perforators & central veins | venous hemodynamics
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
What is another term for perforating veins?
Perforators
Perforating veins are vessels that (1)________ or go through the (2)________ that covers the (3)________.
Perforate
Fascia
Muscle
Perforating veins form connections between the ___________ and ___________ systems.
Superficial
Deep
Perforating veins accompany what vessels?
Perforating arteries
Name an example of a perforating vein and what it helps connect.
Connects GSV to deep system
Communicating veins are vessels that connect veins within the _____ system.
For example, ______-______ or _____________-____________ venous systems.
Same
Deep-deep, superficial-superficial
What vein connects the GSV and SSV?
Would this vein be a perforating or communicating vein?
Vein of Giacomini
Communicating veins
What is the typical diameter of a normal and competent communicating vein?
Less than 2 mm
Are communicating veins seen routinely during an US?
If not, why is that?
No
Because of their small size
The calf muscle pump mechanism helps to promote (1)_______ return during (2)_________ or __________.
Venous
Walking or running
The calf muscle pump is a way for blood to get back to the…
Heart
Peripheral veins can be found in what areas?
These veins have valves that direct flow (towards/away) from the limbs and (towards/away) from the heart.
Arms and legs
Away, towards
Valves maintain _____________ flow.
Unidirectional
Veins located in large muscle groups, ex. calves, undergo compression whenever the muscles…
They will undergo decompression when the muscles…
Contract
Relax
The calf muscle pump is essentially normal cycles of ___________ and ___________ of the vein.
Compression
Decompression
Perforators help to maintain an (1)_______ movement of blood with assistance of the (2)_________________ mechanism.
Efficient
Muscle pump
Venous drainage of the lower leg occurs as blood travels from the (1)__________ veins through the (2)__________, into the (3)___________ veins.
Superficial
Perforators
Deep
In normal circumstances, what system drains the subcutaneous tissues?
This system will periodically empty into which system?
This is done through what vessels?
Superficial
Deep
Perforating
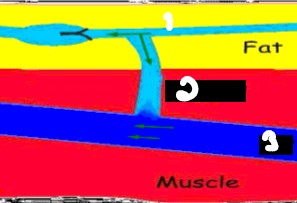
Label the crossed-out parts of this image.
Superficial system
Perforating veins
Deep system
Each lower extremity can contain as many as __-__ perforators.
80 - 140
What is another term for posterior arch vein?
Posterior accessory great saphenous vein
The posterior accessory great saphenous vein is important because it represents a (1)__________ connection of the three (2)______ perforating veins.
Superficial
Ankle
Which vein plays a major role in the development of venous stasis ulcers?
Posterior arch vein
The posterior accessory great saphenous vein extends superior from the (1)______ to the (2)______________ vein.
Ankle
Great saphenous vein
The posterior arch vein receives blood from the ________________ perforators.
Posterior tibial
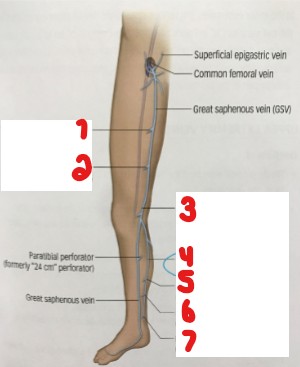
Label the parts of this perforator anatomy image.
Perforator of femoral canal (Hunter’s)
Perforator of femoral canal (Dodd’s)
Para tibial perforator (Boyd’s)
Posterior accessory GSV (Posterior arch vein)
Upper posterior tibial perforator (Cockett III)
Middle posterior tibial perforator (Cockett II)
Lower posterior tibial perforator (Cockett I)
What are the two other terms for the perforator of femoral canal?
Hunter’s
Dodd’s
What is the name of the medial thigh perforator?
Perforator of femoral canal (Hunter’s and Dodd’s)
The perforator of femoral canal drains blood from the (1)_____ and (2)______ thigh, and goes into the distal (3)__________ vein.
GSV
Distal
Femoral
What is another term for Para tibial perforator?
Boyd’s
List the 3 posterior tibial perforators.
Upper
Mid
Lower
What is another term for upper posterior tibial perforator?
Cockett III
What is another term for mid posterior tibial perforator?
Cockett II
What is another term for lower posterior tibial perforator?
Cockett I
The three posterior tibial perforators connect the (1)_____ and the posterior (2)______ veins.
GSV
Tibial
In the lower extremities, the venous sinuses are dilated ________ located in the calf muscles.
Channels
Venous sinuses allow venous blood to accumulate and then drain into the (1)_________________ and (2)_________ veins.
Posterior tibial
Peroneal
These large (1)________ saccular muscle veins of the (2)________ and (3)____________ muscles act as a major part of the calf muscle pump.
Sinusoid
Soleal
Gastrocnemius
What is the main venous sinus?
Gastrocnemius vein
A thrombus is considered bad when found in the (superficial/deep) system.
Deep
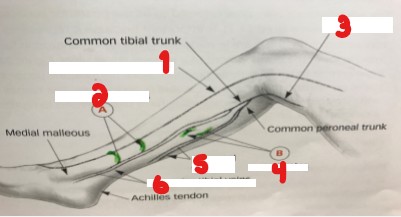
Label the veins on this image.
Great saphenous vein
Perforating veins
Popliteal vein
Soleal veins
Peroneal veins
Posterior tibial veins
What is another term for venous sinuses?
Soleal veins
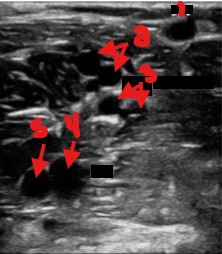
Label the parts of this vessel image.
Small saphenous vein
Lateral gastrocnemius
Medial gastrocnemius
Popliteal vein
Popliteal artery
Blood in the head and upper extremities empty into the…
Innominate veins
The innominate veins form the…
Superior vena cava
The superior vena cava empties into the ______ atrium of the heart.
Right
The lower half of the body empties into the…
Common iliac veins
The common iliac veins join together to form the…
IVC
The inferior vena cava empties into the _____ atrium of the heart.
Right

Label the structures the blood goes through from the upper extremities to the right atrium.
Innominate veins
SVC
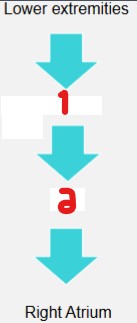
Label the structures the blood goes through from the lower extremities to the right atrium.
Common iliac veins
IVC
The main portal vein is formed from the ____________ vein and ____________ vein.
Superior mesenteric vein
Splenic vein
Which vein supplies 70-80% of blood to the liver?
Main portal vein
Which vein supplies 20-30% of blood to the liver?
Hepatic artery
Which blood flow is normal: hepatopedal or hepatofugal?
Hepatopedal
Hepatopedal flow is (1)________ the (2)______.
Towards
Liver
What diameter measurement is considered normal for the main portal vein?
Less than 13 mm
Hepatic veins carry blood from the (1)_____ into the (2)___.
Liver
IVC
Hepatic vein flow is characterized as ____________ flow.
Hepatofugal
Hepatofugal flow is (1)________ the (2)______.
Away from
Liver
What two factors are demonstrated in the waveform of hepatic veins?
Cardiac pulsatility
Respiratory phasicity
Respiratory phasicity refers to varied _________.
Breathing
The renal veins drain blood from the (1)_________ and carry it to the (2)____.
Kidneys
IVC
Which two other vessels have similar waveforms to that of the renal vein?
Hepatic veins
IVC
The renal vein, hepatic vein, and IVC have what waveform in common?
“Flying W”
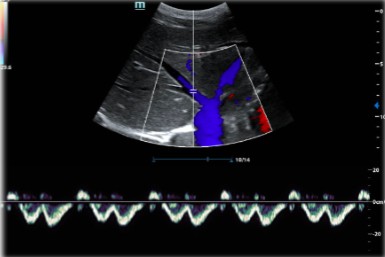
Which vessel is being dopplored here?
What is the name for this vessel pattern?
What is being demonstrated here?
Hepatic vein
Flying W
Cardiac pulsatility
A fully distended cross-sectional area of a vein is __-__ times that of the corresponding artery.
3 - 4
Is a vein typically larger or smaller than its corresponding artery?
Larger
The vein can carry more blood without an increase in…
Pressure
What is the primary function of the venous system?
To return blood to the heart
Which veins carry about 2/3 of the blood in the body?
Extrapulmonary veins
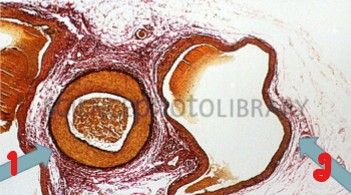
Label the vessels seen here.
Artery
Vein
List the 3 pressure/volume relationships.
Intraluminal pressure
Interstitial pressure
Transmural pressure
Intraluminal pressure is pressure exerted on the venous walls from _________ the veins.
Within
Interstitial pressure is pressure exerted on the venous walls from _________ the veins.
Outside
What is transmural pressure?
The pressure within the vein versus the pressure outside of the vein.
Transmural pressure is related to the _______ or _______ of blood in the vein.
Amount
Volume
Transmural pressure will determine the ______________ shape of the vein.
Cross-sectional
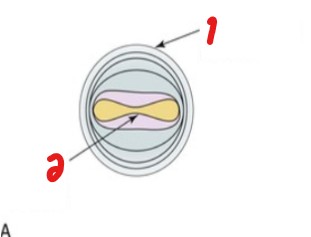
Label which shapes are a certain transmural pressure.
High transmural pressure
Low transmural pressure
High transmural pressure will have a _____ amount of blood.
__________ shaped vein.
High
Circular
Low transmural pressure will have a _____ amount of blood.
__________ shaped vein.
Low
Dumb-bell
Unlike arteries, veins are highly…
Compliant
A vein is highly compliant, meaning it will ________ easily.
Compress
A vein will expand into a circular cross-sectional shape as intraluminal pressure __________.
Increases
A vein will expand into a dumb-bell cross-sectional shape as intraluminal pressure __________.
Decreases
Because veins are seldom completely full of blood, as with arteries, their flattened (more elliptical) shape offers ____ resistance.
More
When veins are full distended, their more circular shape offers much _____ resistance to flow.
Less
A dumb-bell shape = _____ resistance
More
A circular shape = _____ resistance
Less
Hydrostatic pressure is equivalent to the weight of a (1)________ of blood extending from the (2)______ to the level where the (3)________ is being measured.
Column
Heart
Pressure
A higher column of blood = _____ hydrostatic pressure
More
Hydrostatic pressure can be determined by which two factors?
Blood density
Acceleration of gravity
What is the lengthened formula for calculating hydrostatic pressure in this lecture?
Specific Gravity of Blood (p) x Acceleration Due to Gravity (g) and Distance From The Heart (h)
What is the short formula for calculating hydrostatic pressure in this lecture?
HP= pgh
What is the hydrostatic pressure in a supine patient?
0 mmHg
What is the hydrostatic pressure at the ankles when a patient is standing?
Will it be the same for everyone?
100 mmHg
No, depends on the height
What affects hydrostatic pressure the most?
Height
Since hydrostatic pressure is related to (1)______ and distance from the (2)_____, the pressure will decrease if the extremity is (3)__________ the level of the heart. It will be (4)___ mmHg.
Gravity
Heart
Raised above
-50
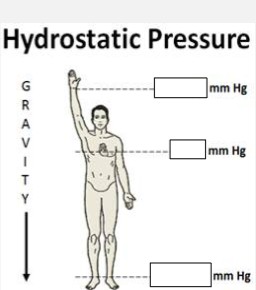
Label the hydrostatic pressures at each blank level:
Raised arm=
Heart level=
Ankle=
-50 mmHg
0 mmHg
100 mmHg
At rest, what do the veins act as?
Reservoirs for blood collection