Forouzan's Introduction to Physical Layer
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Data can be ______ and ______
digital, analog
Both analog and digital signals can take one or two forms, which are
periodic and non-periodic (aperiodic)
A _______ completes a pattern within a measurable time frame, called a _________
periodic signal, period
A _________ signal changes without exhibiting a pattern or cycle that repeats over time
non-periodic
The ________ is the most fundamental form of a periodic analog signal
sine wave
A sine wave can be represented by three parameters. Name them.
peak amplitude
frequency
phase
For electric signals, peak amplitude is normally measured in ______
volts
Period refers to the amount of ________ a signal needs to complete _______
time (in seconds), 1 cycle
Frequency is measured in ____
Hertz (Hz)
A ms is equal to
10-3 s
What’s the phase of a sine wave?
The term phase, or phase shift, describes the position of the waveform relative to time 0.
Phase is measured in _____ or ______
degrees, radians
The wavelength is normally measured in _______
micrometers (microns)
What’s bandwidth?
Bandwidth is the range of frequencies contained in a composite signal. It’s the difference between the highest and the lowest frequencies contained in that signal. B = f2 - f1
True or false: A digital signal can have more than two levels
True, a digital signal can have more than two levels
If a signal has L levels, each level needs ______ bits
log2L
The bit rate is _________
the number of bits sent in one second
The bit rate is expressed in ______
bits per second (bps)
The bit length is
the distance one bit occupies on the transmission medium
[Formula] bit length =
propagation speed x bit duration
A digital signal is _________
a composite analog signal with an infinite bandwidth
Baseband transmission requires that we have a _____
low pass channel
Attenuation means
a loss of energy
To show that a signal has lost or gained strength, engineers use the unit of the ________.
decibel (dB)
The decibel measures __________
the relative strengths of two signal or one signal at two different points
A decibel is negative if a signal is ______
attenuated
A decibel is _________ if a signal is amplified
positive
How can we find the dB given the powers of a signal ?
We do dB = 10log10(P2/P1)
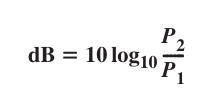
How can we find the dB given the voltages of a signal ?
We do dB = 20log10(V2/V1)
Distortion means that the signal changes its _____
form or shape
Name the types of noise
Thermal noise
Induced noise
Crosstalk
Impulse noise