Mechanical Ventilation Modes
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
control ventilation
basic description
all breaths are mandatory
patient “locked out” of spontaneous breaths
control ventilation
waveforms
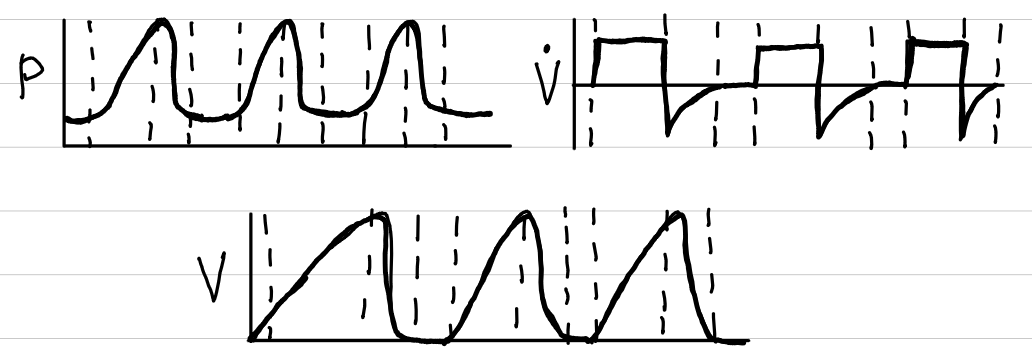
control ventilation
control
volume
control ventilation
trigger
time
control ventilation
limit
volume, flow, time
control ventilation
cycling
volume
control ventilation
indication
patients who can’t participate in WOB (i.e., transected C2 or C3 nerve)
volume control-assist control (VC-AC)
basic description
consistent volume; variable pressure
spontaneous breaths are assisted
volume control-assist control (VC-AC)
waveforms
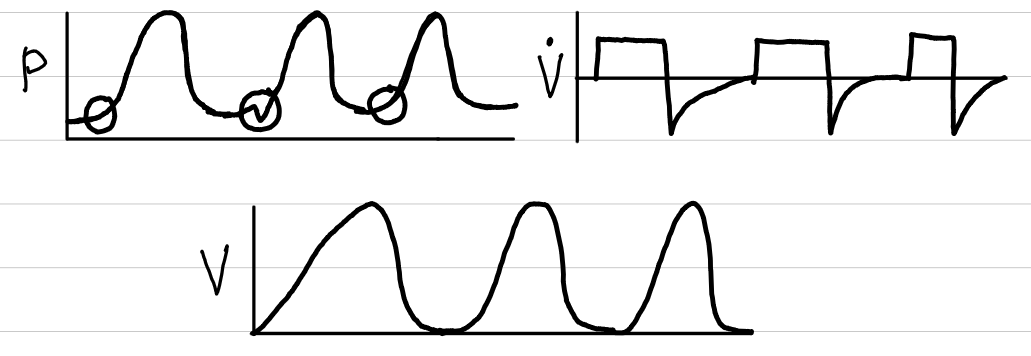
volume control-assist control (VC-AC)
control
volume
volume control-assist control (VC-AC)
trigger
time, patient
volume control-assist control (VC-AC)
limit
none
volume control-assist control (VC-AC)
cycling
volume
volume control-assist control (VC-AC)
indication
guaranteed VT and VE
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
basic description
consistent volume
spontaneous breaths not synched with ventilator
causes “breath stacking”
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
waveforms
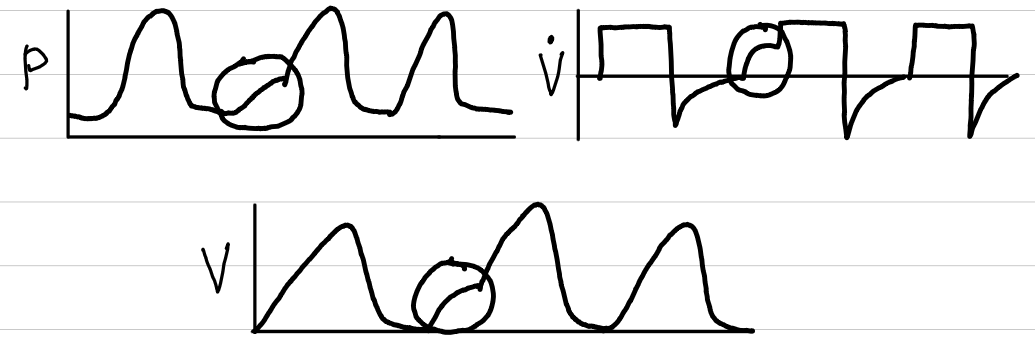
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
control
volume
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
trigger
time
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
limit
volume, flow, time
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
cycling
volume
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
spontaneous variables
none
volume control-intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-IMV)
indication
guaranteed VT and VE
patient can breathe between set breaths
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
basic description
consistent volume
spontaneous breaths synched with ventilator
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
waveforms
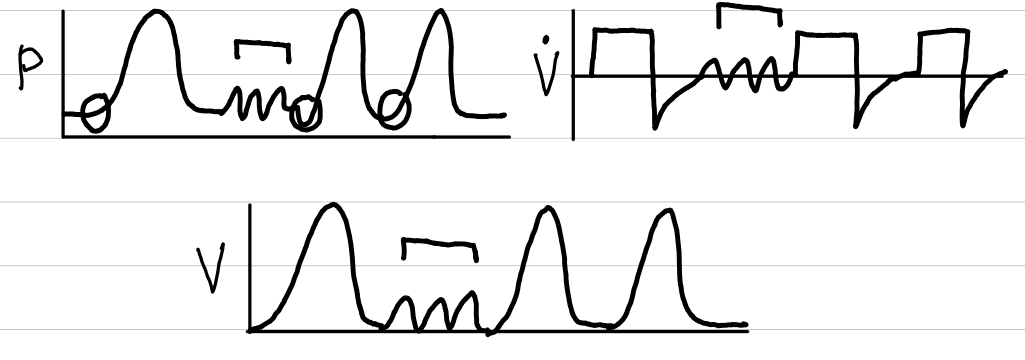
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
control
volume
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
trigger
time, patient
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
limit
none
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
cycling
volume
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
spontaneous variables
none
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (VC-SIMV)
indication
allows patient to breathe between set breaths
weaning off ventilator
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation with pressure support (VC-SIMV w/ PS)
basic description
consistent volume
spontaneous breaths synchronized with ventilator
spontaneous breaths are pressure-supported
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation with pressure support (VC-SIMV w/ PS)
waveforms
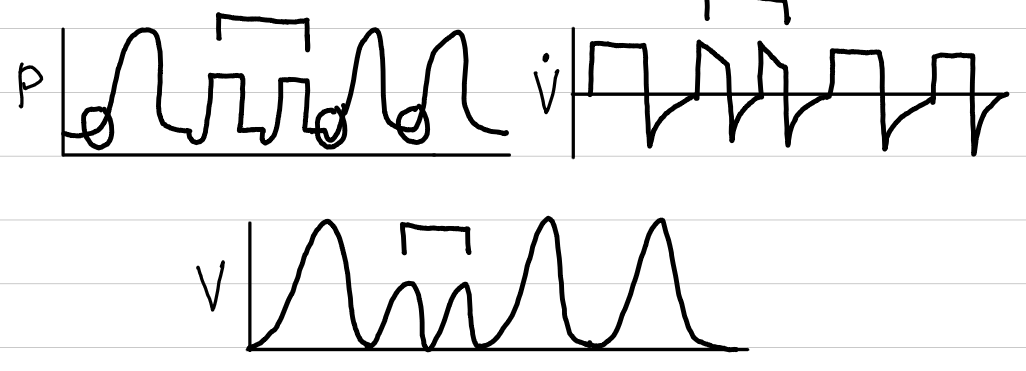
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation with pressure support (VC-SIMV w/ PS)
control
volume; pressure (PS)
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation with pressure support (VC-SIMV w/ PS)
trigger
time, patient
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation with pressure support (VC-SIMV w/ PS)
limit
none; pressure (PS)
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation with pressure support (VC-SIMV w/ PS)
cycling
volume; flow (PS)
volume control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation with pressure support (VC-SIMV w/ PS)
indication
weaning from ventilator
can postpone extubation if not used properly
volume control-inverse ratio ventilation (VC-IRV)
basic description
consistent volume
inverse I:E ratio
volume control-inverse ratio ventilation (VC-IRV)
waveforms
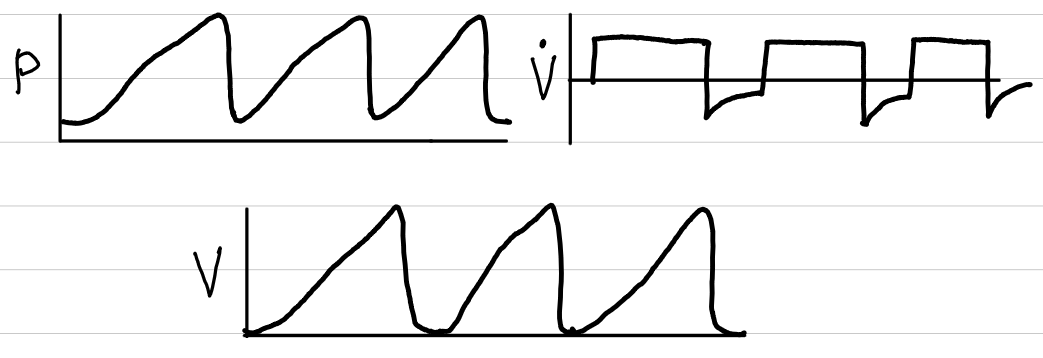
volume control-inverse ratio ventilation (VC-IRV)
control
volume
volume control-inverse ratio ventilation (VC-IRV)
trigger
time (patient?)
volume control-inverse ratio ventilation (VC-IRV)
limit
none
volume control-inverse ratio ventilation (VC-IRV)
cycling
volume
volume control-inverse ratio ventilation (VC-IRV)
indication
guaranteed VT and VE
patients who are paralyzed and sedated
oxygenation (maintain MAP)
continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
basic description
patient breathes against constant positive pressure via mask
continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
waveforms
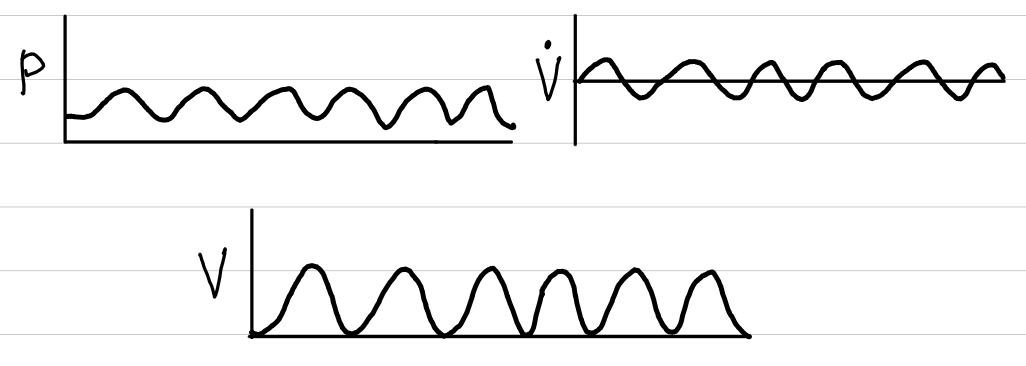
continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
indication
OSA
oxygenation for respiratory distress
continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (CPAP w/ PS)
basic description
patient breathes against constant positive pressure via mask
breaths are pressure-supported
continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (CPAP w/ PS)
waveforms
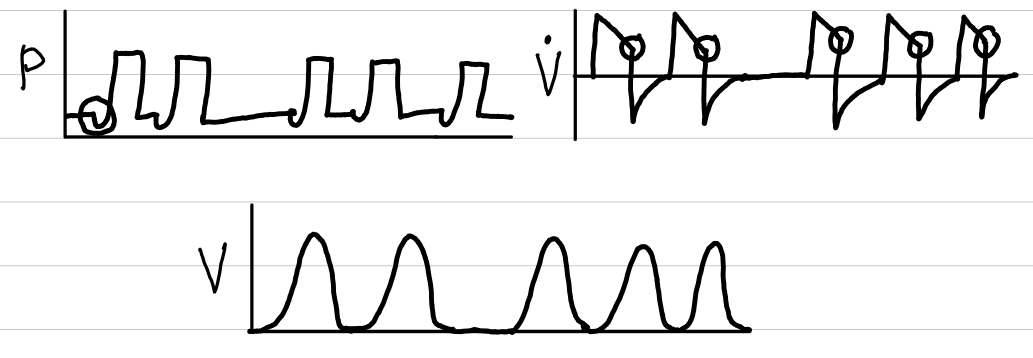
continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (CPAP w/ PS)
control
pressure
continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (CPAP w/ PS)
trigger
patient
continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (CPAP w/ PS)
limit
pressure
continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (CPAP w/ PS)
cycling
flow
continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (CPAP w/ PS)
indication
OSA
oxygenation for respiratory distress needing pressure support
pressure control-assist control (PC-AC)
basic description
consistent pressure; variable volume
pressure control-assist control (PC-AC)
waveforms
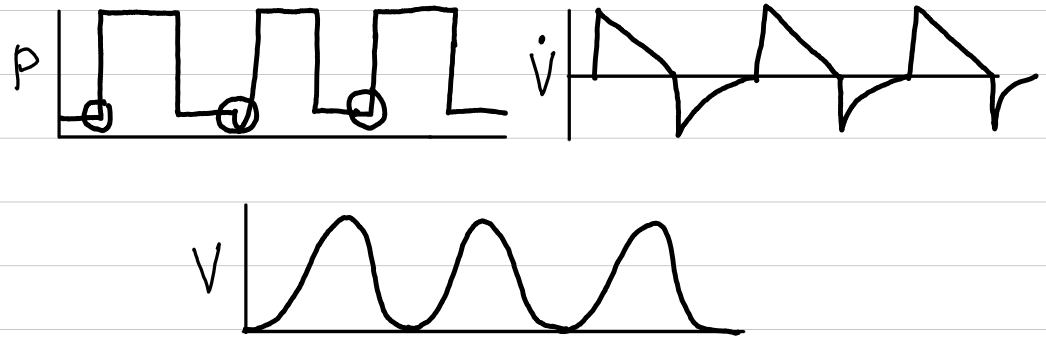
pressure control-assist control (PC-AC)
control
pressure
pressure control-assist control (PC-AC)
trigger
time, patient
pressure control-assist control (PC-AC)
limit
pressure, time
pressure control-assist control (PC-AC)
cycling
time
pressure control-assist control (PC-AC)
indication
lung protection against barotrauma
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
basic description
consistent pressure
spontaneous breaths synchronized with ventilator
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
waveforms
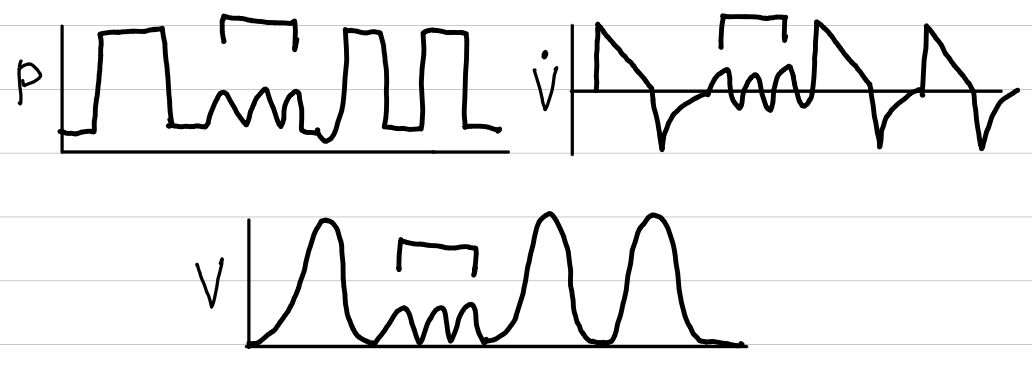
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
control
pressure
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
trigger
time, patient
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
limit
pressure, time
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
cycling
time
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
spontaneous variables
none
pressure control-synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (PC-SIMV)
indication
lung protection against barotrauma
allow spontaneous breaths
pressure control-inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
basic description
consistent pressure
inverse I:E ratio
pressure control-inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
waveforms
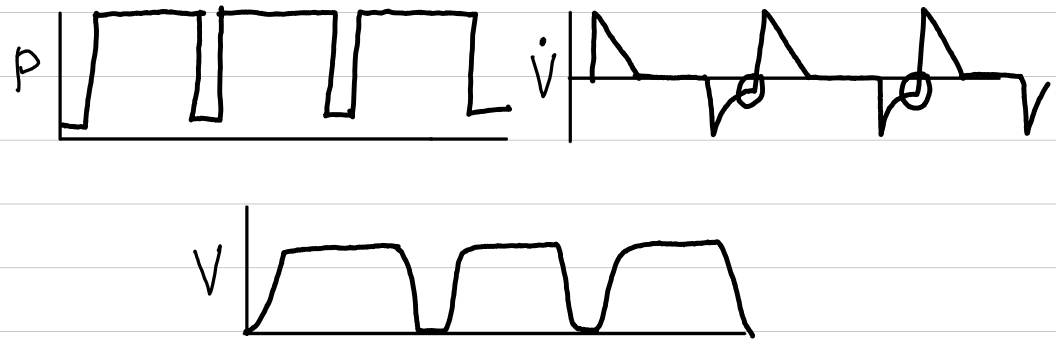
pressure control-inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
control
pressure
pressure control-inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
trigger
time (patient?)
pressure control-inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
limit
pressure, time
pressure control-inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
cycling
time
pressure control-inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
indication
lung protection against barotrauma
oxygenation
bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP)
non-invasive ventilation
patient breathes against two pressures (IPAP and EPAP) to guarantee a VT and to aid in ventilation
used to treat CO2 retention (i.e., COPD)
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
basic description
set high/low pressures
patient can breathe between set breaths
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
waveforms
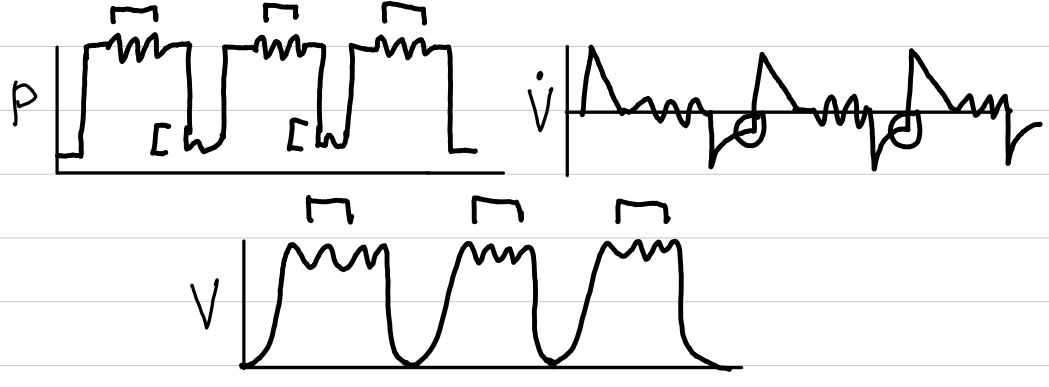
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
control
pressure
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
trigger
time (high/low)
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
limit
time; pressure (PS)
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
cycling
time; flow (PS)
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
indication
oxygenation
patient comfort
(i.e., ARDS)
jet/oscillatory ventilation
basic description
ventilation with set rates up to 60 b/min or higher
jet/oscillatory ventilation
waveform
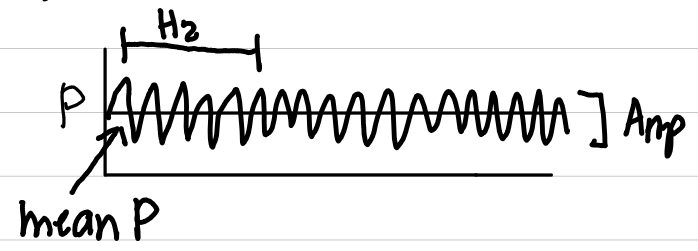
jet/oscillatory ventilation
indication
premature infants
adults when conventional ventilation has failed
volume support (VS)
basic description
all breaths spontaneous
pressure changes to maintain target volume
volume support (VS)
waveforms
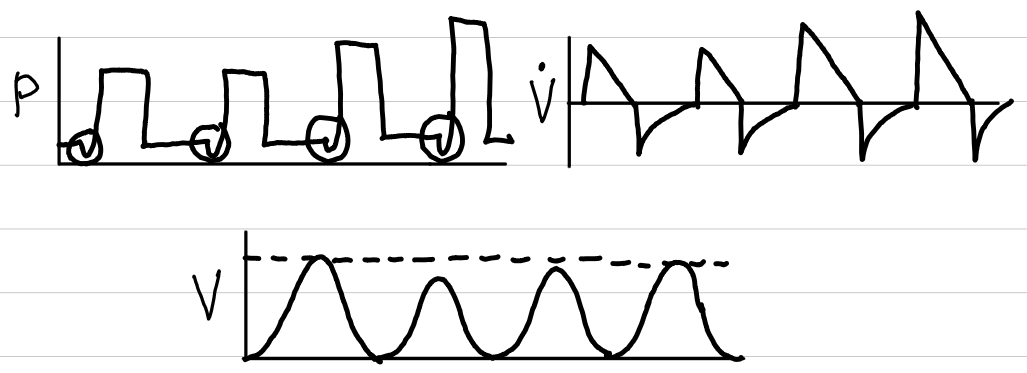
volume support (VS)
control
pressure (target volume)
volume support (VS)
trigger
patient
volume support (VS)
limit
none
volume support (VS)
cycling
flow
volume support (VS)
indication
patients who can breathe on their own but need assistance with target VT
pressure regulated volume control (PRVC)
basic description
pressure changes to maintain target volume
patient can breathe between set breaths
pressure regulated volume control (PRVC)
waveforms
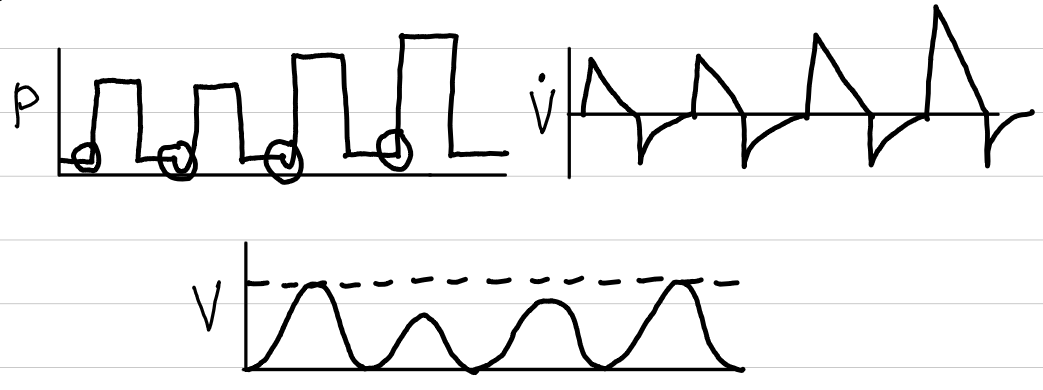
pressure regulated volume control (PRVC)
control
pressure (target volume)
pressure regulated volume control (PRVC)
trigger
patient, time
pressure regulated volume control (PRVC)
limit
time
pressure regulated volume control (PRVC)
cycling
time