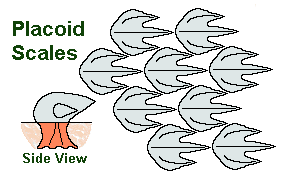
Cycloid
dermal scales with no enamel layer
circular
thin bony dermal plate replaces ganoine
lack ctenii, instead contaning breeding tubercules and contact organs
anterior portion depressed in dermis due to unequal pulling of muscles of fishes
covered by the posterior margin of preceeding scale
Layers:
→ surface bony layer containing claclium phosphate and calcium carbonate
→ Fibrillary plate: Collagen
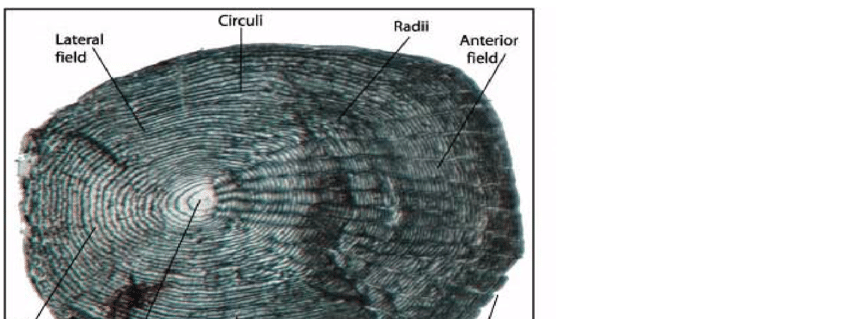
Ctenoid
→ riunded, dermal scales with no enamal layer
→ contain ctenii
→ thin bony dermal plate replaces ganoine
anterior portion depressed in dermis due to unequal pulling of muscles of fishes
covered by the posterior margin of preceeding scale
Layers:
→ surface bony layer containing claclium phosphate and calcium carbonate
→ Fibrillary plate: Collagen
Scales can be crenate, spinoid, peripheral or transforming
made of organic protein, albuminoids(collagen)
white muscle
muscle in a fish that is used anaerobically
lacks myoglobin
fatigues quickly, mostly used in short durations
red muscle
muscle that forms a thin sheet under the skin; invovled in sustained swimming
hard to fatigue
abundant in myoglobin
1
amount of circut systems in a fish
alimentary canal
digestive system of a fish;
includes mouth, buccal cavity, foregut, intenstive, rectum
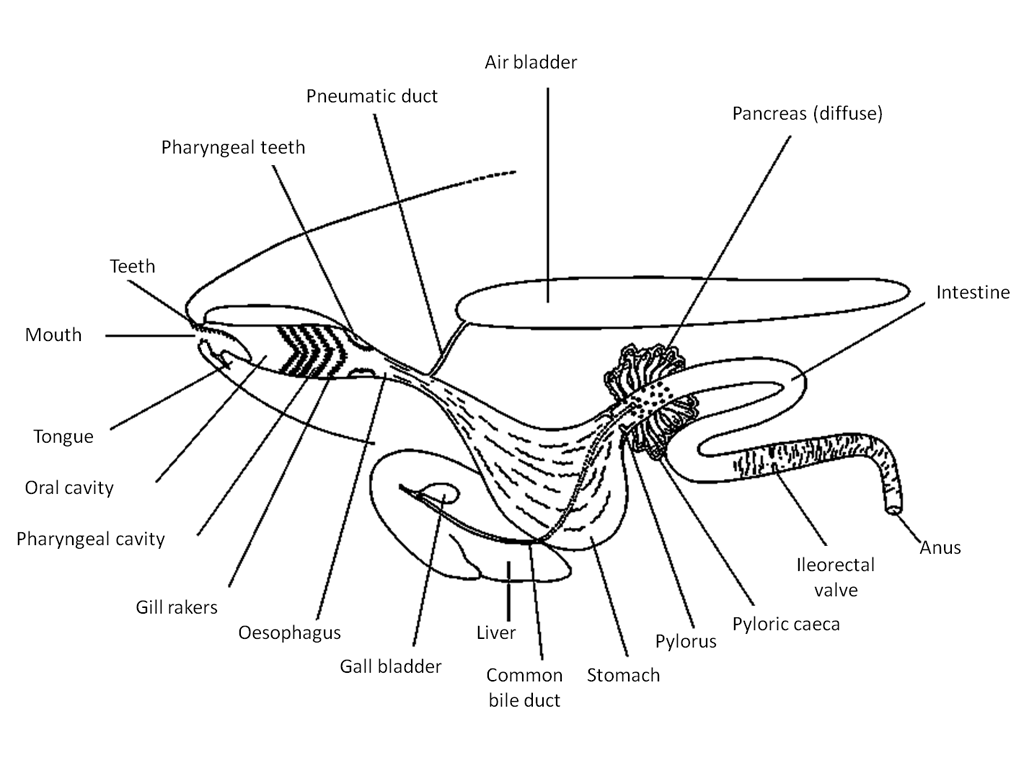
spiral
shape of Chondrichtyes and other primitive fishes intestine that increases the surface area of the stomach

gonopodium
modified anal fin for spermatophore tranfer in livebearing fish
ex: mollies
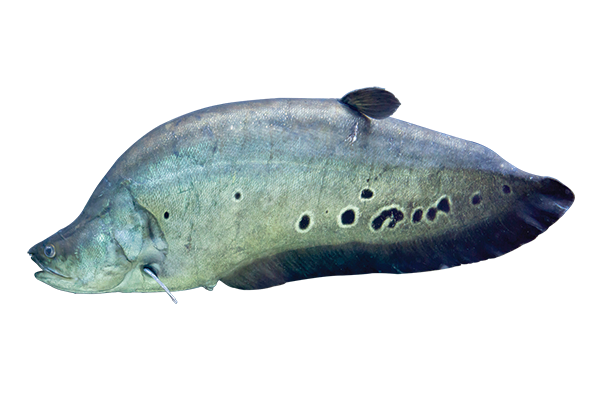

Gymnotiformes
group of fish whose anal fin is elongated and used for locomotion
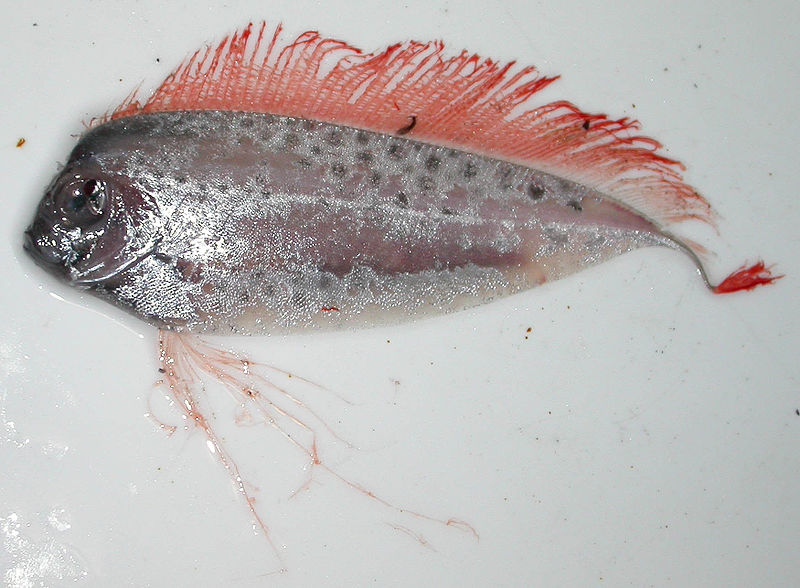

Ribbon fishes
group of fish whose anal fin is reduced or lost

Gadidae
family of fish with an isocercal tail
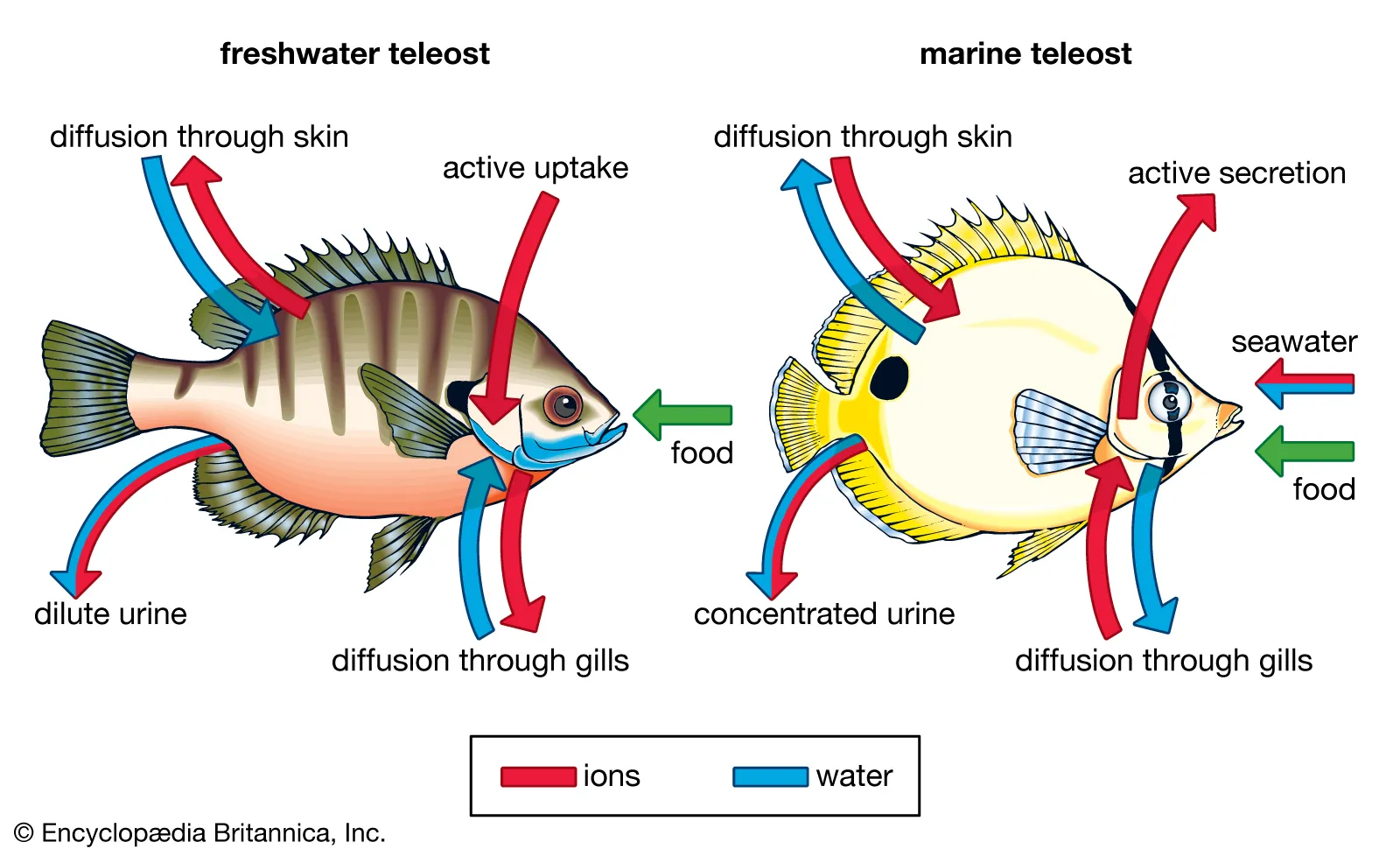
kidneys
primary organs invovled in exrection and osmoregulation
→ FW: produced highly dilute urine
→ SW: extremely low volume of highly concentrated urine
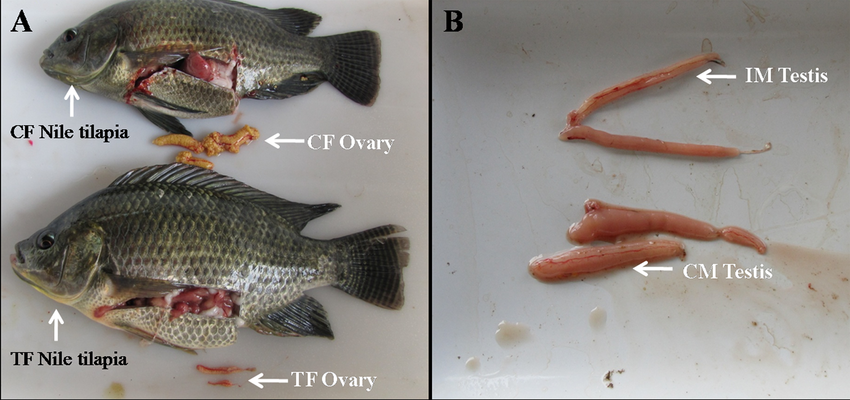
testes
male internal organ, longitidual, and paried
→ can constitute as much as 12% body mass
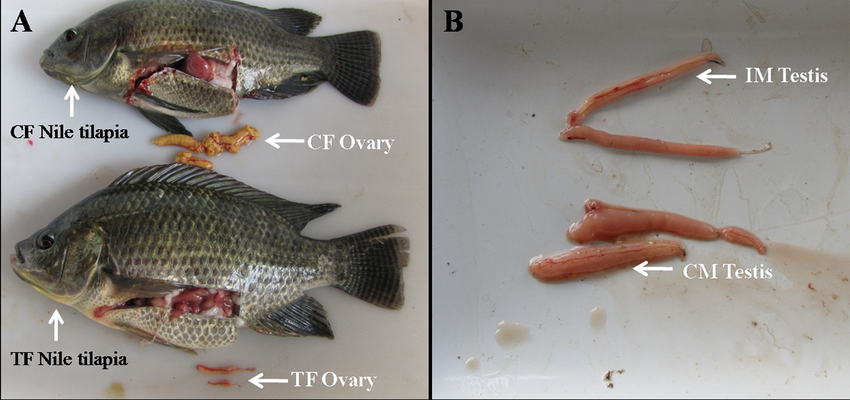
ovaries
female gonad internal, usually longitudinal, and paired or fused
→ 70% of body mass
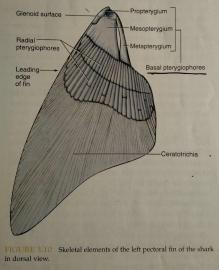
ceratotrichia
horny fin rays made of elasin and dermal cells that support fin rays in Chondrichtyes
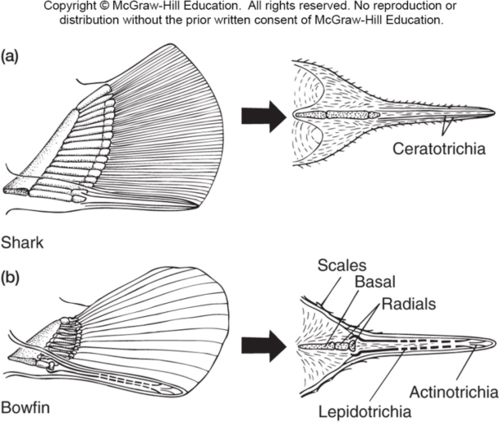
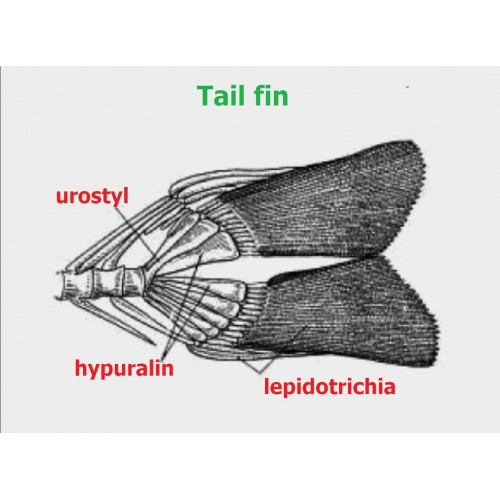
lepidotrichia
bony supporting elements in median fins in bony fishes. replaces ceratotrichia in ontogeny. dervied from scales
Morphometric
measurable characteristics such as fin lengths, eye diameter, or ratios between such characters
Anatomical
characters of the skeleton (osetology) and characters of the soft anatomy
→ color, patterns, sexually dimoprhic stutuctures
Molecular
characters of nuclear or mitcohdonrial DNA used for classifcation
Meristic
characters that correspond to body segments(myomeres), such as number of vertbrae, fin rays; also number of scales, gill rakers, cephalic pores
→ counts are reproduced