ECON 248 14.3 The Aggregate-Demand Curve
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
The () is the relationship between quantity of Real GDP demanded and the price level.
Aggregate Demand Curve
The AD curve can be derived by adding up the () demand curves in the whole economy.
Individual
When price level increases, real GDP demanded (), and vice versa.
Decreases
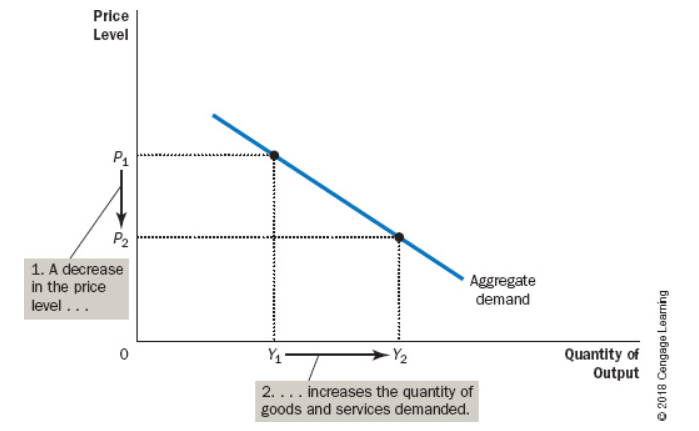
The 4 variables which shift the aggregate demand curve are…
Consumption, Investment, Government Purchases, Net Exports
A reason why aggregate demand might shift right is due to an () in consumption of goods.
Increase
A reason why aggregate demand might increase could be due an increase in (), which causes interest rate to increase.
Investment
An decrease in government purchases shifts the aggregate demand curve to the ().
Left
When imports increase, due to an increased (), aggregate demand shifts ().
Price level, Left
A reason why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward is that a rise in price level reduces the wealth of each person. As a result, people () more money and spend less, lowering demand. This is called the ().
Save, Wealth Effect
A reason why the aggregate demand curve slopes downwards is because of a substitution effect where price level increases also raises intrerest rate, which discourages people from () or (). This is called the ().
Borrowing, Spending, Interest Rate Effect
A reason why the aggregate demand curve slopes downwards is because of a substitution effect where an increase in a domestic good’s price causes people to import more, which decreases GDP. This is called the ().
Real Exchange Rate Effect