AP BIO: Unit 6: Gene Expression and Regulation
0.0(0)Studied by 0 people
Card Sorting
1/70
Last updated 12:35 AM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
6\.1
DNA and RNA Structure
2
New cards
What is the primary source of hereditary material?
DNA and sometimes RNA
3
New cards
How is genetic material stored?
* It is stored in DNA and RNA in a sequence of bases
* DNA is packaged into chromosomes and passed from the parent to the daughter cells.
* Viruses use RNA to encode their genetic information
* DNA is packaged into chromosomes and passed from the parent to the daughter cells.
* Viruses use RNA to encode their genetic information
4
New cards
Compare and contrast DNA and RNA
* Both are polymers with nucleotides and both follow base pairing rules
* DNA: AT CG, RNA: AU, CG
* DNA: found in the nucleus. RNA: found in the nucleus and the cytosol
* DNA: AT CG, RNA: AU, CG
* DNA: found in the nucleus. RNA: found in the nucleus and the cytosol
5
New cards
Purines and Pyrmidines
The base pairing rules are conserved through evolution
* Pyrimidines: Uracil, Cytosine, Thymine, single ring structure
* Purines: Adenine, Guanine, double ring structure
* Pyrimidines: Uracil, Cytosine, Thymine, single ring structure
* Purines: Adenine, Guanine, double ring structure
6
New cards
Compare and Contrast prokaryotes and eukaryote genomes
* Prokaryotes and eukaryotes both can contain plasmids- small circular DNA molecules(prokaryotic plasmids- cytosol, eukaryotic plasmids- nucleus)
* Prokaryotic genome is smaller than eukaryotic genome
* Prokaryotes have circular chromosomes; eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes
* Prokaryotic genome is smaller than eukaryotic genome
* Prokaryotes have circular chromosomes; eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes
7
New cards
6\.2
Replication
8
New cards
What is the purpose of hereditary replication?
To ensure continuity of hereditary information
* DNA is copied to allow transmission of the complete genome from one generation to the next
* DNA is copied to allow transmission of the complete genome from one generation to the next
9
New cards
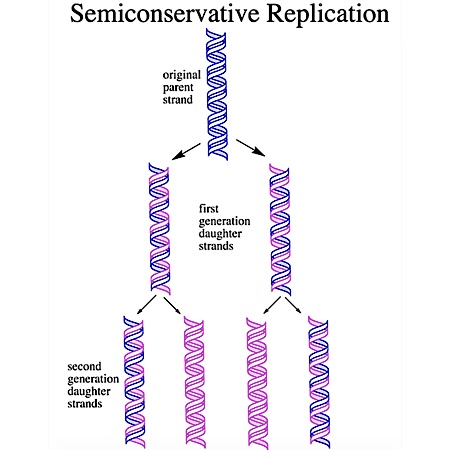
What does it mean when DNA replication is semiconservative
The complementary strand will use the original strand as a template when replicating
10
New cards
How does DNA directionality influence the replication process?
* DNA strands run antiparallel to each other(going in opposite directions)
* the 5’ of strand is opposite to the 3’ of the other strand
* The 5’ is where the phosphate terminus is
* The 3’ is where the hydroxyl terminus is
* Nucleotides can only be added to the growing strand from the 5’ to 3’ direction
* Leading strand: strand will be replicated continously
* Lagging strand: strand will be replicated non-continously
* the 5’ of strand is opposite to the 3’ of the other strand
* The 5’ is where the phosphate terminus is
* The 3’ is where the hydroxyl terminus is
* Nucleotides can only be added to the growing strand from the 5’ to 3’ direction
* Leading strand: strand will be replicated continously
* Lagging strand: strand will be replicated non-continously
11
New cards
What is helicase?
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA strand
12
New cards
What is topoisomerase?
An enzyme that relaxes the supercoil at the replication fork
* The replication fork is where the two strands separate from each other
* The replication fork is where the two strands separate from each other
13
New cards
What is DNA polymerase?
Synthesizes new strands
* Requires RNA primers to initiate synthesis
* Attaches to the 3’ of the template
* Builds the new strand in 5’ to 3’ direction
* Requires RNA primers to initiate synthesis
* Attaches to the 3’ of the template
* Builds the new strand in 5’ to 3’ direction
14
New cards
What is ligase
Joins the DNA fragments on the lagging strand
15
New cards
6\.3
Transcription and RNA Processing
16
New cards
What does genetic information flow?
It flows from DNA to RNA to a protein
DNA- stores the genetic information
RNA- uses DNA information to facilitate protein synthesis
Ribosomes- use RNA to make proteins
DNA- stores the genetic information
RNA- uses DNA information to facilitate protein synthesis
Ribosomes- use RNA to make proteins
17
New cards
What is transcription?
The formation of a mRNA molecule
* DNA is spilt into two strands- one being the non-coding/template strand and the other being the coding/non-template strand
* The gene that needs to be transcribed is on the coding strand
* RNA Polymerase will synthesize mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction by reading in the 3’ to 5’ direction
* DNA is spilt into two strands- one being the non-coding/template strand and the other being the coding/non-template strand
* The gene that needs to be transcribed is on the coding strand
* RNA Polymerase will synthesize mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction by reading in the 3’ to 5’ direction
18
New cards
What is mRNA?
* Messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA to the protein and is made during transcription
19
New cards
What is a codon?
Three base sequence found on mRNA
Start codon: AUG
Stop codons: UGA, UAA, UAC
Start codon: AUG
Stop codons: UGA, UAA, UAC
20
New cards
What is tRNA?
It is used in the ribosomes to make the polypeptide chain during translation
21
New cards
What is an anti-codon?
It is a three base sequence on a tRNA
* If the corresponding tRNA is matched with the corresponding mRNA then an amino acid will be released and form a polypeptide chain
* If the corresponding tRNA is matched with the corresponding mRNA then an amino acid will be released and form a polypeptide chain
22
New cards
What is rRNA?
It is the functional part of the ribosome in which is the protein in made
* Creates primary polypeptides as tRNA released amino acids
* Creates primary polypeptides as tRNA released amino acids
23
New cards
What are the modifications that occur in mRNA during transcription (Poly A- tail, GTP cap,
* Poly-A tail: 100-200 adenine nucleotides(3’)
* Increases stability
* Helps with exporting from the nucleus
* GTP cap: modified guanine nucleotide(5’)
* Helps ribosomes attach to the mRNA transcript
* Increases stability
* Helps with exporting from the nucleus
* GTP cap: modified guanine nucleotide(5’)
* Helps ribosomes attach to the mRNA transcript
24
New cards
Introns vs Extrons + primary/mature transcript
Introns: mRNA sequences that do not code for amino acids; removed during RNA processing
Exons: mRNA sequences that do code for amino acids; are not removed during RNA processing
Primary transcript: introns + exons
Mature transcript: just exons
Exons: mRNA sequences that do code for amino acids; are not removed during RNA processing
Primary transcript: introns + exons
Mature transcript: just exons
25
New cards
Alternative splicing
* The splicing(removing) of introns from the primary transcript to the mature transcript
* One primary transcript can be used to make multiple transcripts by reordering the exons
* One primary transcript can be used to make multiple transcripts by reordering the exons
26
New cards
6\.4
Translation
27
New cards
What is translation?
mRNA forms a polypeptide in the ribosome
Prokaryotes: have only ribosomes in the cytoplasm (happens during transcription)
Eukaryotes: have ribosomes in the cytoplasm & rough ER
Prokaryotes: have only ribosomes in the cytoplasm (happens during transcription)
Eukaryotes: have ribosomes in the cytoplasm & rough ER
28
New cards
What are the three steps of translation?
Initiation: the process is started; the codons and anti codons will match up starting to form that polypeptide chain
Elongation: the process will make the chain longer
Termination: the process will halt when a stop codon is read leaving just a polypeptide chain
Elongation: the process will make the chain longer
Termination: the process will halt when a stop codon is read leaving just a polypeptide chain
29
New cards
Initiation
rRNA interacts with mRNA at the first start codon (AUG- codes for amino acid methionine)
30
New cards
Elongation
* The tRNA anti codon must complement the mRNA codon so that the tRNA carries the correct amino acid to the correct space
* The rRNA will add the amino acid to the growing peptide chain
* The rRNA will add the amino acid to the growing peptide chain
31
New cards
Termination
* Once tRNA reads the stop codon, translation ends and polypeptide chain is released
32
New cards
How do retroviruses transcript and translate?
* They start off with RNA and is copied into DNA by enzyme reverse transcriptase
* The DNA is integrated into the host genome and transcripted and translated like normal
* The DNA is integrated into the host genome and transcripted and translated like normal
33
New cards
How does translation show common ancestery?
* Nearly all organisms use the same genetic code (DNA & RNA are the same among all organisms)
* Allows host cell genome to work with viral cell genome
* Allows host cell genome to work with viral cell genome
34
New cards
6\.5
Regulation of Gene Expression
35
New cards
What is gene expression?
The process in which DNA instructions are transcribed and translated into a functional protein
36
New cards
What are regulatory sequences/proteins?
Regulatory Sequences: stretches of DNA that can be used to either promote or inhibit proteins synthesis
Regulatory Proteins: used to assist the promotion or inhibition of protein synthesis
Regulatory Proteins: used to assist the promotion or inhibition of protein synthesis
37
New cards
What are epigenetic changes?
Reversible modifications of DNA or histones
* Histones: proteins used to wrap DNA around (found in the chromatin)
* These modifications cause the DNA to be either tightly or loosely packed & overall gene expression
* If the gene can not be reached (transcribed/translated) then a protein can’t be formed
* Histones: proteins used to wrap DNA around (found in the chromatin)
* These modifications cause the DNA to be either tightly or loosely packed & overall gene expression
* If the gene can not be reached (transcribed/translated) then a protein can’t be formed
38
New cards
What do cells in the same multi-cellular organism have in common?
All cells have the same DNA sequences
39
New cards
What are tissues?
Cells with the same function
* Since there are specific proteins in the tissues it gives the tissues their function
* Since there are specific proteins in the tissues it gives the tissues their function
40
New cards
How is the phenotype of a cell determined?
* The combination of multiple genes that are expressed
41
New cards
What is the difference between cell differentiation?
Cells within the same organism having different phenotypes
42
New cards
What are transcription factors?
They regulate gene expression by promoting or inhibiting transcription of a gene
* Various transcription factors determine how the cell differentiates
* Various transcription factors determine how the cell differentiates
43
New cards
What are operons?
Closely linked genes that produce a single mRNA molecule during transcription
* They are under control of the same regulatory sequence
* They are under control of the same regulatory sequence
44
New cards
What is an operator?
It is a sequence that either promotes or inhibits transcription by binding to regulatory proteins
45
New cards
How are structural proteins controlled?
Structural proteins with related functions are encoded together into one genome
* They are controlled by a single regulatory sequence
* They are controlled by a single regulatory sequence
46
New cards
Why is the lac operon considered inducible?
* It is usually turned off
* When a regulatory proteins is bound to the operator, RNA polymerase can’t bind to the regulatory sequence and transcribe this gene
* When a regulatory proteins is bound to the operator, RNA polymerase can’t bind to the regulatory sequence and transcribe this gene
47
New cards
What are inducers and how do they allow RNA Polymerase to transcribe the gene?
Inducers change the shape of a regulatory protein
* By changing shape the regulatory protein is released from the operator and the RNA polymerase is free the transcribe the gene
* By changing shape the regulatory protein is released from the operator and the RNA polymerase is free the transcribe the gene
48
New cards
What are some transcription factors that help the lac operon operate?
* More glucose = more transcription
* cAMP and CAP are transcription factors that bind to the regulatory sequence to promote transcription (not present when glucose levels are high)
* cAMP and CAP are transcription factors that bind to the regulatory sequence to promote transcription (not present when glucose levels are high)
49
New cards
6\.6
Gene Expression and Cell Specilization
50
New cards
What are promoters?
A region upstream from transcription start site that initiates transcription
51
New cards
The interaction of promoters and other transcription factors help determine
The phenotypic differences between tissues within an organism
52
New cards
What do negative regulatory molecules do?
They inhibit gene expression by blocking transcription (the regulatory molecules binds to the promoter region meaning RNA Polymerase can’t bind there)
53
New cards
What do cells in the same organism have in common?
The same DNA
54
New cards
What can small RNA fragments do in regulating gene expression?
* Can break down mRNA during transcription
* Block translation from happening since the ribosome can’t read the mRNA
* Block translation from happening since the ribosome can’t read the mRNA
55
New cards
6\.7
Mutations
56
New cards
What is a mutation?
* Changes in the genome of an organism
* Can be positive, negative, neutral (depends on environment)
* Are the primary source of genetic variation
* Can be positive, negative, neutral (depends on environment)
* Are the primary source of genetic variation
57
New cards
What are gene mutations?
* Changes in the nucleotide sequence
Substitution
* Considered neutral if the end protein is the same
* Considered negative if a new protein is formed and it harms the cell (vice versa for positive)
Substitution
* Considered neutral if the end protein is the same
* Considered negative if a new protein is formed and it harms the cell (vice versa for positive)
58
New cards
Insertion & Deletion
* They change the order of the gene sequence
* They can cause no protein to be formed or additional proteins to be formed
* They can cause no protein to be formed or additional proteins to be formed
59
New cards
What can cause random mutations
* Radiation, Errors in DNA replication, Errors in DNA repair, Harmful Chemicals
60
New cards
What is triploidy and polyploidy?
* Triploidy: having three copies of a particular chromosome(can’t reproduce/make seeds)
* Polyploidy: having multiple sets of homologous chromosomes(increased vigor- size)
* Polyploidy: having multiple sets of homologous chromosomes(increased vigor- size)
61
New cards
What is natural selection?
Organisms that are better adapted to the environment are more likely to survive and pass along that trait to their offspring
62
New cards
What is horizontal transfer of genetic information?
* Genetic information is exchanged between organisms of the same generation through conjugation
* Primarily happens in prokaryotes & increases genetic variation
* Primarily happens in prokaryotes & increases genetic variation
63
New cards
What is transformation, transduction, conjugation, transposition?
* Prokaryotic cell takes up naked DNA(not protected by any proteins)
* PC obtains foreign DNA into a cell when viral genome integrates with host genome
* Cell to cell exchange of small DNA (horizontally through plasmid)
* Exchange of DNA between DNA molecules and within them
* PC obtains foreign DNA into a cell when viral genome integrates with host genome
* Cell to cell exchange of small DNA (horizontally through plasmid)
* Exchange of DNA between DNA molecules and within them
64
New cards
How can viruses combine genetic information?
* Related viruses can combine viral genetic information to form a new viral combination within the host genome
65
New cards
Which processes increase genetic variation?
1. Independent Assortment
2. Random Fertilization
3. Crossing Over
66
New cards
6\.8
Biotechnology
67
New cards
What are some processes that can change/manipulate DNA & RNA?
* Gel electrophoresis
* Polymerase Chain Reaction
* DNA sequencing
* Polymerase Chain Reaction
* DNA sequencing
68
New cards
How does gel electrophoresis work?
Gel electrophoresis separates DNA fragments based on size and charge
* DNA is negatively charged and will move towards the positive side
* Smaller molecules will be closer to the positive side because they can move through the small pores in the gel
* DNA is negatively charged and will move towards the positive side
* Smaller molecules will be closer to the positive side because they can move through the small pores in the gel
69
New cards
How does PCR work?
PCR amplifies a smaller amount of DNA
* Denaturation: the DNA strands are separated due to the high heat
* Annealing: Primers are added and temperature is cooled down
* Extension: Taq polymerase with replicate the DNA
* Denaturation: the DNA strands are separated due to the high heat
* Annealing: Primers are added and temperature is cooled down
* Extension: Taq polymerase with replicate the DNA
70
New cards
How is DNA incorporated into bacterial chromosomes?
Bacteria only uptakes DNA at specific times & when it’s incorporated into the chromosomes it will form a plasmid
* Can used for medicines, to modify food, or amplify DNA
* Can used for medicines, to modify food, or amplify DNA
71
New cards
How is DNA sequencing used to determine the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule?
* Nucleotides can be colored with dye to read and build copies of DNA
* DNA can be run through a capillary gel and the sequence can be read through a detector
* DNA can be run through a capillary gel and the sequence can be read through a detector