Special Testing PPOM 1 Block 3
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Purpose: Tests for supraspinatus tendon injury (rotator cuff tear or tendinopathy)
How to Perform:
Patient's arm abducted to 90° and moved forward 30° (scapular plane)
Thumbs pointing down (as if emptying a can)
Examiner applies downward pressure on the arms while patient resists
Positive Test:
Weakness or pain with resistance indicates supraspinatus injury
Empty Can Test (Jobe’s Test)
Purpose: Also assesses for supraspinatus tear
How to Perform:
Patient fully abducts the arm
Patient is asked to slowly lower the arm to their side
Positive Test:
Sudden dropping of the arm or inability to smoothly lower it indicates full-thickness rotator cuff tear, especially of the supraspinatus
Drop Arm Test
Purpose: Tests for shoulder impingement, especially of the supraspinatus tendon under the acromion
How to Perform:
Flex shoulder and elbow to 90°
Internally rotate the arm while stabilizing the scapula
Apply gentle pressure downward on the wrist
Positive Test:
Pain in the superior shoulder suggests subacromial impingement
Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Test
Purpose: Also tests for subacromial impingement
How to Perform:
Examiner stabilizes the scapula
Patient’s arm is passively flexed (raised) overhead in internal rotation
Positive Test:
Pain during flexion indicates rotator cuff impingement (especially supraspinatus or long head of biceps tendon)
Neer Impingement Test
Purpose: Diagnostic for De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis (inflammation of APL & EPB tendons)
How to Perform:
Patient tucks their thumb into a fist
Examiner ulnarly deviates the wrist (bends it toward the pinky)
Positive Test:
Pain at the radial styloid indicates tenosynovitis of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis
Finkelstein’s Test
Purpose: Tests for nerve irritation or entrapment
How to Perform:
Examiner taps over the course of a nerve:
At wrist (median nerve) → for carpal tunnel syndrome
At elbow (ulnar nerve) → for cubital tunnel syndrome
Positive Test:
Tingling or “electric shock” sensation in the nerve distribution (e.g., first three digits for median nerve, 4th/5th for ulnar)
Tinel’s Sign (at the Wrist or Elbow)
Purpose: Tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
How to Perform:
Patient flexes both wrists and presses backs of hands together (reverse prayer position) for 30–60 seconds
Positive Test:
Numbness or tingling in the median nerve distribution (thumb, index, middle, and radial half of ring finger)
Phalen’s Test
Purpose: Assess for medial (golfer’s) or lateral (tennis) epicondylitis
A. Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
Passive pronation + wrist flexion
Resisted wrist extension
Positive Test: Pain at the lateral epicondyle
Elbow Provocation Tests for Epicondylitis
Passive supination + wrist extension
Resisted wrist flexion
Positive Test: Pain at the medial epicondyle
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)
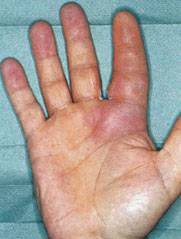
Purpose: Diagnose septic flexor tenosynovitis
Signs (must evaluate together):
Fusiform swelling of the digit
Finger held in slight flexion
Pain with passive extension
Tenderness along the flexor tendon sheath
Interpretation:
Presence of these 4 signs strongly suggests infected flexor tendon sheath, which requires urgent surgical intervention
Kanavel’s Signs (not a single test but a group of signs)
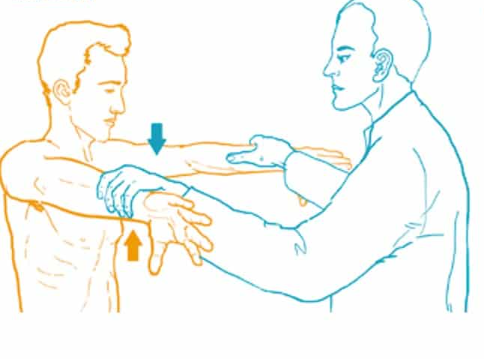
What does a positive Empty Can test indicate?
Weakness or pain with resistance indicates supraspinatus injury
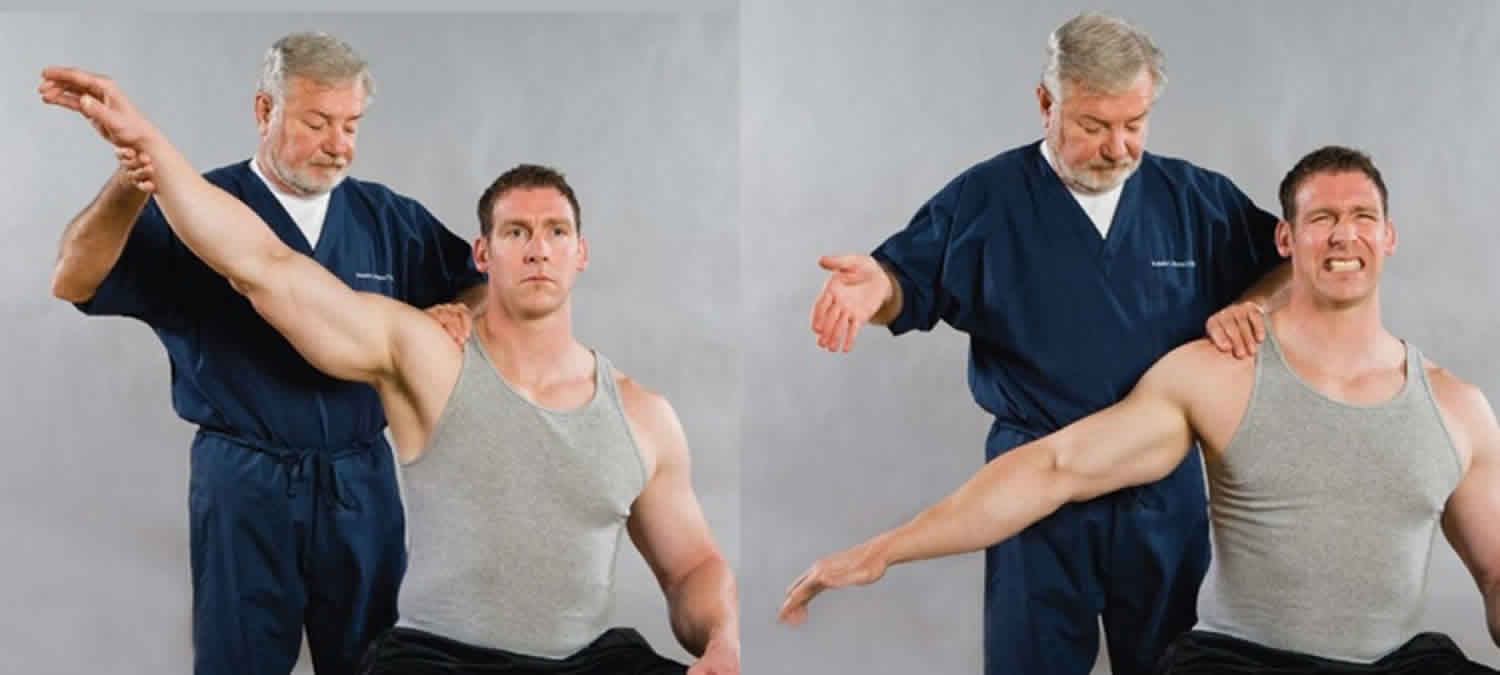

What does a positive Drop Arm test indicate?
Sudden dropping of the arm or inability to smoothly lower it indicates full-thickness rotator cuff tear, especially of the supraspinatus
What does a positive Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement test indicate?
Pain in the superior shoulder suggests subacromial impingement
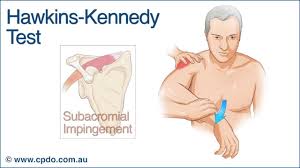
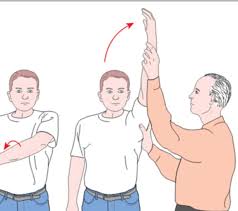
What does a positive Neer impingement test indicate?
Pain during flexion indicates rotator cuff impingement (especially supraspinatus or long head of biceps tendon)
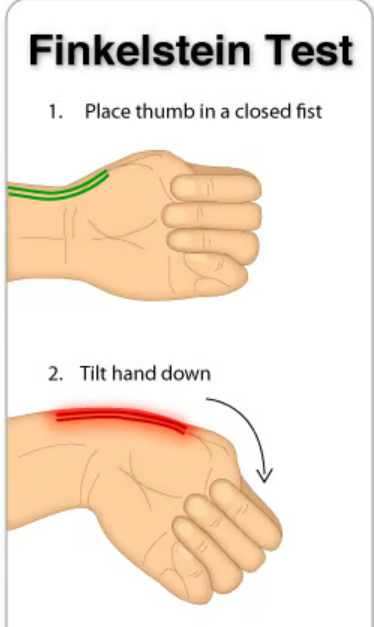
What does a positive Finklestein’s test indicate?
Pain indicates tenosynovitis of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis
(De Quervian’s Tenosynovitis)
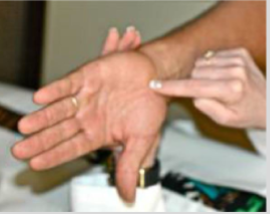
A positive Tinel’s sign at the wrist indicates what?
Tingling at wrist (median nerve) → for carpal tunnel syndrome
A positive Tinel’s sign at the elbow indicates what?
Tingling at elbow (ulnar nerve) → for cubital tunnel syndrome
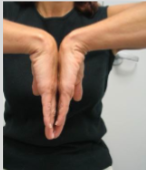
What is a positive Phalen’s test indicate?
Tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
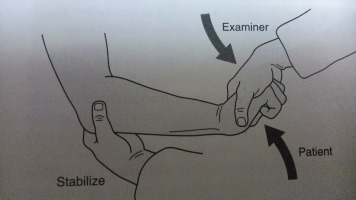
What does a positive Cozen’s test indicate?
Positive for lateral epicondylitis or “tennis elbow”
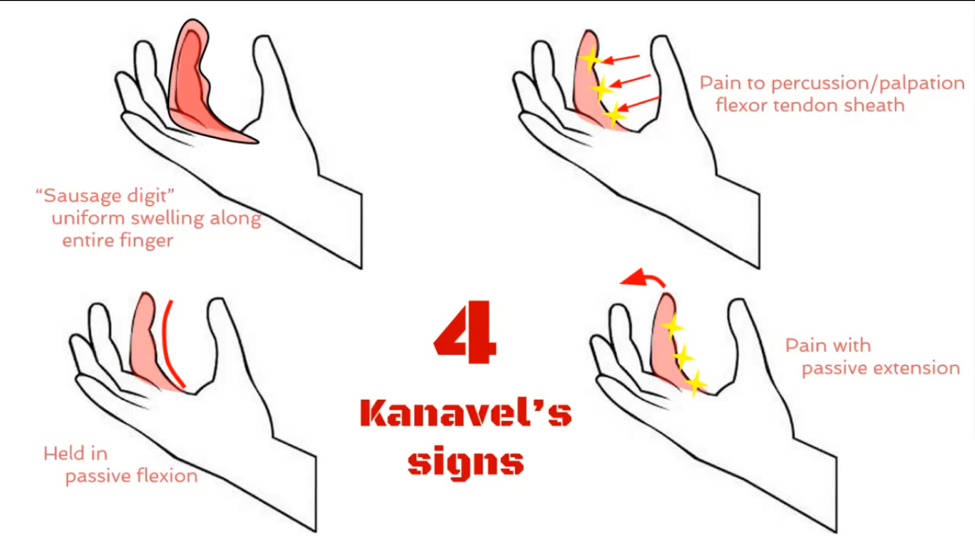
What does presence of the Kanaval’s signs indicate?
Presence of these 4 signs strongly suggests infected flexor tendon sheath
Purpose: Differentiates between muscular vs. nerve root causes of neck pain.
Description: Examiner lifts the patient's head (traction). Relief of symptoms indicates nerve root compression.
Indicative of: Nerve root impingement (if pain is relieved with distraction).
Distraction Test