ANP Kidneys??
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
What does the urinary system do?
Makes and stores urine, controls body fluid levels, excretes water-soluble wastes, and regulates body fluid electrolytes
What are the four organs of the urinary system?
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra
What is the function of the kidneys?
To filter blood and form urine
What is the function of the ureters?
To transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
To collect and store urine
What is the function of the urethra?
To convey urine from the urinary bladder to outside the body
Where are the kidneys located?
On both sides of the vertebral column; left is slightly higher than right
What surrounds the kidneys?
Fibrous renal capsule, adipose tissue, and connective tissue
What is the renal medulla composed of?
Renal pyramids and nephrons
What are nephrons?
Urine producting structures
What is a renal pyramid?
A triangular-shaped structure that contains the part of the nephron responsible for collecting urine
What part of the nephron is located in the renal pyramids?
The collecting duct
What is the renal papilla?
The tip of a renal pyramid that allows urine to pass into the ureter
What are renal columns?
Extensions of the cortex that dip into the medulla
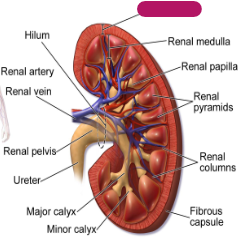
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal cortex
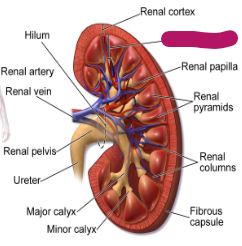
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal medulla
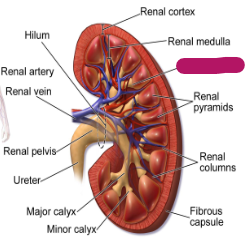
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal papilla
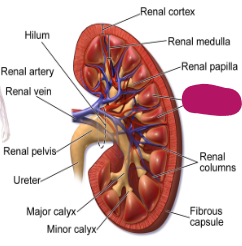
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal pyramids
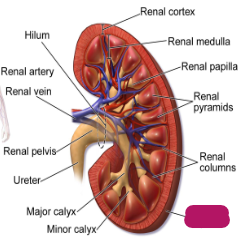
Label this part of the kidney.
Fibrous capsule
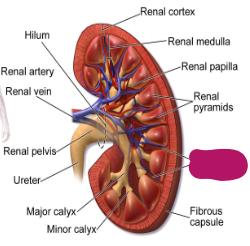
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal columns
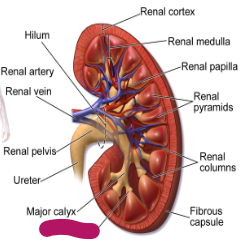
Label this part of the kidney.
Minor calyx
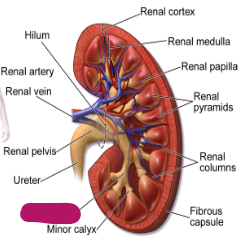
Label this part of the kidney.
Major calyx
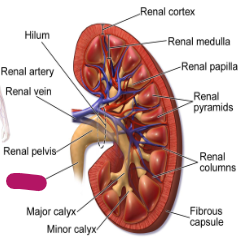
Label this part of the kidney.
Ureter
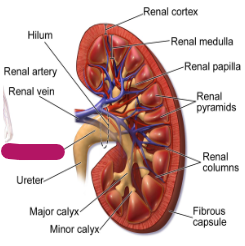
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal pelvis
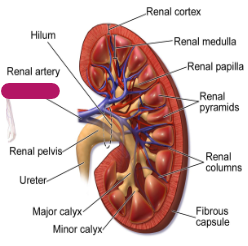
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal vein
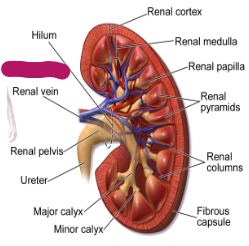
Label this part of the kidney.
Renal artery
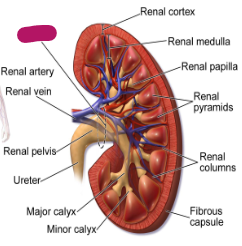
Label this part of the kidney.
Hilum
What are renal columns?
Extensions of cortex that dip into medulla
What is the hilum?
Entrance to renal sinus
What is the renal sinus?
Space that allows for entry of large blood vessels and collection of urine for all nephrons
What is the renal pelvis?
Funnel-shaped sac on superior end of ureter
What are major calyces?
Large tubes that merge to form renal pelvis
What are minor calyces?
Small tubes that merge to form major calyces
What is the renal capsule?
Fibrous capsule around the kidney
What are the major arteries/veins of the kidney?
Renal, segmental, interlobar, arcuate/arciform
Where is the renal artery?
Branching off abdominal aorta and enters kidney through hilum
Where are the segmental arteries?
Branching off renal artery
Where are the interlobar arteries?
Branching off segmental arteries, flowing between renal pyramids
Where are the arcuate/arciform arteries?
Branching of interlobar arteries, arching around renal pyramids
What vein do the arcuate veins drain into?
Interlobar
What vein do the interlobar veins unify into?
Segmental
What vein do the segmental veins merge to create?
Renal
What does the renal vein drain into?
Vena cava
What hormone do the kidneys secrete?
Erythropoietin
What is erythropoietin?
Hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells
T/F: The kidneys excrete metabolic and nitrogenous waste from blood.
True
T/F: The kidneys filter hydrophobic hormones from the blood.
False
What is another word for red blood cells?
Erythrocytes
What is another name for White blood cells?
Leukocytes
What is another name for platelets?
Thrombocytes
What do RBCs do?
carry oxygen via hemoglobin
What do WBCs do?
Defend against infection
What do platelets do?
Initiate clotting
What is plasma?
A light yellow liquid that carries water, electrolytes, and proteins
What proteins are found in the blood?
Albumin and antibodies
What are albumin and antibodies?
Proteins of the immune system that bind to pathogens
How does RBC formation occur?
Low blood oxygen causes kidneys and liver to release EPO which stimulates production in red bone marrow
What are the nutritional requirements for erythropoiesis?
Vitamin B12, folic acid, and iron
What is anemia?
When oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is reduced due to the deficiency of RBCs or hemoglobin
What medicine must renal failure/dialysis patients take?
Synthetic EPO
What is azotemia?
Increase in blood urea nitrogen and nitrogenous wastes in blood
What is uremia?
Toxic effects/organ failure as wastes accumulate
How is blood volume and pressure regulated?
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
What does ADH cause?
Increase in thirst, vasoconstriction, retention of water
What is another name for ADH?
Vasopressin
What type of hormone is ADH known as?
The freshwater hormone
What does aldosterone cause?
Sodium and water retention, potassium loss, increase in blood volume, increase in blood pressure
ADH causes a(n) ________ in thirst.
Increase
ADH causes vaso-
constriction
ADH is known as the
Freshwater hormone
Aldosterone causes a(n) ______ in blood pressure.
Increase
Aldosterone causes a(n) _______ in blood volume.
Increase
Aldosterone is known as the _______ hormone.
Saltwater
Aldosterone causes _______ in potassium.
Loss
What two organs keep blood pH within normal range?
The kidney and lungs
What is pH defined as?
The negative log concentration of hydrogen ions
What happens when pH falls below 7.35?
Acidosis
What happens when pH falls above 7.45?
Alkalosis
When are acid-base disturbances frequently encountered?
With chronically ill and hospitalized patients
How is blood pH measured?
By analyzing pH and bicarbonate levels and carbon dioxide levels in the arterial blood aka arterial blood gases
What type of acidosis or alkalosis is caused by the lungs?
Respiratory
Wat type of acidosis or alkalosis is caused by factors other than the lungs?
Metabolic
What controls CO2?
Lungs
What controls bicarbonate (HCO3)?
Kidneys
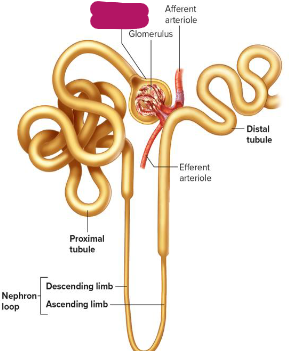
Label this section of the nephron.
Glomerular capsule
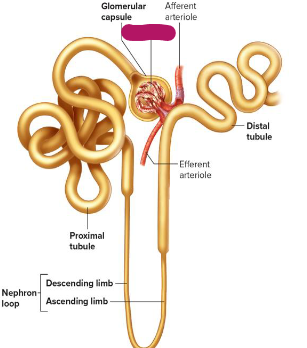
Label this section of the nephron.
Glomerulus
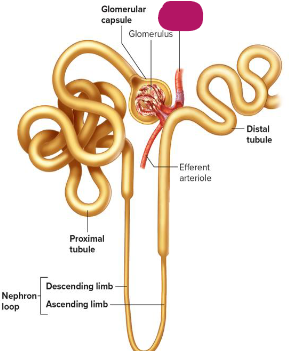
Label this section of the nephron.
Afferent arteriole
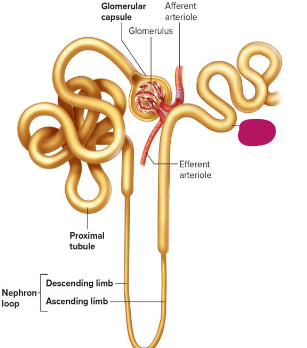
Label this section of the nephron.
Distal tubule
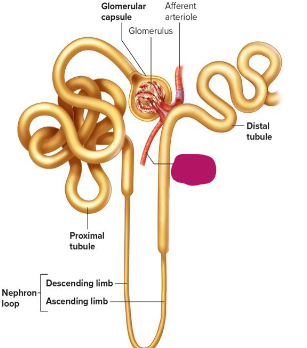
Label this section of the nephron.
Efferent arteriole
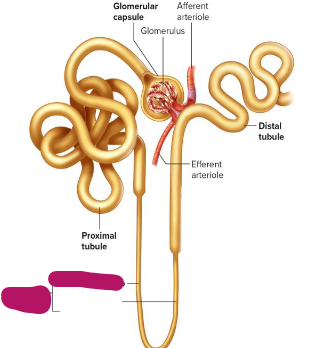
Label this section of the nephron.
Descending limb of nephron loop
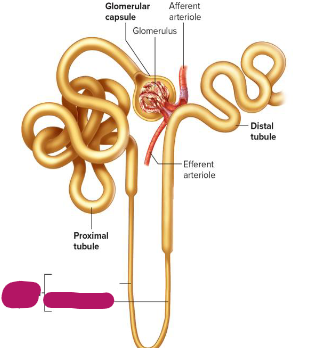
Label this section of the nephron.
Ascending limb of arteriole
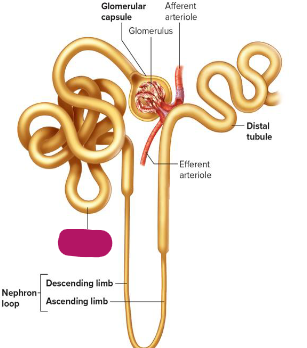
Label this section of the nephron.
Proximal tubule
What are the four parts of the renal tubule?
Proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct/tubule
What is the function of the peritubular capillaries?
Receive substances removed from the urine that will be reabsorbed by the body, and remove substances from the blood that could not be filtered by the glomerulus
What is reabsorption?
When the nephrons of the kidney reclaim nutrients from teh urine
What is secretion?
Energy driven process in which waste is deposited into the urine by ATP-dependent transporters
What is at the start of the renal tubule?
The Bowman’s capsule
What is inside the Bowman’s capsule?
The glomerulus
How does blood flow into the glomerulus?
By the afferent arteriole
How does blood leave the glomerulus?
By the efferent arteriole