Communication for Various Purposes in Public Speaking
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Non-Verbal Communication
Use of body language, gestures, facial expressions, and other non-verbal cues to convey a message.
Body Language
Speaker's body movements.
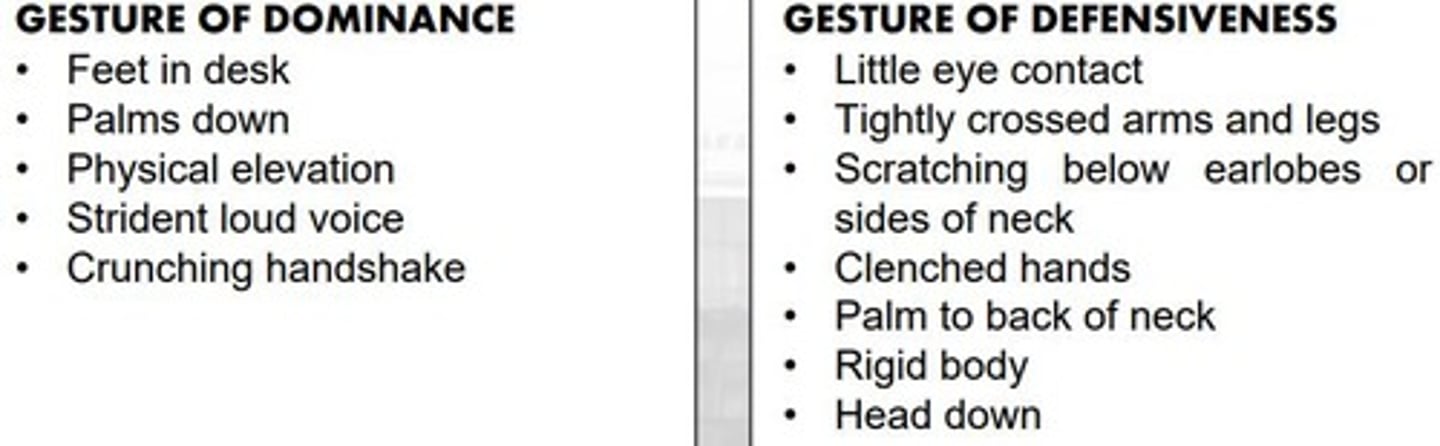
Eye Contact
Detect how confident the speaker is.
Public Speaking
The process or act of performing a presentation focused on an individual directly speaking to a live audience in a structured, deliberate manner to inform, influence, or entertain them.
Facial Expressions
Express emotion through face.
Gestures
Movement of hand and any other parts that carry meaning.
Material
The subject that the speaker explores or discusses during their presentation or speech; it is the central idea or theme.
Message
The main points to the central idea that the speaker wants to convey to the audience; it serves as a guide for all other elements.
Methods of Delivery
The style of delivery; the way in which a speaker presents their speech or presentation to the audience.
Manuscript
Reads their speech word-for-word from a prepared script.
Memorized
Memorizes their entire speech and delivers it from memory without notes or prompts.
Impromptu
Without any prior preparation or planning.
Extemporaneous
Prepared and planned, but not read word-for-word from a script.
Manners in Speech
The way in which a speaker uses their voice and language to communicate their message effectively to the audience.
Good Posture
The position of the body; it shows confidence and elicits a positive impression from the audience.
Clothing and Appearance
Influence the audience's perception of the speaker and the message being conveyed.
Vocal Elements
Characteristics of the voice that affect communication.
Pitch
The highness or lowness of the voice.
Volume
The loudness or softness of the voice.
Rate
The speed at which the speaker speaks.
Tone
The quality of the speaker's voice, such as the level of friendliness, confidence, or authority.
Articulation
The clarity and distinctness of speech.
Pauses
Deliberate breaks in speech for effect or emphasis.
Articulation
the clarity and distinctness.
Pauses
the intentional breaks.
Pronunciation
the correct way of saying words, including the accent, syllable stress, and intonation.
Proxemics
The space and distance between the speaker and the audience. It is an invisible wall that defines how comfortable the speaker is at a distance from the people they are talking to.
Boredom or disinterest
Lousy handshake.
Secretiveness and dishonesty
Touching nose while speaking; tugging ear while speaking; rubbing behind ear while speaking; covering mouth while speaking; scratching head.
Colors
reflect people's personality and reveal character.
Red
most dynamic and passion color that symbolizes love, rage, and courage.
Yellow
It is a truly joyous and radiant color. The happiest of the colors.
Orange
an optimistic color. It helps you look at the bright side of life despite difficulties.
Green
color of spring which represents growth and renewal. It is a color that resonates energy and positivity.
Blue
color of depth, stability, and independence. This is best for studying and working because it helps in relaxing and stimulating the mind.
Purple
It combines stability of blue and energy of red. It is associated with royalty. It symbolizes power, nobility, luxury, and ambition. It conveys wealth and extravagance.
White
It suggests goodness, purity, and innocence.
Black
a mysterious color because it can have different interpretations. It can mean power, elegance, formality, death, evil, or grief.
Audience Analysis
a process of looking into the behavior, values, beliefs, or even the culture of the audience. This is done so the speaker will know what and what not to say, how to say it, and when to say it.
Touch
physical contact. It can be interpreted differently in various cultures. It is used to communicate love, care, or comfort.
Impromptu Speech
to be done without being planned, organized, or rehearsed.
Characteristics of an impromptu speech
Limited to no preparation time (three minutes or less); Short presentation time (two to seven minutes); Points are organized spontaneously; Has a more conversational and informal tone; Relies on research, clear organization, and practiced delivery; Speech is delivered spontaneously, using only an outline or notes.
To Inform (Exposition)
to explain the context
Past, Present, Future
organizes ideas into three parts: past, present, and future. It involves reflecting on the past related to the topic, describing the current situation in the present, and sharing thoughts or predictions for the future.
To Entertain
about making the speech pleasant to listen to from beginning to end.
To Persuade
making a clear point, providing a reason, giving an example or explanation, and then restating the point to summarize the key ideas.
Point-Reason-Example/Explanation-Point (Prep)
making a clear point, providing a reason, giving an example or explanation, and then restating the point to summarize the key ideas.
Pathos
an emotional appeal.
Ethos
In rhetoric, ethos can be understood as the audience's perception of the speaker's ethical character.
Opening, Rule of Three, Clincher
It starts with a strong opening, followed by three supporting details or information, and ends with a clincher that leaves a lasting impression.
Logos
the use of reasoned arguments to convince an audience.
Bridging
building a connection between what the speaker do not know and what they know. It is a technique used to transition smoothly from one topic or question to another.
Reframing
The speaker takes a statement or question and rephrases it in a way that shifts the focus or changes the perspective on the topic.
Playing The Devil's Advocate
Taking a position that is contrary to one's own opinion or beliefs to stimulate critical thinking, or challenge assumptions.
Extemporaneous Speech
without a prepared script or memorized content. Instead, the speaker relies on notes, outlines, or mental preparation to organize their ideas and key points.
Characteristics of an extemporaneous speech
Flexible and adaptable.
Annotated Research Bibliography
a list of sources that have been researched by an individual or group for a specific purpose, with annotations or brief descriptions accompanying each source.
Annotations
Provide a summary of the source's content.
Monroe's Motivated Sequence
A five-step process to engage an audience: (1) Grab attention, (2) Establish need, (3) Present solutions, (4) Help visualize benefits, (5) Call for action.
Thesis Statement
The main point or central argument of the speech, expressing the speaker's stand on the issue and supported by convincing evidence.
Outline
A condensed version of a text in a linear, structured format that organizes main topics, sub-topics, and supporting details.
Workplace Communication
The exchange of information, ideas, opinions, feedback, and instructions among individuals and teams within an organization.
Effective Workplace Communication
Important for achieving organizational goals, building strong relationships among employees, and ensuring a positive work environment.
A.F.O.R.E.S.T.
A technique for speech writing that includes anecdotes, facts and figures, opinion, rhetorical questions, emotive language, superlatives, and tripling.
Problem-Solution
Identify the problem and provide a solution showing its practicality.
Problem-Cause-Solution
Identify the problem, analyze the causes, and provide a solution to the problem.
Comparative Advantages
Identify the problem and present at least two solutions to the problem.
Task Roles
Roles that help the team carry out tasks and get the work done.
Relationship Roles
Roles that strengthen or maintain team relationships.
Self-Centered Roles
Roles that interfere with the team's ability to complete tasks.
Diversity in the Workplace
Differences in gender, ethnicity, language, beliefs, and other attributes within a workforce.
Organizational Culture
The way an organization operates, the attitudes employees have, and the overall tone and approach to operations.
Shared Leadership
The distribution of leadership responsibilities within a team that can influence the functionality of its members.
Team Building
The process of creating a cohesive team that works well together.
Principles of Workplace Communication
Includes being diverse, purposeful, and straightforward.
Diverse Communication
Emerges due to globalization and includes cross-cultural or multilingual communication.
Straightforward Communication
Presents facts and information honestly and directly.
Authoritative
The ability to command, done to exude credibility in relaying information.
Upward communication
Communication from subordinates to their superiors.
Lateral communication (Horizontal)
Communication between people of equal level or status, typically within the same division or department.
Downward communication
Communication from superiors to their subordinates.
Outward communication
Communication intended for workers outside the workplace.
Business letters
Written communications typically sent between individuals, organizations, or companies in a business context, used to convey information, make requests, provide updates, and exchange ideas in a formal manner.
Technical writing
A form of professional writing that aims to communicate technical information using specialized terminology, graphics, and tools.
Letter of Inquiry
Also known as a letter of interest, it is written to ask for specific information regarding a particular subject matter.
Letter of Claim
Used in legal matters to assert wrongdoings, notifying the responsible party and demanding a response.
Adjustment Letter
A response to a letter of claim, addressing the claimant's statements, whether the claims are welcomed or not.
Letter of Request
Reports situations that demand actions and decisions to be acted upon.
Memorandum
A written message serving as a reminder, relaying information to many readers at the same time.
Instruction Memo
Directives that organization members need to follow.
Request Memo
A request for the provision of facilities and services.
Announcement Memo
Notice of an important event in the organization.
Transmittal Memo
Notice that officially announces the release of a report.
Authorization Memo
Grants permission for the undertaking of an operation in the organization.
Accurate
It deals with facts that are completely true, using words, sentences, numbers, or figures that exactly express the intended message.
Clear
Be able to easily understand the main message or point of the written work.
Formal
Follow the prescribed writing standards which include structure, pattern, format, and language.
Graphical
Tables, charts, figures, diagrams, and other illustrations that support the written information provided in technical writing.
Practical
Be practical in the way that it functions according to its purpose.
Procedural
Forms of technical writing that provide sets of instructions, such as user manuals and laboratory reports.