D103 Intracellular Signaling Components & Secondary Messengers (ALS 18, Vid 31)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what performs intracellular signal transduction
both proteins and small molecules
changes in conc of small molecules, such as cyclic nucleotides, Ca2+, and lipids can also convey signals that diffuse from their subcellular site of production
small molecules that transduce signals via a change in theri conc are referred to as “second messengers”
how are small molecules synthesized
by enzymes using readily available precursors, or can be released from subcellular stores
second messengers
small intracellular signaling molecules that relay the initial signaling response inside the cell (ex - second messengers include Ca2+, IP3, DAG)
does not include all components (does not include PKC)
usually small, non-protein diffusable molecules who intracellular conc can be changed rapidly during signaling
5 common intracellular second messengers
cAMP: activates PKA (hydrophilic)
cGMP: activates PKG and opens cation channels in rod cells (hydrophilic)
DAG: activates PKC (hydrophobic)
IP3: opens Ca2+ channels in the endoplasmic reticulum (hydrophilic)
Ca2+: released from ER or mito; 4x greater mag than in resting cell or cytoplasm (hydrophilic)
rate of conc change of second messengers
intracellular conc can be changed rapidly during signaling
regulated via synthesis, degradation, or channels and pumps for Ca2+
qualities of second messengers
chemically diverse (lipids, inorganic ions, cyclic nucleotides)
function in discrete subcellular components
encoded by a change in conc of second messenger
how is the net conc of a second messenger determined
the sum of its rate of synthesis and degradation by enzymes, some of which are the direct targets of the heterotrimeric g protein
enzymes/channels that modulate intracelluar levels can switch on and off rapidly to quickly change conc
4 major target proteins of activated trimeric g proteins
adenylyl cyclase
phospholipase c
cGMP phosphodiesterase
K+ ion channel
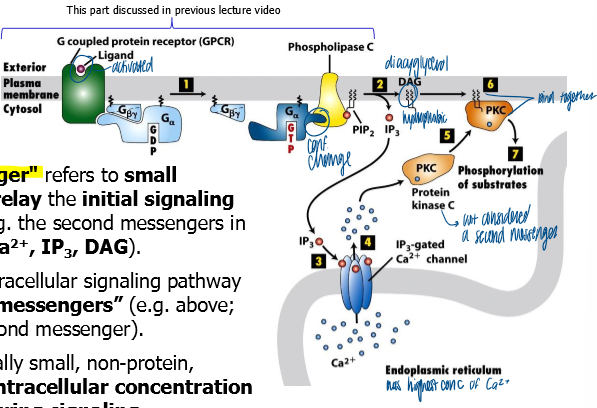
what doesd phospholipase C prduce
IP3 that stimulates the release of calcium ions from the ER
generates DAG and IP3 from PIP2
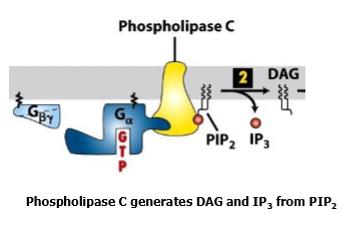
how does phospholipase C work
activated by Ga subunit of heterotrimeric GTPase
cleaves PIP2 to produce 2 independent second messengers IP3 and DAG
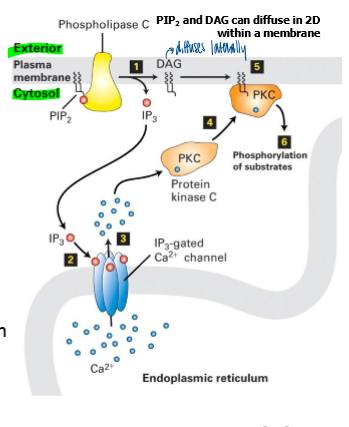
DAG
hydrophobic lipid that can diffuse in 2D within the inner leaflet of the lipid bilayer
IP3
a hydrophilic molecule that can diffuse rapidly thr =u the cytosol
can bind IP3 receptors on surface of ER and mediate rapid release of Ca2+ (another second messenger)
Ca2+ in phospholipase C pathway
once released from ER after IP3 receptor-ligand binding, Ca2+ can bind to and activate PKC
can also bind to calmodulin
what does PKC do once activated
phosphorylates target proteins on serine and threonine residues
what do IP3 receptors mediate
in response to stim, IP3 receptors in ER mediate rapid release of calcium from ER into cytoplasm
IP3 receptors are highly dynamic
Ca2+ is quickly released and reabsorbed
what does phospholipase CB activate
serves as an enzyme that activates an inositol phospholipid signaling pathway
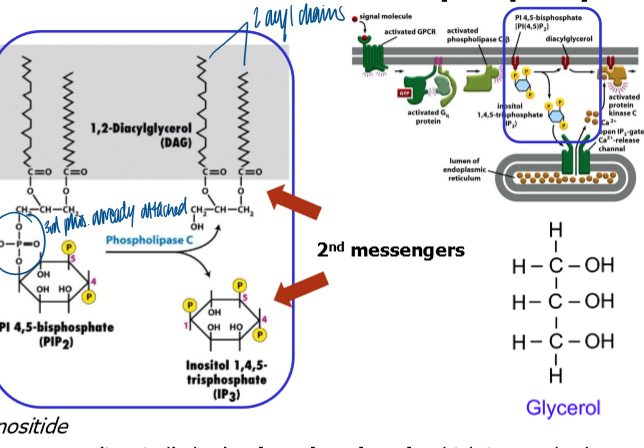
phosphatidyl inositol (PI)
a sugar (inostial) that’s phosphoryalated, which is attached to a glycerol moelcule that has 2 fatty acyl chains
can be further modified by lipid kinases (PI3 kinase, PI4 kinase, PI5 kinase) or phosphatases
cleaage of PIP2 by PLCB generates two second messengers: one hydrophilic (IP3), one hydrophobic (DAG)
pleckstrin homology domain
found on phospholipase C to help localize the enzyme to its substrates via binding to PIP2
PH domains can bind to PI(4,5)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3
PH and C2 domains in PLC’s help target the PLC to its membrane-localized substrate
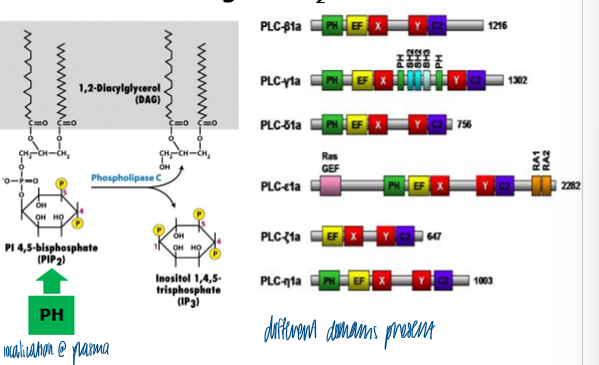
how do phospholipases differ
different phospholipases (C, D,A) can cleave PIP2 at different locations to generate different molecules that affect additional signaling pathways
C = DAG + IP3
D = phosphatidic acid
A = arachidonic acid

arachidonic acid
important intermediate in synthesis of prostaglandins that play important roles in inflammation
how is signaling via PLCB turned off
many PKC isoforms remain active from extended periods
IP3 is rapidly dephosphorylated by lipid phosphatases to form IP2
IP3 can also be phosphorylated by lipid kinase to form IP3 (IP4 can also function as a signaling molecule, but targets are poorly understood)
DAG can be phosphorylated by DAG kinase to produce phosphatidic acid
how is ca2+ store in the er regenerated
ca2+ released to the cytosol is rapidly pumped out of the cytosol by calcium ATPase pumps and anti-porters
when Er Ca2+ decreases, STIM1 oligomerizes and activates Orai1, allowing rapid influx of Ca2+ into cytosol, near ER
once in the cytosol, ER Ca2+-store pumps rapidly move Ca2+ back into the ER lumen
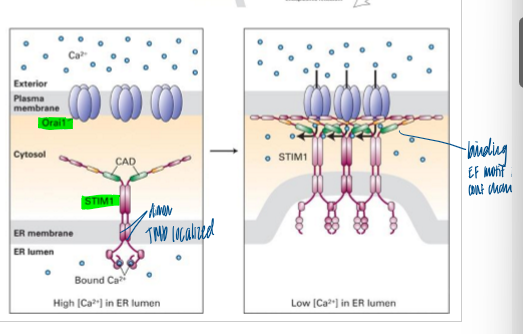
STIM1
an ER transmembrane protein that has an ER-lumenal EF-hand domain that senses Ca2+ levels
can also regulate TRP channel opening
Orai1
an example fo a CRAC (Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+) channel
where is PKC found
plasma membrane, cytoskeleton, and nucleus
PI-PLCs in vertebraes
have 13 different kinds
enables tissue-specific coupling of various receptors to production of IP3 and DAG
PKCs in vertebrates
> 10 different PKCs
provides a tissue specific and selective response to various lipid second messengers
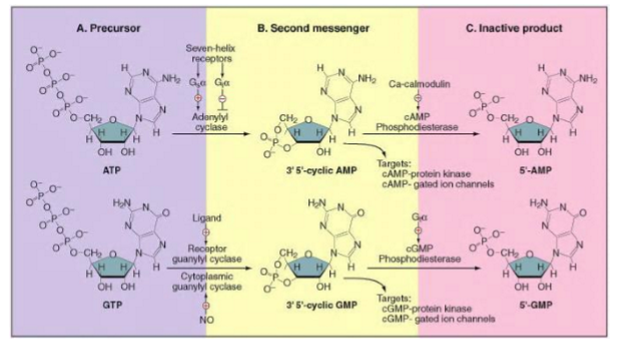
adenylyl cyclase
an effector enzyme that produces cAMP
large multiple TM domain protein
> 8 isoforms in mammals
catalytic domain is located on cytosolic face of membrane
most isoforms are regulated by GPCR and Ca2+
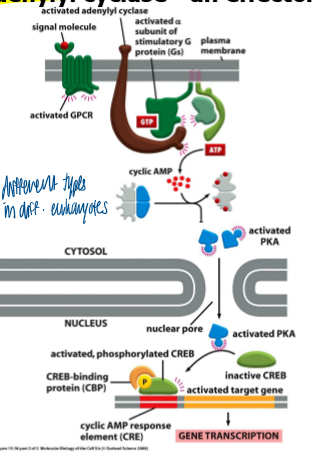
G(as)
stimulates AC by mediating a conformational change in catalytic doamins of AC Z
what does activation of adenylyl cyclase result in
increases the cellular concentration of cAMP
cAMP acts as a small intracellular mediator in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
cAMP prodiced from ATP via action of adenylyl cyclase
cAMP synthesis
constantly synthesized at relatively low levels in cells, and is being constantly broken down by constitutively active cAMP phosphodiesterases
in resting cells, there is usually a high rate of turnover of cAMP (lifetime of a cAMP molecule is relatively short
conc of cAMP in cytosol
around 10^-7 M, but this can change by around 20x within seconds of a receipt of a signal
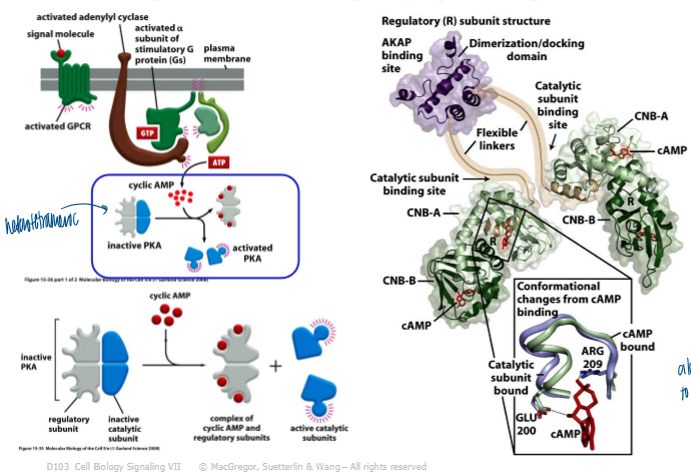
activation of PKA
via binding of cAMP
causes a conf change in the regulatory subunits which results in release of catalytic subunits
CNB: cyclic nucleotide binding site (2 of these per regulator subunit)
activation of target gene expression via PKA/ CREB
CREP cAMP response element
CREB: protein that binds to CRE sequences
catalytic subunit of PKA phosphorylates CREB, which inducs CREB to recruit CBP
PKA can have additional effects on the cell, not just via CREB
targets for PKA differ depending upon specific cell type
second messengers - related cyclic nucleotides cAMP and cGMP
2 cyclic nucleotide monophosphates
adenosine 3,5-cyclic monophosphate
guanosine, 3,5-cyclic monophosphate
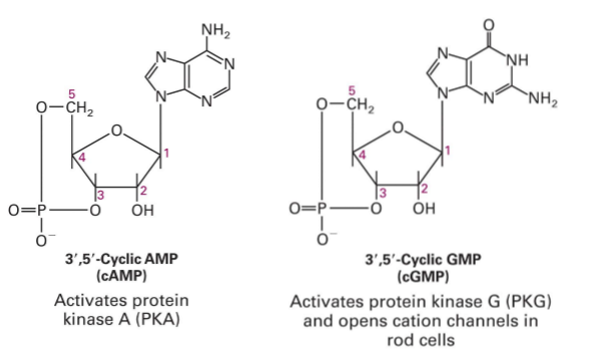
how are cAMP and cGMP similar
similar mechanisms of synthesis and degradation
enzymes that produce (cyclases) or degrade (phosphodiesterases) the cyclic nucleotides determine the steady-state conc of these messengers inside the cell
adenylyl cyclase and guanylyl cyclase are closely related enzymes: changing 2 AAs is sufficient to convert adenylyl cyclase into a guanylyl cyclase
where is ca2+ found
in cytosol
where is DAG found
lipid bilayer
Ca2+ vs cGMP/cAMP rate of diffusion
Ca2+ = lower
cGMP/cAMP and IP3 = higher
which of the following is false?
A. Cleavage of PIP2 produces two independent hydrophobic second messengers.
B. Viagra is an inhibitor of cGMP phosphodiesterase, which can affect vision.
C. IP3 can be phosphorylated to produce IP4.
D. Ca2+ and DAG each bind to and help activate PKC.
E. Diacylglycerol (DAG) can translocate in the inner leaflet of the lipid bilayer.
A. Cleavage of PIP2 produces two independent hydrophobic second messengers.
Which of the following directly helps PKC phosphorylate cytosolic proteins located close to the plasma membrane?
A. IP4
B. Orai channels
C. PIP2
D. DAG
E. GPCR
DAG
Which of the following is a mechanism that helps to end an IP3-mediated Ca2+ response ?
A. Delaying phosphorylation of IP3
B. Adding a phosphate to IP3
C. Converting IP3 to DAG
D. Pumping Ca2+ into the cytoplasm.
E. Increasing synthesis of PIP2.
B. Adding a phosphate to IP3