Hazards and uses of nuclear radiation: Atomic structure: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Irradiation
When an object is exposed to nearby nuclear radiation; the irradiated objects do not become radioactive themselves

Sterilisation
The process used to ensure that a sample contains no living things
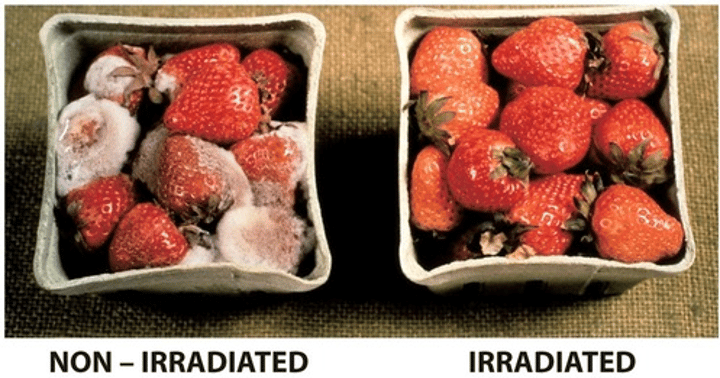
Using irradiation to sterilise food
By exposing fruit to gamma rays which destroy any bacteria on the fruit but do not affect the fruit itself
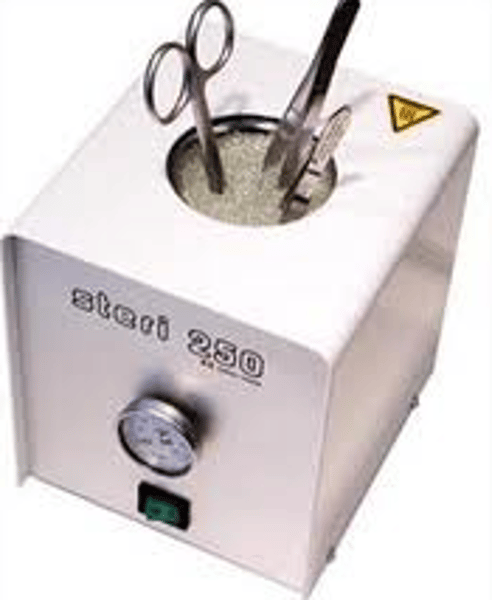
Using irradiation for medical purposes
To sterilise surgical instruments and kill cancerous tumours deep inside the body using beams of gamma rays (a gamma knife)

Radioactive contamination
When unwanted radioactive atoms are mixed with other materials causing the materials to become radioactive as well

Using contamination for medical tracers
A radioactive isotope (beta or gamma emitter) is injected into the body, then later passes out of the body where it is detected and used to form an image
Using contamination to check for leaks in water pipes
A radioactive isotope (beta or gamma emitter) is added to the water supply and if there is a crack, contaminated water will leak into the ground causing a build-up of radiation that can be detected
Factors to consider when choosing a radioactive source
The type of radiation it emits, the half-life and the toxicity (whether it is poisonous or not)
Why a source with a long half life is unsuitable for use inside the body
The damaging effects of the radiation would last for too long and the patient would receive too high a dose
When alpha radiation is most dangerous
Inside the body
Why alpha radiation is most dangerous inside the body
Alpha radiation is strongly ionising and cannot penetrate through skin so it is highly likely to ionise cells within the body
Dangers of irradiation and contamination
Irradiation or contamination from radioactive decay damages living cells and causes mutations which can lead to radiation sickness or cancer
How to reduce irradiation
Irradiation can blocked with suitable shielding and will stop as soon as the source is removed
Why it is difficult to reduce contamination
Once an object is contaminated, the radiation cannot be blocked from it and it is usually very difficult to remove all of the contamination from material
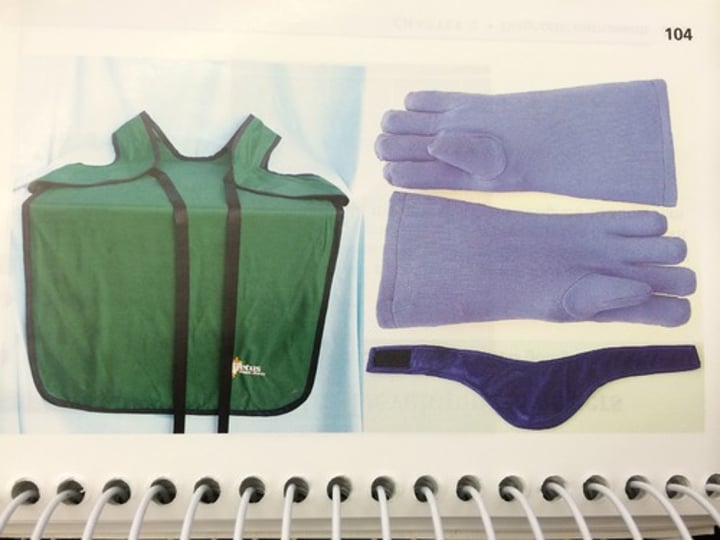
Precautions to take when using radioactive sources
Keep sources in a lead-lined box when not in use, wear protective clothing, avoid contact with bare skin, limit exposure time, use tongs to handle sources, monitor exposure etc
