Special Senses: Ear Lecture
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
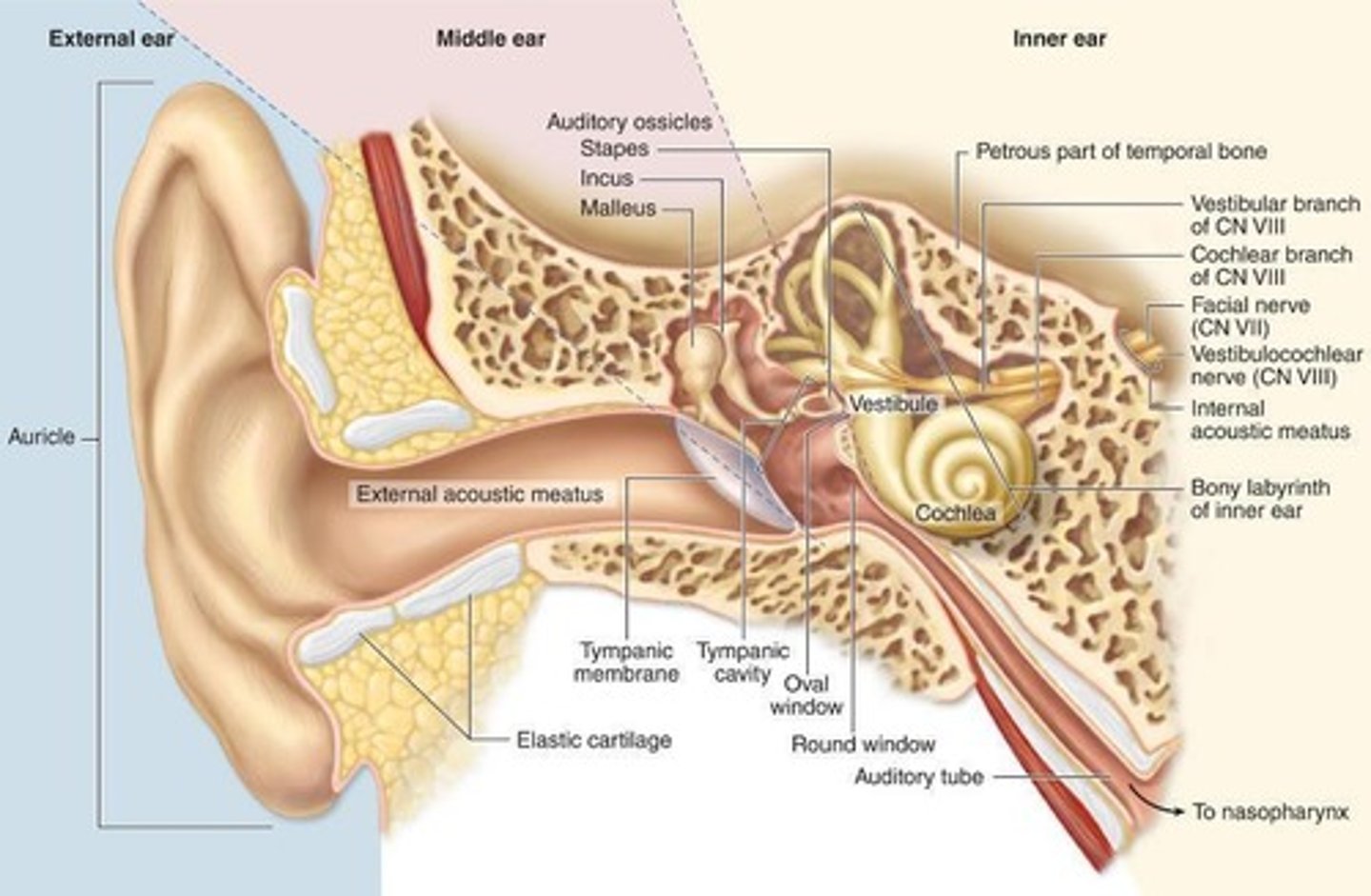
Parts of the External Ear
auricle, external acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane
Tissue of the mucosa of the external acoustic meatus
lined with stratified squamous epithelium
Mucosa of the external acoustic meatus
lamina propria of loose connective tissue
Submucosa of external ear
Consists of:
Hair follicles, sebaceous glands and ceruminous glands (modified apocrine sweat glands)
Submuscosa of external ear location
Located near the opening of the meatus
Ceruminous Glands
Modified apocrine glands producing earwax.
Elastic cartilage of external ear
supports outer third of the walls if the external acostic meatus
What is the inner part of the external ear enclosed by?
Osseous tissue (temporal bone)
Tympanic membrane or eardrum externally
Fibroelastic tissue covered with epidermis.
Tympanic membrane internally
lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
Middle Ear
Continuous with the nasopharynx and the mastoid cells of temporal bone
Tissue within the middle ear
Lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
What does the middle ear become in the auditory tube?
respiratory epithelium
Lamina propria of loose CT in middle ear is continuous with?
periosteum (CT covering bone)
Ossicles are covered with what tissue
periosteum and simple squamous epithelium
Tensor Tympani Muscle
Skeletal muscle attached to the malleus.
Stapedius Muscle
Skeletal muscle attached to the stapes.
Internal Ear
Contains bony and membranous labyrinths.
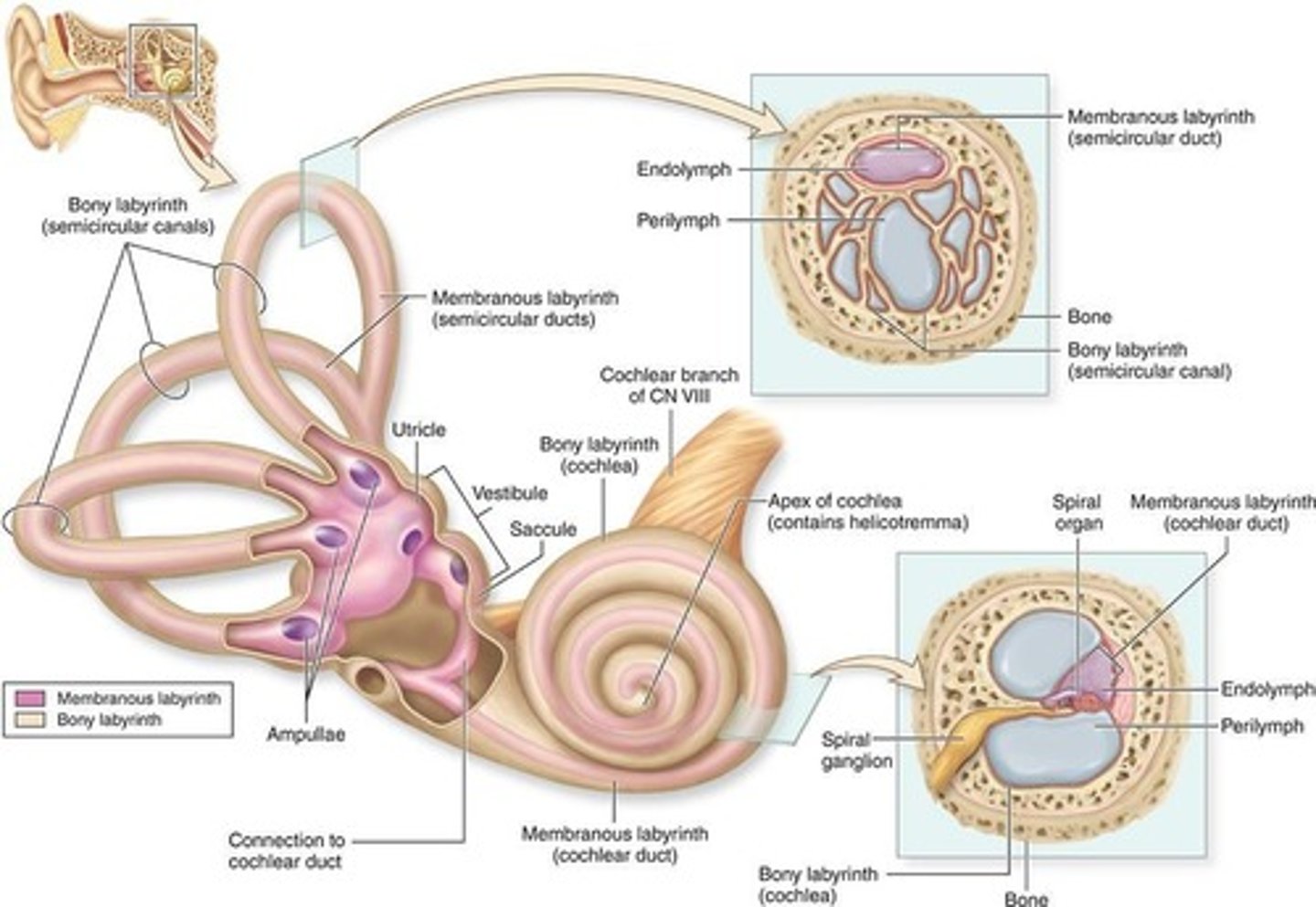
Bony Labyrinth
Rigid structure contains perilymph fluid.
Membranous Labyrinth
Flexible structure filled with endolymph fluid.
What type of tissue is the membranous labyrinth covered with?
lined with epithelium
Divisions of membranous labyrinth
1. Utricle + saccule (interconnected)
2. Three semicircular ducts (continuous with utricle)
3. Cochlear duct (continuous with saccule)
Utricle and Saccule
Interconnected
Semicircular Ducts
continuous with utricle
Cochlear Duct
continuous with saccule
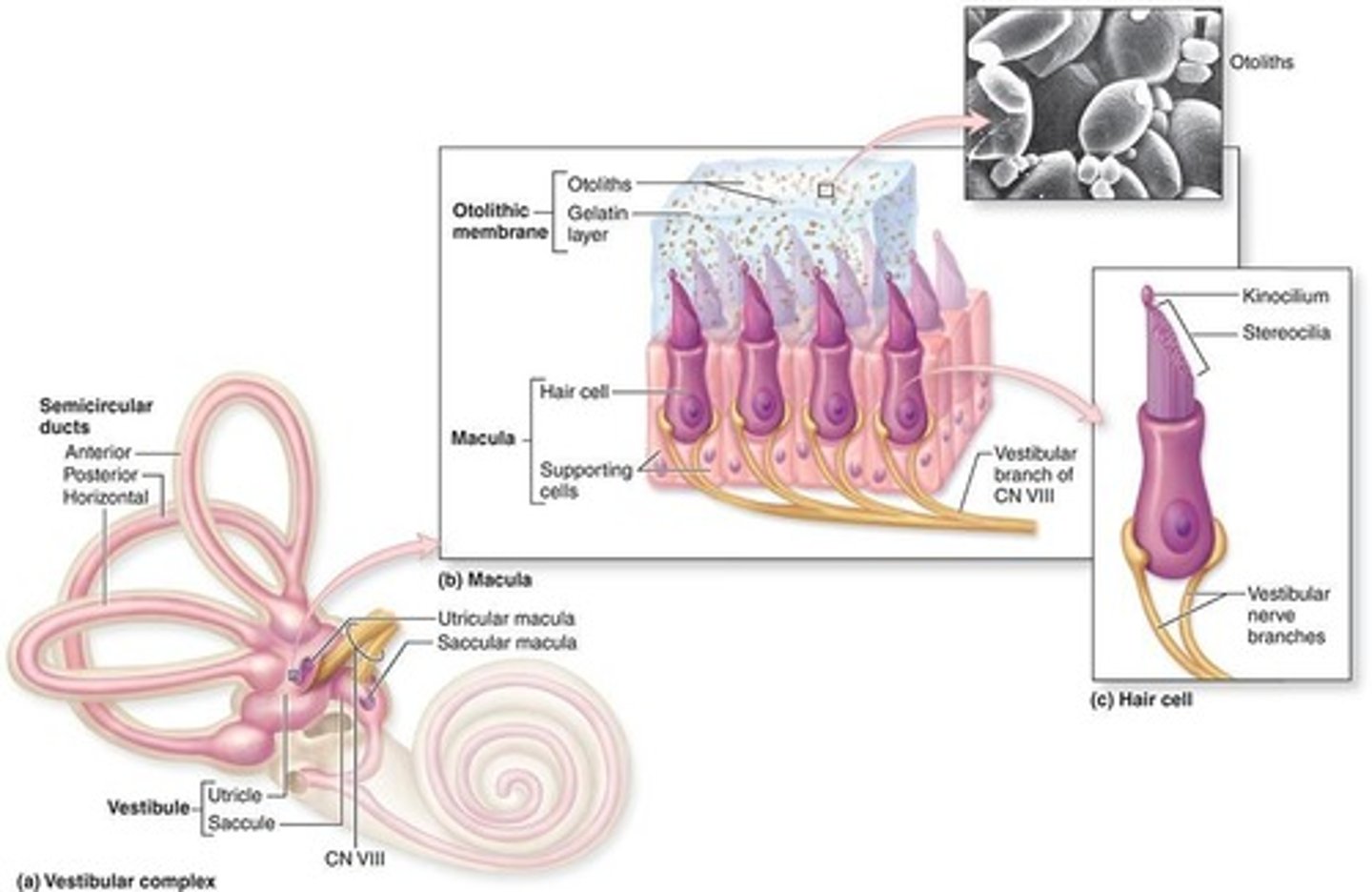
Hair Cells
Mechanoreceptors within the sensory regions.
Hair cells are found:
maculae, cristae ampullares, organ of Corti
Maculae are found
one in utricle and one in saccule
Cristae Ampullares are found
ampullae of semicircular canals
Spiral Organ or Organ of Corti are found
cochlear duct
Regions of bony labyrinth
1. vestibule
2. semicircular canals
3. cochlea
Modiolous of bony labyrinth
-Surrounded by the cochlea
-Blood vessels
-Surrounds the cell bodies and processes of acoustic branch of VIII cranial nerve
What type of tissue is utricle and saccule?
Very thin CT sheaths lined with simple squamous epithelium
How is the utricle and saccule attached to the periosteum?
bound to the periosteum of bony labyrinth by a vascularized layer of collagen fibers
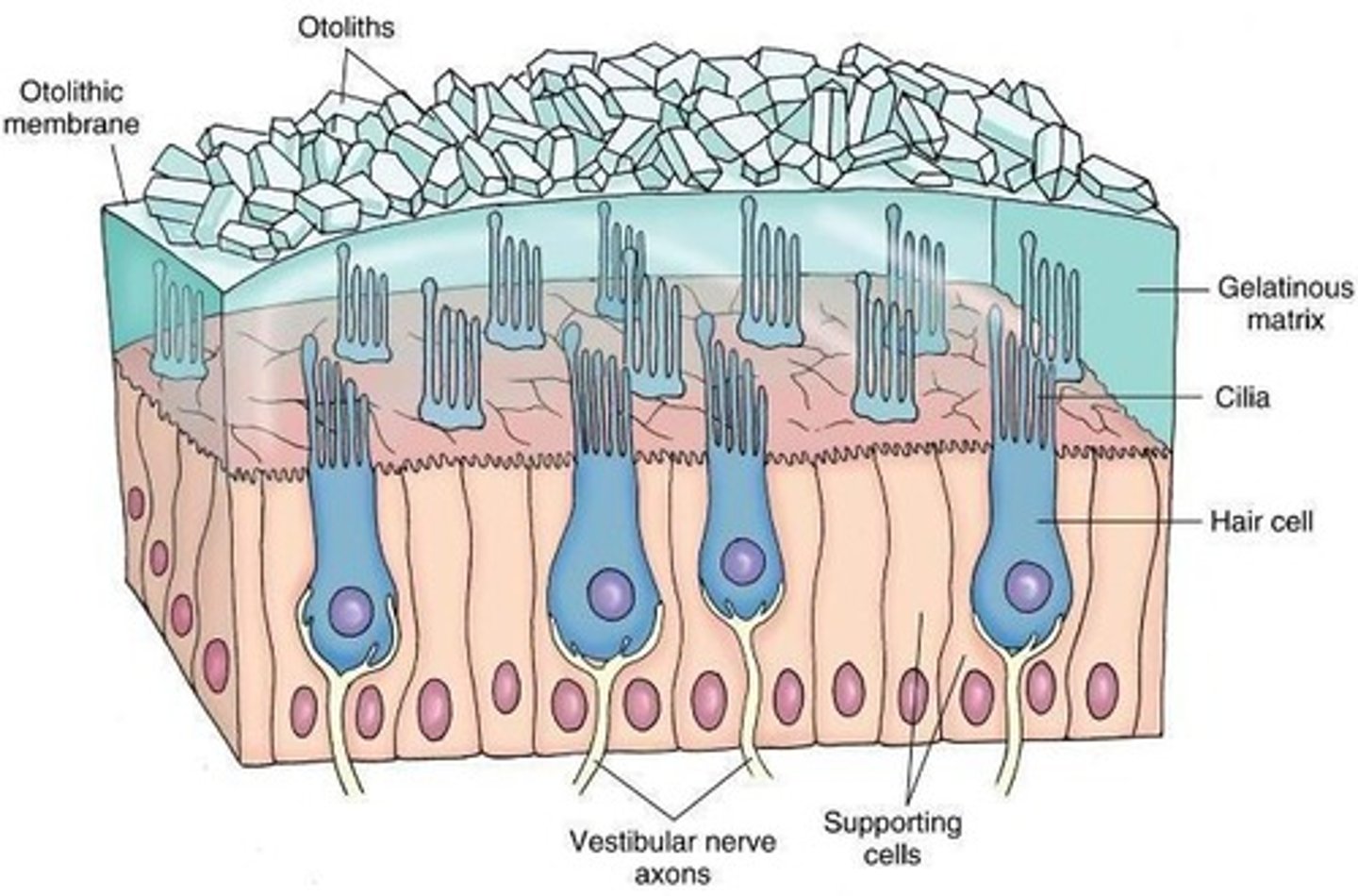
Maculae
Areas of columnar neuroepithelial cells (inneverated by branches of VIII nerve)
Macula of saccule position
Macula of saccule lies perpendicular to the macula of the utricle
What surrounds columnar hair cells?
surrounded by supporting cells and synaptic connections
Function of maculae
Static position and linear acceleration of the head
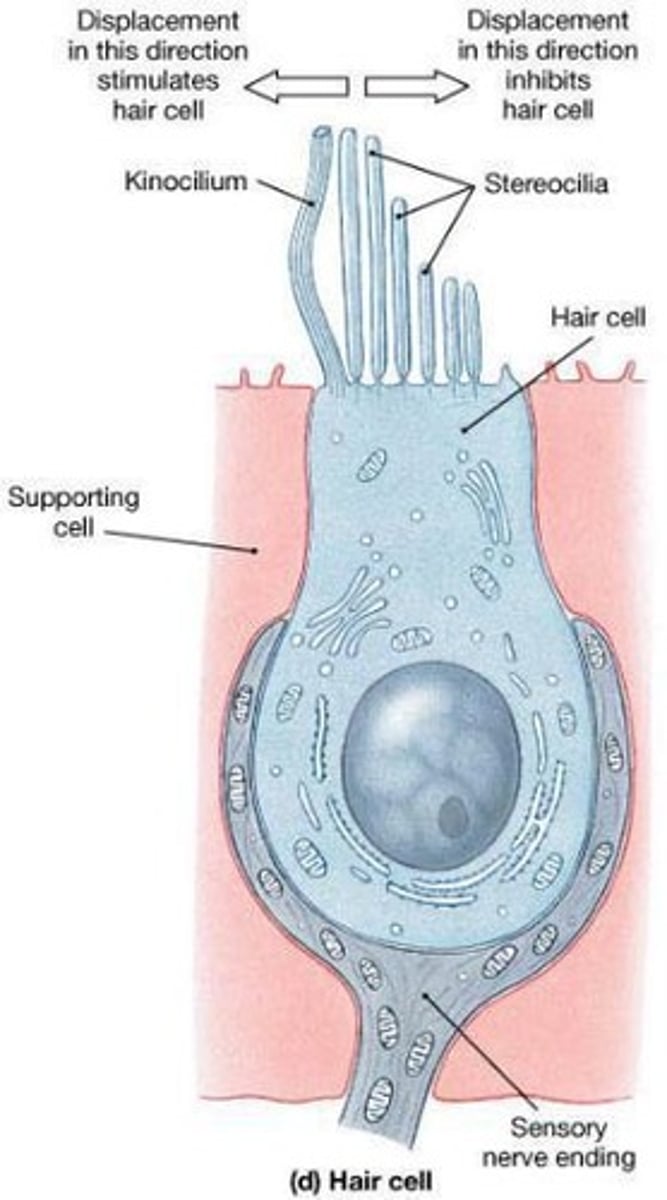
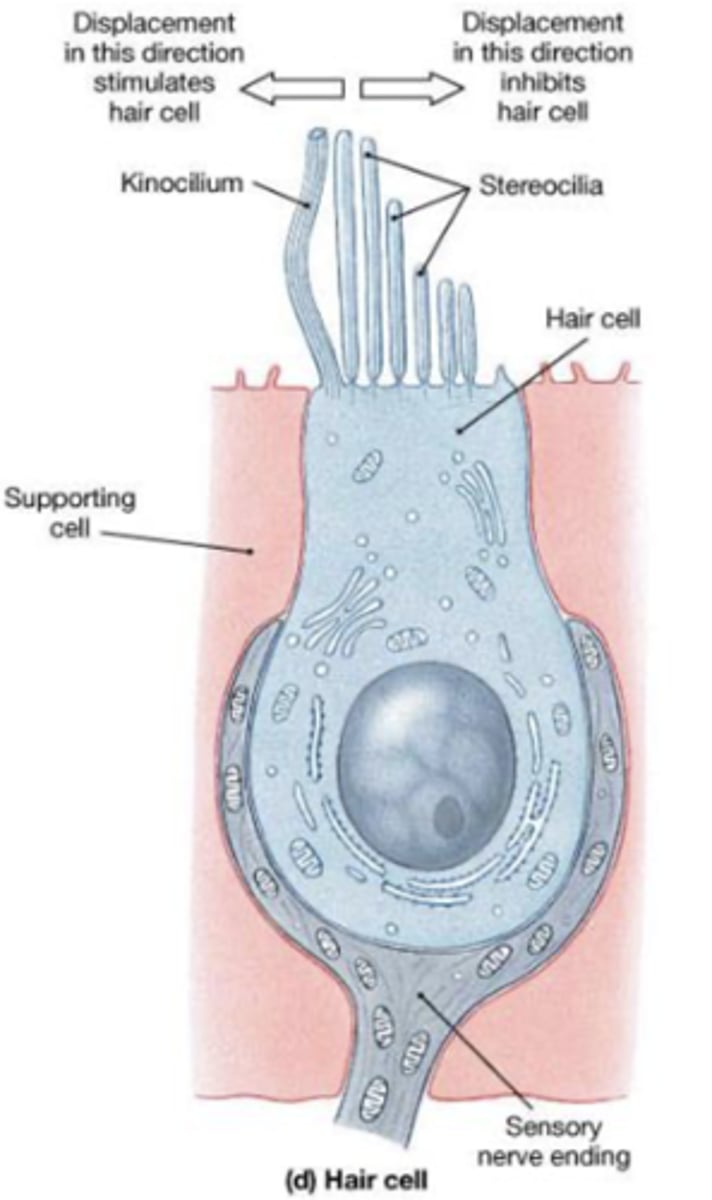
Hair cells structure
One apical, long, rigid kinocilium
Bundle of 30-50 rigid, unbranched stereocilia
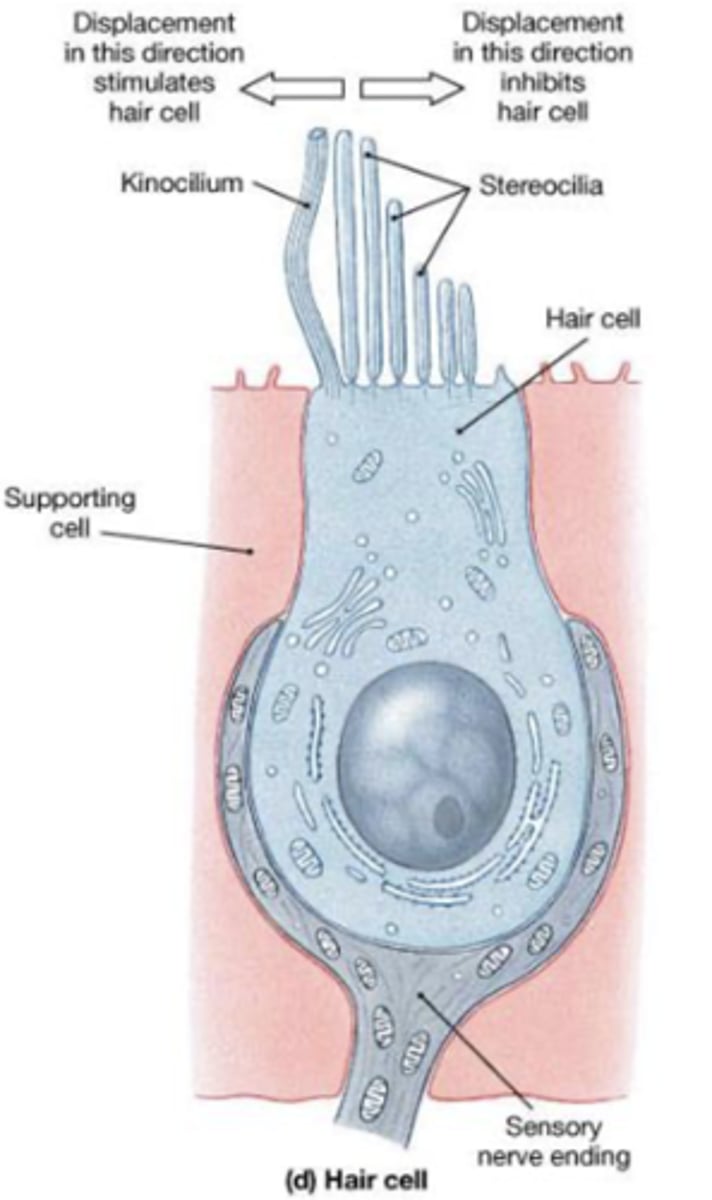
How is the stereocilium connected?
connected to an actin-rich region in the apical cytoplasm: the cuticular plate
How is the stereocilia arranged?
In rows of decreasing length: the longest adjacent to
the kinocilium.
Types of hair cells
Two types with basal synapses with afferent nerve endings
Type I Hair cells
rounded basal ends completely surrounded by an afferent terminal calyx
Type II hair cells
These types of hair cells are more numerous, and are columnar, with bouton endings from afferent nerves.
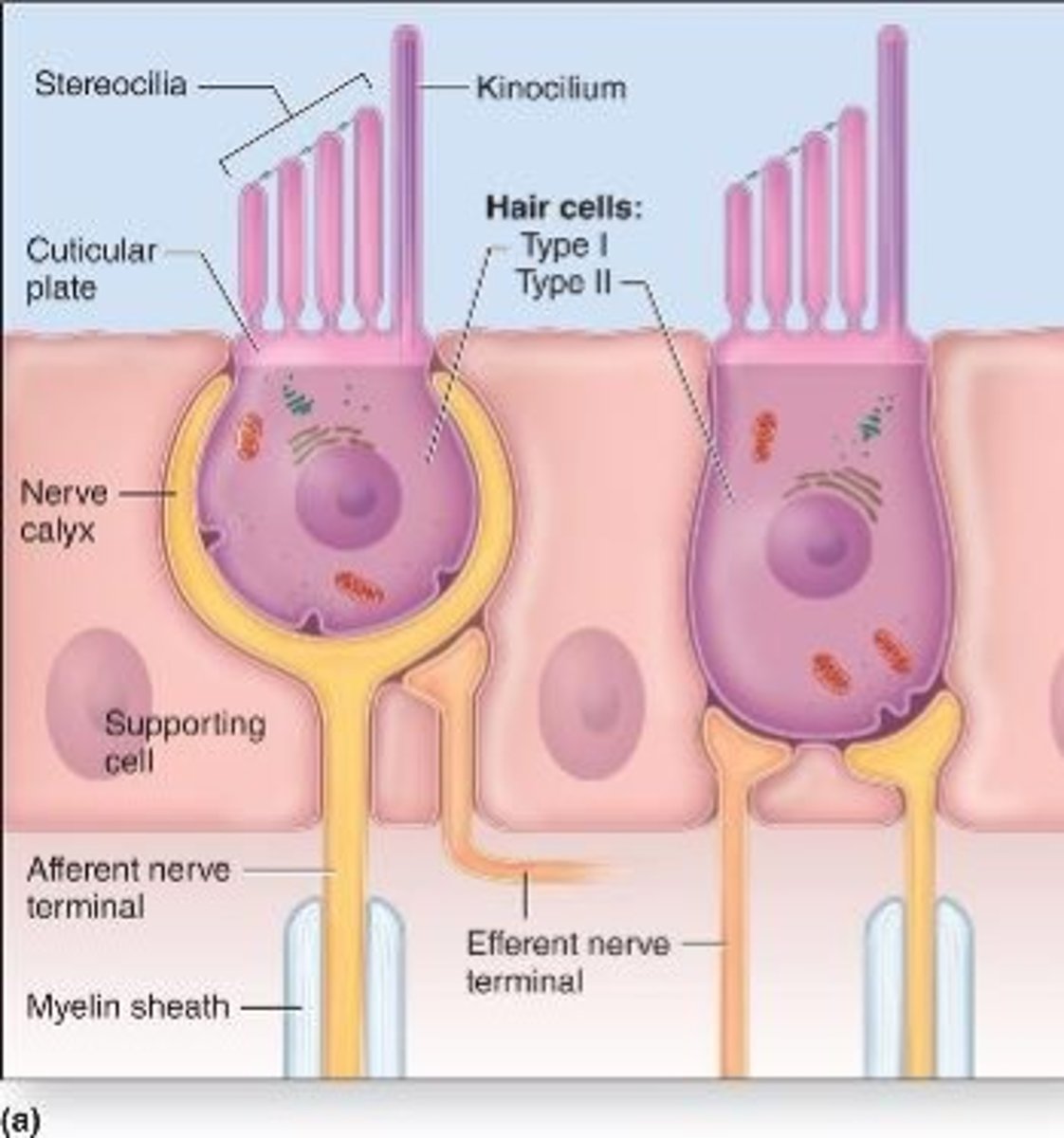
Similarities between type I and type II hair cells
Both are associated to efferent nerve fibers from the brain (modulation)
Supporting cells of hair cells
provide metabolic and physical support for the mechanoreceptors
Otolithic membrane
Gelatinous material with otoliths (otoconia) located in the outer region of the macula
Otolithic membrane contains
proteins and CaCO3
What is embedded in the otolithic membrane?
Tips of kinocilium and stereocilia
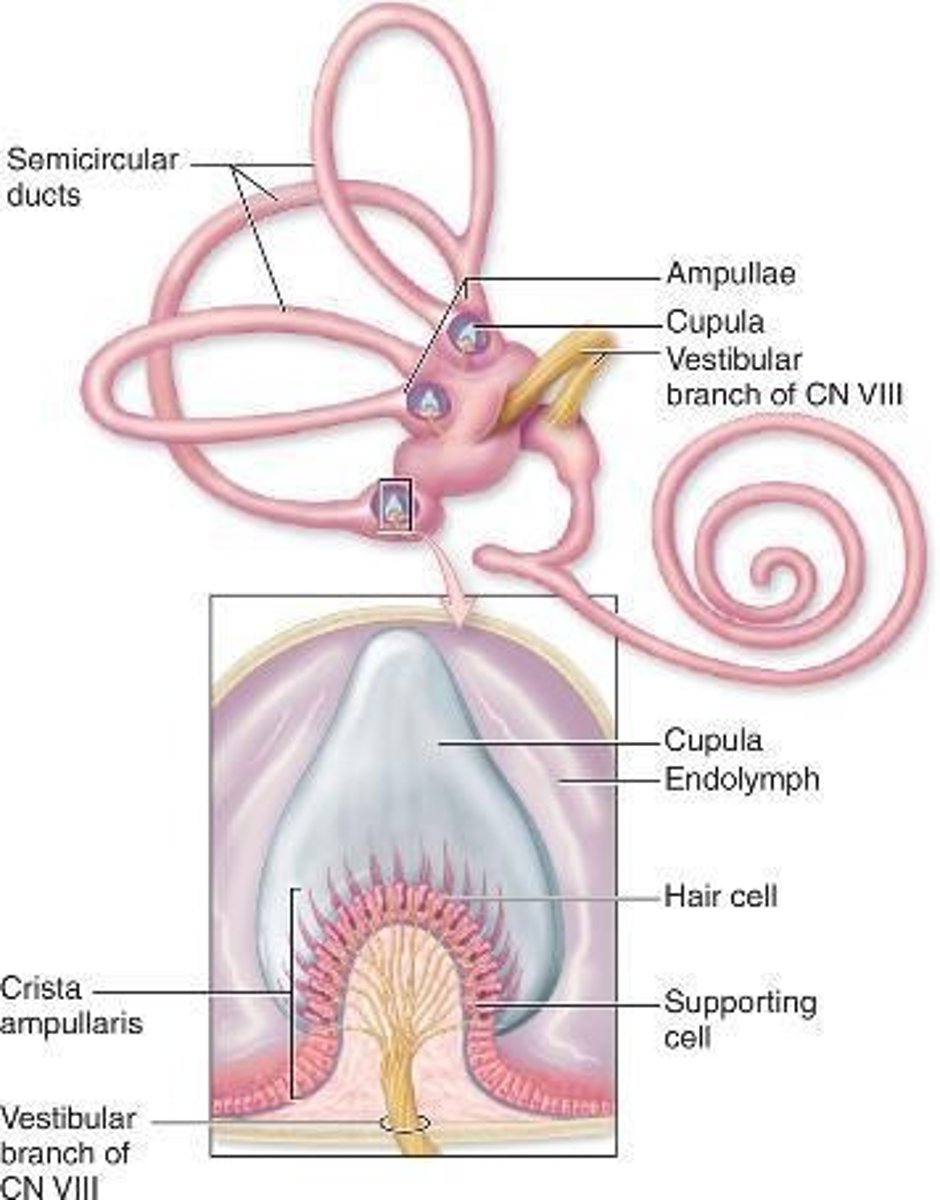
Semicircular ducts
Extend from and return to the wall of the utricle
How many planes does the semicircular ducts have?
three
Each duct consists of what?
ampulla with hair cells and supporting cells on a crest of the wall: the crista ampullaris
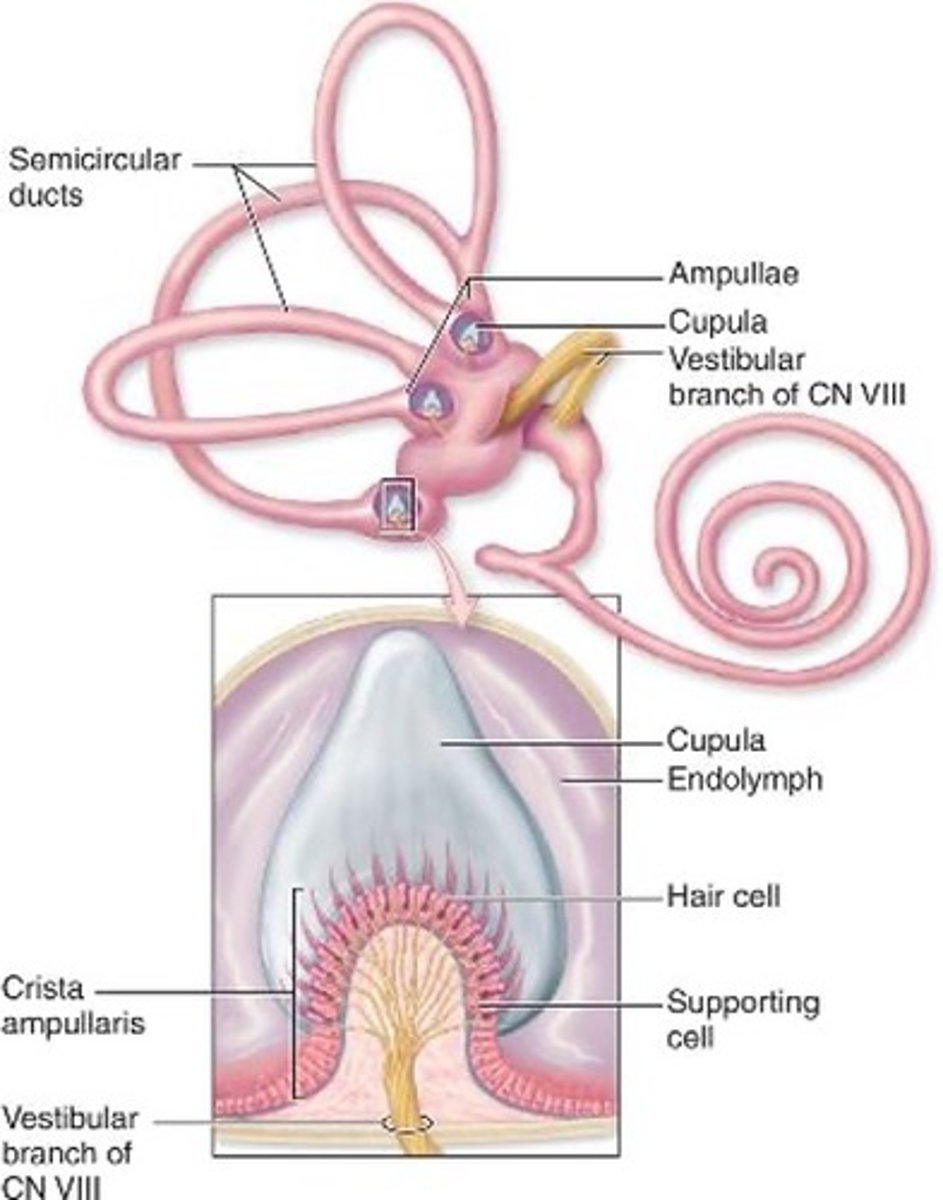
Differences between cristae and maculae
1.The proteoglycan layer is called the cupula,
2. Is attached to the apical part of the hair cells
3. Lacks otoliths
4. Is thicker
Location of cupula
extends across the ampulla and reaches the non-sensory wall
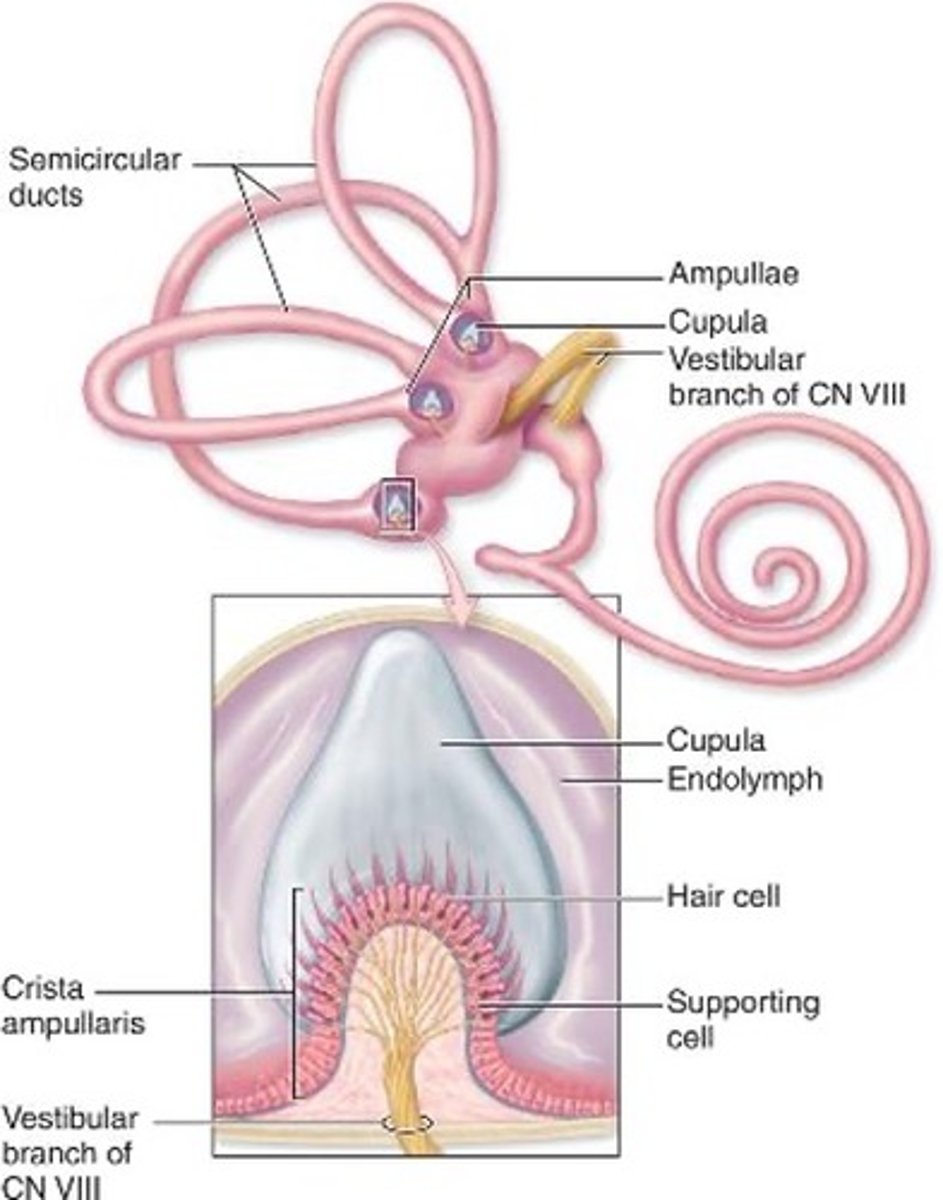
Mechanoreceptors of semicircular ducts
detect rotational movements of the head as the endolymph moves within the ducts
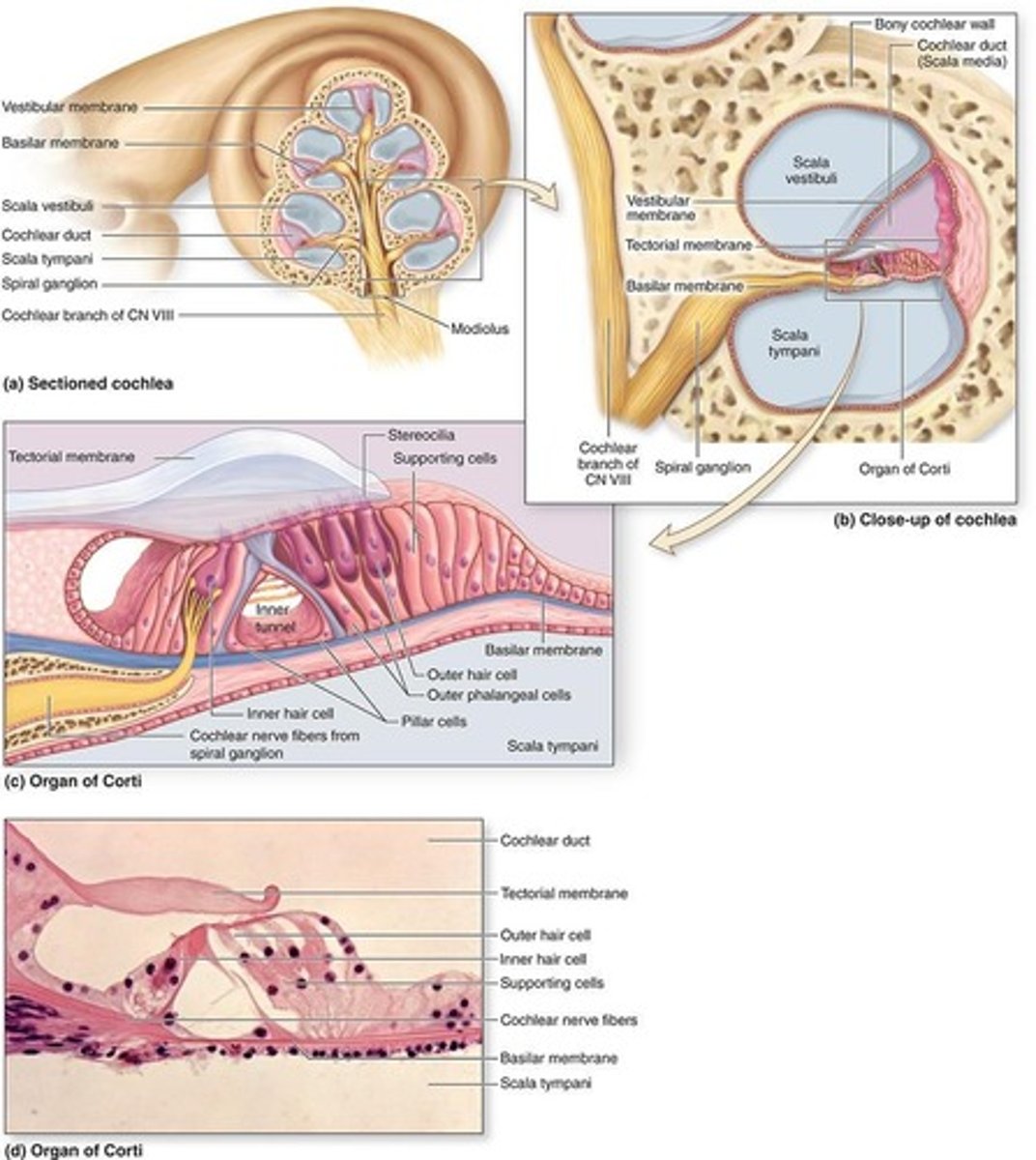
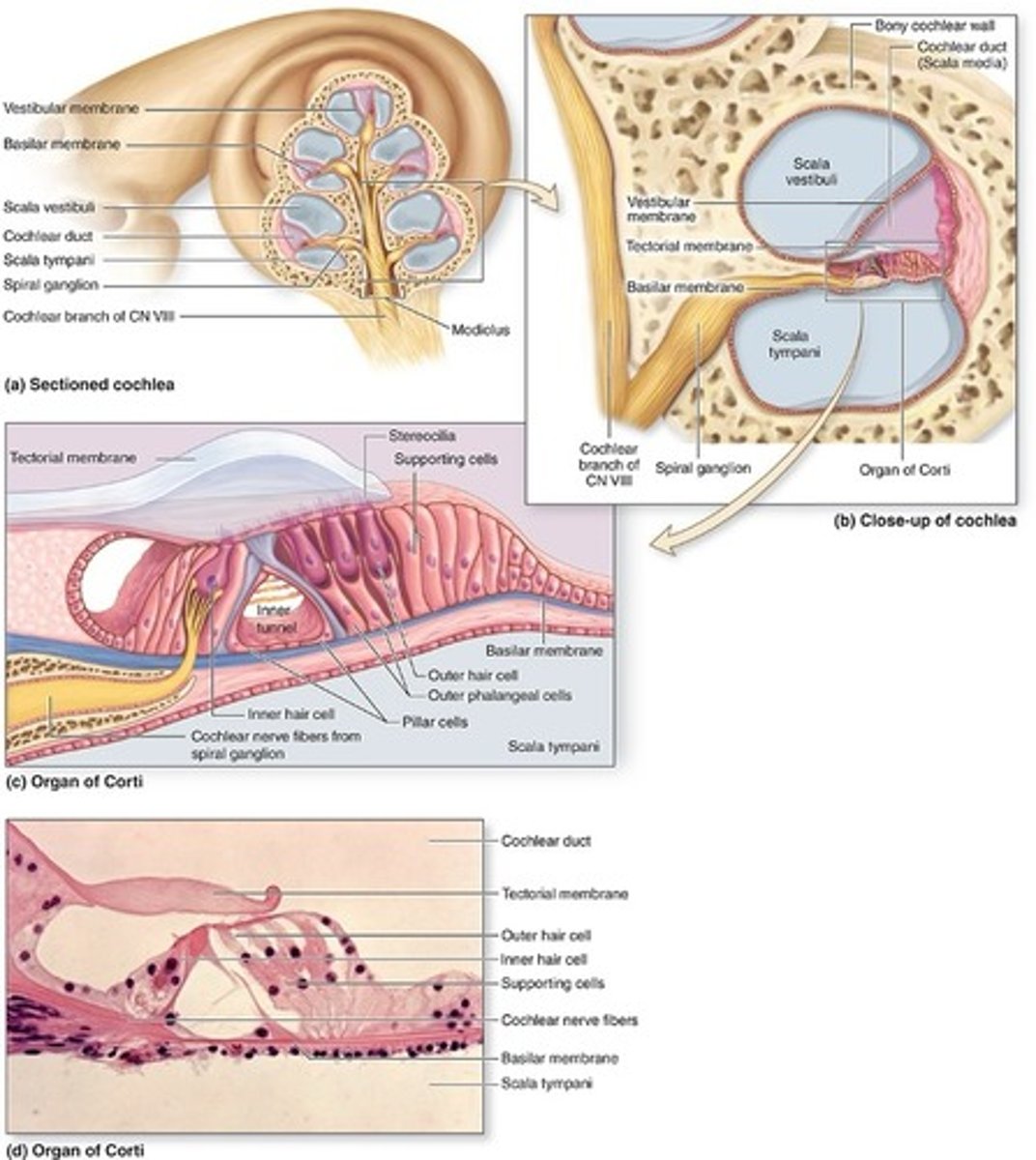
Cochlear duct
A spiral tube with the hair cells and other structures
How many ducts or scalae does the cochlear duct form?
three parallel ducts or scalae that coil 2 ¾ turns within the cochlea
What are the three scalae in cochlear duct?
scala media, scala vestibuli, scala tympani
Scala media
middle chamber filled with endolymph, continuous with the saccule and ending at the apex of cochlea
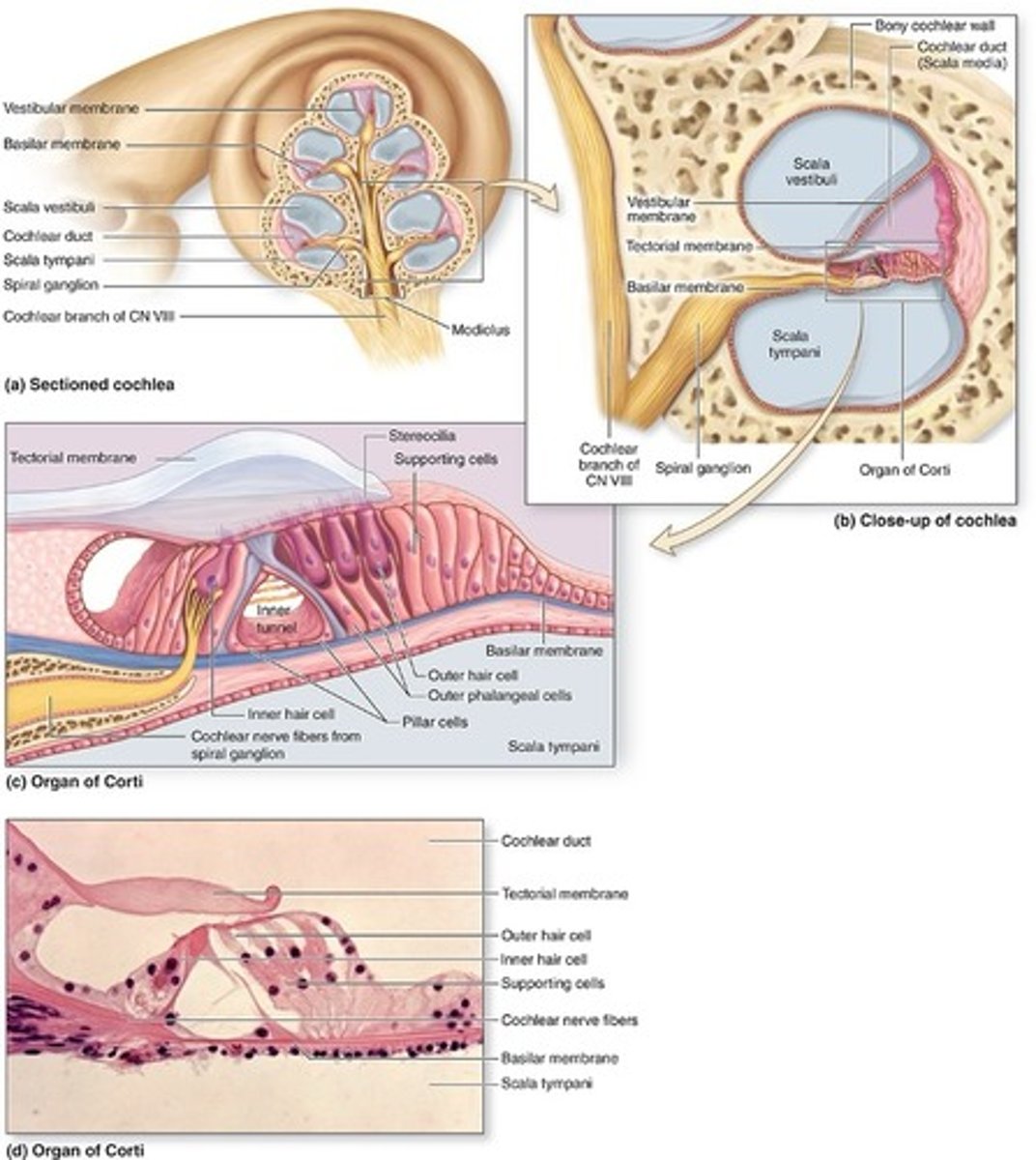
Scala vestibuli
upper chamber contains perilymph, separated by the scala media by the vestibular (Reissner) membrane
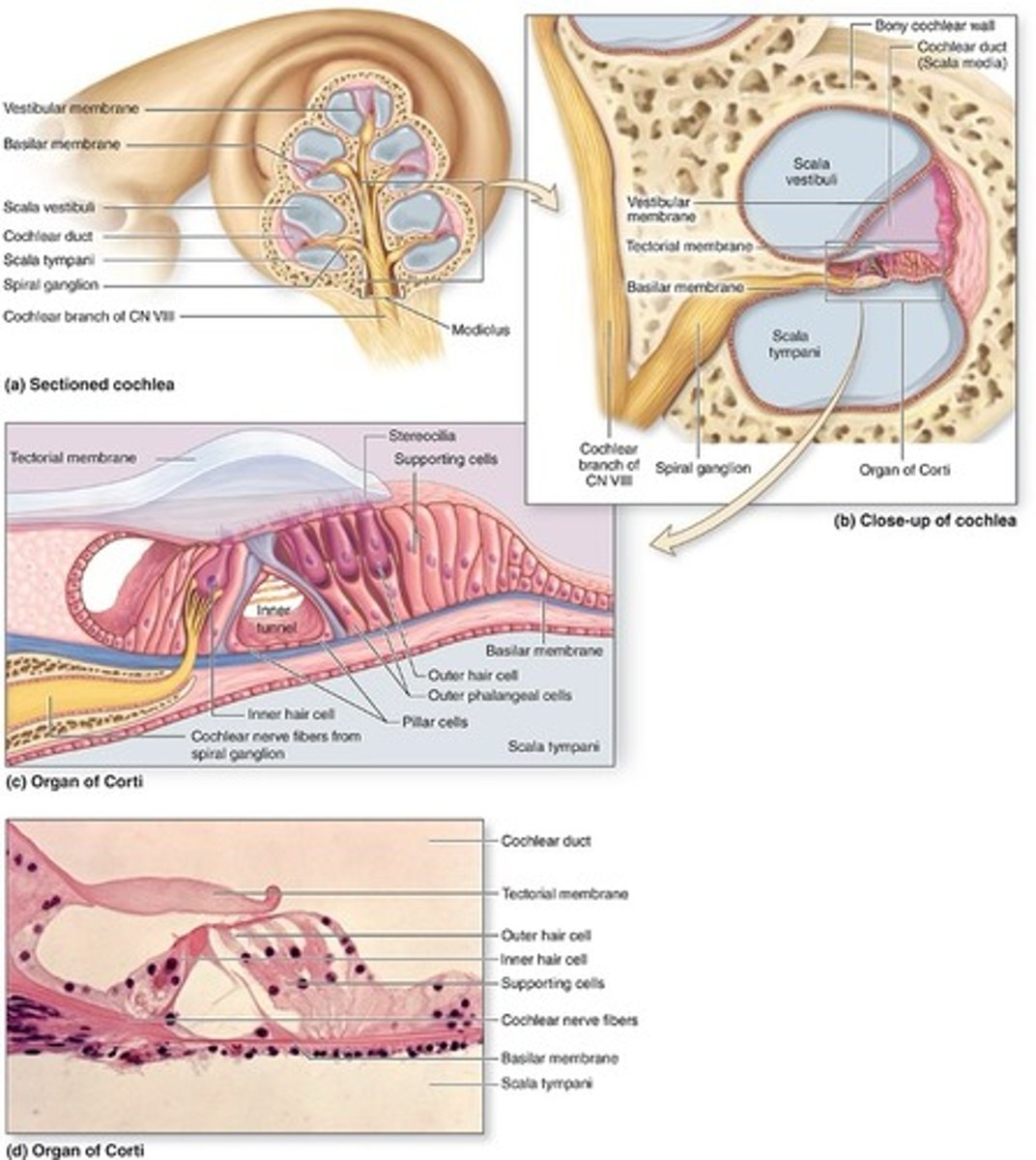
Reissner membrane
lined by simple squamous epithelium on each side
What membrane separates scala vestibuli and scala media?
vestibular (Reissner) membrane
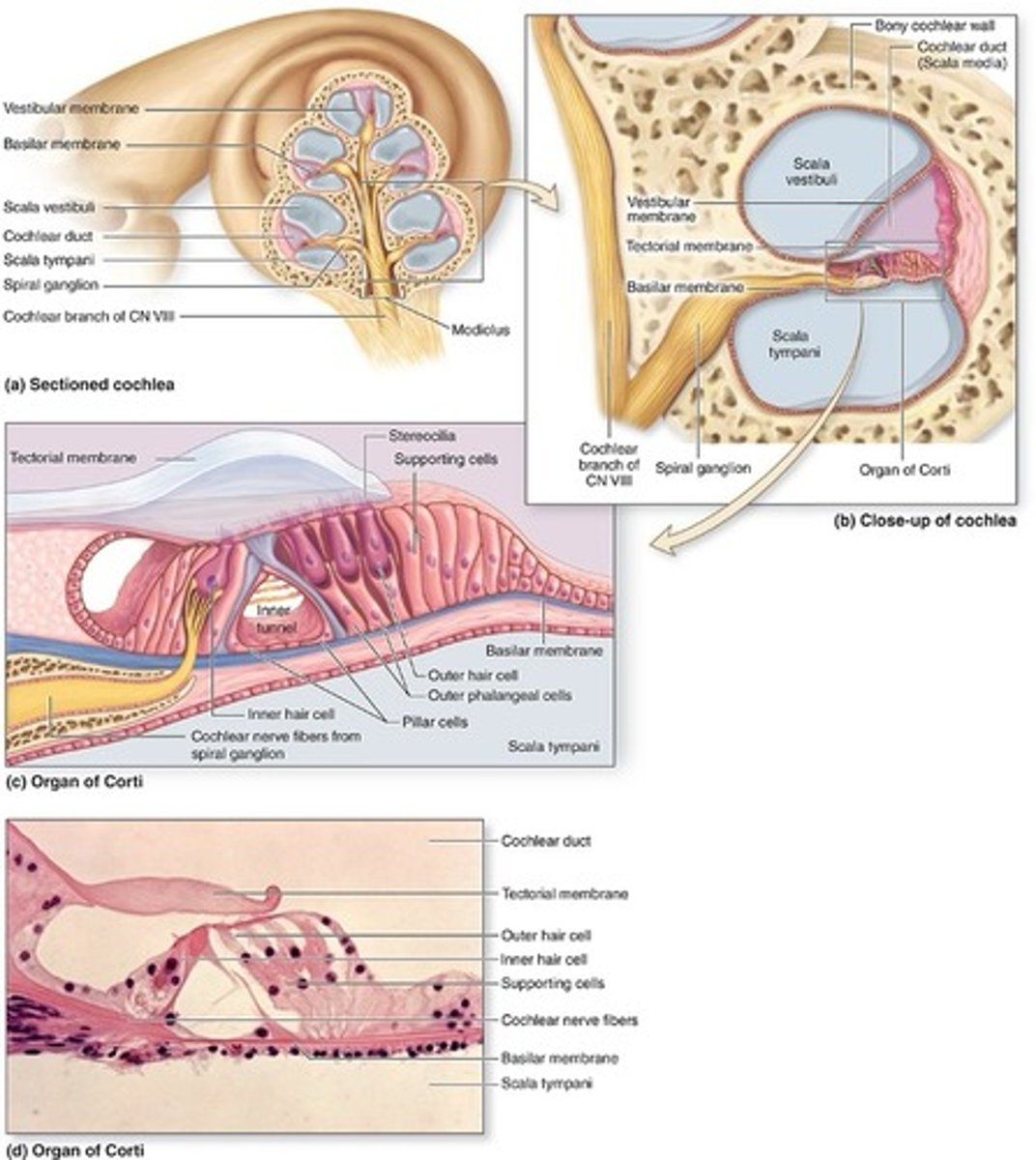
Scala tympani
contains perilymph, separated from the
scala media by the fibroelastic basilar membrane
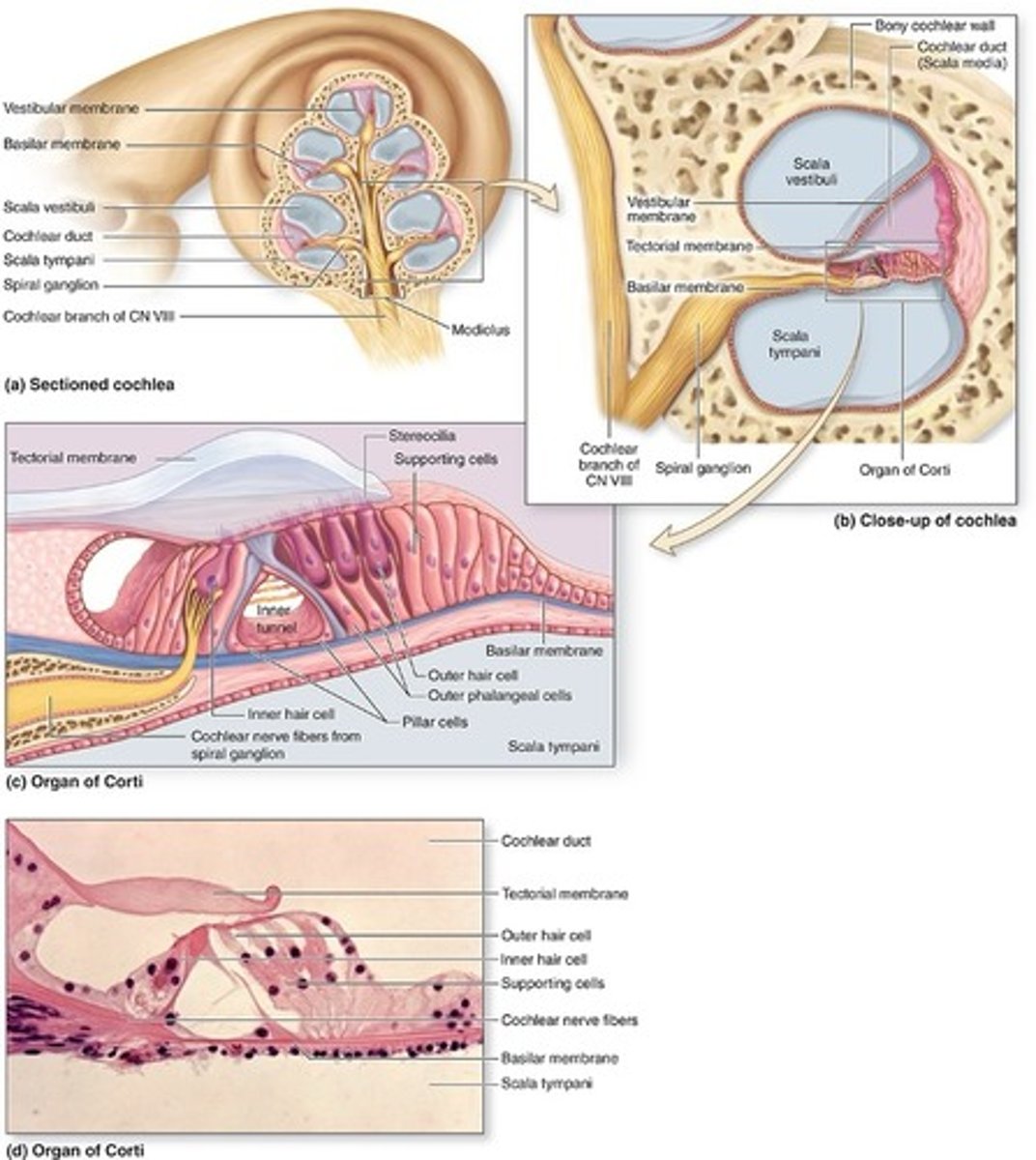
What membrane separates scala tympani and scala media
basilar membrane
Where does the scala vestibuli begin?
oval window
Where does the scala tympani end?
round window
Where do the scala vestibuli and scala tympani communicate?
at the apex via the helicotrema
Helicotrema
where the perilymph of scala vestibuli and perilymph of scala tympani will meet
Stria Vascularis
Produces K+-rich endolymph in scala media.
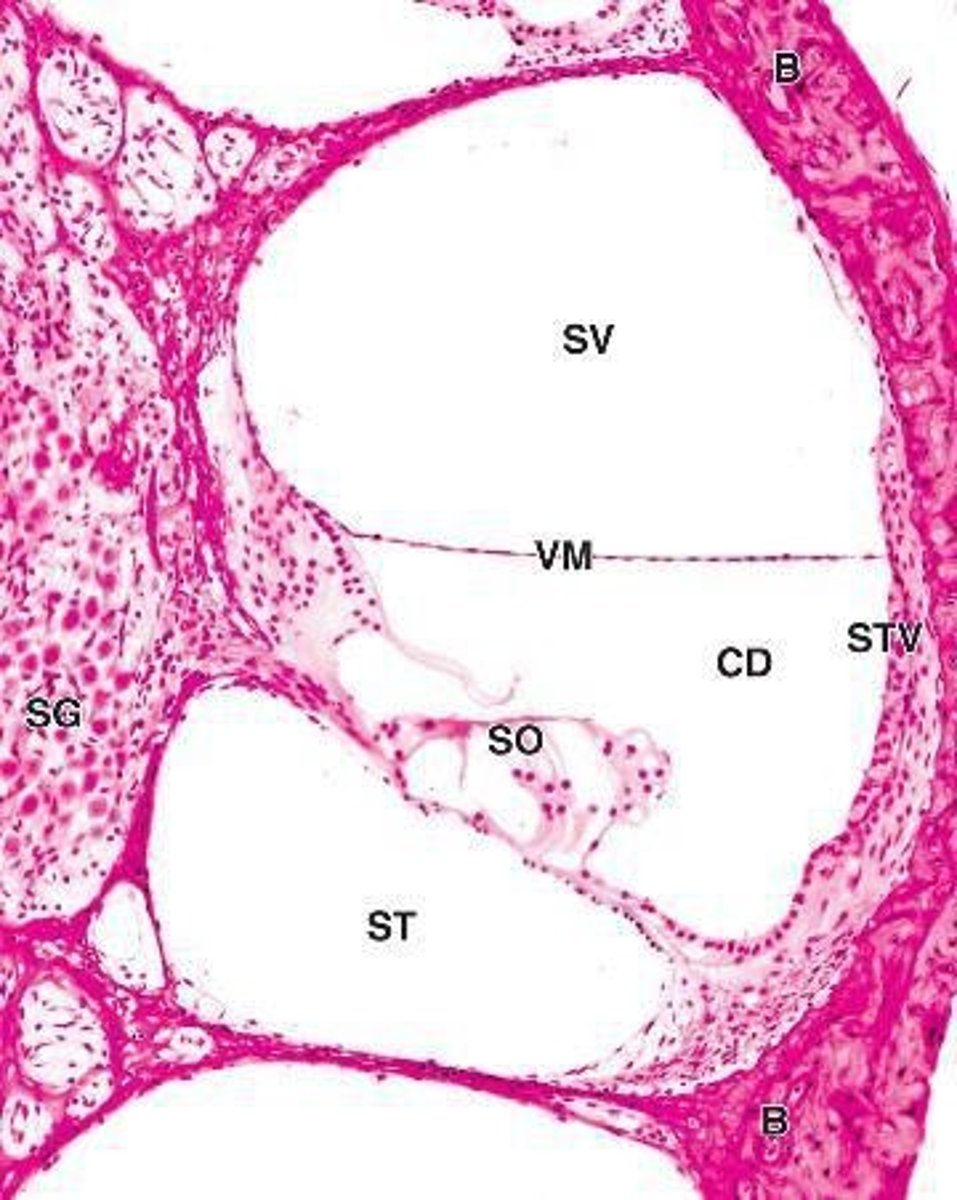
Tissue of stria vascularis
stratified epithelium
Where is the stria vascularis?
lateral wall of scala media
function of stria vascularis
surrounds capillaries and produce K+ rich endolymph
What is unusual about the stria vascularis?
unusual intraepithelial plexus
Organ of corti
Detects sound vibrations of different frequencies
What is organ of Corti consist of?
Inner and outer hair cells in a V-shaped arrangement
Major characteristics of organ of Corti
No kinocilum, only stereocilia
Supportive cells present of the basilar membrane
inner and outer phalangeal cells; pillar cells
Inner and outer phalangeal cells
Apical processes surround and support basolateral parts of inner and outer hear cells and synaptic nerve endings
Pillar cells
stiffened by bundles of keratin and outline the inner tunnel
Inner tunnel
Triangular space between outer and inner complexes of hair cells and phalangeal cells
Tectorial membrane
•Gel-like
•Bundles of collagen (type II. V, IX, and XI)
•Contains the tips of tallest stereocilia of hair cells
What type of collagen is in tectorial membrane?
type II, V, IX, and XI
Spiral ganglion
•Afferent bipolar neurons
•Found in the modiolus
Outer hair cells structure
columnar cells
Outer hair cells number
12,000
Outer hair cells arrangment
Organized in three rows up to five rows near the apex
Outer hair cells consists
Each bears a V-shaped bundle of stereocilia
Inner hair cells structure
shorter than the outer hair cells
Inner hair cells arrangement
Form a single row of approximately 3,500 cells
How is the sterocilia in inner hair cells?
Stereocilia are shorter in a more linear arrangement