APUSH: Road to Civil War
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Period 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
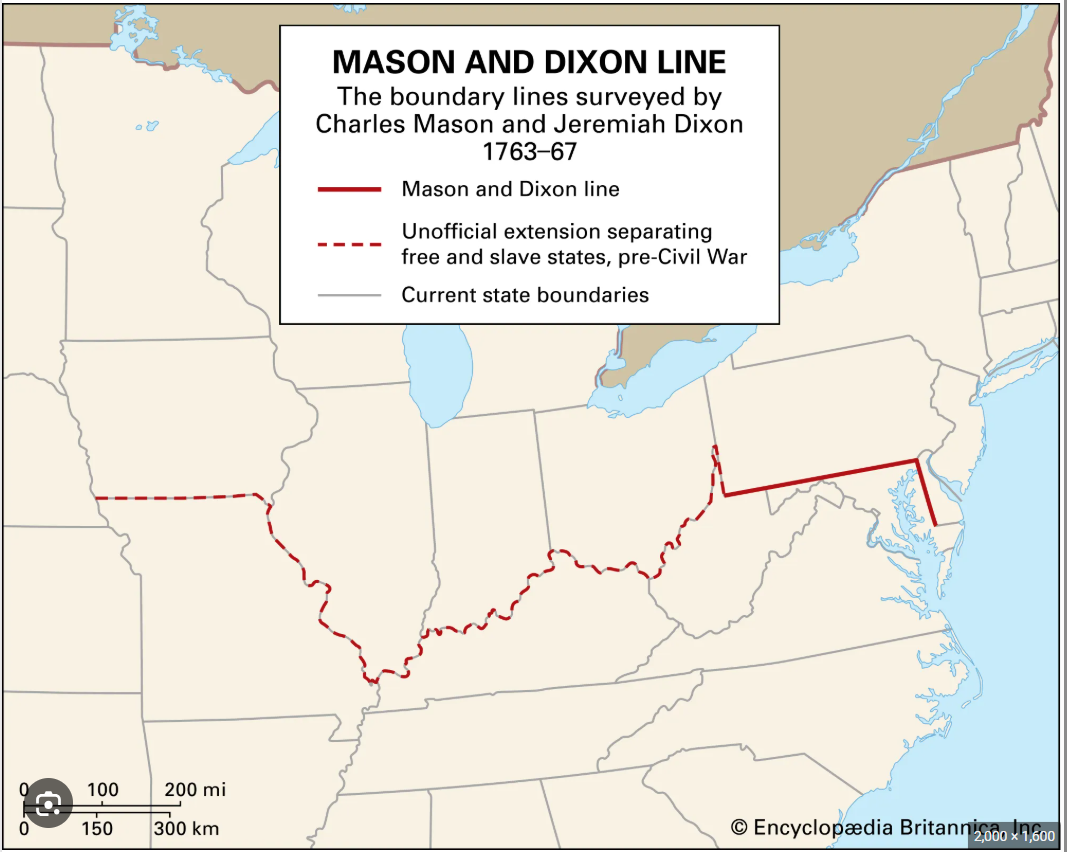
Mason–Dixon line
Historic boundary that came to symbolize the divide between the North and South, especially regarding slavery in the 19th century
Also became a symbolic dividing line in the debates over slavery, especially during:
The Missouri Compromise (1820) and
The Compromise of 1850
Free Soil Ideology
Free Soil ideology was a political belief system in the mid-19th century United States that opposed the expansion of slavery into the western territories. It was most prominently represented by the Free Soil Party, founded in 1848.
-ran Martin Van Buren for president in 1848.
-short lived party
Free Soil ideology was rooted in the belief that slavery should not be allowed to spread because it threatened the rights and economic independence of free white laborers (slaves=wealthy land owners). It was a powerful force in antebellum politics and laid the groundwork for the anti-slavery platform of the Republican Party.
Nativism
the ideology that the nation’s culture and identity should be protected from “foreign” influences.
NOT a support of the indigenous people but rather the descendants of white Protestants.
Know- Nothing Party
American Party
came out of the idea of nativism
supported by middle and working class, professional and skilled men, former artisans and relocated farmers
Strongly anti-immigrant and anti-Catholic (Papists)
peak of popularity by 1855
California Gold Rush
1848
during the construction of a sawmill at Sutter’s Mill, California (halfway between Reno and San Francisco), workers literally struck gold in the river soil. The following year a rush of settlers from all over the world, known as “forty-niners,” flooded the state to pan for gold, enough to qualify California as a state only 2 years later, in 1850
Important abolitionists
Frederick Douglass, William Lloyd Garrison, and Harriet Tubman
Uncle Tom’s Cabin
Harriet Beecher Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1852) stirred anti-slavery sentiment in the North.
Compromise of 1850
California admitted as a free state.
Fugitive Slave Act enforced stricter return of escaped slaves—angered Northerners.
Popular sovereignty allowed territories to vote on slavery
Slave trade abolished in Washington, D.C
Texas-New Mexico boundary adjusted
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Repealed the Missouri Compromise.
Let settlers decide on slavery (popular sovereignty).
Led to “Bleeding Kansas”—violent conflict between pro- and anti-slavery settlers.
Dred Scott Decision
Supreme Court ruled that African Americans were not citizens and Congress couldn't ban slavery in territories (In another way saying that Missouri Compromise of 1820, which banned slavery north of the 36°30′ line, was unconstitutional)
Infuriated the North, delighted the South.
Part of the ruling “"Upon these considerations, it is the opinion of the court that the act of Congress(that is, the Missouri Compromise) which prohibited a citizen from holding and owning property of this kind in the territory of the United States north of the line therein mentioned, is not warranted by the Constitution, and is therefore void; and that neither the plaintiff himself, nor any of his family, were made free by being carried into this territory; even if they had been carried there by the owner, with the intention of becoming a permanent resident."
Lincoln-Douglas Debate
Debates over slavery's expansion gained Abraham Lincoln national attention.
Lincoln opposed the spread of slavery(free soil), not its immediate abolition.
Women reform movements in the antebellum period
Many women argued that their roles as mothers and wives gave them a unique understanding of the nature of and solutions to social ills.
Major focus of antebellum reform
Prison reform
Reformers sought to improve conditions in prisons.
They aimed to promote rehabilitation instead of just punishment.
Efforts included separating prisoners by gender and offense, improving sanitation, and providing education or religious instruction.
Putting out system in the antebellum period
pre-industrial method of manufacturing where:
Merchants supplied raw materials to workers in their homes.
Workers (often family members) produced finished goods like textiles or shoes in their own houses.
Merchants then collected the goods to sell or distribute.
Election of 1860
Abraham Lincoln got ZERO votes in southern states, but more than 40% popular votes, and higher electoral votes
but he won electroral votes of the Northern and Midwestern states as well as CA and Oregon
Secession of States
11 States that left the union and formed the confederacy
AFTER LINCOLN’s ELECTION:
South Carolina (first), Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas (So My Father Ate Grapes Last Tuesday)
After FORT SUMTER(start of civilwar):
Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina (Very Awesome Tart Nibbles)
Border States
Slave states that did not secede
Kentucky, Missouri, Maryland, Delaware (Miss Mary Dated Ken)
Slave owning in the south before civil war
½ of the slaveowners owned 5 or fewer slaves (but that’s 200000 out of 400000 slaveowners)