Unit 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Human Phys)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Who coined the term “homeostasis”?
Walter Cannon
Walter Cannon’s 4 Postulates
role of nervous system in preserving “fitness” of internal environment
tonic level of activity
antagonistic controls for same parameters
chemical signals have diff. effect on diff. tissues
Tonic Level of Activity
postulate 2; means always a background level of activity; ex. engine in car still runs when car is in park
Antagonistic Controls for Same Parameters
postulate 3; need something to raise or lower a parameter; ex. insulin and glucagon
Homeostasis
body has methods that keep it in living limits; does not involve keeping conditions static but instead keeps them within tightly regulated physiological tolerance limits; can also be maintained by up- and down-regulation of receptors
Blood Parameter
5L/body (half plasma)
BPM Parameter
60-80; avg. 70
BP Parameter
120/80 MMHG
pH Parameter
7.35-7.45
Respiratory Rate (RR) Parameter
12-15/min
BLGLU Parameter (blood sugar)
100 MG/DL
O2 Parameter
98% saturated
Temperature Parameter
97 degrees F
Hypo-
lower than normal in EXTRACELLULAR concentration
Hyper-
higher than normal in EXTRACELLULAR concentration
Normo-
normal in EXTRACELLULAR concentration
-Emia
concentration in in EXTRACELLULAR fluids
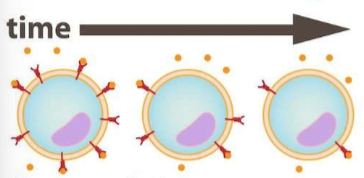
Upregulation
lower signals so more receptors
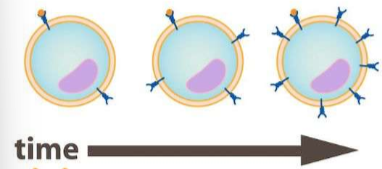
Downregulation
a lot of signals so reduce receptors
Basic Principles
govern physiological interactions and the maintenance of homeostasis
Basic Principles Examples
shape controls function
move water, move solute first
blood pressure = blood volume
loss of compartment integrity = disease/death
bircarb eqn
Loss of Compartment Integrity
fluids should stay in their compartments; ex. blood out of blood vessels
Bicarb Equation
H2O + CO2 ←> H2CO3 ←> HCO3- + H+; happening all the time; shifts pH; more CO2 = more H+
Epithelial
border things/liners; minimal matrix; no direct blood supply; have microvilli and cilia; covers body surface; lines cavities and hollow organs, and tubes; secretory glands; variable # of layers (1 to many); cells flattened, cuboidal, or columnar
4 Types of Mammal Tissues
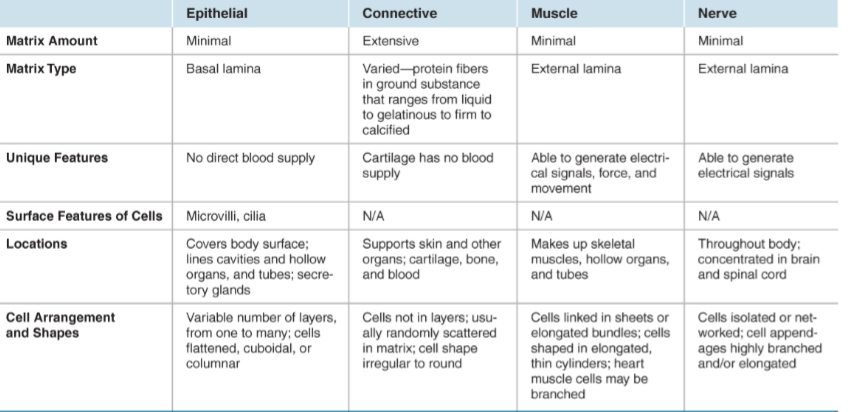
Connective Tisues
most diverse; in a matrix; ex. blood (liquid), fat (adipose), and bone
Tendons
connect muscle to bones
Cartilage
flexible; cells are chondrocytes
How do fluid compartments differ?
conc. of major ions and proteins; proportions within the body fluids
Na+
[outside] > [inside]; rushes in as first step of AP
K+
[inside] > [outside]; wants to leave inside of cell
What side of a cell is more -?
the inside
Are DNA and proteins charged?
yes (negatively)
Pathology (disease)
what happens when fluid volume and distribution are in conflict
Osmo-
relates to water
Osmotic Pressure
in mmHG or atm; amount of force required to prevent movement of water across a barrier; solute in high conc., water in low conc.
Osmolarity
comparative measure of the total # of dissolved particles per liter of soln.; always compare iso, hypo, and hyper-osmotic
Tonicity
determined by the relative concentrations of non-penetrating solutes across the membrane; what is going to happen to a cell (in real life - shrink, swell, or stay the same)
What happens if solutes can’t cross the membrane?
water will move to reach equilibrium
NaCl
solute; dissociates; neither one changes net conc. across membrane; when measuring in osmoles, assume already dissociated so count them separately
Urea
solute; freely penetrates membranes
Glucose
crosses according to conc. but disappears bc as soon as it crosses the membrane, it gets phosphorylated
Tonicity of Solutions
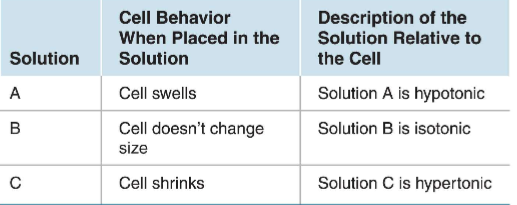
Relative Osmolarity
likelyhood that water will move
Rules for Osmolarity and Tonicity
assume all intracellular solutes are nonpenetrating
compare osmolarities before cell is exposed to soln.
tonicity of soln. describes vol. change of cell at eq.
determine tonicity by comparing non-penetrating solute conc. in cell and soln.; net water movement is into compartment w/ higher conc. of non-penetrating solutes
hyposmotic solns. always hypotonic
Plasma Membrane
semi-permeable; allows cells to maintain conc. gradients
4 Major Functions of Membrane Proteins
structural, enzymatic, receptor, and transport
Channel Proteins
allow material through the membrane; flips between open and closed
Carrier Proteins
move material across the membrane; like a revolving door (can only move sm things at a time); ex. glucose/larger things are moved by these
Do O2 and CO2 require proteins to move across the membrane?
no; they move freely across the membrane
Secondary Active Transport
uses PE of a conc. gradient of 1 substance to move another; enhances movement of materials
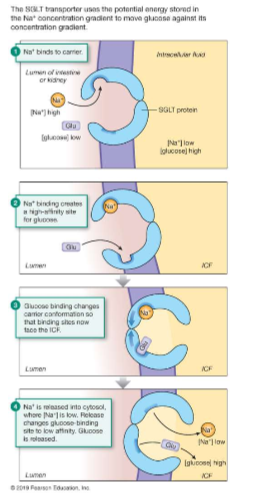
What is membrane equilibrium determined by?
electrical and chemical gradients; Na (sodium) in and K (potassium) out
Depolarization
Na+ (sodium) in
Repolarization
K+ (potassium) out
Glucose Transport
across epithelial cells it requires diff. mechanisms for apical and basolateral membranes
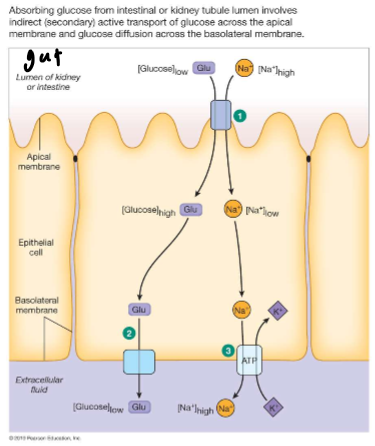
Lumen
way you measure light; the open space
Apical
brings glucose in
Basolateral
pushes glucose out
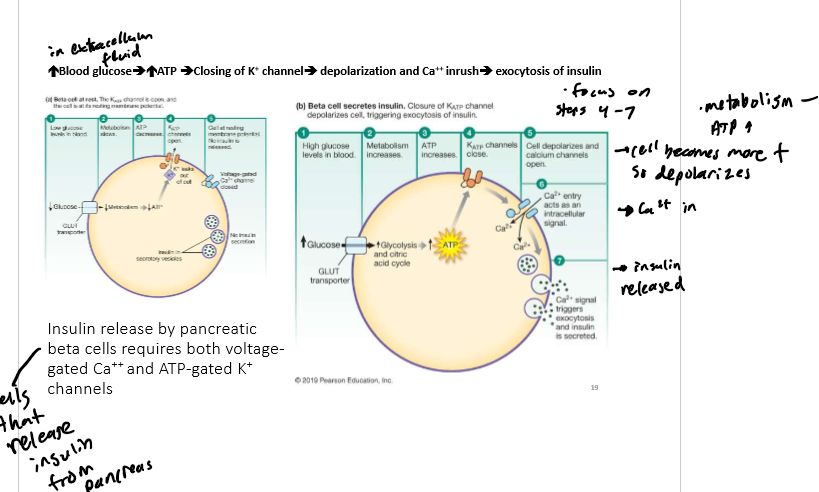
Chemical Signals
can be used for local or long-distance communication; gap junctions, autocrines, paracrines, endocrines, and neurotransmitters; can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic
Gap Junctions
openings that allow ions and things to pass between cells; form direct cytoplasmic connections between adjacent cells; important in the heart
Autocrines Signals
act on same cell that secreted them
Paracrine Signals
secreted by one cell and diffuse to adjacent cells; local in nature (anything that can be reached w/o using the vascular system - no traveling through the blood)
Endocrines
released by glands and use the vascular system to get to its destination; ex. hormones
Neurotransmitters
chemicals secreted by neurons that diffuse acrosss a small gap to the target cell
Water and Lipid Soluble Signals Differ
in how they move through the blood and cell membrane (or not)
What happens once a signal reaches its target cell?
message is transduced and amplified
Transduction
transferring a signal from outside to inside the cell
Hydrophilic Signals
have a rapid response rate; short half life; ex. insulin
Enzyme Cascades
fast and large responses through condurction caused by membrane reception
Arachidonic Acid
derived from membrane phospholipids; precursor for important inflammatory molecules; paracrine
Eicosanoids
fatty acid derived paracrines; lipogenase and cyclooxugenase pathways
Lipoxygenase Pathway
leukotrienes - chemotaxis of leukocytes, mediates inflammation, asthma
Cyclooxygenase Pathway
Prostaglandins and thromboxane
Prostaglandins
cox 1 - gastric protection; helps produce things that protect the stomach lining; smooth muscle contraction
cox 2 - inflammation, fever, and pain; produces things that are involved in these
Thromboxane
in the cyclooxygenase pathway; blood vessel constriction; increased platelet activation
Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
can’t use them to treat chronic pain bc get immune to it; ex. cortisone
Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
cox 1 and 2 inhibitors → ex. aspirin; cox 2 only inhbitors (celebrex and vioxx)
What effects signal efficacy?
function of receptor specificty and competition
Agonist
also activates the receptor
Antagonist
blocks receptor activity

Same Signal, Different Effects
one of Cannon’s postulates; applies to signal specifity
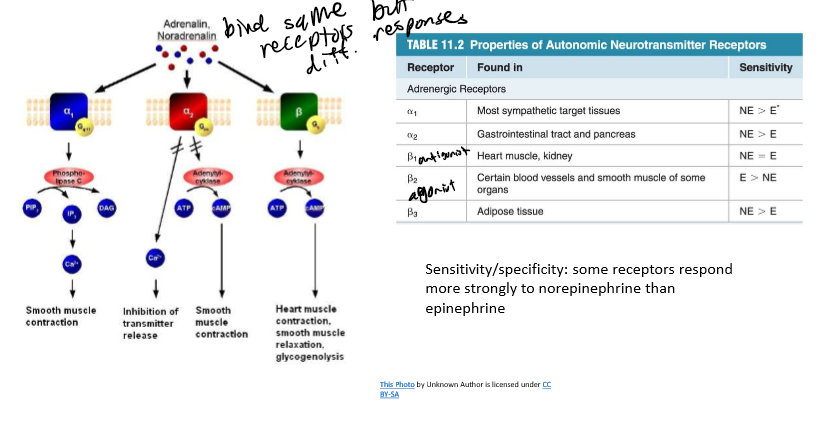
What does up/down regulation allow for?
modification of response based on signal frequency
too much signal → down reg (less receptors)
too little signal → up reg (more receptors)
Endrocine Disrupters
chemicals that mimic endocrine structure; may enhance or reduce an endocrines response
Obesogens
endrocrine disrupters that may specifically affect cortisol activities
Cortisol
long-term stress hormone; increase in this increases fat cells (adipose) (more energy)
Silphion/Silphium
contained an endocrine disrupter that prevented pregnancy or early term abortions; natural bc; important for the Greeks/Romans and would only grow in Cyrene; hunted into extinction
Estrogen System
demonstartes both Cannon’s postulate/evidence of predator-prey adaptation
How do plants fight?
w/ secondary compounds that they don’t use for their own metabolism
Vasopressin
helps to maintain BP
Signaling Systems
exhibit both tonic and antagonistic controls
What happens when a signal rate descreases?
blood vessel relaxes and opens up (increased diameter)
What happens when a signal rate increases?
blood vessel constricts
What does tonic signaling do?
maintain blood vessel diameter; therefore controls speed of fluid moving through it
Antagonistic Controls
speed up/slow down heartrate