10 d - cerebellum
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
what comprises the cerebellum
Two hemispheres (cerebellar hemispheres), separated by vermis (band of cortex)
Folia cerebelli (aka gyri)
Arbor vitae - Connects cerebellar cortex with cerebellar peduncles (superior, middle, inferior)
what seperates the left and right hemispheres
longitudinal fissure
what are the lobes of the brain
Four lobes
Frontal - conscious control of
skeletal muscles
parietal - conscious perception of
touch, pressure, vibration, pain,
temperature, and taste
occipital - perception of visual
stimuli
temporal - conscious perception
of auditory and olfactory stimuli/deep is
the insula
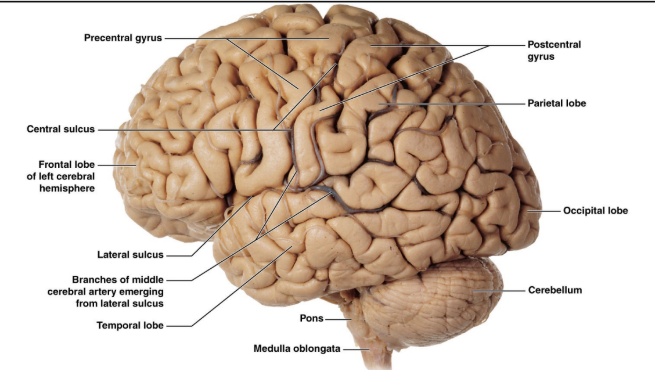
where is the precentral gyrus and what does it do
Anterior to the central sulcus
Consists of primary motor cortex (M1, or Brodmann area 4)
Neurons direct voluntary movements by controlling somatic motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord
where is the postcentral gyrus and what does it do
Posterior to the central sulcus
Consists of the primary somatosensory cortex (BA #3,1,2)
Neurons receive somatic sensory information for touch, pressure, pain, taste, and are associated with visual cortex, auditory cortex, olfactory cortex, and gustatory cortex
motor in front of central sulcus and sensory behind
what are the different cerebral association areas
Somatosensory (just behind post central gyrus) : allows for the understanding of size, form, and texture
Premotor cortex : uses memories of learned movement to coordinate motor activities - if damaged it can affect motor memory and coordination
Visual association : visually recognizes and interprets objects
Auditory association : recognizes sound, recognizing peoples voices
what are cerebral association areas
cc. primary areas
Areas associated with integrating and understanding sensory or motor
information
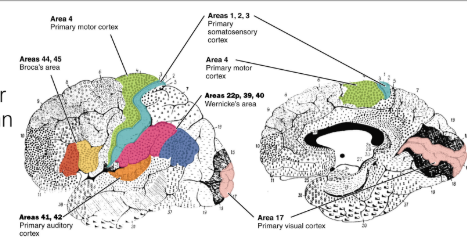
what do each of the following areas do : brocas area, prefrontal cortex, wernickes area
broca’s area - production of speech, sequence of motor movements to talk, regulates breathing pattern for speech
prefrontal cortex - decision making, personality, performs complicated learning and reasoning functions
wernicke’s area - understanding context and language, deriving meaning, language comprehension
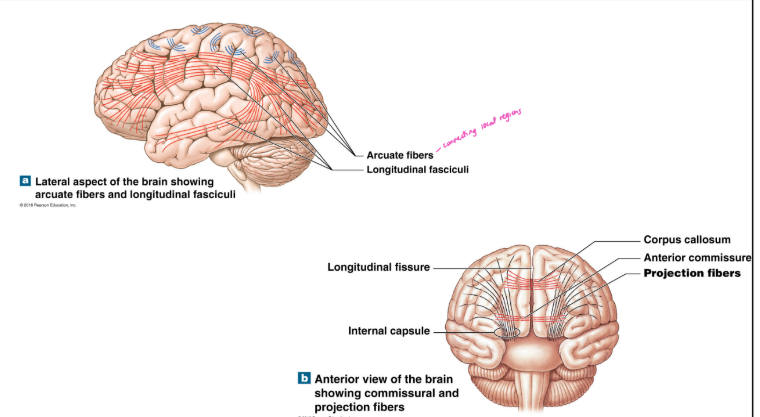
what are the different white matter tracts and their function
association fibers - interconnect cortical areas within the same hemisphere
arcuate fibers - interconnect gyri within a lobe, short distance between regions
longitudinal fasciculi - interconnect frontal lobe with other cerebral lobes, same hemisphere longer fiber
commissural fibers (corpus callosum, anterior commissure) - interconnect corresponding lobes of different hemispheres
projection fibers - connect cerebral cortex to diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord