Clin Path MCQ1
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cardiovascular + Respiratory Systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
left sided heart failure effect on respiratory system
increased pulmonary pressure —> pulmonary oedema —> dyspnoea, tachypnoea, crackles
right sided heart failure effect on respiratory system
secondary to pulmonary hypertension —> from chronic hypoxia or interstitial lung disease
congenital heart disease effect on respiratory system
abnormal shunts (e.g. patent ductus arteriosus) —> over circulation of lungs —> congestion, respiratory distress
pericardial disease (tamponade) effect on respiratory system
decreased cardiac output —> poor pulmonary perfusion, hypoxia
patterns and appearance of bronchopneumonia
cranioventral consolidation, moist, firm, exudate-filled airways
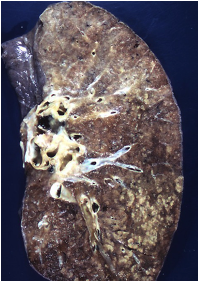
patterns and appearance of pleuropneumonia
severe cranioventral pneumonia, fibrin on pleura, pleuritis
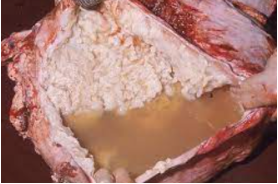
patterns and appearance of pleuritis
fibrin, adhesions, thickened pleura

patterns and appearance of emphysema
enlarged, overinflated alveoli, air bubbles in interlobular septa or subpleura
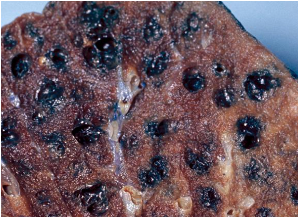
patterns and appearance of atelectasis
dark red, firm collapsed tissue often lobular and sunken
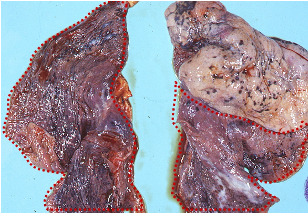
patterns and appearance of fibrinous inflammation
acute, yellow-tan fibrin exudate, easily peeled from serosal surfaces
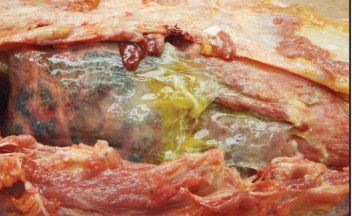
patterns and appearance of fibrous inflammation
chronic, dense, fibrous tissue, firmly adhered
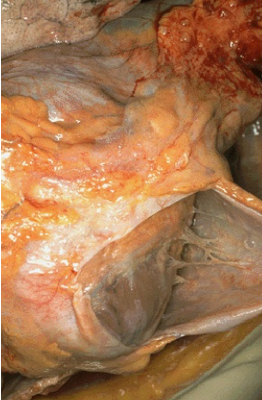
cause of cranioventral pulmonary lesions
aerogenous dispersion, gravity, airflow patterns favour pathogen settlement e.g. Bronchopneumonia, aspiration pneumonia
cause of caudodorsal pulmonary lesions
haematogenous, area with good blood supply e.g. Embolic pneumonia, metastatic neoplasia
cause of diffuse (interstitial) pulmonary lesions
viral, toxic, or allergic aetiologies, alveolar septa affected e.g. interstitial pneumonia
cause of focal/nodular pulmonary lesions
granulomas, neoplasia, abscesses e.g. TB nodules, metastases, embolic abscesses
cause of right middle lobe pulmonary lesions
predisposed to aspiration e.g. aspiration pneumonia
what is a restrictive respiratory issue
decreased lung compliance/expansion
restrictive respiratory pathology
pleural effusion, pulmonary fibrosis, oedema, mass
restrictive respiratory pathophysiology
decreased tidal volume, normal/increased respiratory rate
restrictive respiratory blood gasses
decreased PaO2, normal or decreased PaCO2 = type I respiratory failure
restrictive respiratory clinical signs
tachypnoea, shallow breathing, shortness of breath when lying down
what is an obstructive respiratory issue
airway narrowing or obstruction
obstructive respiratory pathology
asthma, chronic bronchitis, laryngeal paralysis
obstructive respiratory pathophysiology
increased airway resistance, air trapping
obstructive respiratory blood gases
decreased PaO2, increased PaCO2 = type II respiratory failure
obstructive respiratory clinical signs
expiratory dyspnoea, wheezing, prolonged expiration
pathogenesis of strangles (equine)
streptococcus equi equi causes lymph node abscessation and rupture
clinical signs of strangles (equine)
fever, mucopurulent nasal discharge, dyspnoea, lymphadenopathy (LN enlargement)
laryngeal paralysis pathogenesis
denervation of cricoarytenoid muscle (especially the left recurrent laryngeal nerve - longer path, looping around aortic arch in chest before ascending larynx = more susceptible to injury/degeneration)
laryngela paralysis clinical signs
inspiratory stridor (roaring), dyspnoea, poor performance
brachycephalic airway syndrome pathogenesis
congenital stenotic nares, long soft palate, hypostatic trachea
brachycephalic airway syndrome clinical signs
stertor (low pitched, noisy breathing sound), cyanosis, syncope, sleep apnoea
aspiration pneumonia pathogenesis
inhalation of food, milk or vomit —> chemical and bacterial injury
aspiration pneumonia clinical signs
productive cough, halitosis, dyspnoea, fever, commonly in right middle lobe
pulmonary oedema pathogenesis
increased hydrostatic pressure (LSHF), increased permeability (toxins), decreased oncotic pressure
pulmonary oedema clinical signs
moist cough, frothy fluid, crackles, tachypnoea
bovine tuberculosis pathogenesis
Mycobacterium bovis causes granulomatous pneumonia
bovine tuberculosis clinical signs
chronic cough, weight loss, lymph node enlargement, caseous nodules
equine exercise induced pulmonary haemorrhage pathogenesis
high pulmonary capillary pressures during exercise causes rupture
equine exercise induced pulmonary haemorrhage clinical signs
post-exercise epistaxis, poor performance, tracheal blood
pneumothorax pathogenesis
air leaks into pleural space —> lung collapse
pneumothorax clinical signs
sudden dyspnoea, reduced dorsal lung sounds, hyperresonance
pleural effusion pathogenesis
accumulation of fluid in pleural space (e.g. hydrothorax, chylothorax, haemothorax)
pleural effusion clinical signs
muffled lung sounds, tachypnoea, ventral dullness
what does sustained excessive preload cause
volume overload e.g. mitral or aortic regurgitation
what does sustained excessive afterload cause
pressure overload e.g. aortic stenosis, hypertension
what does altered contractility cause
dilated cardiomyopathy, infarction, myocarditis
what does rate/rhythm disturbances cause
AV bocks, atrial fibrillation, tachyarrhythmias
mechanisms of LSHF
pulmonary venous congestion —> pulmonary oedema
clinical signs of LSHF
dyspnoea, cough, exercise intolerance, pulmonary crackles
RSHF mechanism
systemic venous congestion —> ascites, oedema
RSHF clinical signs
ascites, jugular distension, hepatomegaly, peripheral oedema
forward (acute) heart failure mechanism
inadequate CO —> poor tissue perfusion
forward (acute) heart failure clinical signs
lethargy, pale MM, syncope, cold extremities
backwards (congestive) heart failure mechanism
inadequate venous drainage —> fluid accumulation
backwards (congestive) heart failure clinical signs
dyspnoea (LSHF), ascites (RSHF), oedema
what does sympathetic stimulation cause
increased HR, increased contractility, vasoconstriction = increased afterload
what does RAAS activation cause
vasoconstriction, Na/H2O retention = increased preload/afterload
what does ADH increase cause
water retention = increased preload
what does increased atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and B-type ANP cause
vasodilation, natriuresis = decreased preload and afterload
describe valvular endocarditis
bacterial infection —> vegetative valve lesions
valvular endocarditis clinical signs
fever, new murmur, thromboembolism, lethargy
describe valvular endocardiosis
degeneration of AV valves (especially mitral valve)
valvular endocardiosis clinical signs
cough, murmur, syncope, pulmonary oedema
describe stenosis (e.g. pulmonic stenosis)
narrow valve —> outflow obstruction
stenosis clinical signs
systolic murmur, cyanosis, exercise intolerance, right ventricular hypertrophy
define thrombus
a solid clot formed in situ from platelets and fibrin. May occlude vessels.
define thromboembolism
detached thrombus that travels through the bloodstream adn lodges distally
define embolism
any intravascular material (thrombus, fat, air, tumour) that occludes a vessel
pathology of dilated cardiomyopathy
chamber dilation, systolic failure
chamber size of dilated cardiomyopathy
thin walls
function affected of dilated cardiomyopathy
enlarged, goboid ventricles
common breeds affected by dilated cardiomyopathy
large breed dogs
clinical signs of dilated cardiomyopathy
weak pulse, systolic murmur, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy pathology
left ventricle wall thickening, diastolic dysfunction
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wall thickness
thick walls
function affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
decreased filling = stiff ventricle
common species affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
cats (esp. Main Coons and Ragdolls)
clinical signs of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
thromboembolism, dyspnoea, sudden death