Electric fields
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What creates an electric field around it?
charged object
Electric field defintion:
Region where an electric charge experiences a force
What is a point charge?
For a point outside a spherical conductor, the charge of the sphere may be considered to be a point charge at its centre
electric field lines around a spherical conductor are ____ to those around a point charge
same
example of a spherical conductor is a ________
charged sphere
Field lines:
Radial
Go towards centre of a conductor
Pos —> neg
direction of electric fields is represented by
electric field line
uniform electric field has the same ______ throughout the field
electric field strength
how to represent uniform electric field?
equally spaced field lines
stronger field is represented by the field lines ____
are closer together
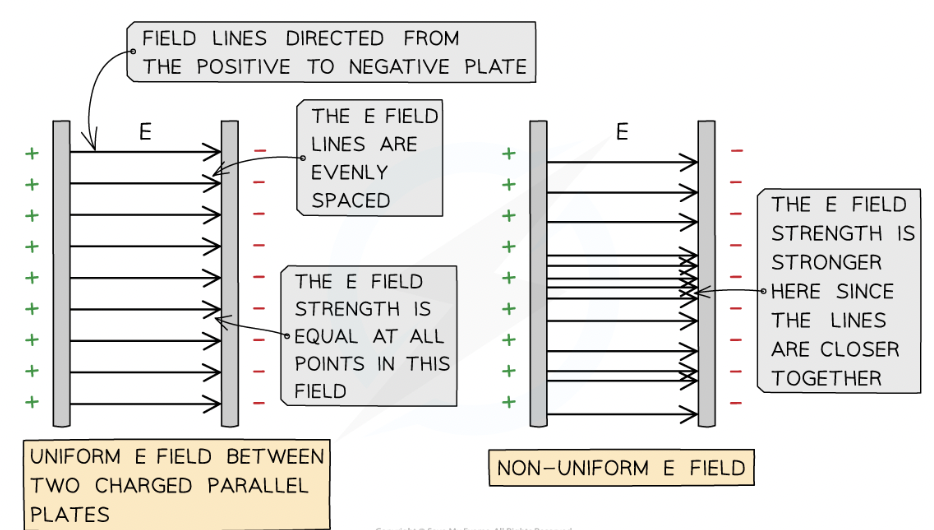
radial field is considered a ______ field
non-uniform
electric field strength definition:
electrostatic force per unit positive charge acting on the charge at that point
units of electric field strength
V m−1 or N C−1
What equation shows magnitude of the electric field strength in a uniform field between two charged parallel plates:
E= V/d
What can equation not show?
cannot be used to find the electric field strength around a point charge (since this would be a radial field
direction of the electric field is from the plate connected to the positive terminal of the cell to the plate connected to the negative terminal
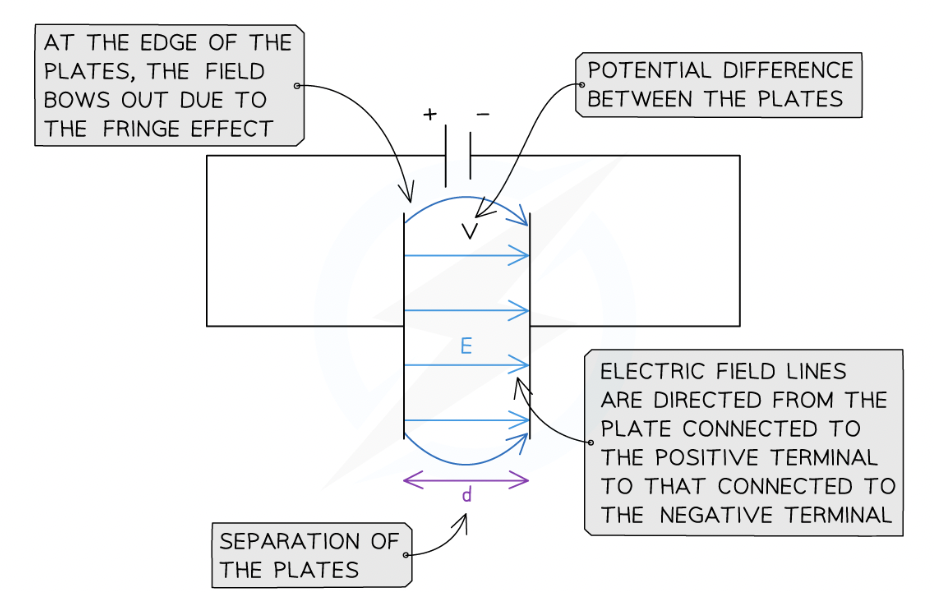
How does potential difference form in field?
two points in electric field have different potential
When a charge moves across a p.d what happens?
Work is done
P.d. defintion
energy transfered per unit charge
V= W/Q
Remember
equation for electric field strength with V and d is only for parallel plates and not point charge (use E=F/Q)
Coulomb’s law
The electrostatic force between two point charges is proportional to product of charges and invesly prop to square of seperation
e.g. F-=Qq/4 Pie E0 r2
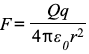
What units mean in :
F= electrostatic force (N)
Q,q= magnitudes of charges (C)
r= distance between centres of two charges (m)
ε0 = permittivity of free space
what is value for permittivity of air?
taken to be the same as ε0
Coulomb's law can only be applied to charged spheres whose size is much smaller than their separation. Only in this case, the point charge approximation is valid. You must remember that the separation r must be taken from the centres of the spheres.
cannot use Coulomb's law to calculate the electrostatic force between charges distributed on irregularly-shaped objects.
a point charge produces a ____ field
radial
What equation is used to find electric field strength E at distance r to point charge Q in free space:
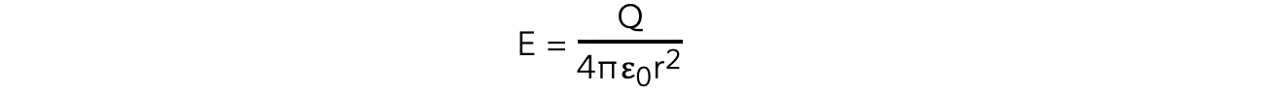
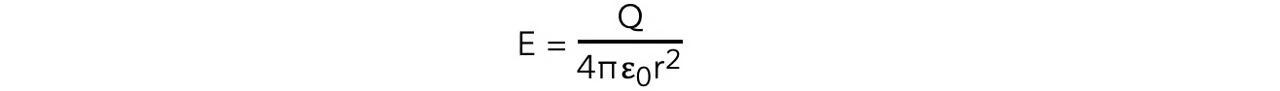
units:
Q- point charge producing the radial electric feild (C)
r- distance from centre of charge (m)
ε0 = permittivity of free space (F m−1)
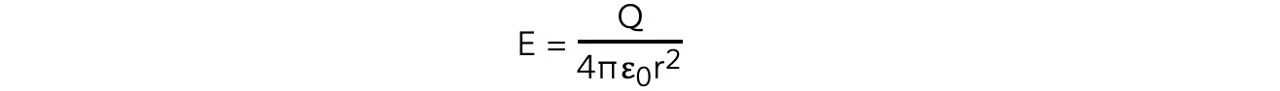
what does this equation show:
Electric field strength in radial field is not constant
As distance from charge increase, E decreases by factor 1/r2
What is permittivity?
measure of how easy it is to generate an electric field in a certain material
What is a dielectric constant?
relativity of permittivity εr
relativity of permittivity εr
The ratio of the permittivity of a material to the permittivity of free space
equation of Er (learn):
Where:
εr = relative permittivity
ε = permittivity of a material (F m−1)
ε0 = permittivity of free space (F m−1)
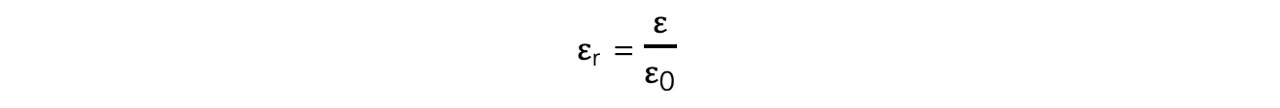
What happens when the polar molecules in a dielectric (poor conductor of electricity but good supporter of electric fields) align with the applied electric field from the plates?
each produce own electric field, which opposes electric field from plates
larger opposing electric field from the polar molecules in the dielectric= larger permittivity
opposing electric field reduces the overall electric field, which decreases the potential difference between the plates
Therefore, the capacitance of the plates increases

units:
C = capacitance (F)
A = cross-sectional area of the plates (m2)
d = separation of the plates (m)
εr = relative permittivity of the dielectric between the plates
ε0 = permittivity of free space (F m−1)
charged particle in an electric field will experience a ____ on it that will cause it to ____
force
move
if a charged particle remains still in a uniform electric field
move parallel to the electric field lines (along or against the field lines depending on its charge
If a charged particle in motion travels initially perpendicular through a uniform electric field:
constant electric force and travel in a parabolic trajectory
What direction will charge move?
positive charge will be deflected towards the negative plate
negative charge will be deflected towards the positive plate
force on the particle is the same at all points and is always in the same direction
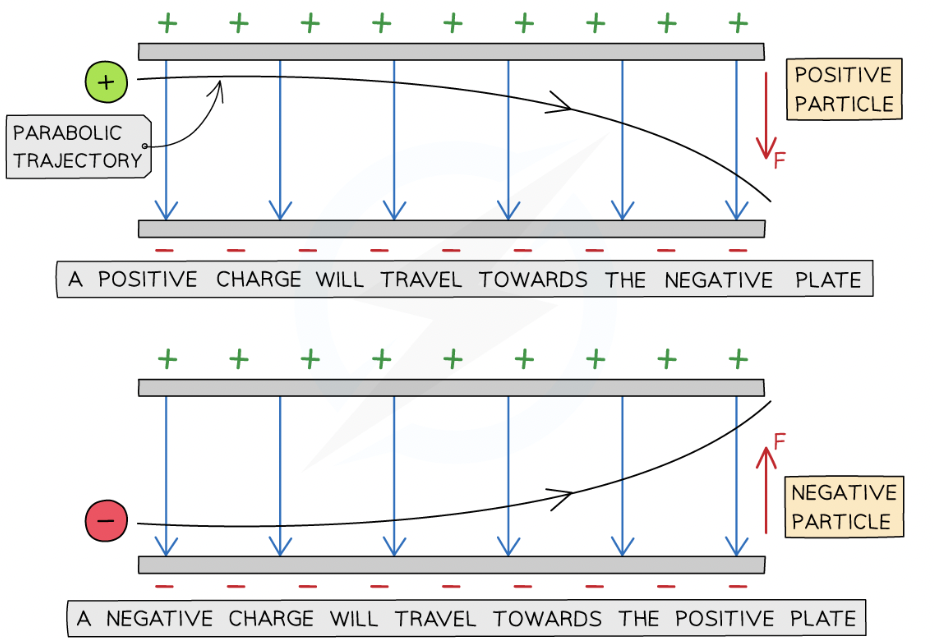
how will uncharged particle act in electric field?
travel straight through the plates undeflected
amount of deflection depends on the following properties of the particles:
Mass – the greater the mass, the smaller the deflection and vice versa
Charge – the greater the magnitude of the charge of the particle, the greater the deflection and vice versa
Speed – the greater the speed of the particle, the smaller the deflection and vice versa
electrostatic field definition:
electric force per unit charge exerted on a small positive test charge
Radial fields always have an inverse square law relationship with distance
Equipotential surfaces for both gravitational and electric fields are spherical around a point mass or charge and equally spaced parallel lines in uniform fields
when drawing field lines:
electric FL always at right angle to surface of conductor
increased field strength = lines closer together
we consider a charge a point charge if:
separation of object is greater than size of object
if charge doesn’t affect electric field its in
Motion of particle
Electric field strength- E=V/d
Force on charged particle- F=EQ (=Ee for electrons)
Work done by particles- W=Vq
When particle travels at right angle to electric field, motion is parabolic path
Horizontal- no a, t=L/v
Vertical- a=F/m= EQ/m
Vv= u+ at
= 0 + (EQ/m)(L/v)
particle accelerators:
Electron beam usually produced in vacuum tube by thermionic emission from heated cathode
Electrons are accelerated from cathode (-) and anode (+) with small hole in it which allows some electrons through
electrons are focused into beam by further electrodes + coils
electron leaves hot cathode with horizontal acceleration
in uniform electrostatic field, beam is deflected in similar way to mass projected horizontally in earths gravitational field
linear accelerator consists of long series of electrodes connected alternately to a source of alternating p.d
electrodes are hollow coaxial cylinders in long evacuated tube
charged particles released at one end of tube are accelerated to nearest electrode which they pass through as alternating p.d. reverses polarity
particles then repelled on leaving this electrode and are attracted to next electrode, so that charged particles gain KE each time they pass between electrons
If a charge is to move with an electric field
field does work on charge
If charge is to move against the field
work must be done on charge
equation to learn
V=W/Q
Electric potential= electric potential energy/ Q
Features of Force against separation graph:
shows Columbus law
AREA= work done
Total work done= EPE ∴ E=Qq/4 PIE E0 r (between 2 charges)
equation for EP:
V=Q/4 PIE E0 r
If we say Fr=Work done what do we assume?
F is constant
deflection is related to …
force
definition of electrical potential at point in space:
work done per unit charge in bringing a positive charge from infinity to a point