Movement In and Out of Cells
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
There are 3 main ways in which substances move in or out of cells, they are:
Diffusion
Osmosis
Active Transport
Whats Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration down a concentration gradient as a result of their random movement. Particles would diffuse until there is a balance
Factors that influence diffusion
Surface Area
Temperature
Distance
Concentration Gradient
Surface Area
The larger the Surface Area, the higher the rate of diffusion (a larger surface area provides more space for molecules to come into contact with each other, thus increasing the rate of diffusion. This is because there are more opportunities for molecules to move across the surface and interact with other molecules.)
Temperature
The higher the temperature the higher the rate of diffusion (this is because molecules are faster and have more kinetic energy with higher temperature)
Concentration
The higher the Concentration Gradient the higher the rate of diffusion ( as there is a steeper difference in concentration between two regions, leading to faster movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.)
Distance
The shorter the distance the higher the rate of diffusion (the shorter the distance the particles have to move, the quicker the process is going to be)
Whats Osmosis
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of high water potential (dilute solution) to an area of low water potential (concentrated solution) through a semipermeable membrane
Why do we use water potential
When we are talking about water we cannot use the term concentration anymore because a concentration shows the amount of substance dissolved in water and since water cant be dissolved in water we need to use water potential
High water potential
For a very dilute ("Dilute" describes a solution with a low concentration of solute, meaning there is a relatively small amount of solute dissolved in a larger amount of solvent. For example, a solution of 1 teaspoon of sugar dissolved in 1 liter of water would be considered dilute.) solution, because it has a lot of water it has a high water potential
Low water potential
For a very concentrated (describes a solution with a high concentration of solute, indicating that there is a large amount of solute dissolved in a smaller amount of solvent. For instance, a solution of 5 teaspoons of sugar dissolved in 1 liter of water would be considered concentrated.) solution because it has less water it has a low water potential
Whats a solute
The solute is the substance that is dissolved in a solution. It is present in a smaller amount compared to the solvent. For example, if you dissolve sugar in water to make a sweetened drink, the sugar is the solute.
Whats a solvent
The solvent is the substance in which the solute is dissolved to form a solution. It is typically present in a larger amount compared to the solute. In the example of a sweetened drink, water is the solvent in which the sugar (solute) is dissolved.
Role of water as solvent in organisms:
Substances dissolve in water so water acts as the medium in which substances move around the body
Transport: Water is important for transport, dissolved substances can be easily transported around organisms
Digestion: Water is need for digestion, once the food in our body is digested the nutrients need to be moved to cells all over the body and water allows this transport
Excretion: Waste substances such as urea dissolve in water and this makes it easy for it to be removed from the body through urine
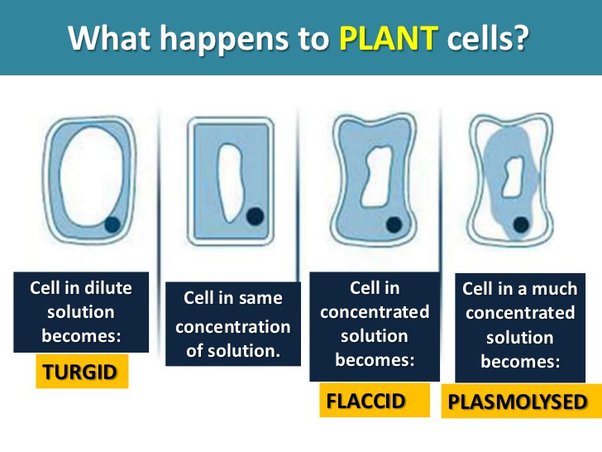
What if you add a cell into water
There will be a higher water potential outside the cell than inside the cell and therefore water will move into the cell
As water enters the cell, they become turgid or swollen due to the high water content
An animal cell can burst if too much water enters
A plant cell has support from its cell wall and therefore will most likely maintain its turgidity without bursting
Turgor Pressure: Pressure on the cell wall from the cell membrane pushing upon it

Adding cell into concentrated solution
There will be a higher water potential inside the cell than outside and therefore water will mve out of the cell
As the water moves out cells becomes flaccid (shrinks)
A plant cell can become plasmolyzed if too much water is lost, this is when the cytoplasm shrinks due to the loss of water but the cell wall fails to shrink due to its tough structure
The cytoplasm eventually tears away from the cell wall
The Importance of Water Potential and Osmosis in the uptake and loss of water by organism
Plants obtain water by osmosis through their roots
Osmosis takes place at the roots because of the difference in water potential between the soil and the inside of the roots
The water is important because it transports the minerals and nitrate ions
The water also maintains the turbidity of the cell, this provides support and strength for the plant
If the plant loses more water than it gains the cells will become flaccid and the plant will wilt
Active Transport
This is the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration thats against a concentration gradient using energy from respiration
Process of active transport
Active transport uses energy to oppose the concentration gradient and forcefully transport molecules against it
In the cell membranes of all cell there are certain embedded protein molecules or protein carriers that carry out this process
The protein basically captures the molecule from 1 side of the cell and it changes shape in a way to transport the captured molecules to the other side of the cell
Energy from respiration is required to alter the protein shape
When is active transport needed
Used in situations where diffusion and osmosis cant be relied upon
For example what if a cell wanted to absorb extra nutrients from outside of the cell despite having a higher concentration of those nutrients inside the cell
Diffusion wouldnt work because the concentration gradient is going the opposite way
Hypotonic meaning
Imagine you have two compartments separated by a membrane, and one compartment has a lower concentration of solutes (like salt or sugar) compared to the other. In a hypotonic solution, there's less "stuff" outside the cell than inside. So, water will move into the cell to try to balance things out, causing the cell to swell or even burst if too much water enters. It's like pouring water into a cup until it overflows.
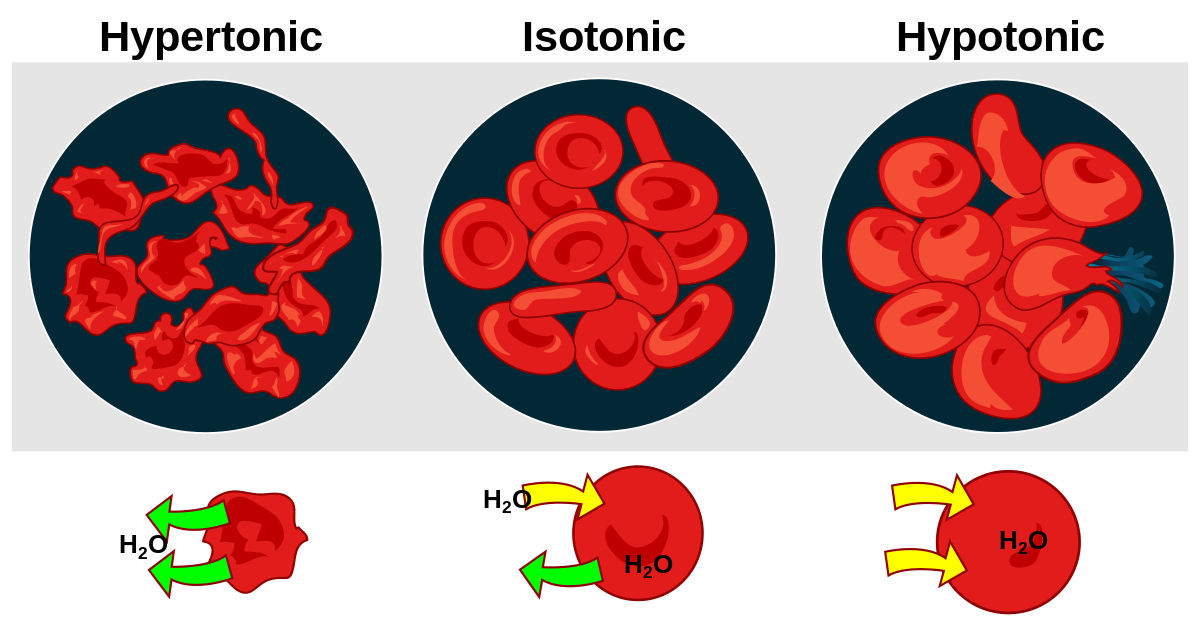
Hypertonic
Now, flip the situation. In a hypertonic solution, there's more "stuff" outside the cell than inside. So, water will move out of the cell into the surrounding solution, causing the cell to shrink or shrivel up. It's like a sponge drying out when you leave it in a salty solution.
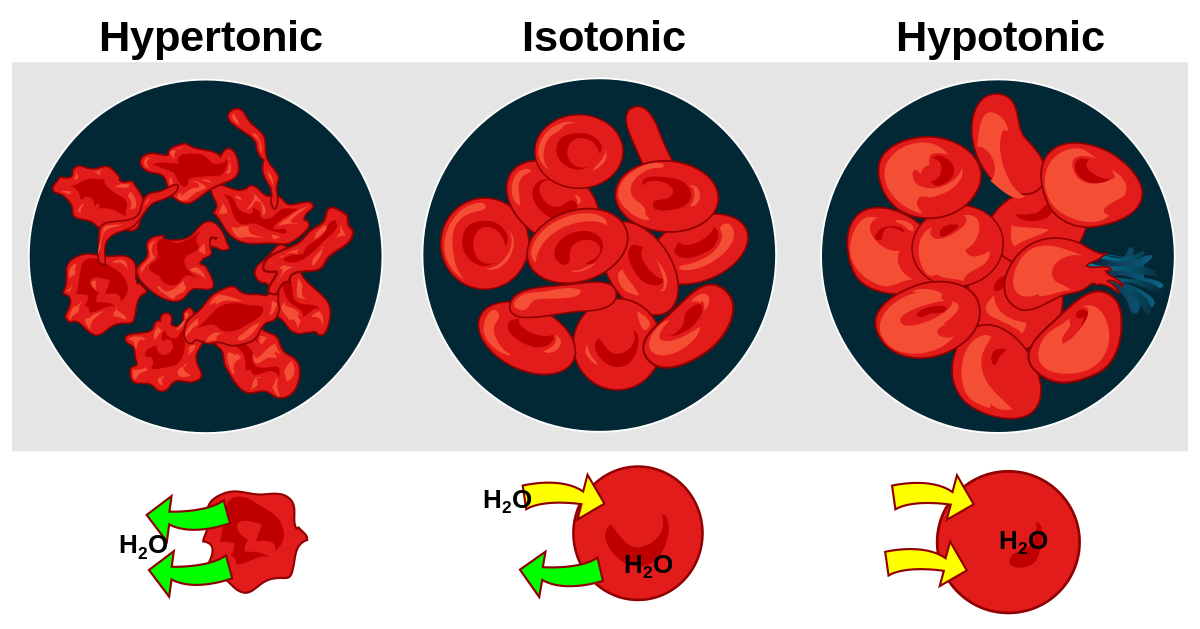
Isotonic
In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside and inside the cell is the same. So, water moves into and out of the cell at the same rate, maintaining its size and shape. It's like a perfect balance where nothing changes.
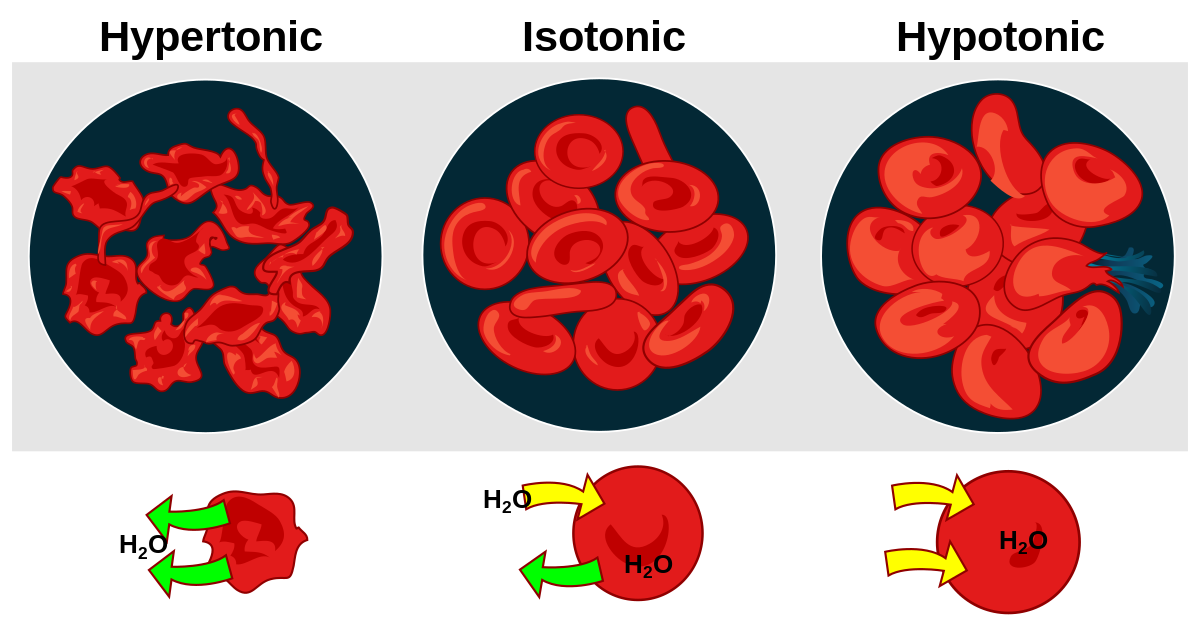
Plasmolysis meaning
In plasmolysis, water moves out of the plant cell, causing the cell membrane to shrink away from the cell wall. As a result, the cell's contents shrink and pull away from the cell wall, creating a gap between the cell membrane and the cell wall. This process can cause the plant cell to look wilted or shriveled.
Imagine a balloon losing air and shrinking because it's in a room with lower air pressure. Plasmolysis is like that, but instead of air, it's water leaving the cell, causing it to shrink and pull away from its outer boundary.