Unit 2 AP Psychology Terms
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Sensation
Process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive + represent stimulus energies from environment
Perception

Process of organizaing and interpreting sensory info to make sense of the world
Brain interprets sensory inputs
Can be influenced by past experiences, expectations, and context
Transduction
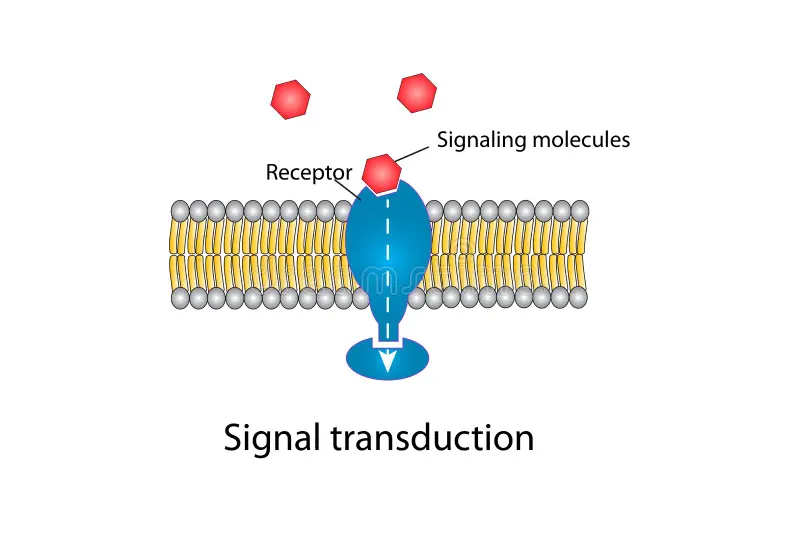
Conversion of sensory stimuli into neural impulses that can be understood by brain
Physical energy → electrochemical signals
Allows brain to interpret and perceive sensory information
Absolute Threshold
Minimum amount of stimulation for stimuli to be detected by sensory system
Point at which stimulus becomes noticeable (at least 50% of the time)
Just-Noticeable Difference (JND)

Smallest change in stimulus that one can detect
Minimal difference needed for a person to perceive that a change has occurred
Weber’s Law
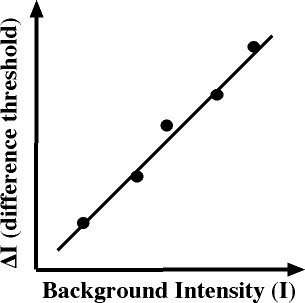
Perceived difference in stimulus must be proportional to original intensity of stimulus
Bigger something is, more you need to change it to notice a difference
Sensory Adaptation

Process where sensory receptors become less responsive to constant stimulus over time
Synesthesia

Condition where stimulation of one sensory pathway leads to automatic, involuntary experiences in another sensory pathway
Retina
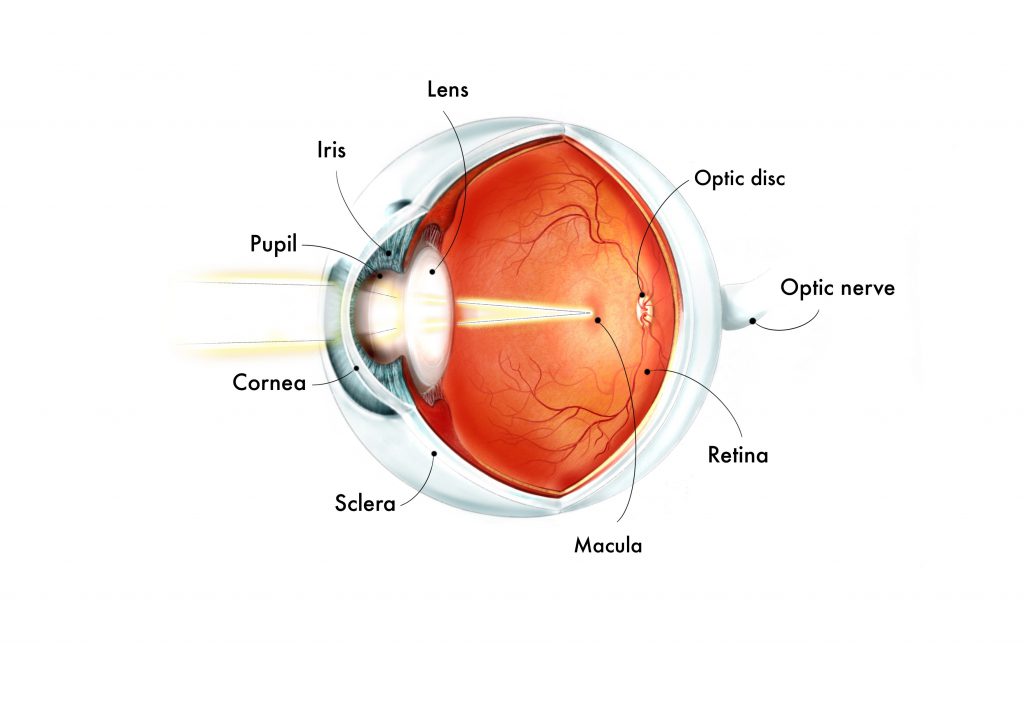
Light-sensitive inner surface of the eye
Contains photoreceptor cells that convert light → neural signals
Rods
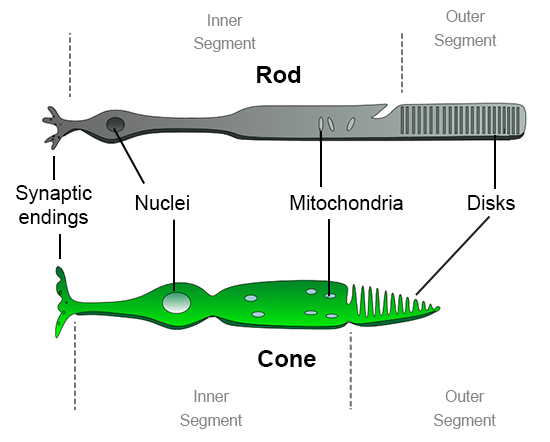
Photorecepor cells in the retina
Responsible for vision in low light conditions and detecting motion
Provides black-and-white vision and is highly sensitive to light
Cones

Photoreceptor cells in the retina
Responsible for color vision and detail in bright light
Enables us to perceive colors and fine visual details (reading and distinguishing different hues)
Fovea
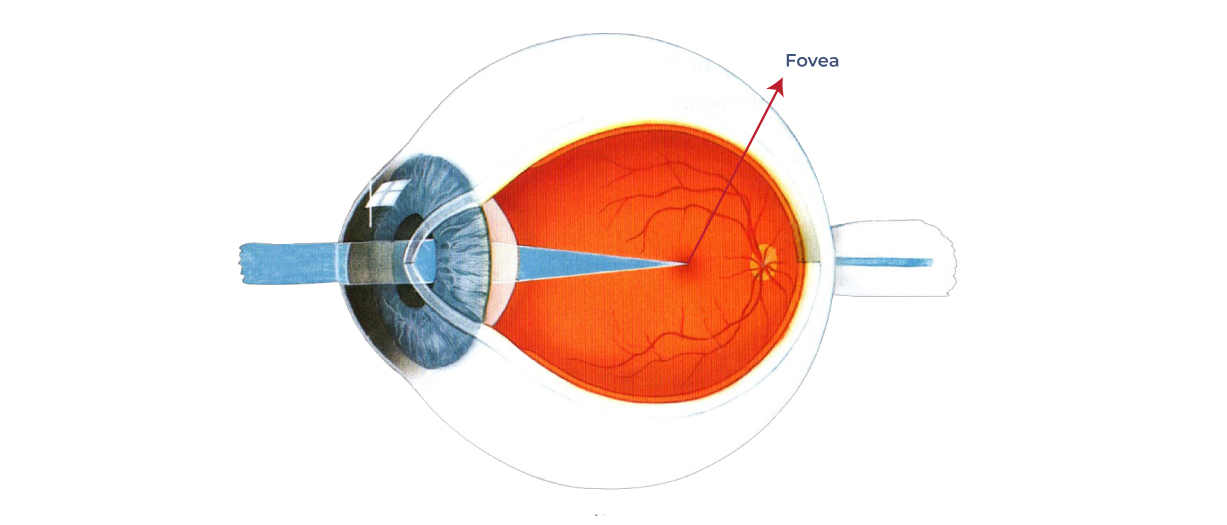
Central area of the retina
Responsible for sharp central vision
Contains high concentration of cone cells but no rods
Enables detailed and colored vision
Blind Spot
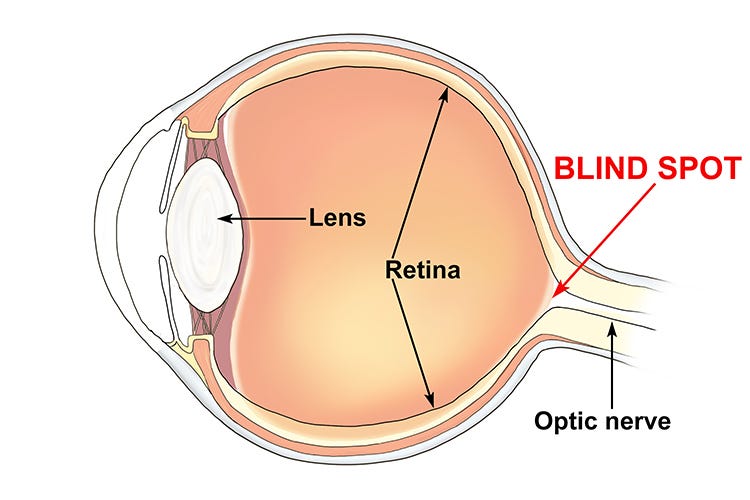
Area on retina where optic nerve exits the eye
Lacks photoreceptor cells
Spot where vision is absent due to no light-sensitive cells to detect visual stimuli
Ganglion Cells
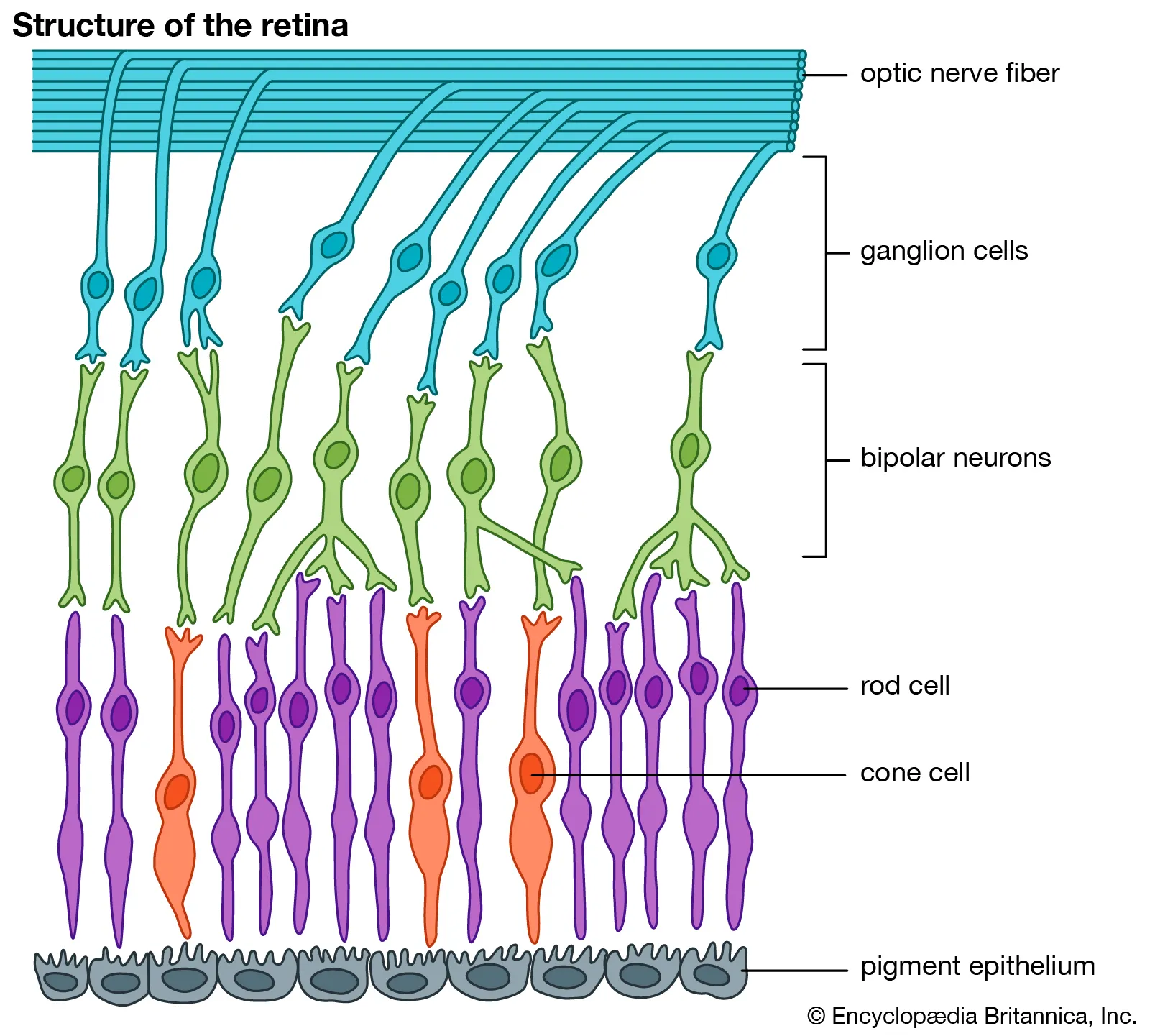
Neurons in the retina that receives visual information from bipolar cells
Transmits them to the brain via optic nerve
Helps process visual signals
Sends visual signals to brain for further interpretation
Lens
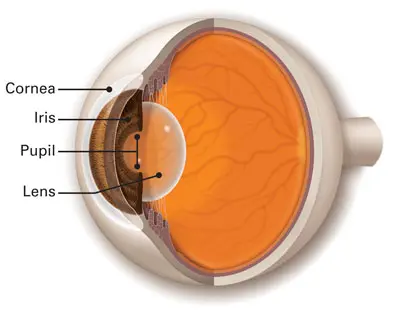
Transparent structure in the eye
Role is to focus light onto the retina
Adjusts shape to help eye properly refract light, enabling clear vision
Accommodation
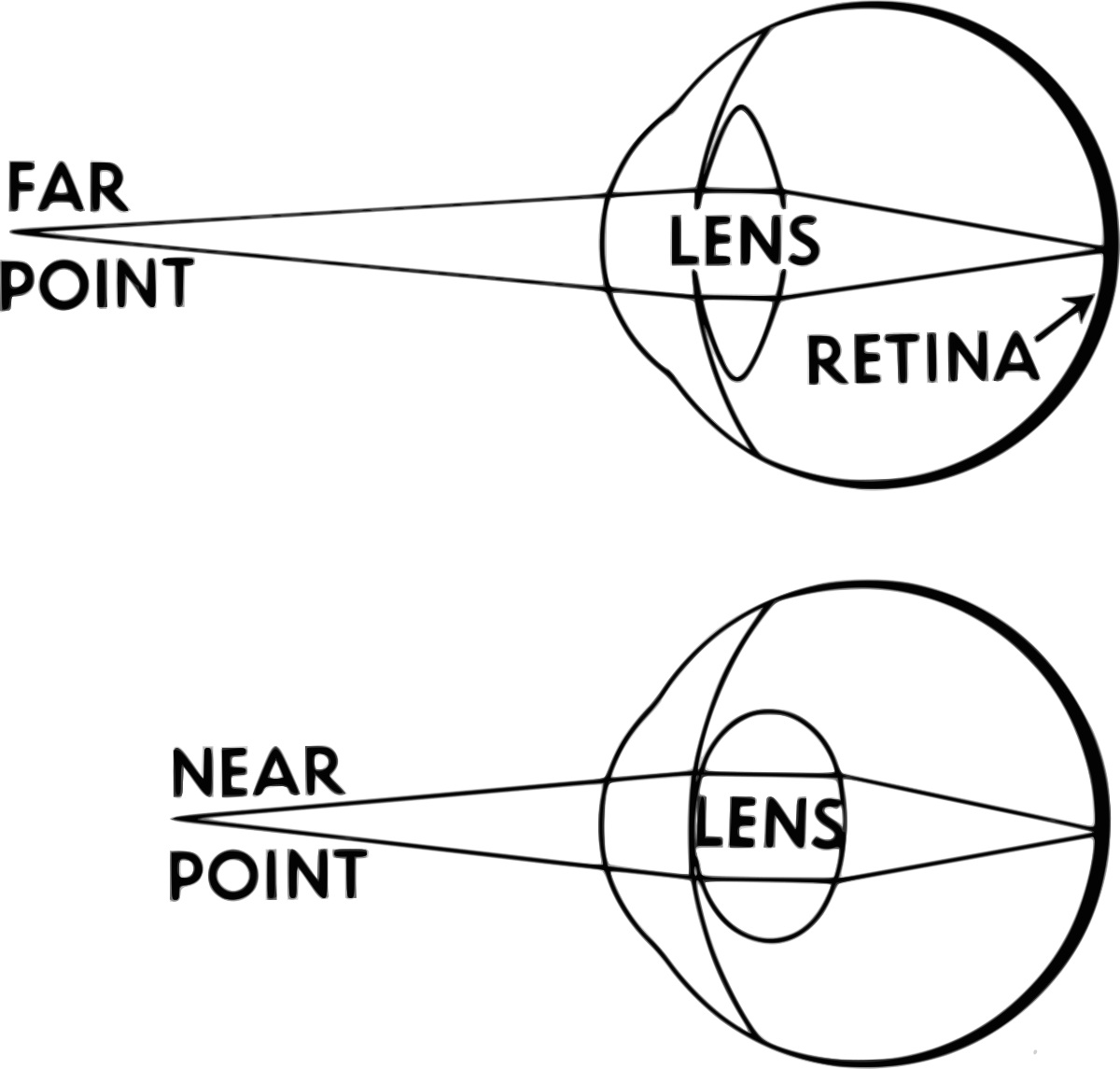
Process by which lens of the eye changes shape to focus on objects at different distances
Allows for nearby and distant clear vision
Adjusts curvature of the lens
Nearsightedness

Common vision condition where close objects appear clear & distant objects appear blurry
Happens when eye is too long or cornea is too curved
Causes light to focus in front of the retina instead of on it
Farsightedness

Vision condition where distant objects are more clear than close ones
Happens when eyeball is too short or cornea is too flat
Causes light to focus behind the retina instead of on it
Trichromatic Theory
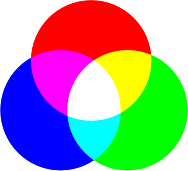
Theory proposing that color vision is based on 3 types of cone receptors
Each are sensitive to different light wavelengths
Brain combines signals from these cones to create perception of wide range of colors
Opponent-Process Theory
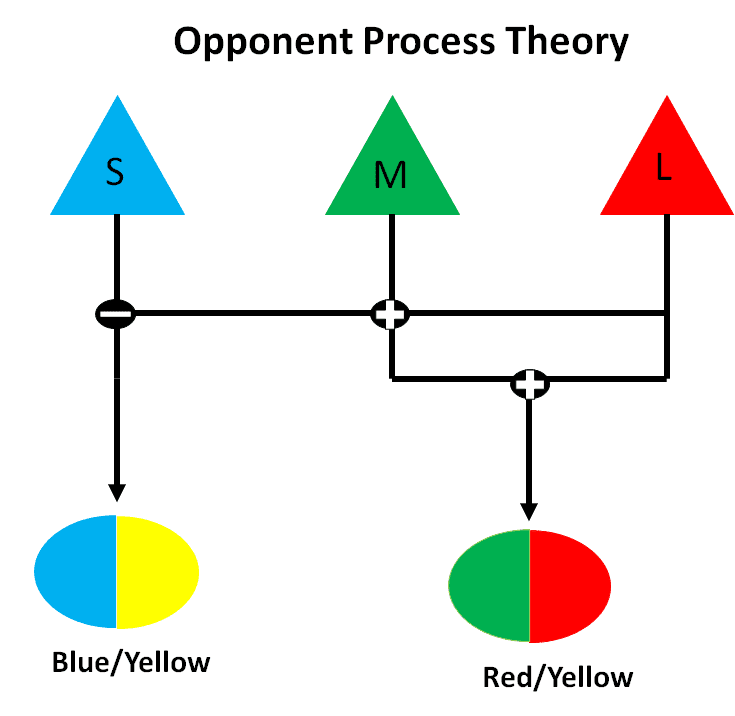
Theory proposing that color vision is based on pairs of opposing color process
(Blue + yellow, red + green, black + white)
Activation of one color inhibits the other
Leads to perception of color afterimages
Explains certain aspects of color vision
Afterimages

Visual sensations that persist after a stimulus is removed
Occur due to temporary overstimulation of cone cells in retina
Results in brief perception of inverted/complementary images
Dichromatism
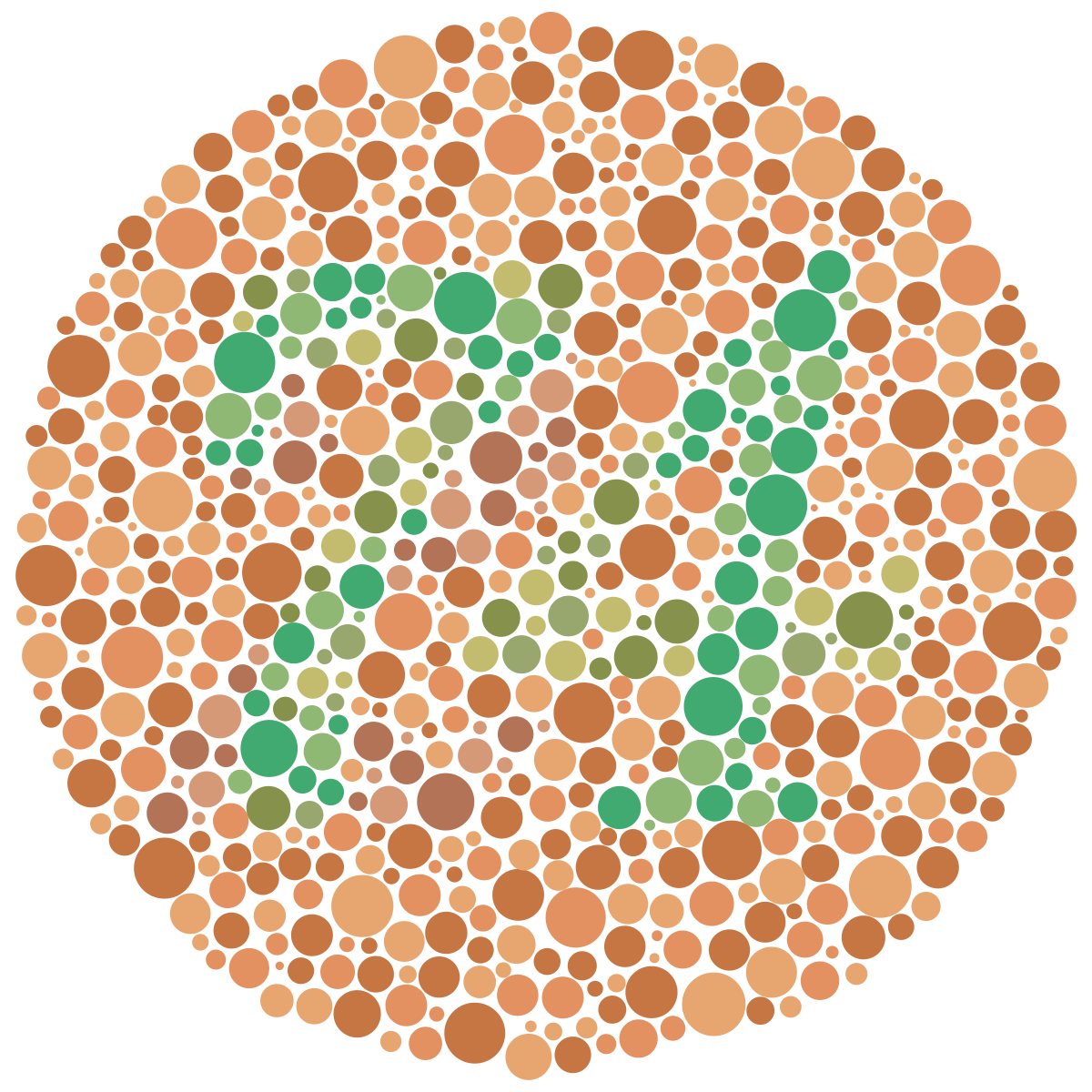
Type of color vision defiency
Individuals affected only have 2 types of functioning cone cells (instead of 3)
Results in difficulty distinguishing between certain colors
Monochromatism
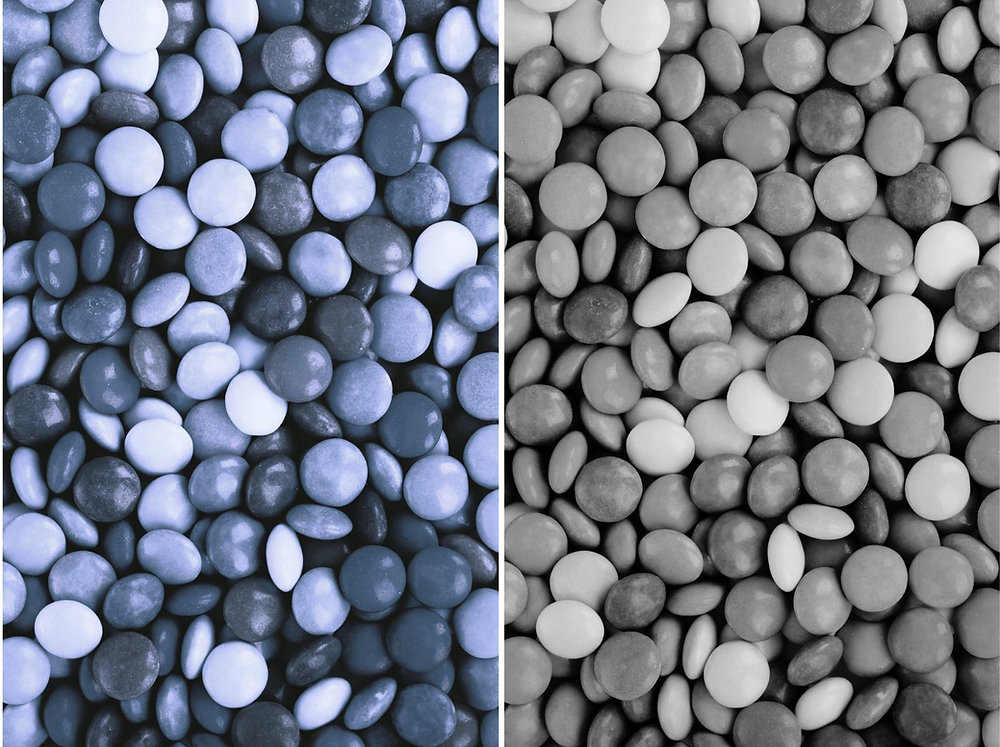
Rare form of color blindness
Individual only has one type of functioning cone cell or none at all
Results in inability to perceive colors
Sees the world in shades of gray
Blindsight
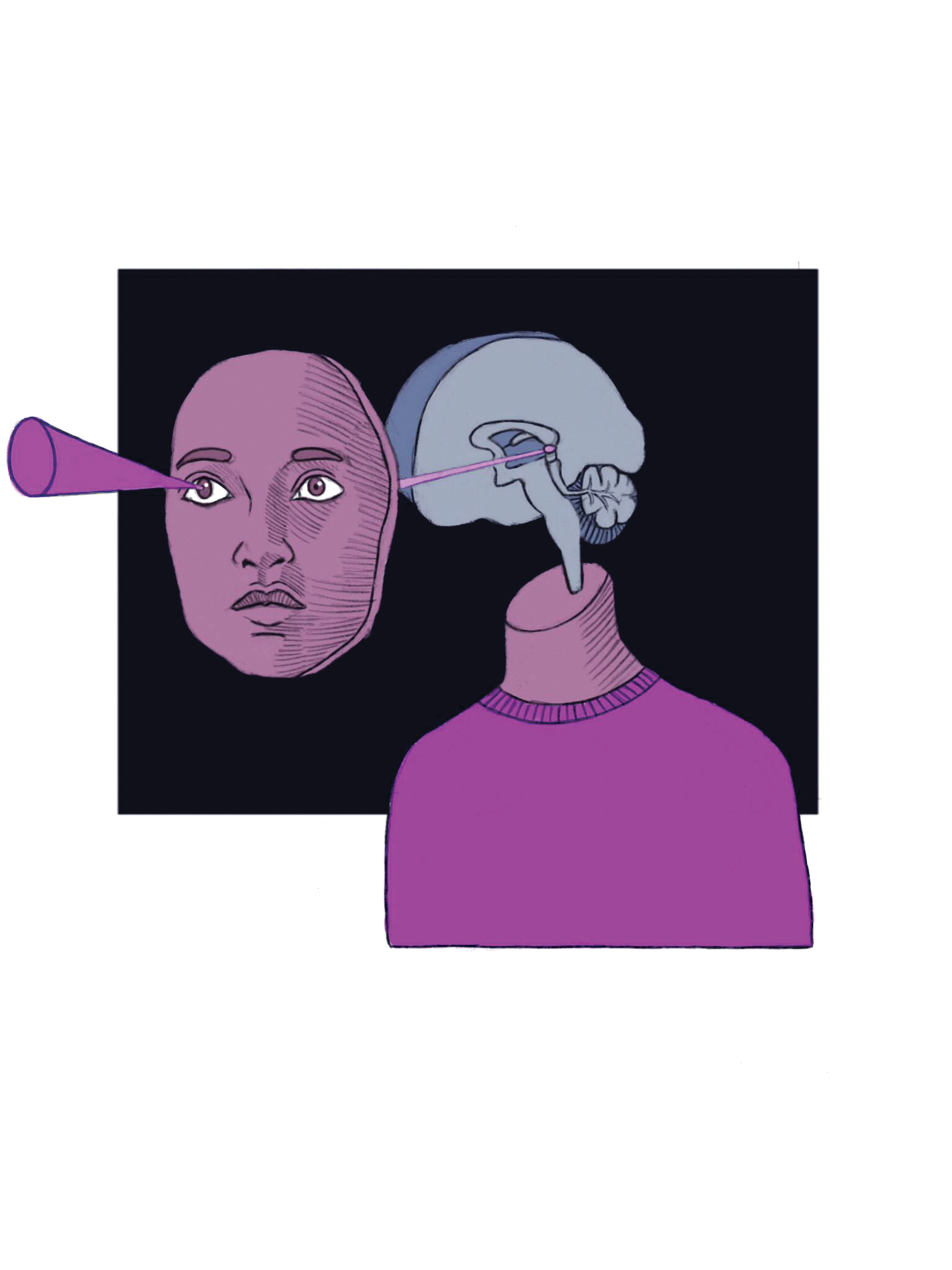
Phenomenon affecting individuals with damaged visual cortex
They can respond to visual stimuli without consciously perceiving them
Suggests that visual processing can occur unconsciously
Bypasses traditional pathways in the brain
Prosopagnosia

Neurological condition characterized by the inability to recognize familiar faces
Happens despite intact vision and intellect
Referred to as face blindness
Wavelength
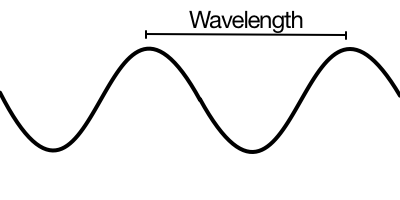
Distance between sound wave peaks
Shorter wavelengths → higher-pitch
Longer wavelengths → lower-pitch
Amplitude
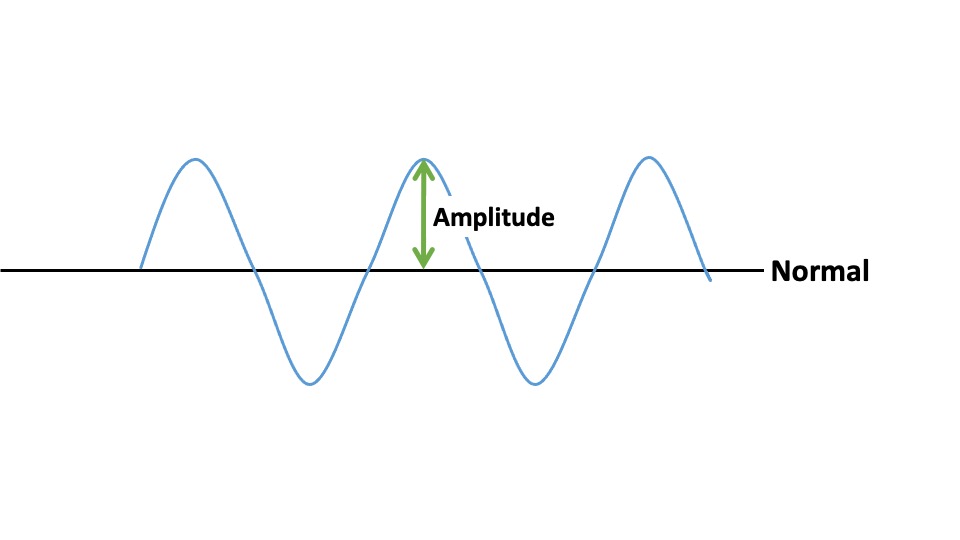
Measure of intensity/loudness of a sound wave
Represented by height of its peaks
Greater amplitudes → louder sounds
Lower amplitudes → softer sounds
Pitch Perception
Brain’s interpretation of frequency of sound waves
Determines if sound is high/low in tone
Higher frequencies → higher pitches
Lower frequencies → lower pitches
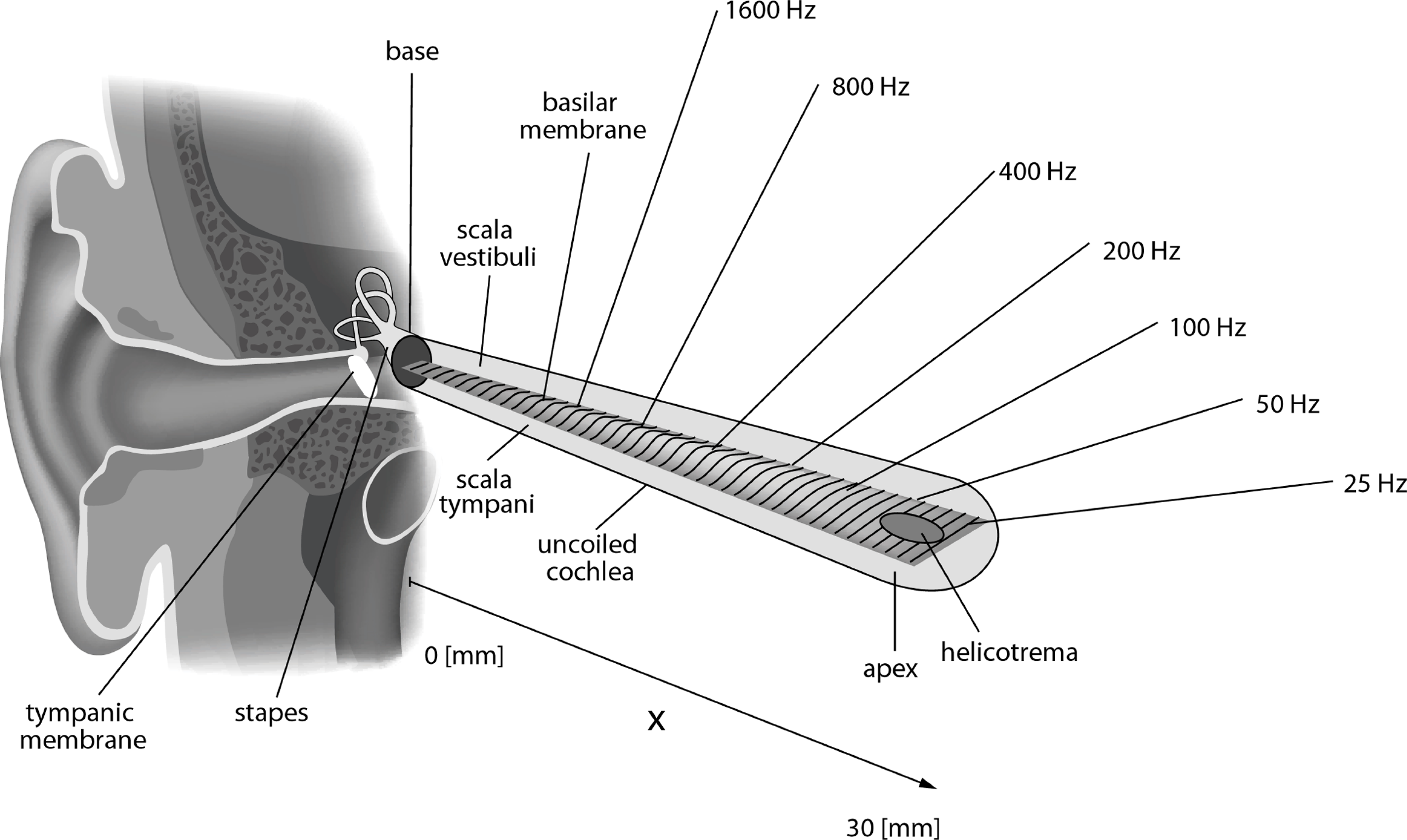
Place Theory
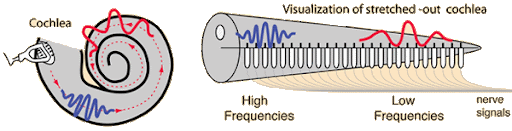
Idea that different parts of inner ear detect different sound frequencies
High pitches sensed near entrance
Low pitches sensed near the end
Frequency Theory
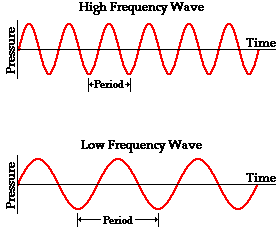
Theory proposing that frequency of sound wave directly corresponds to rate at which auditory nerve fibers fire
Higher frequency → faster firing rates
Volley Theory
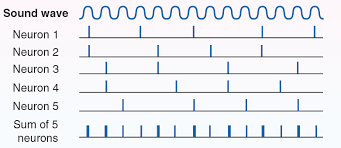
Theory proposing that groups of auditory neurons fire in rapid succession (“volleys”)
Allows brain to encode frequencies above 1000Hz
Sound Localization
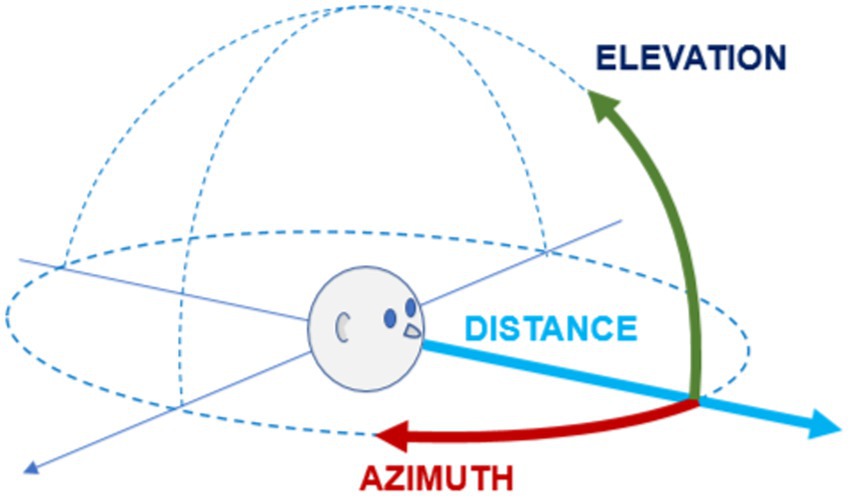
Brain’s ability to determine location of sound source in a space
Relies on cues like differences in arrival time, intensity between the ears, and spectral cues
Conduction Deafness
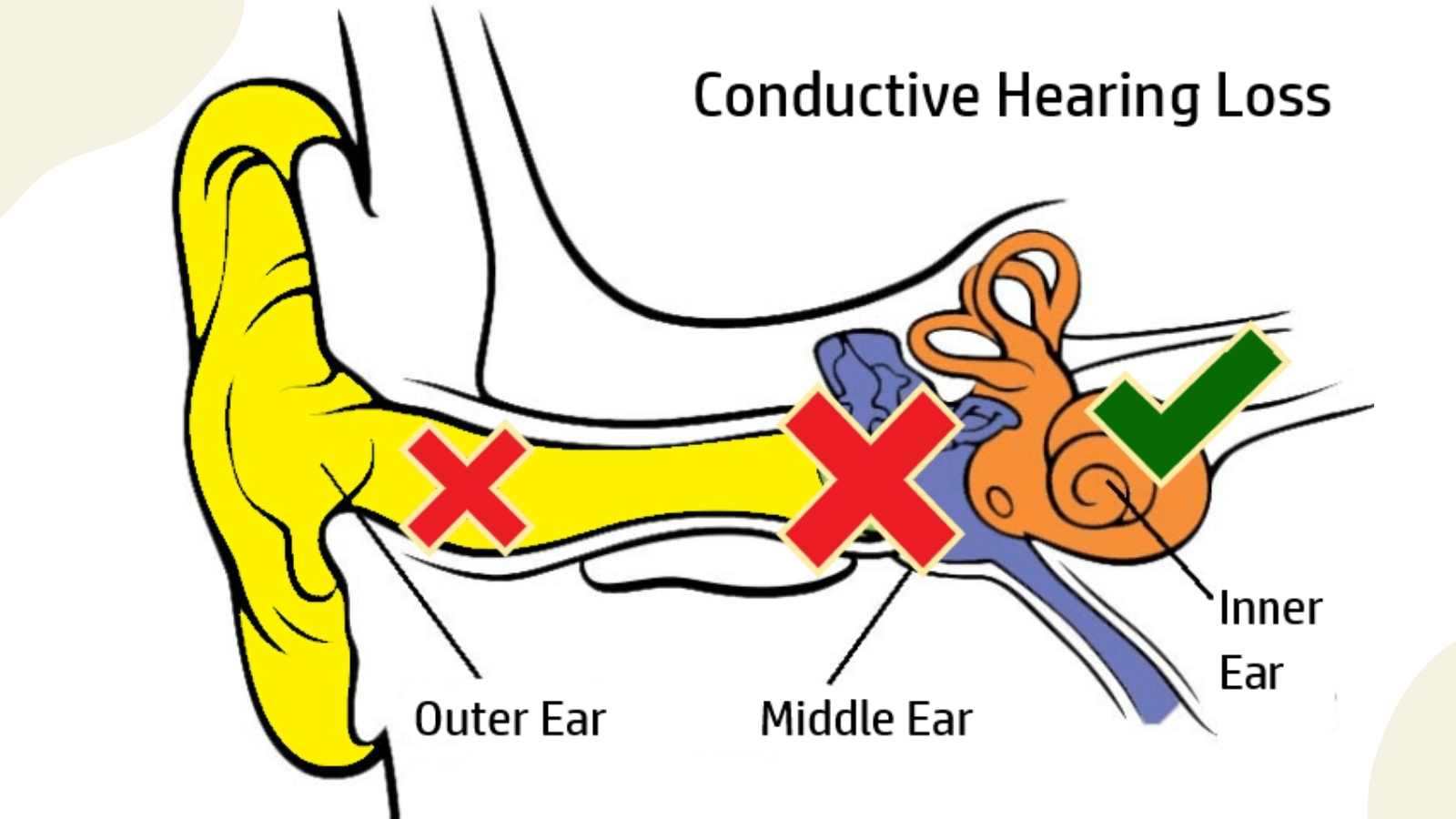
Hearing impairness caused by problems to outer or middle ear
Damage to ear canal, eardrum, or middle ear bones
Results in difficulty hearing soft sounds and can be treated medically/surgically (temporary)
Sensorineural Deafness
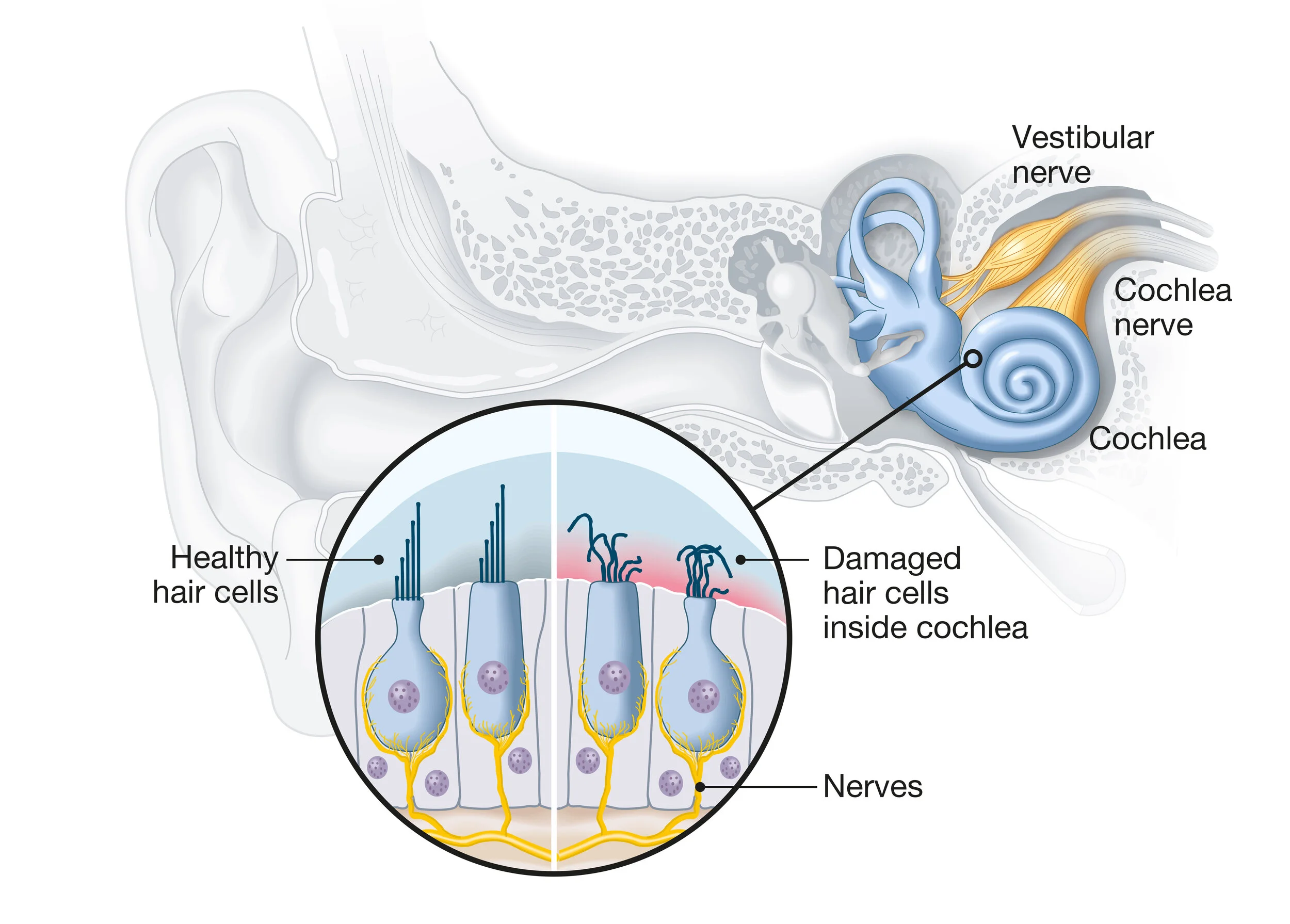
Hearing loss caused by damage to inner ear or auditory nerve
Results in difficulty hearing soft sounds and understanding speech
Often permanent
Caused by aging, exposure to loud noises, and certain medical conditions