Maternal & Baby Exam 1
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OB 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
The nurse is preparing to teach a client about the cardiovascular changes that occur during pregnancy. Which of the following decrease of remained unchanged?
Blood pressure.
The nurse has provided dietary teaching for a pregnant client who has iron deficiency anemia. Which of the following meal options selected by the client indicates that teaching has been effective?
Grilled steak, creamed spinach, and an apple.
The nurse is caring for a client who is pregnant. The first day of the last menstrual period was October 11th. Using Naegeles rule, the nurse calculates the estimated date of delivery to be:
July 18th…Oct 18th?
The nurse is caring for a pregnant client who is recently diagnosed with PICA. Which of the following Hgb levels should the nurse expect to find in the clients chart?
Low Hgb (Normal range is 12-18)
** PICA is associated with iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women.
The nurse is caring for a client who is at 38 weeks gestation and in a supine position for a pelvic examination. The client reports feeling dizzy and nauseated, upon assessment her skin feels damp and cool. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Turn the client on to her side
** Vena Cava BP drops so turn client to the side.
The nurse is caring for a client who is a primigravida in her 3rd trimester and is experiencing shortness of breath when walking up the stairs, which of the following statements by the nurse is appropriate?
This can be uncomfortable, try taking breaks and use good posture.
The charge nurse is discussing probable signs of pregnancy with a newly hired nurse. What are probable signs on pregnancy?
Amenorrhea
Braxton-hicks contractions
Hearing fetal heart tones
Breast tenderness
Positive pregnancy test
Visualizing the fetus
✅ Probable Signs Include:
Braxton Hicks contractions
Positive pregnancy test (due to elevated hCG levels)
Goodell’s sign – softening of the cervix
Chadwick’s sign – bluish discoloration of cervix/vagina
Hegar’s sign – softening of the lower uterine segment
Ballottement – fetus rebounds when tapped during pelvic exam
Abdominal enlargement
The nurse caring for a pregnant client who is of Asian decent. Which of the following cultural influences should the nurse consider FIRST when providing nutritional care
Food preferences, methods of preparation, and restrictions.
✳ Why this matters first:
Many individuals of Asian descent may follow traditional diets that emphasize:
Rice, vegetables, soy, fish, and tea
Limited dairy intake due to common lactose intolerance
Yin and yang (hot vs. cold foods) in some cultures like Chinese or Vietnamese health beliefs
The nurse is talking to a client who is 18 weeks pregnant about preparing her 7-year-old daughter for the new sibling. Which of the following recommendations is BEST for the nurse to make based on the child’s age?
“Tell you daughter the story of her own birth”
A nurse is teaching a client about symptoms to report during her pregnancy. Which of the following statements by the client indicates a correct understanding of the teaching?
“If I have any bleeding before 20 weeks, I should report it”
**report any headaches that wont go away.
The nurse is caring for a client who is at 15 weeks gestation and has an immune rubella titer. Which of the following actions is appropriate for the nurse to take?
Tell the client that she has immunity at this time. If she doesnt have immunity she would need the vaccine after delivery of the baby.
The nurse is teaching a pregnant client about possible complications of pregnancy. Which of the following client statements requires follow up by the nurse?
“I will change my cats litter box daily because it could contain harmful bacteria”
❗ Risk:
Cat feces can contain Toxoplasma gondii, which can cause toxoplasmosis—a serious infection that may lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, or congenital abnormalities in the baby.
The nurse is teaching a client who is in the 10th week of pregnancy about morning sickness. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching?
Alternate dry carb foods with fluids every hour.
✅ A. Eat dry crackers or toast before getting out of bed in the morning
✅ C. Eat small, frequent meals throughout the day
✅ D. Avoid spicy, greasy, or strong-smelling foods
The nurse is collecting data from a client who is confirmed pregnant. The client tells the nurse nurse that she had 1 pregnancy that she delivered at 38 weeks; 1 pregnancy she delivered at 34 weeks with twins; 1 pregnancy she delivered at 31 weeks; and 1 pregnancy she delivered at 18 weeks. Which of the following is the correct way to document the client’s gravidity, term births, preterm births, abortions, and living children (GTPAL)?
1 term birth at 38 weeks → T = 1
1 preterm birth at 34 weeks with twins → P = 1, L = 2
1 preterm birth at 31 weeks → P = 1, L = 1
1 pregnancy loss at 18 weeks → This is considered an abortion (A), as it was before 20 weeks → A = 1
G=5, T=1, P=2, A=1, L=4
The nurse is caring for assigned clients. Which of the following assessment findings should the nurse recognize as consistent with a client in the second stage of labor?
The client has the urge to push.
First stage: Onset of regular contractions → full cervical dilation (0–10 cm)
Second stage: Full dilation (10 cm) → birth of the baby
Third stage: Birth of the baby → delivery of the placenta
Fourth stage: Recovery (first 1–2 hours postpartum)
Signs Consistent with the Second Stage of Labor:
✅ Cervix is fully dilated (10 cm)
✅ Strong, intense contractions every 2–3 minutes
✅ Urge to bear down or push
✅ Increased bloody show
✅ Perineal bulging or visualization of the fetal head (crowning)
✅ Grunting or involuntary pushing efforts
The nurse is caring for a client who received an epidural 10 mins ago. The client now reports dizziness, lightheadedness, and nausea. After checking the client’s blood pressure, which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Rationale:
Epidural anesthesia can cause vasodilation and hypotension due to sympathetic nervous system blockade.
Elevating the feet (or placing the client in a lateral or Trendelenburg position) helps increase venous return and improve cardiac output.
The nurse is caring for a client who is in labor and has spontaneous rupture of the membranes with a large amount of clear fluid noted. Which of the following, if observed by the nurse, indicates cord compression?
The most reliable and immediate sign of cord compression is seen on the fetal heart rate (FHR) monitor.
***Variable Decelerations***
Variable decelerations are abrupt drops in the fetal heart rate that vary in timing and duration.
They are commonly caused by umbilical cord compression, which impedes blood flow to the fetus.
This can occur after membrane rupture due to a sudden shift in uterine pressure or cord displacement.
The nurse is preparing to teach a group of primipara clients about active relaxation techniques for pain control. Which of the following statements by a client requires follow up by the nurse?
“I will listen to an audio recording of a crying baby to help relax me for labor”
This statement requires follow-up because a crying baby is not a calming or relaxing stimulus—in fact, it may increase stress, anxiety, or emotional tension during labor.
Appropriate relaxation techniques may include:
Listening to soothing music or nature sounds
Practicing deep breathing
Using guided imagery
Focusing on positive affirmations
Doing progressive muscle relaxation
Using aromatherapy (as appropriate)
The nurse is caring for a client whose membranes ruptured 8 hours ago. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Check the client’s temperature every 2 hours to assess for infection.
Rationale:
After rupture of membranes (ROM), the protective barrier between the uterus and the external environment is lost, increasing the risk of ascending infection, such as chorioamnionitis.
Monitoring maternal temperature regularly (typically every 1–2 hours after ROM) helps detect early signs of infection.
Fever is a key early sign of intra-amniotic infection.
The nurse is preparing an educational staff meeting about maternal behaviors during the early phase of labor. Which of the following behaviors should the nurse include in the teaching plan?
Able to talk during contractions.
✅ Behaviors the Nurse Should Include in the Teaching Plan:
Talkative and sociable – The mother is often excited and happy that labor has started.
Able to walk and talk through contractions – Pain is usually mild to moderate.
Cooperative and open to instruction – This is an ideal time for education and emotional support.
Focused on breathing and relaxation techniques – May begin using them to cope with contractions.
Mild anxiety but still in control – Emotionally stable, may express nervousness.
Resting or napping between contractions – Especially if labor starts at night.
The nurse teaching a client about the causes of indicated pre-term labor. Which causes identified by the client from the box below indicate teaching has been effective?
1.Adv maternal age
Peridontal disease
Obesity
High stress
Limited education
Gestational diabetes
Adv maternal age, Obesity, Gestational diabetes. 1,3,6
The nurse is teaching a client in active labor who is experiencing significant back pain with each contraction about how to relieve the back pain. Which of the following client statements indicates that further teaching is necessary?
“I will lie down in a flat reclining chair”.
The nurse is assessing the contractions of a client on a fetal monitor. The client had the following activity according to the monitor:
*Contraction at 0905 lasting 30 seconds
*Contraction at 0915 lasting 40 seconds
*Contractions at 0935 lasting 30 seconds
*Contractions at 0939 lasting 40 seconds
Which of the following is the correct assessment to document regarding the frequency of the contractions?
A.5-20 mins
B.4-20 mins
C.4-5 mins
D.5-34 mins
B. 4-20 mins
Contraction Start Times from the Scenario:
0905
0915 → 10 minutes apart from 0905
0935 → 20 minutes apart from 0915
0939 → 4 minutes apart from 0935
Now Calculate Frequency Ranges:
Between 0905 and 0915 = 10 min
Between 0915 and 0935 = 20 min
Between 0935 and 0939 = 4 min
So the range of contraction frequency is from 4 to 20 minutes.
The nurse working in the labor unit has become aware of the following client situations. Which of the following clients should the nurse assess FIRST?
The client who is asking for a bed pan to move her bowels.
This is the second stage of labor (often the urge to push) Baby is ready for delivery.
The nurse working in the labor and delivery unit is caring for a client whose membranes have just ruptured. After assessing the FHR, which of the following actions is the priority?
Report the color and consistency of the clients amniotic fluid.
Usual Order of Immediate Actions After Membrane Rupture:
Assess FHR – already done in this case.
✅ Check for umbilical cord prolapse.
Document color, amount, and odor of amniotic fluid.
Monitor maternal temperature (to detect infection over time).
Continue to observe for signs of labor progression or infection.
The nurse is teaching a newly hired nurse about signs to expect in the first phase of the first stage of labor. Which of the following signs referenced by the newly hired nurse indicates a need for further teaching?
“The client is relaxed and excited”
✅ Expected Signs in the Latent (Early) Phase:
Cervical dilation from 0–3 cm
Mild to moderate contractions every 5–30 minutes, lasting 30–45 seconds
Mother is typically talkative, excited, and able to cope
Bloody show may be present
Mild anxiety, but generally under control
Possible rupture of membranes
The nurse is caring for clients who have oxytocin prescribed to induce labor. Which of the following clients requires follow-up with the PCP?
Primigravida who has placenta previa.
This patient requires a C-Section and should not be given oxytocin.
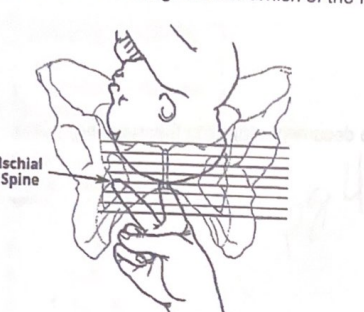
The nurse has performed a vaginal exam on a client and notes that the fetal head is at the level indicated in the image below. What should the nurse document?
0 Station
The nurse is planning a staff development conference about indications for labor induction. Which of the following statements, if made by a participant, indicates a correct understanding of the conference?
“Induction would be contraindicated for a client with complete placenta previa.”
A client who has had a cesarean birth asks the nurse about the possibility of a vaginal birth after cesarean. Which of the following is a contraindication to VBAC?
Hx of classical uterine incision
The nurse is caring for a client who is in active labor. Which of the following observed by the nurse indicates head compression?
Early decelerations
Early decelerations are gradual decreases in the FHR that mirror contractions in timing and shape.
They begin with the contraction, reach the nadir (lowest point) at the peak of the contraction, and return to baseline as the contraction ends.
This pattern is caused by fetal head compression, which stimulates the vagus nerve and leads to a reflex slowing of the heart rate.
Early decels are benign and do not require intervention.
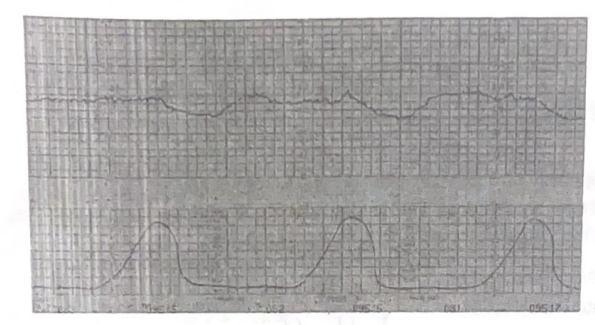
The nurse is caring for a client in labor and observes the fetal monitor strip below. Which of the following is the correct assessment to document regarding fetal deceleration?
Late decelerations
The nurse is caring for a female client of Chinese culture. The client is 6 cm dilated and the nurse notes facial grimacing and both hands clutching the bed linens. The nurse offered pain medication, but the client refused. Which of the following interventions should the nurse implement to assist with decreasing the client’s pain?
Review the client’s chart for pain management preferences.
The nurse caring for a group of clients who are in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Which of the following clients should the nurse assess first?
Client who has 60mL of yellow urine in 3 hours.
Rationale:
In the third trimester, a low urine output of only 60 mL in 3 hours is a potential sign of decreased renal perfusion or preeclampsia-related complications, and could indicate:
The nurse is explaining the 3-hour oral glucose tolerance test to a client suring a prenatal visit. What statement by the nurse is appropriate to include in the teaching?
“You will have your blood drawn after ingesting the glucose load”
You will need to fast overnight before the test. When you arrive, your blood will be drawn to check your fasting glucose level. Then you'll drink a sweet glucose solution, and your blood will be drawn again at 1, 2, and 3 hours afterward to see how your body processes sugar
The nurse is assessing a client who is 32-weeks pregnant. Which client report is a priority for the nurse to follow up?
Blurred vision
*This may indicate preeclampsia.
The nurse is developing a teaching plan for a primigravida client at 30 weeks gestation who has preeclampsia and is being cared for at home. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client to report.
***Severe headache, decreased fetal movement (less than 10 kicks an hour, visual disturbances, swelling in face or hands, N/V, signs of labor (regular contractions, rupture of membranes, vaginal bleeding). SOB/Chest pain.
The nurse is caring for multiple clients in labor. Which of the following clients should the nurse assess first?
client who has a new onset of headache with nausea and right rib pain.
**Classic warning sign of worsening preeclampsia
The nurse is caring for a primigravida client who is in early labor and has ruptured membranes. The client has a BP of 168/102, her face and hands are swollen, and she has 3+ protein in her urine. Which of the following medications should the nurse expect to be initially prescribed to this client?
Magnesium Sulfate
This primigravida client is showing signs of severe preeclampsia:
BP 168/102 (severe hypertension)
3+ proteinuria
Swelling of face and hands (edema)
➡ Magnesium sulfate is the first-line medication used to prevent seizures (eclampsia) in clients with severe preeclampsia.
The nurse is caring for a group of clients at 39 weeks gestation. Which of the following clients should the nurse recognize is experiencing a possible abruptio placenta?
✅ Key Signs of Abruptio Placentae:
Sudden-onset, intense abdominal pain
Firm, rigid ("board-like") uterus
Dark red vaginal bleeding (may be absent if concealed)
Signs of fetal distress (abnormal fetal heart rate or decreased fetal movement)
Uterine tenderness
Increased uterine resting tone
Shock symptoms (pallor, tachycardia, hypotension in severe cases)
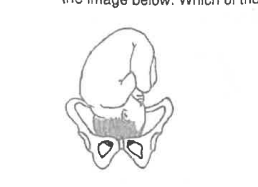
What is a correct description for the fetal position shown?
Right occipital anterior
The nurse caring for a client who is at 38 weeks gestation and arrives at the emergency department in active labor. What should the nurse expect to assess upon examination?
✅ Expected Findings in Active Labor:
Cervical dilation of 4 to 7 cm
This indicates the active phase of the first stage of labor.
Regular, strong contractions
Typically occurring every 3–5 minutes, lasting 45–70 seconds.
Increasing in intensity and frequency.
Effacement of 40% to 80%
The cervix is thinning in preparation for birth.
Fetal descent
The fetus may be at station 0 or lower (engaged in the pelvis).
Increased discomfort or pain
Contractions are more intense than in early labor.
Possible rupture of membranes
If not already ruptured, this may occur during active labor.
Bloody show
A pink or blood-tinged mucus discharge from cervical changes.
The nurse is teaching a pregnant client at 38 weeks gestation who is in labor and has a complete placenta previa. What prescription would require follow up with PCP?
Any vaginal examination or vaginal ultrasound.
The nurse is teaching a pregnant client who has gestation diabetes about insulin needs during pregnancy. What statement is correct
Insulin dosages will remain stable during the entire pregnancy
The nurse is caring for a pregnant client at 32 weeks’ gestation. The client reports occasional contractions and bright red vaginal bleeding. Which of the following conditions does the nurse expect the client is experiencing?
**Placenta previa
The nurse is caring for a client who is primipara 6 cm dilated, 75% effaced, and 0 station. which of the following stages of labor is the client experiencing?
First stage of labor
The nurse working in an outpatient clinic is assessing primigravida clients. Which of the following client findings should the nurse report to the PCP?
36 weeks gestation and respirations of 10
The nurse is caring for a client admitted with preeclampsia and receiving magnesium sulfate IV. The client becomes drowsy, lethargic, and develops respirations of 11. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse expect to administer?
Magnesium sulfate toxicity signs include:
Respiratory depression (respiratory rate <12/min)
Decreased level of consciousness
Absent or diminished deep tendon reflexes
Hypotension and bradycardia (in severe toxicity)
Calcium gluconate is the antidote for magnesium sulfate toxicity and should be readily available at the bedside when magnesium sulfate is being administered.
The nurse is caring for a client admitted with preeclampsia. Upon entering the client’s room, the nurse notes the client is in bed and disoriented with muscular twitching. Which of the following actions should the nurse expect to initially implement?
Protect the client from injury.
Rationale:
Muscular twitching and disorientation are early signs of an impending eclamptic seizure.
Turning the client to her side:
Prevents aspiration if a seizure occurs
Helps maintain an open airway
After positioning, the nurse should:
Call for help
Stay with the client
Ensure oxygen and suction equipment are available
Prepare to administer magnesium sulfate if not already ordered
Monitor vital signs and fetal status
The nurse is teaching a client who is being discharged following a cerclage placement. Which of the following statements but the client indicates correct understanding of the teaching?
The cerclage is placed because my cervix is weak.
Cerclage is typically placed between 12 and 24 weeks gestation for cervical insufficiency. After the procedure, the client needs to monitor for signs of preterm labor, ruptured membranes, or infection, which could signal complications.