Managerial Final Exam Tips
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Special or Custom Order
Selling Price-Variable Costs=Contribution Margin
If CM p/u is positive, accept the order. If CM p/u is negative, decline the order.
Keeping or Dropping a Product Line
Selling Price-Variable Costs=Contribution Margin
If CM p/u is positive, keep the product line. If CM p/u is negative, drop the product line.
Product Mix Decisions
Calculate CM per hour. Focus on product line that has higher CM p/h. Use remaining hours on the other product lines.
Making or Buying a Product
Make: (VC x units)+FC
Buy: (Outsource Cost x units)+FC
Choose the option with the lowest answer.
Sell or Process Further
Keep at Split-Off or Process Further=New Revenue-New Costs. Choose the highest yielding products and subtract joint costs from the total of those choices.
Regular Pricing Decisions
Use the Sales-COGS=GP formula. Sales will always equal 100% so use algebra to solve for whatever the problem is asking for.
Annuity
"next X years"
"yearly payments"
"per year"
"a year"
Single Sum
"one-time cost"
"invest a certain amount today"
"fixed amount today"
selling an asset since you only sell the item one time
Semi-Annual
Multiply payments times 2 and divide interest by 2
Sales Budget
Unit Sales
x Selling Price
=Total Sales
Cash Receipts or Collections Budget
Total Sales
x % Cash Collections
x % Credit Collections
Total Credit Sales
X% this month
+X% previous month
=Total Credit Receipts
+Cash Collections from Above
=Total Cash Collections
Production or Purchases Budget
Expected Unit Sales
+Desired Ending Units
-Beginning Inventory
=Total Required Units
x Cost per Unit
=Total Production Cost
Cash Disbursements Budget
Total Production Cost
X% this month
+X% previous month
=Total Cash Payments for Purchases
Cost Center
Manager only responsible for managing their departments costs (expenses).
Ex. Accounting, H/R, Legal
Revenue Center
Manager focused on increasing department revenue and managing their expenses.
Ex. Salesperson
Profit Center
Manager responsible for revenue and expenses within their center.
Ex. Store manager, restaurant manager
Investment Center
Manager accountable for investments, revenues, and costs
Ex. Finance
Static or Master Budget
Budget based on the level of output (units) planned at the start of the budget period
Flexible Budget
A budget prepared for various levels of sales volume. Variable costs change in proportion to sales volume but fixed costs stay the same.
Sales Volume Variance
=Flexible Budget - Static Budget
Variance due to difference in actual units sold vs budgeted.
Flexible Budget Variance
=Flexible Budget - Actual Results
Variance due to company earning more or less than expected for the ACTUAL level of output.
Both Variances Together
=Static Budget Variance
Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculates how much income is generated in proportion to its assets.
=Operating Income/Total Assets
Residual Income (RI)
= Income - (Target Rate of Return x Total Assets)
Positive # means managements expectation were exceeded.
Negative # means target rate of return was not met.
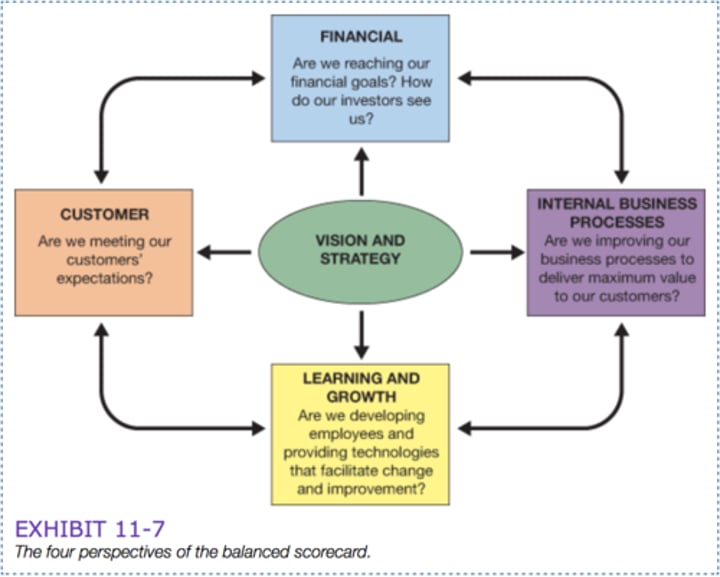
Balanced Scorecard
4 aspects:
Employee Learning and Growth
Operational Efficiency/ Internal Business
Customer Satisfaction
Financial Profitability
Direct Materials Price Variance
(actual price - standard price) x purchased quantity
Direct Materials Quantity Variance
(actual quantity - standard quantity) x standard price
Direct Labor Rate Variance
(actual rate - standard rate) x actual hours
Direct Labor Efficiency Variance
(actual hours - standard hours) x standard rate
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance
(actual hours - standard hours) x standard rate
Variable Overhead Rate Variance
(actual rate - standard rate) x actual hours
Fixed Overhead Budget
Actual $ - Budgeted $
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance
budgeted fixed overhead - applied fixed overhead (based on predetermined OH rate)