Invertebrates Modules 1-4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/444
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:43 AM on 12/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
445 Terms
1
New cards
What percentage of all species is invertebrates?
95%
2
New cards
If two branch points are the same length, what does this mean about how long those species have been evolving?
They have been evolving for the same amount of time
3
New cards
Population status of invertebrates
going extinct at an alarming rate
4
New cards
Invertebrates are model organisms for
biomedicine, genetics, and neurobiology
5
New cards
When did our solar system form? (including Earth) and what eon is it?
4\.6 BYA, Hadeon eon with no fossils
6
New cards
When was the first evidence of microbial life? and which eon is it?
3\.7 BYA, Archaean eon
7
New cards
When might have the first eukaryotes appeared?
2\.7 BYA
8
New cards
How old are the earliest fossils?
About 1.6-1.8 billion years old
9
New cards
Fossils form in what type of environments?
Low O2 environments like deserts and sediments in bodies of water
10
New cards
Low probability events for fossils to happen
material must be preserved before decomposition, rock must be exposed for discovery, someone must find it
11
New cards
Fossils are mostly based on what?
Morphological characters, rarely behavior and physiology
12
New cards
Taphonomy
the study of the fossilization process
13
New cards
Taphonomic bias
difference between what was once alive and its representation in the fossil record
14
New cards
You are more likely to find ____ fossilized material
recently
15
New cards
Sources of taphonomic bias
pre and post fossilization filters
16
New cards
Pull of the recent
the quality of the fossil record gets worse the farther back in time you look
17
New cards
Absolute dating
numerical dating with radioactive decay (knowing exact years)
18
New cards
Most fossils require ____ dating
relative (not knowing the specific age, just whether it’s old or young)
19
New cards
Hierarchy of time intervals
Eon > Era > Period > Epoch > Age
20
New cards
What are the time intervals defined by
a set of diagnostic fossils and bounded by mass extinction events
21
New cards
Which eon did photosynthetic bacteria/multicellular eukaryotes appear in?
Proterozoic eon
22
New cards
What era was the Cambrian explosion?
Paleozoic 298.9 MYA-541 MYA
23
New cards
What are the 5 extinctions?
Terminal-Ordovician, Late Devonian, End-Permian, End-Triassic, Cretaceous-Paleocene
24
New cards
Which era was the rise of mammals?
Cenozoic (era right now)
25
New cards
Which eon was the Precambrian?
Archean Eon
26
New cards
Great oxygen explosion happened in what eon?
Proterozoic
27
New cards
What was the great oxygen explosion?
anaerobic organisms killed off cause they were not adapted to O2
28
New cards
Oldest known eukaryotes are from what eon?
Proterozoic
29
New cards
What happened in the Phanerozoic Eon?
animals developed hard shells
30
New cards
Prokaryotic cells existed ____ eukaryotic cells
before
31
New cards
The endosymbiont theory explains
the origin of eukaryotes
32
New cards
Oldest eukaryotic fossils
Grypania spiralis-possibly oldest known eukaryotic alga
33
New cards
What are the oldest known protists?
complex unicellular bodies
34
New cards
What is “The Boring Billion?”
years in Proterozoic Eon between origin of Eukaryota and explosive radiation that began in the Ediacaran. First eukaryotes appeared at the start, and at the end first animals appeared
35
New cards
The first oxygen producing bacteria appeared in what eon?
Archean
36
New cards
Did the first eukaryotes appear before or after the Great Oxidation Event?
After
37
New cards
What does proterozoic mean?
early animal
38
New cards
What was in Ediacaran Period and when was it?
macroscopic animals (first evidence of animals), happened at the end of Proterozoic Eon
39
New cards
When is it likely that “modern life” began to evolve and why?
Paleozoic Era because of the oxygenated atmosphere
40
New cards
When did the first evidence for some bilaterally symmetric animals appear?
Ediacaran Period (635-541 mya)
41
New cards
What changes were seen in the Cambrian Explosion?
Different feeding strategies, more plants, burrowing in sand, higher diversity, predation, body parts for swimming
42
New cards
Chengjiang Biota Cambrian fossil site
oldest occurrences of well preserved soft and hard body animals (many arthropods)
43
New cards
Qingjiang Biota Cambrian fossil site
Cnidarians, annelids, and complete echinoderms appear
44
New cards
Burgess Shale Cambrian fossil site
dominated by arthropods
45
New cards
The Cambrian Explosion was marked, in part, by the evolution of?
Bilaterally symmetrical, segmented organisms. By the end, nearly all of the major, modern animal phyla had appeared
46
New cards
What is a possible explanation for the Cambrian Explosion?
increase in nutrients in the ocean (phosphorous and potassium)
47
New cards
Morphological diversity of the Cambrian Explosion
tissue types, developmental patterns, bilateral symmetry, heads\*, segmentation, appendages
48
New cards
How many present day animal phyla are there?
31 (most are arthropods)
49
New cards
The Burgess Shale is now estimated to contain fossils of how many animal phyla?
About the same number as those today
50
New cards
What era took out the dinosaurs?
Mesozoic
51
New cards
Cretaceous-Paleocene Extinction
small mammals survived, but caused extinction of 75% of all species
52
New cards
Likely consequences of the Chicxulub meteorite that took out the dinosaurs:
acid rain, global cooling, tsunami in Gulf of Mexico, earthquakes of huge magnitude
53
New cards
Why do we see an explosion of fossils from Cambrian Era?
Hard parts (exoskeletons/shells) formed which fossilize well
54
New cards
Linnean taxonomy ordered species how?
according to their characteristics
55
New cards
Hierarchical organization of larger taxonomic groups
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
56
New cards
Which hierarchy is most specific, and which is most general?
Species is very specific whereas kingdom is very general
57
New cards
Taxonomy
Field of biology concerned with naming living (extant) and ancient (extinct) plants, animals, and other organisms
58
New cards
Phylogenetics
study of evolutionary relationships among organisms visualized with tree-like diagrams called phylogenies
59
New cards
Lineages with the ___ similar traits share a more recent common ancestor
most (homologies)
60
New cards
The more ___ the relationship among lineages, the more distinct they are from each other
distant (have had more time to evolve their distinctions since splitting from distant ancestor)
61
New cards
Branch point/node
represents a common ancestor, where lineages diverge
62
New cards
Polytomy
branch point with three taxa attached, represents unresolved pattern of divergence
63
New cards
Basal taxon
outgroup
64
New cards
Is order at the tips of a phylogenetic tree important?
No
65
New cards
Relatedness is determined by ____, not by the order of taxa at the tips of the tree
common ancestry
66
New cards
Evolutionary relationships are depicted solely by
the order of branching in a phylogeny
67
New cards
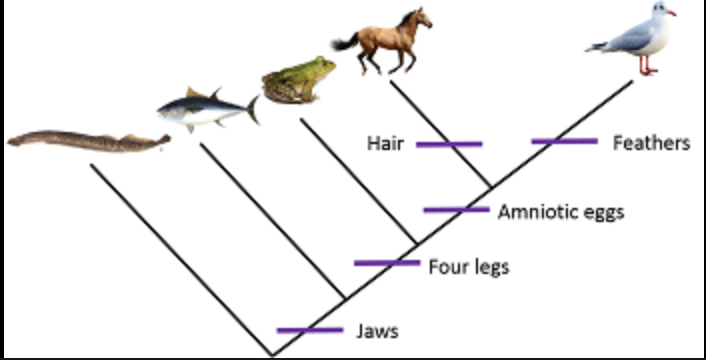
Proper flow of time in a branching diagram
bottom to top depicts oldest to most recent
68
New cards
All extant (living) species have been evolving for
the same amount of time
69
New cards
Long branches ___ indicate taxa with little evolutionary change
don’t
70
New cards
Branch length can be affected by including
more taxa in the phylogeny
71
New cards
Characters are used to
construct phylogenies
72
New cards
A character is
any attribute of an organism that can provide us with insights into evolutionary history (shared ancestry) (morphological, developmental, physiological, biochemical, genetic, behavioral)
73
New cards
Derived and ancestral character states
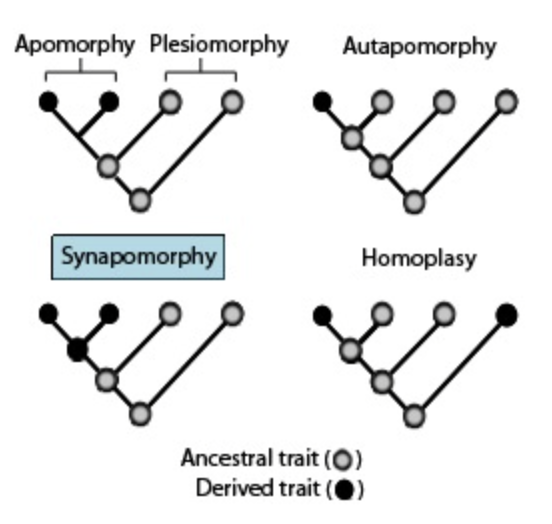
74
New cards
Ancestral and derived are defined relative to
a particular node in the tree
75
New cards
The same trait can be derived or ancestral depending on
which node is considered
76
New cards
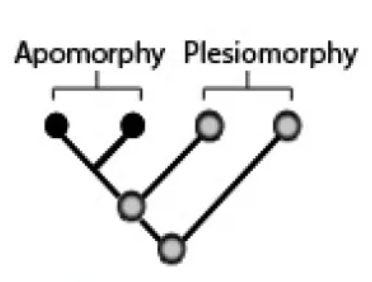
Plesiomorphy
an ancestral character state (any trait that was inherited from the common ancestor of a group)
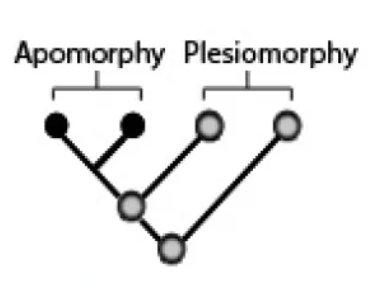
77
New cards
Apomorphy
a derived character state (any trait that is an innovation along an evolutionary lineage)
78
New cards
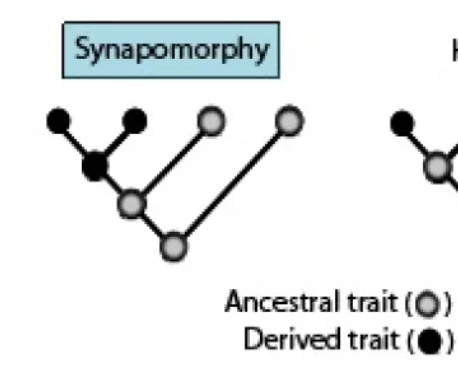
Shared derived homologies
Synapomorphies, homologous characters unique to a group of organisms
79
New cards
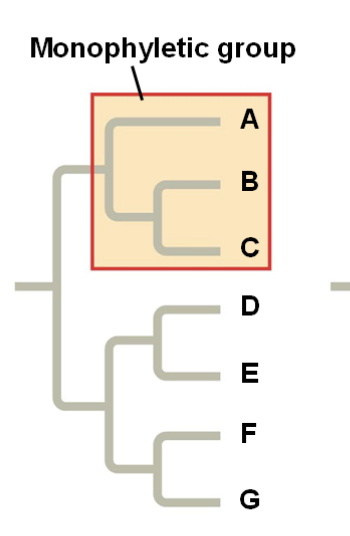
Synapomorphies identify
monophyletic groups (an ancestor and all of its descendants)
80
New cards
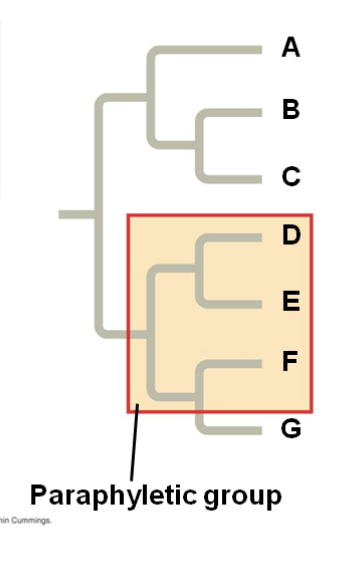
A group consisting of an ancestor and some, but not all of its descendants is described as
paraphyletic
81
New cards
A group that contains some but not all of an ancestor’s descendants and also does not contain the ancestor is called
polyphyletic
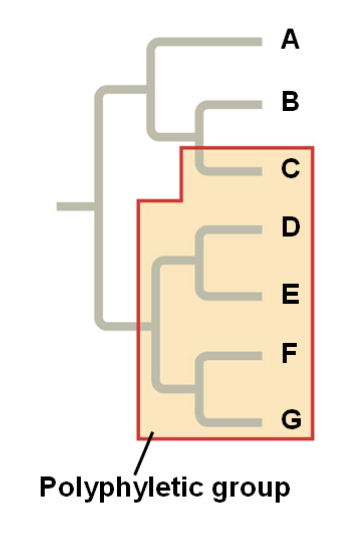
82
New cards
Only under extremely rare circumstances do we know
the true evolutionary history of populations or species by direct observation
83
New cards
A phylogenetic tree represents a
hypothesis
84
New cards
Homoplasy
The independent evolution of a similar character state in different taxa (a characteristic shared by different taxa, but not present in their most recent common ancestor)
85
New cards
Types of homoplasy
convergent evolution, parallel evolution, evolutionary reversal
86
New cards
Convergent Evolution
the process whereby distantly related organisms independently evolve similar traits to adapt to similar necessities (Both sharks and dolphins have similar body forms, yet are only distantly related)
87
New cards
Parallel Evolution
occurs when closely related taxa acquire similar characteristics
88
New cards
Evolutionary reversal
lineage evolves towards one of its ancestral traits, losing a more recently evolved trait
89
New cards
Hypoxia
condition where the body’s tissues are deprived of oxygen
90
New cards
How do we decide if something is convergent evolution or parallel evolution?
different species vs different populations of the same species
91
New cards
Evolutionary radiation
divergent evolution of numerous related lineages within a relatively short time (basically just a bunch of diverging of lineages)
92
New cards
Adaptive radiation
the lineages become modified for different ways of life
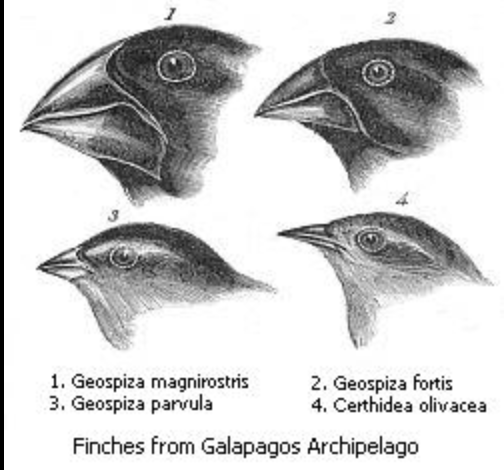

93
New cards
For molecular and genetic analysis, make sure sequences are
homologous
94
New cards
Orthologs
copies of the same gene in different species, related by vertical descent from a common ancestor
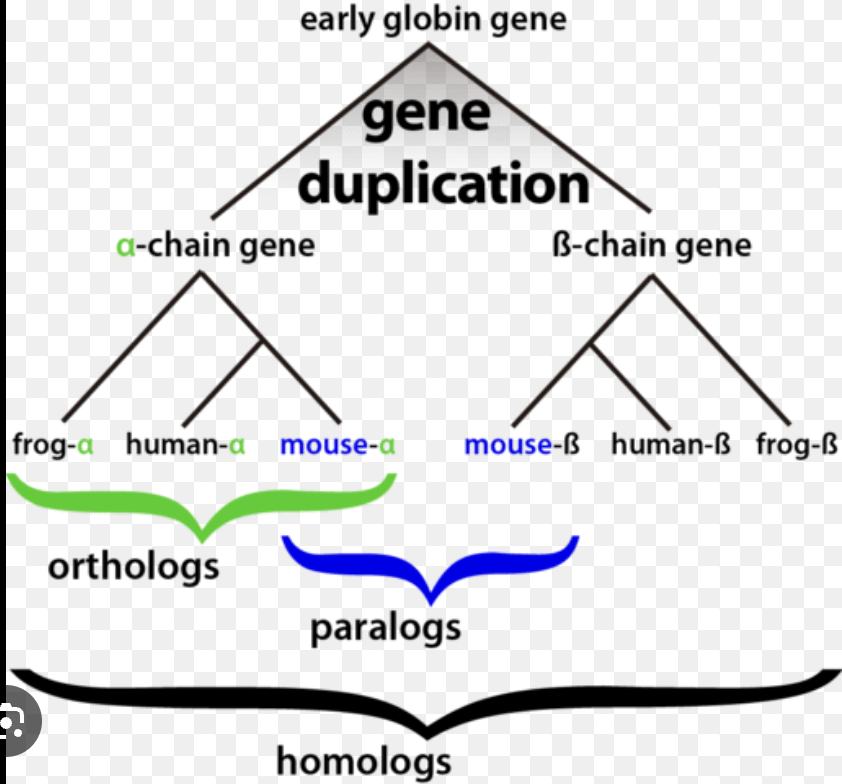
95
New cards
Paralogs
copies of the same gene within a species (ex. gene duplication), horizontal relationship as a result of gene duplication, code for proteins with similar but not identical functions
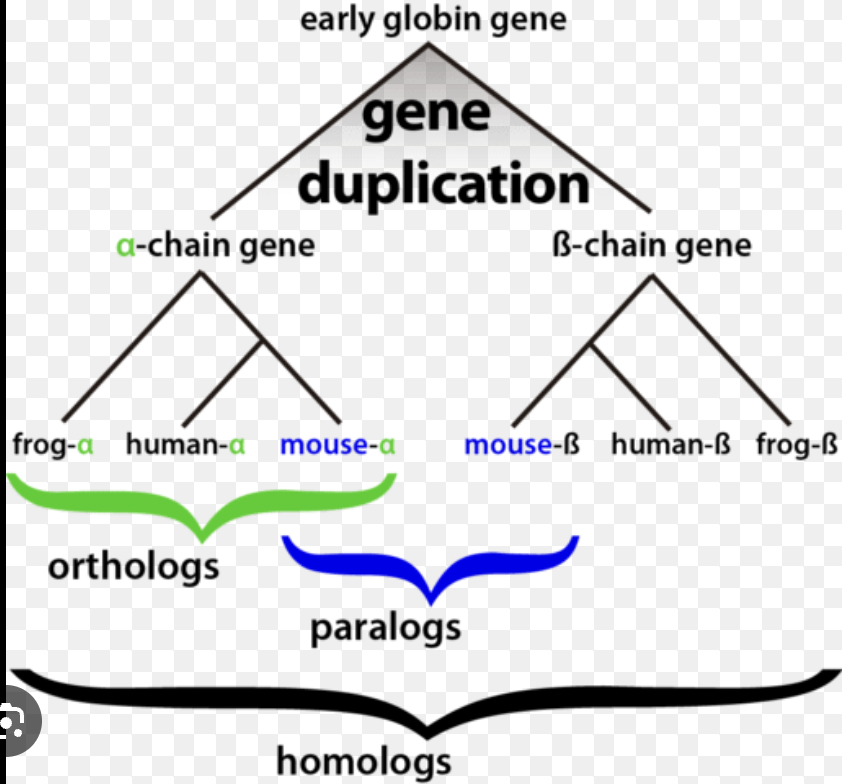
96
New cards
When comparing genes in phylogenetic analysis
they must be orthologous
97
New cards
Molecular clock
in some cases, the rate of evolution of DNA sequences is fairly constant such that sequences in different lineages diverge at a roughly constant rate (can be used to estimate age of some evolutionary events)
98
New cards
All animals have
eukaryotic cells that lack cell walls
99
New cards
All animals are
multicellular
100
New cards
Are animals heterotrophs or autotrophs
heterotrophs