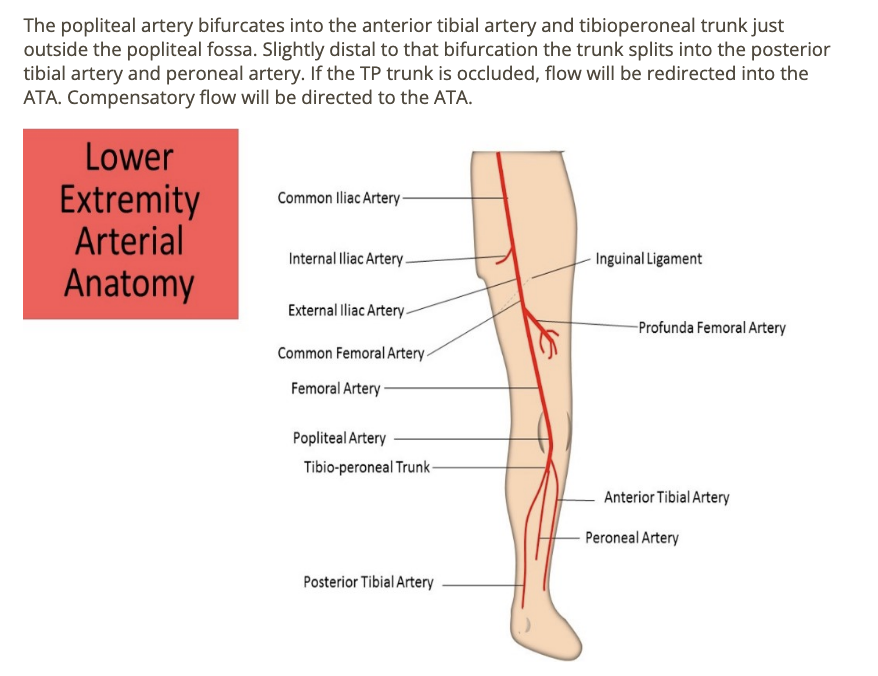
e. extremity artery path
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
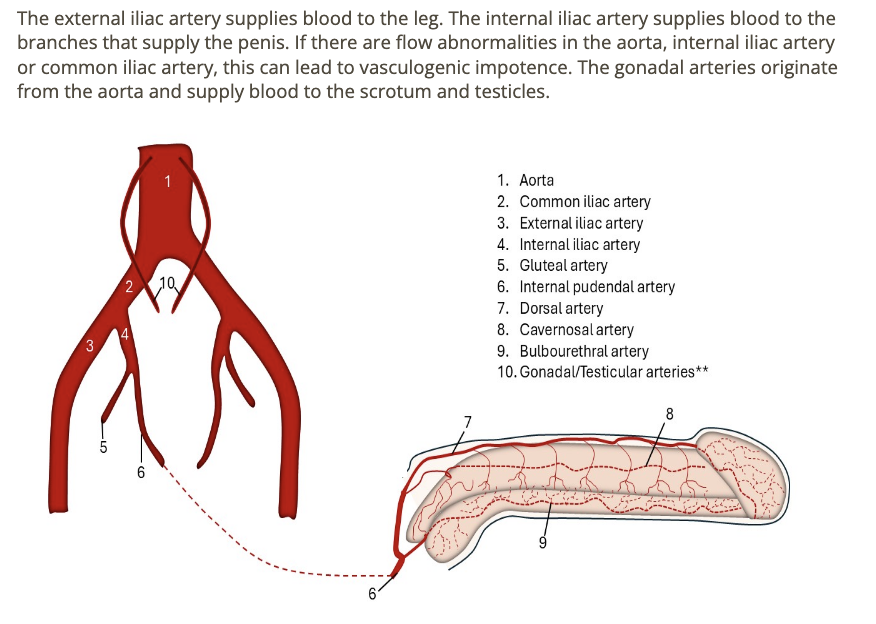
an abnormality in which vessel could be the cause of vasculogenic impotence
.
a) common + internal iliac arteries
b) aorta + gonadal arteries
c) external iliac + femoral arteries
d) internal + external iliac arteries
a) common + internal iliac arteries
the pt would benefit the most from a ____ exam
.
a) aortic duplex
b) arterial duplex
c) renal artery
d) venous duplex
b) arterial duplex

if the distal femoral artery shows a peak velocity of 3.2 m/s, the waveform in the posterior tibial artery will most likely be
.
a) biphasic
b) triphasic
c) monophasic
d) absent
c) monophasic

if there is a 75% stenosis of distal axillary artery, which arteries will show a triphasic waveform
.
a) ulnar
b) brachial
c) radial
d) subclavian
d) subclavian

which measurements is used to differentiate inflow from outflow disease in the lower extremity arteries
.
a) acceleration time
b) S/D ratio
c) resistive index
d) pulsatility index
a) acceleration time

what is the normal value for transcutaneous oximetry [for wound healing potential] exam
.
a) 2.0
b) 70-80mmHg
c) 3.5
d) <40mmHg
b) 70-80mmHg


a 30 yo male has persistent right calf pain w/exercise. this is the right popliteal artery w/foot in neutral + flexed position
.
a) Buerger disease
b) anterior compartment syndrome
c) popliteal entrapment
d) Leriche syndrome
c) popliteal entrapment

an acute occlusion occurs in the common iliac artery on the left side. Which vessels will also have absent flow
.
a) external iliac artery only
b) common femoral artery + saphenous artery
c) internal iliac artery + gonadal artery
d) common femoral, external + internal iliac artery
d) common femoral, external + internal iliac artery
a pt complains of right leg pain + color changes. when he lies down, the right calf + foot become pale. When he stands up, the right calf + foot turn red. the left leg is asymptomatic
.
a) right popliteal stenosis
b) deep venous reflux
c) significant aortic obstruction
d) significant right iliac stenosis
a) right popliteal stenosis

thrombolytic therapy is used to treat
.
a) chronic deep vein thrombosis
b) acute arterial occlusion caused by thrombus
c) venous insufficiency
d) chronic venous disease
b) acute arterial occlusion caused by thrombus

why would exposure to cold increase symptoms of lower extremity arterial disease
.
a) increased resistance due to vasodilation
b) increased resistance due to vasoconstriction + blood becomes less viscous w/cold expsoure
c) increased resistance due to vasoconstriction
d) blood becomes less viscous w/cold exposure
c) increased resistance due to vasoconstriction

a) tumor invasion
b) embolism formation
c) soft plaque formation
d) thrombus formation
d) thrombus formation

a pt has leg pain 2 days after coronary artery catheterization
.
all are important parts of the physical exam except
.
a) eval lower leg for hair loss, dry skin, thick toenails
b) eval groin for bruit
c) eval leg for pallor
d) eval toes for blue discoloration
a) eval lower leg for hair loss, dry skin, thick toenails

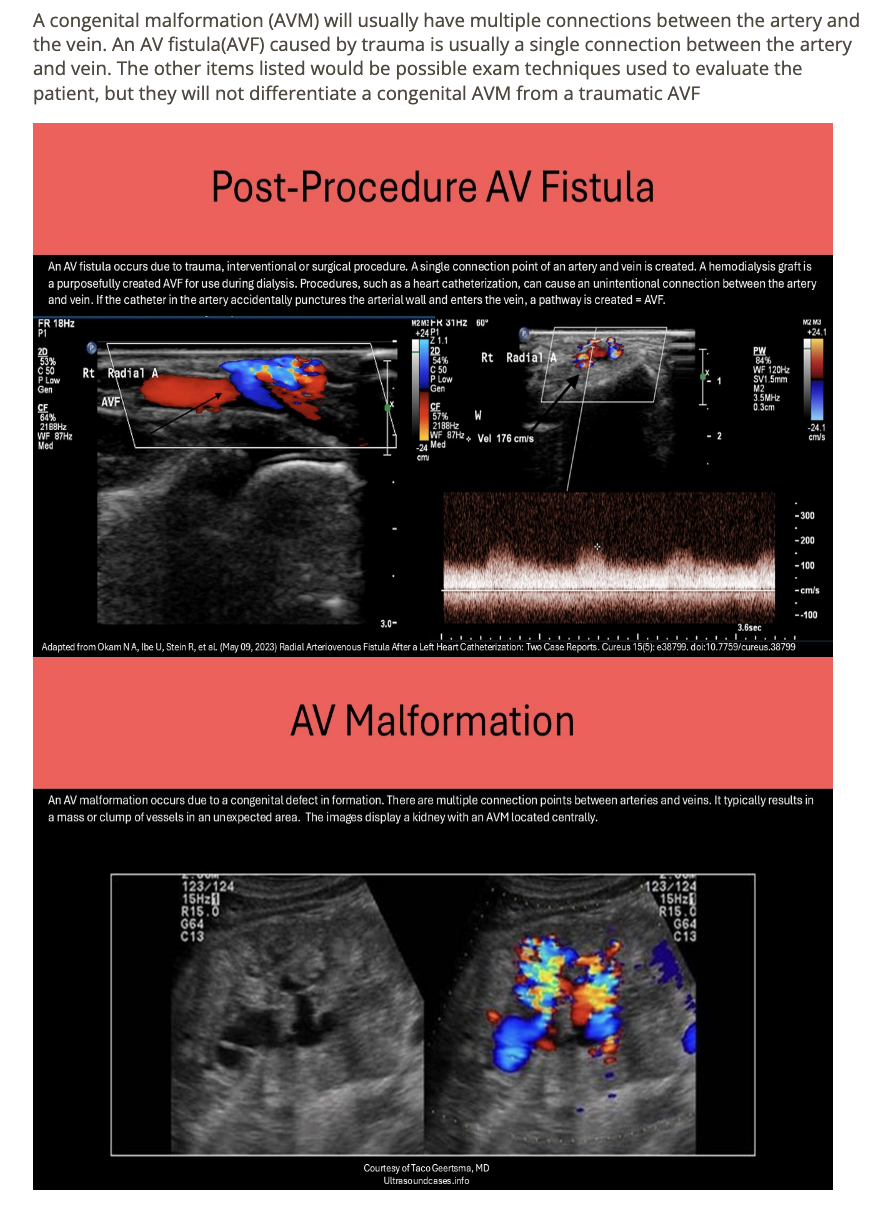
while scanning a pt after a recent car accident, you notice an arteriovenous connection in the left groin
.
how can you determine if this is related to the recent trauma or congenital abnormality
.
a) determine location of AV connection
b) how many connections between artery + vein
c) evaluate deep veins for associated thrombus
d) do a doppler of flow in connected vessels
b) how many connections between artery + vein
which pt would benefit from a percutaneous transluminal angioplasty
.
a) pt w/left ICA occlusion
b) pt w/chornic iliac DVT
c) pt w/80% stenosis in prox SFA
d) pt w/recurrent pulmonary embolism
c) pt w/80% stenosis in prox SFA
which critical finding is associated w/calf paresthesia, localized muscle weakness, pain when stretching calf muscles, and drop foot
.
a) peripheral arterial disease
b) post-phlebitic syndrome
c) popliteal entrapment
d) anterior compartment syndrome
d) anterior compartment syndrome

if the acceleration time is >140 m/s in both common femoral arteries, what disease is suspected
.
a) aortic disease
b) unilateral external iliac
c) bilateral internal iliac
d) normal flow
a) aortic disease

the most common color change shown in a lower extremity w/acute arterial occlusion is
.
a) rubor
b) pallor
c) brawny
d) cyanosis
b) pallor

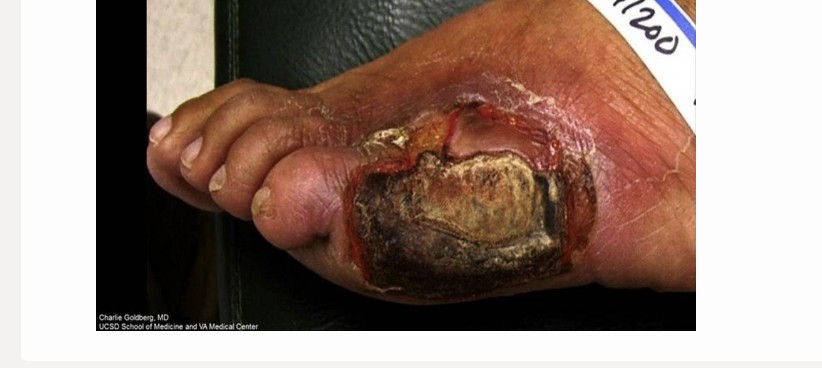
which is used to determine the capability of healing a wound or identifying a site for amputation
.
a) sclerotherapy
b) ascneding venography
c) transcutaneous oximetry
d) photoplethysmography
c) transcutaneous oximetry

if a pt suffers ischemic rest pain in the feet, what maneuver can relieve the pain
.
a) sitting w/elevated legs
b) walking
c) Valsalva
d) standing
d) standing

which is considered a risk factor for peripheral arterial disease
.
a) diabetes
b) excessive, repetitive standing
c) hx of DVT
d) pregnancy
a) diabetes

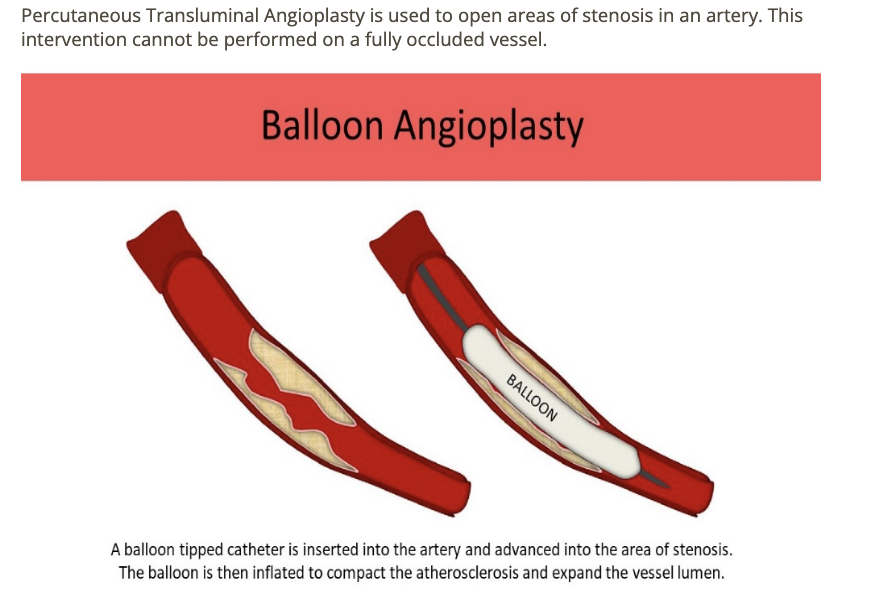
____ procedure uses a balloon tipped catheter to compress atheroma + expand vessel lumen
.
a) atherectomy
b) angioplasty
c) endarterectomy
d) valvulotume [cuts valve out of vein to turn into artery for better blood flow]
b) angioplasty
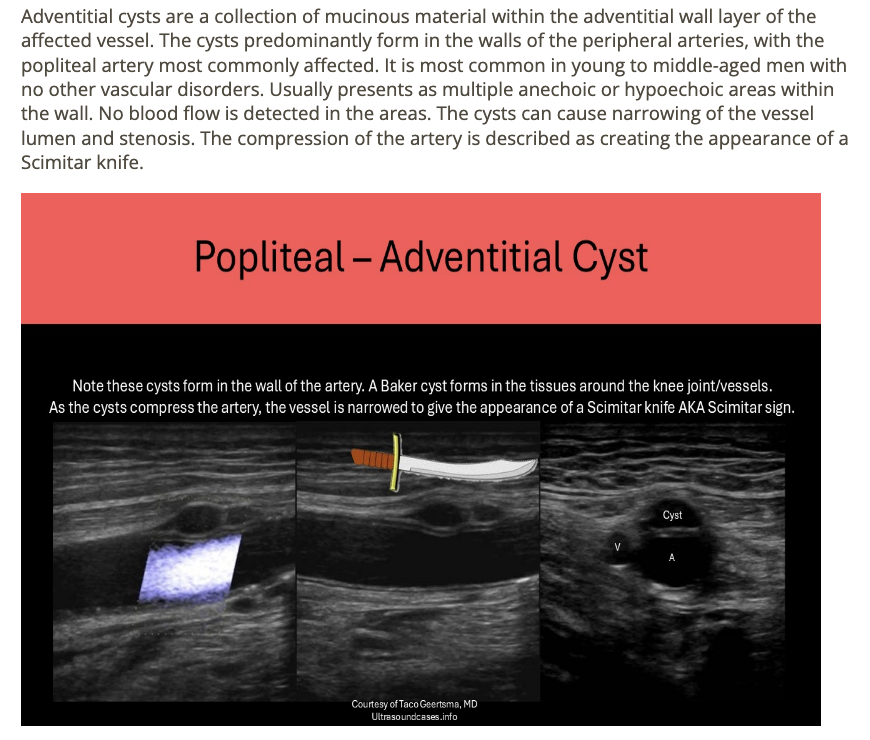
adventitial cysts are
.
a) normal variant seen in 10% of pts
b) usually treated w/bypass graft placement
c) most commonly affects popliteal artery
d) more common in women
c) most commonly affects popliteal artery

which are collagen disorders that have increased risk for arterial dissection
.
a) shone complex + blue toe syndrome
b) Paget Schroetter syndrome + Raynaud syndrome
c) Marfan syndrome + polycythemia vera
d) Marfan syndrome + Ehler Danlos syndrome
d) Marfan syndrome + Ehler Danlos syndrome

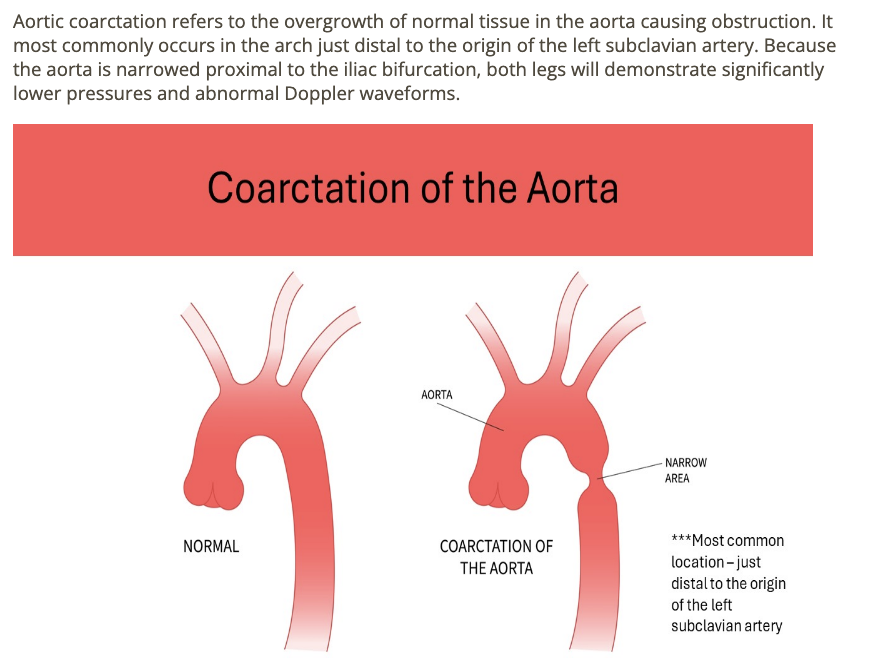
a bilateral decrease in the femoral pulses can be related to
.
a) aortic coarctation
b) DVT formation
c) deep femoral occlusion
d) popliteal artery occlusion
a) aortic coarctation
which arteries are evaluated during a penile duplex exam for erectile dysfunction
.
a) ventral
b) cavernosal
c) dorsal
d) urethral
b) cavernosal


______ refers to a collection of mucinous material within the adventitial wall layer of the affected vessel
.
a) baker cyst
b) mucinous dissection
c) adventitial cyst
d) vasa vasorum
c) adventitial cyst
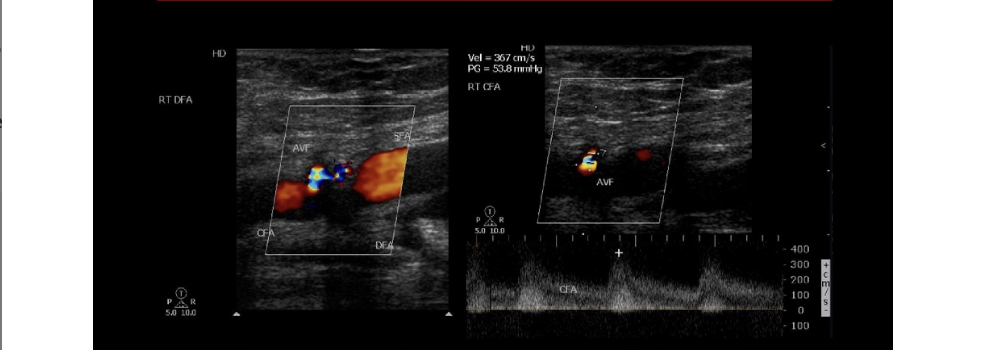
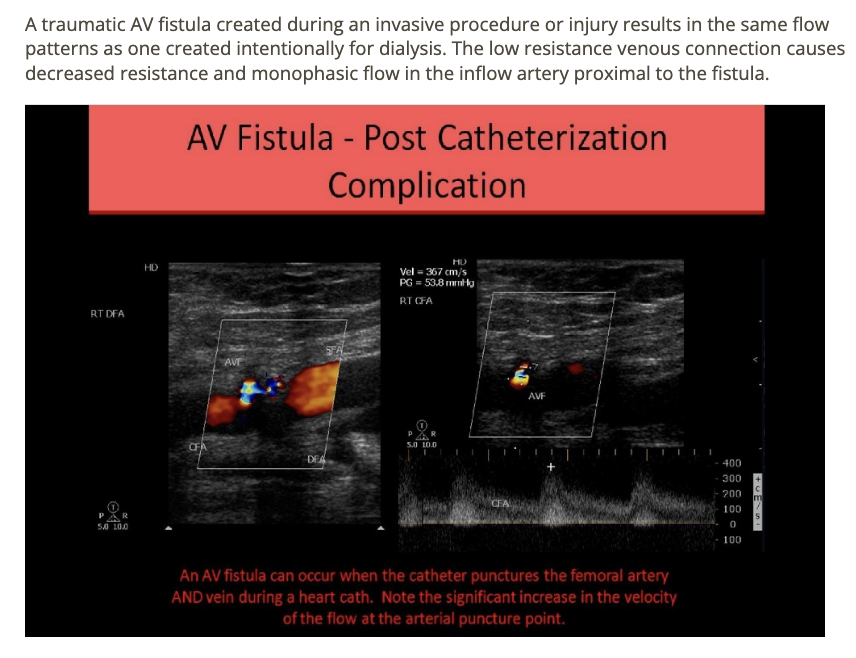
An AV fistula connects the femoral artery + vein at right groin. the doppler evaluation of the common femoral artery will show what pattern
.
a) biphasic flow w/increased diastolic flow
b) monophasic w/minimal diastolic flow
c) peak, triphasic waveform
d) monophasic w/increased diastolic
d) monophasic w/increased diastolic
if there a left subclavian steal, which brachial artery evaluation will be abnormal
.
a) left brachial will have lower BP + blunted/monophasic waveform
b) right brachial will have lower BP + blunted/monophasic waveform
c) right brachial will have higher BP + blunted/monophasic waveform
d) left brachial will have higher BP + triphasic waveform
a) left brachial will have lower BP + blunted/monophasic waveform

which is an expected finding with positive evaluation for thoracic outlet syndrome
.
a) high amplitude PPG digital tracings on affected side w/arm adduction
b) increased resistance in prox subclavian artery on affected side w/arm abduction
c) elevated blood pressure on affected side w/Adson’s maneuver
d) increased flow velocity on affected distal arm /arm adduction
b) increased resistance in prox subclavian artery on affected side w/arm abduction

what is the preferred method to rule out Buerger disease in an upper extremity arterial exam? Evaluate the
.
a) shoulder arteries for extrinsinc compression w/movement
b) hands for vascular changes w/cold sensitivity testing
c) smaller arteries of arm w/duplex + PPG
d) arterial flow at rest + exercise
.
c) smaller arteries of arm w/duplex + PPG
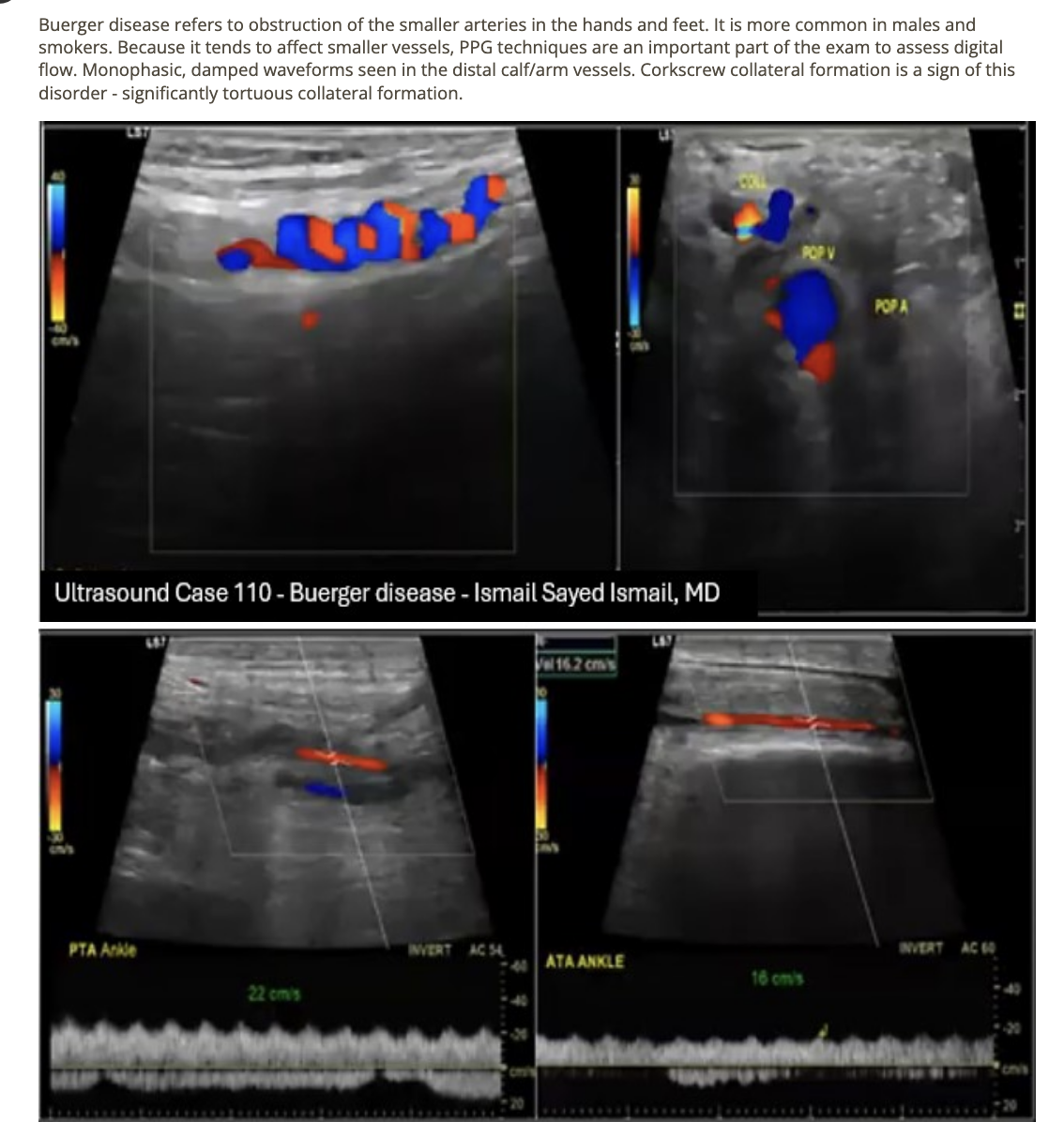
Thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO) where small blood vessels in the hands and feet become blocked by clots. This involves inflammation of
.
a) intimal + medial wall
b) all vessel walls w/no effect on conective tissue
c) intimal wall layer
d) all vessel walls + surrounding connective tissue
d) all vessel walls + surrounding connective tissue

the distal femoral artery measures 2.75 m/s. what hemodynamic changes will be seen in the popliteal artery
.
a) increased acceleration time
b) high velocity, peaked waveform
c) increased diastolic flow reversal
d) decreased acceleration time
a) increased acceleration time

a pt has diminished pulses in right radial + ulnar arteries
.
A right _____ stenosis could cause this symptom
.
a) lateral palmar arch
b) brachial artery
c) superficial palmar arch
d) deep palmar arch
b) brachial artery

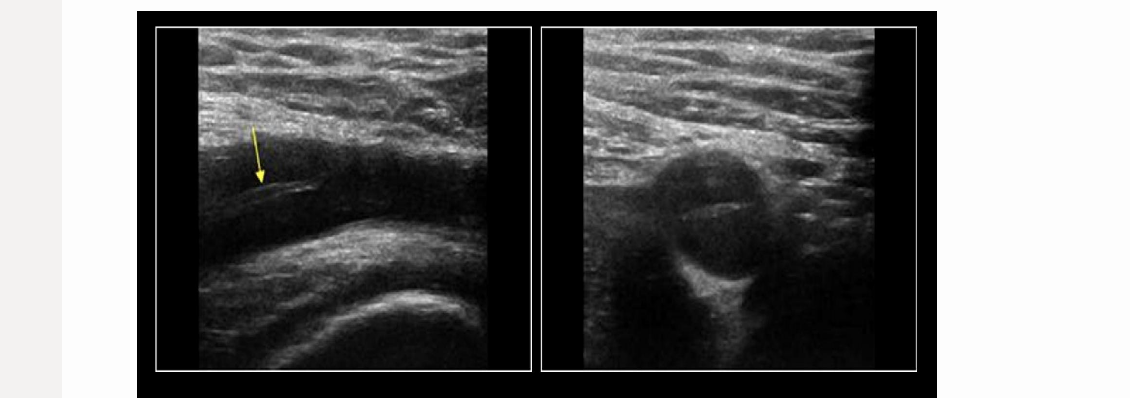
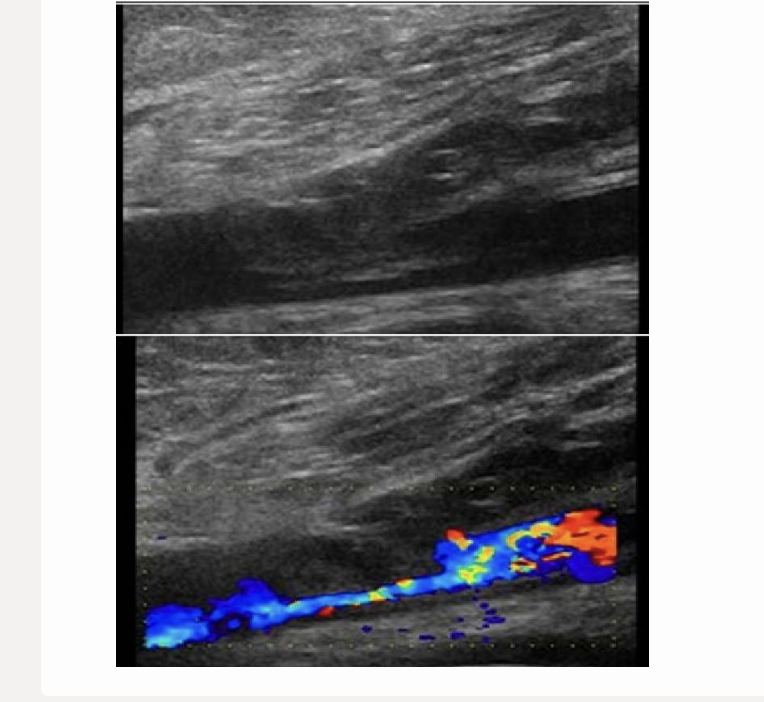
this pic comes from the groin/lower extremity vascular scan
.
a) floating thrombus strand from recanalized DVT in superficial femoral vein
b) normal common femoral artery bifurcation
c) iliac artery dissection
d) floating thrombus strand from recanalized DVT in iliac vein
c) iliac artery dissection
a pt has mild bilateral leg pain. 2D evaluation shows minimal diffuse atherosclerosis bilaterally. The arterial doppler waveforms show biphasic w/increased acceleration time
.
what will explain these findings
.
a) cardiac ejection fraction 85%
b) bilateral popliteal entrapment
c) systemic hypertension
d) cardiac ejection fraction 30%
d) cardiac ejection fraction 30%

which describes an AV malformation
.
a) dilated venous collaterals adj to AOI
b) can be treated using thrombin injection
c) direct connection between single artery + vein
d) caused by trauma/surgical procedures
a) dilated venous collaterals adj to AOI

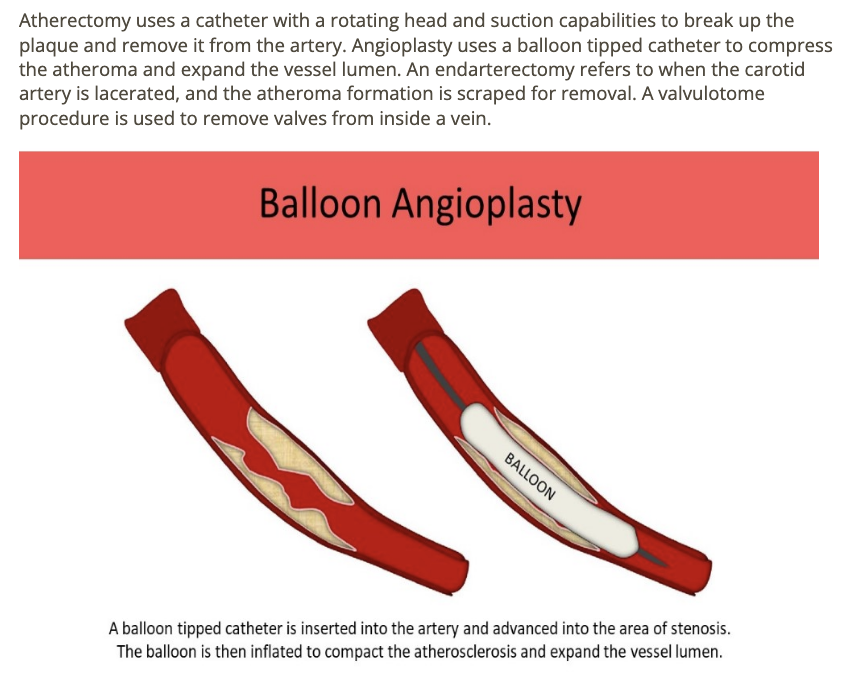
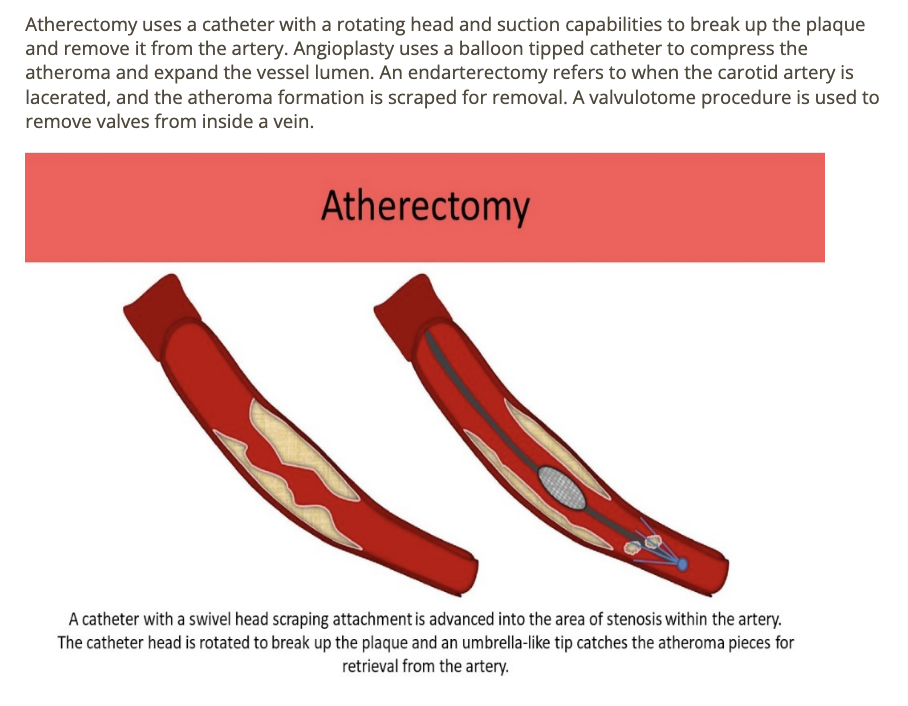
An _____ procedure uses a catheter w/rotating head to break up the plaque + suction capabilities to remove it from the artery
.
a) valvulotome
b) atherectomy
c) angioplasty
d) endarterectomy
b) atherectomy
which describes compartment syndrome
.
a) caused by compression of nerves during normal extremity motion
b) typically occurs below diaphragm in abd
c) most commonly occurs due to trauma
d) typically occurs below diphagram in chest
c) most commonly occurs due to trauma

Secondary Raynaud phenomenon
.
a) functional vasospastic disorder because of kidney disease
b) functional vasospastic disorder because of unobstructed vasc syst
c) occurs in pts w/severe venous disease
d) occurs in pt w/obstructed vasc syst
d) occurs in pt w/obstructed vasc syst

a 70% stenosis in the proximal femoral artery will cause the _____ in the mid femoral artery
.
a) acceleration time to increase
b) Reynold’s number to decrease
c) acceleration time to decrease
d) velocity to increase
a) acceleration time to increase

if an abnormal transcutaneous oximetry reading is obtained, you should
.
a) turn up oxygen level entering pt’s mask
b) move sensor proximally
c) report reading location + end exam
d) move sensor distally
b) move sensor proximally

if the tibioperoneal trunk is occluded, which calf vessel will show increased flow
.
a) posterior tibial artery
b) peroneal artery
c) anterior tibial artery
d) posterior tibial + peroneal artery
c) anterior tibial artery
which is true about the signs + symptoms of lower extremity artery disease
.
Significant ischemic disease in the leg will lead to
.
a) pallor w/dependency
b) rubor w/elevation
c) cyanosis w/elevation
d) pallor w/elevation; rubor w/dependency
d) pallor w/elevation; rubor w/dependency
what arteries are most commonly affected by Takayasu arteritis
.
a) subclavian + common carotid
b) subclavian + brachial
c) forearm
d) calf
a) subclavian + common carotid

which is the most common site for atherosclerosis formation in the lower extremity?
.
a) calf trifurication
b) SFA in adductor canal
c) popliteal
d) CFA birfurication
b) SFA in adductor canal
which abnormalities is best evaluated by asking the pt to hyperextend the leg + point toes
.
a) May Thurner syndrome
b) Raynaud syndrome
c) popliteal entrapment
d) Paget Schroetter syndrome
c) popliteal entrapment

congestive heart failure is more commonly seen with ____
.
distal ischemia is more commonly seen with _____
.
a) AV fistula; hemodialysis fistula
b) distal; prox AV fistula
c) AV malformation; AV fistula
d) prox; distal AV fistula
d) prox; distal AV fistula
paresthesia is
.
a) abn skin sensation, numbness/tingling
b) loss of ability to move extremity/body
c) dizziness related to position change
d) vision loss in 1 eye for short period of time
a) abn skin sensation, numbness/tingling

which symptom is most commonly seen w/peripheral arterial disease
.
a) phlegmasia dolens
b) claudication
c) absent pedal pulses
d) dry ulcerations
b) claudication

which can lead to increase in frequency shift detected in the common femoral artery
.
a) 80% stenosis of SFA
b) prox SFA occlusion
c) 80% stenosis of CFA
d) decreased probe frequency
c) 80% stenosis of CFA

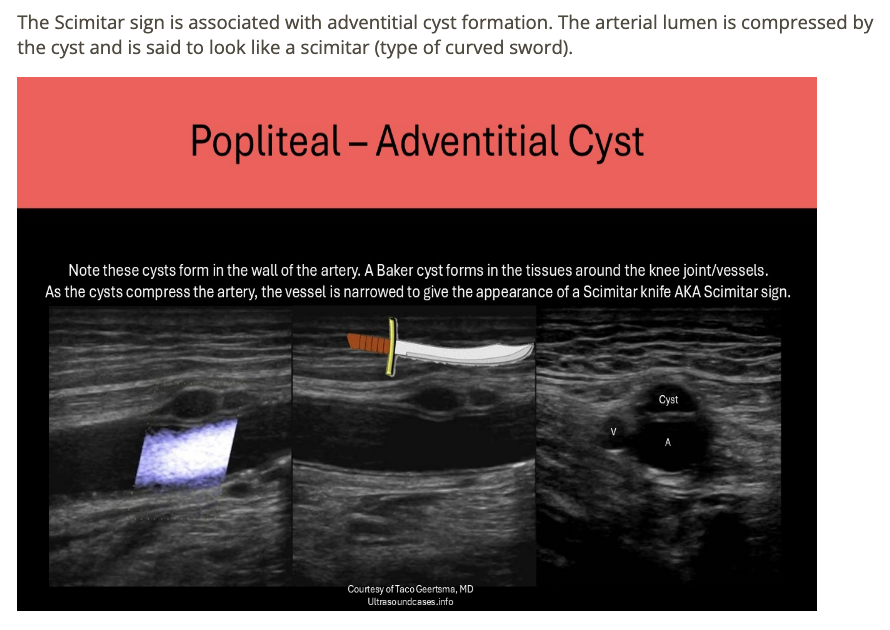
The Scimitar sign is associated with
.
a) femoral-femoral bypass graft
b) bovine arch
c) median arcuate ligament syndrome
d) adventitial cysts
d) adventitial cysts
when thrombin is injected into a pseudoaneurysm, the needle puncture site should be located
.
a) as far from neck as possible
b) within 5mm of neck
c) lateral aspect of groin
d) within 1cm of neck
a) as far from neck as possible

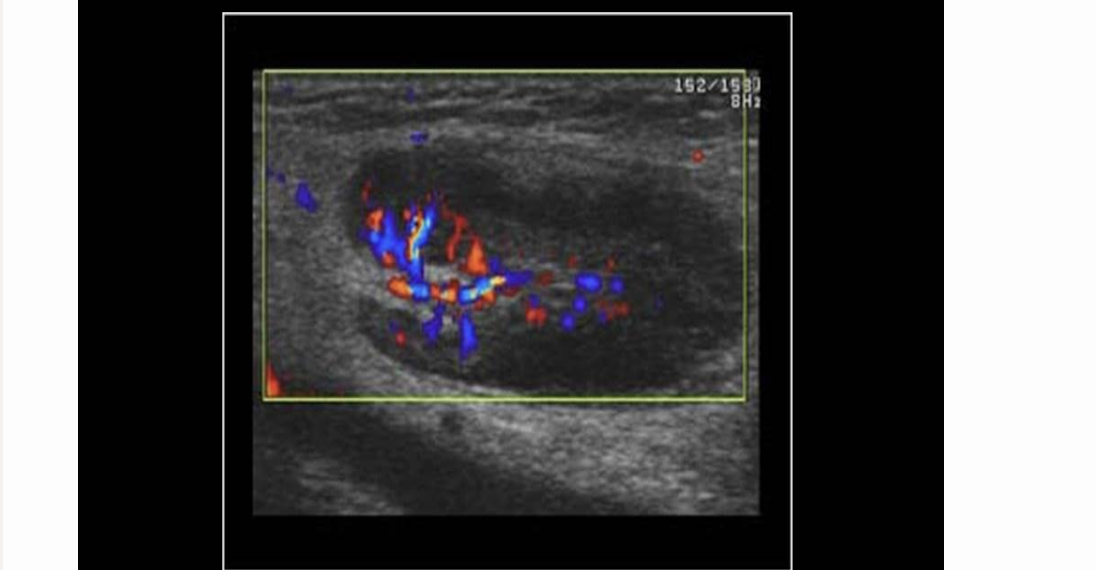
pt has groin pain 3 days after undergoing right femoral artery angioplasty. this is right groin AOI. what should you put in your report
.
a) pseudoaneurysm that’s nearly thrombosed
b) abn enlarged LN
c) pseudoaneurysm requiring immediate attention
d) normal LN
b) abn enlarged LN

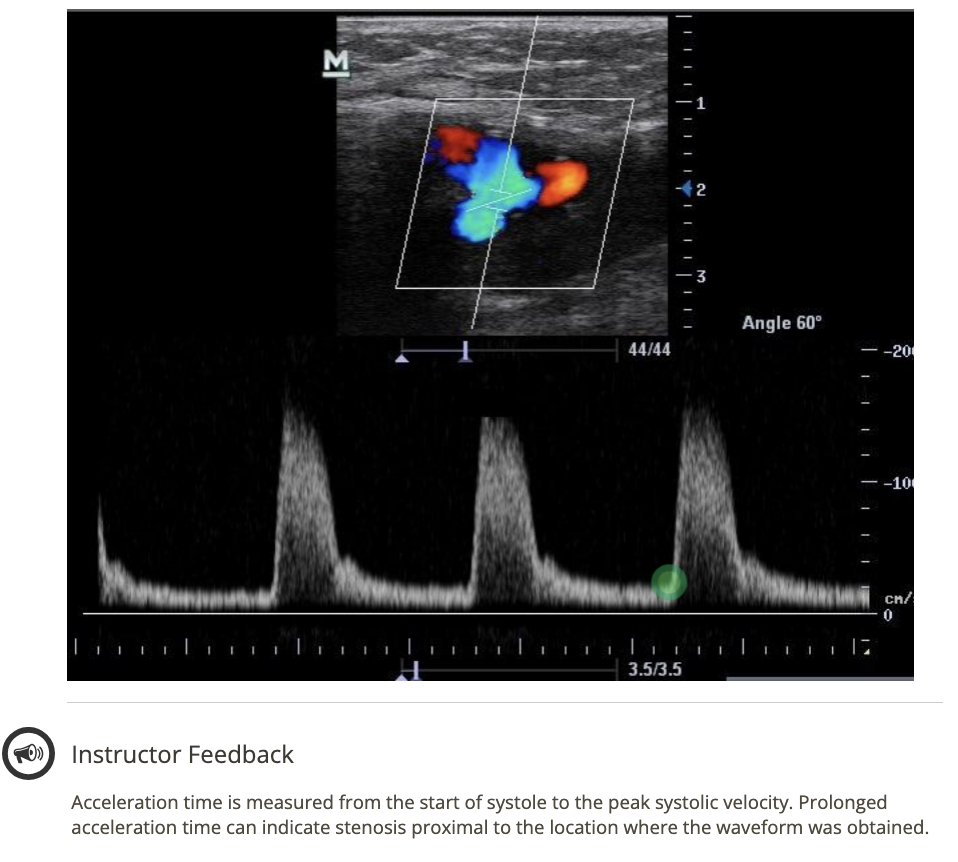
![<p>where does the 1st caliper go when measuring acceleration time? click on the 3rd waveform</p><p>.</p><p>[start of 3rd waveform]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/10a2a0eb-5b9b-4269-8bf3-eb6e5f0a21bd.png)
where does the 1st caliper go when measuring acceleration time? click on the 3rd waveform
.
[start of 3rd waveform]
start of 3rd waveform
which is the 2nd most common site for atherosclerosis formation in lower extremity
.
a) popliteal trifurication
b) CCA bifurcation
c) CFA bifurcation
d) distal SFA in adductor canal
c) CFA bifurcation

which is assoc w/CREST syndrome
.
a) primary Raynaud syndrome
b) superficial phlebitits
c) aortic aneurysm
d) secondary Raynaud phenomenon
d) secondary Raynaud phenomenon

pt w/aortic coarctation distal to left subclavian artery origin will show
.
a) systemic HTN w/increased brachial pressures
b) no change in ankle pressure w/exercise
c) bounding pedal pulses
d) increased bilateral ABIs
a) systemic HTN w/increased brachial pressures

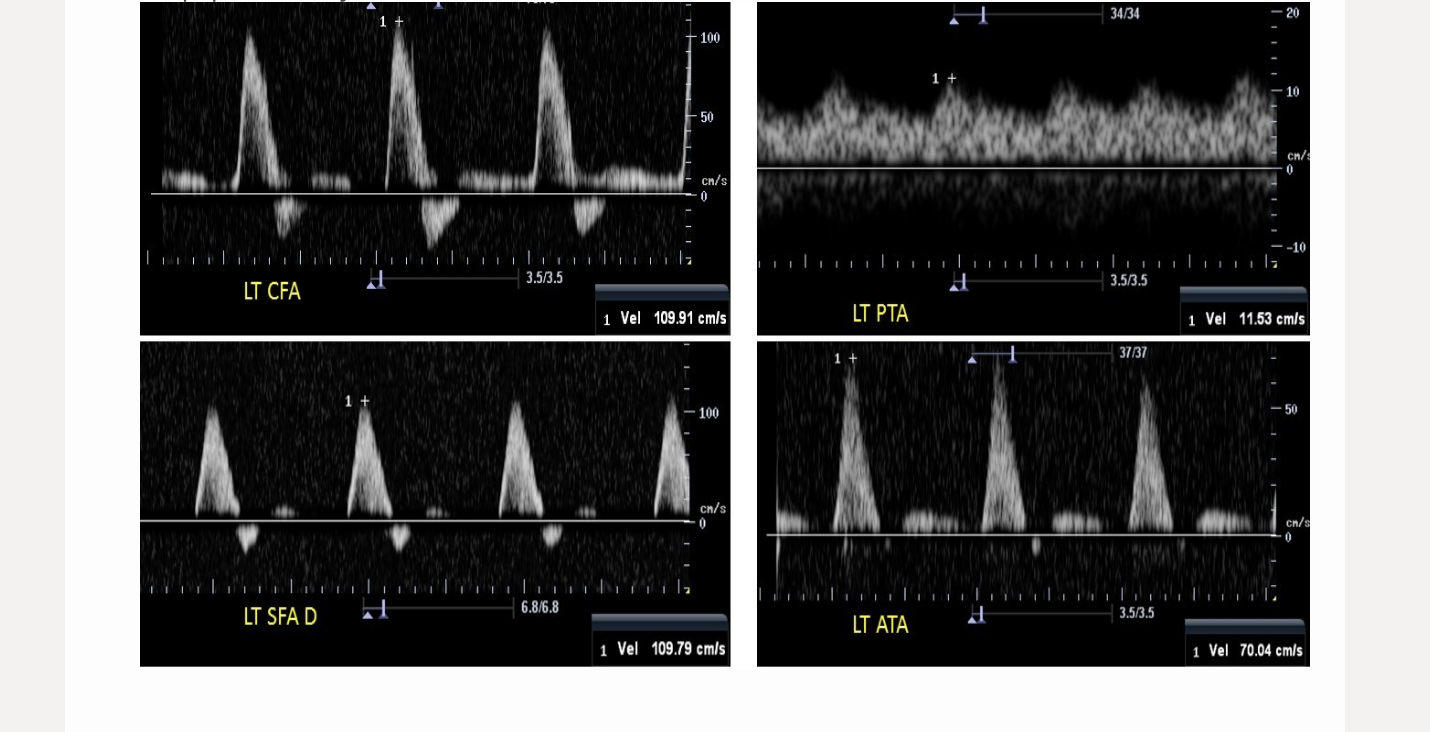
which is a left popliteal artery waveform
.
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
a) A

if the external iliac artery is occluded, what vessels provide potential collateral flow to extremity
.
a) internal thoracic + lumbosacral artery
b) inferior epigastric + deep circumflex artery
c) medial + lateral plantar artery
d) genicular arteries
b) inferior epigastric + deep circumflex artery

pt complains of right leg pain + color changes
.
when he lies down, the leg becomes pale
.
when he stands up, the leg becomes reddened
.
the left leg is asymptomatic
.
a) significant aortic obstruction
b) deep venous reflux
c) significant iliac stenosis
d) popliteal stenosis
c) significant iliac stenosis
