2.3 - Nucleotides and nucleic acids
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
DNA vs RNA
Both carry information
Both polymers of nucleotides
DNA holds genetic information
RNA transfers genetic information form DNA to ribosomes
What are ribosomes made of?
RNA and proteins
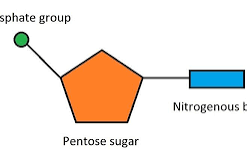
A nucleotide consists of:
Pentose (5-carbon sugar), a nitrogenous organic base and a phosphate group.
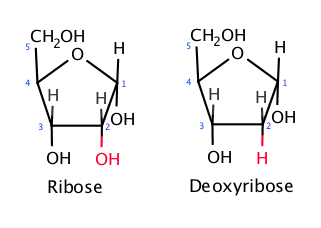
Difference in DNA and RNA
‘Deoxy’ribose (sugar) - contains one less oxygen atom in comparison to ribose (sugar)
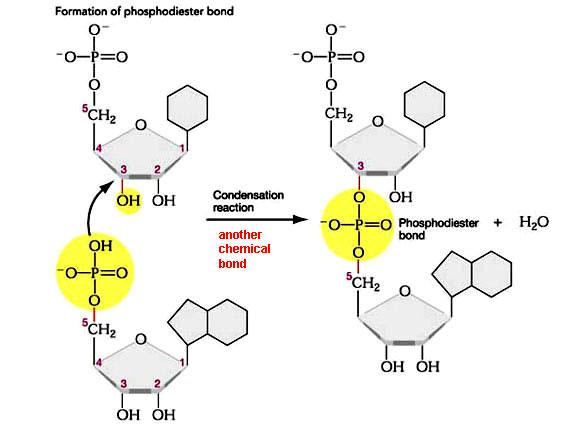
Bonds joining nucleotides together
Phosphodiester bonds
Formed by a condensation reaction between a hydroxyl group of the sugar and the hydroxyl group of the phosphate group of two different nucleotides.
A DNA molecule:
Has a double helix structure,
Created between two polynucleotides joined together by hydrogen bonds that form between the complementary bases.
A molecule of RNA:
In comparison to DNA it is a short, single polynucleotide chain.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
It is a nucleotide derivative
Consists of:
Ribose (sugar)
Adenine (base)
Three phosphate groups
Hydrolysis of ATP
Energy is released
ADP is formed alongside a phosphate molecule
Process is catalysed by ATP hydrolase (an enzyme)
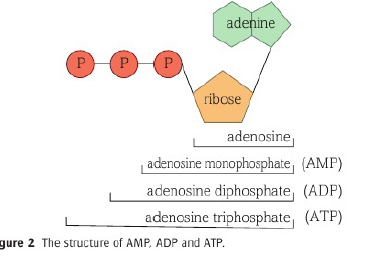
Ribose, adenine, phosphate groups
Can make:
Adenosine (just adenine and ribose)
Adenosine monophosphate (adenine, ribose and one phosphate group)
Adenosine diphosphate - ADP (adenine, ribose and two phosphate groups)
Adenosine triphosphate - ATP (adenine, ribose and three phosphate groups)
Use of inorganic phosphate
Used to phosphorylate other compounds, making them more reactive in result.
How is ATP made
Through the condensation of ADP and an inorganic phosphate catalysed by ATP synthase (an enzyme).
This occurs during photosynthesis and respiration.
Semi-conservative replication
Ensures genetic continuity between generations of cells,.
It is a method where DNA replicates, creating two molecules of DNA that consist of one original DNA strand and one newly synthesised DNA strand.
DNA replication steps:
DNA helicase unwinds and unzips the DNA (breaking hydrogen bonds between complimentary base pairs. Separating the two polynucleotide chains.
Both strands are used as templates and complimentary base pairing occurs between each template strands and free nucleotides.
Adjacent nucleotides are joined by phosphodiester bonds formed in a condensation reaction (done by DNA polymerase).
What is the genetic code?
It is the order of bases on DNA.
Consists of triplets of bases.
A triplet of bases
Known as a codon
Codes for a specific amino acid
Peptide bond
Bond that joins amino acids together
Forming a polypeptide chain
A gene
A sequence of bases on a DNA molecule coding for a sequence of amino acids that form a polypeptide chain.
Non-coding sections of DNA
Introns
Coding regions of DNA
Exons
The genetic code is non-overlapping…
Each triplet is read once and triplets don’t share any bases.
Degenerate
More than one triplet codes for the same amino acid.
Reduces the phenotypic effect (observable characteristics resulting from a mutation) of mutations (mistakes in the base sequence).
Three types of mutations
Base deletion
Base inspersion
Base substitution
What could a change in the base sequence of DNA do.
Alter the sequence of amino acids
Therefore alter the protein.
Examples of harmful mutations.
A mutation that leads to the production of sticky mucus - causes cystic fibrosis
Sickle cell anaemia - a mutated form of haemoglobin distorts the shape of red blood cells.
Start and stop codons
In the genetic code
Start and stop protein synthesis
What are the two stages of protein synthesis?
Transcription
Translation
Enzymes and molecules involved in transcription:
One DNA strand (template/antisense)
A molecule of mRNA
DNA gyrase (unwinds)
DNA helicase (breaks H bonds)
Free nucleotides
RNA polymerase
Process of transcription:
DNA gyrase unwinds the double helix
DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs. The DNA separates into its two polynucleotide strands.
One DNA strand is used as the template (antisense) strand; free nucleotides line up along the template strand by complementary base pairing. RNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides through phosphodiester bonds.
A single-stranded molecule of mRNA is formed.
The mRNA moves out of the nucleus through the nuclear pores…
Enzymes and molecules involved in translation:
A molecule of mRNA
tRNA
Ribosomes
Amino acids
A polypeptide chain
Process of translation:
mRNA attaches to a ribosome (in the cytoplasm or on a rough endoplasmic reticulum).
tRNA collects an amino acid from the cytoplasm and carries it to a ribosome.
tRNA attaches itself to mRNA by complimentary base pairing, forming temporary hydrogen bonds between the codon (on mRNA) and anticodon (on tRNA). Two at a time.
The amino acids that are attached to the tRNA molecules are joined by peptide bonds.
tRNA molecules detach from the amino acids, leaving them behind.
This is repeated, forming a polypeptide chain until a stop codon is reached on the mRNA and protein synthesis has ended.
The tRNA picks up another amino acid in the cytoplasm and comes back, continuing the chain if another codon codes for this specific amino acid.
tRNA
Is a single stranded molecule
Has a binding site at one end - so it can only carry one type of amino acid.
Has a triplet of bases at the other end - the triplet of bases is the anticodon complimentary to a mRNA codon and the amino acid.